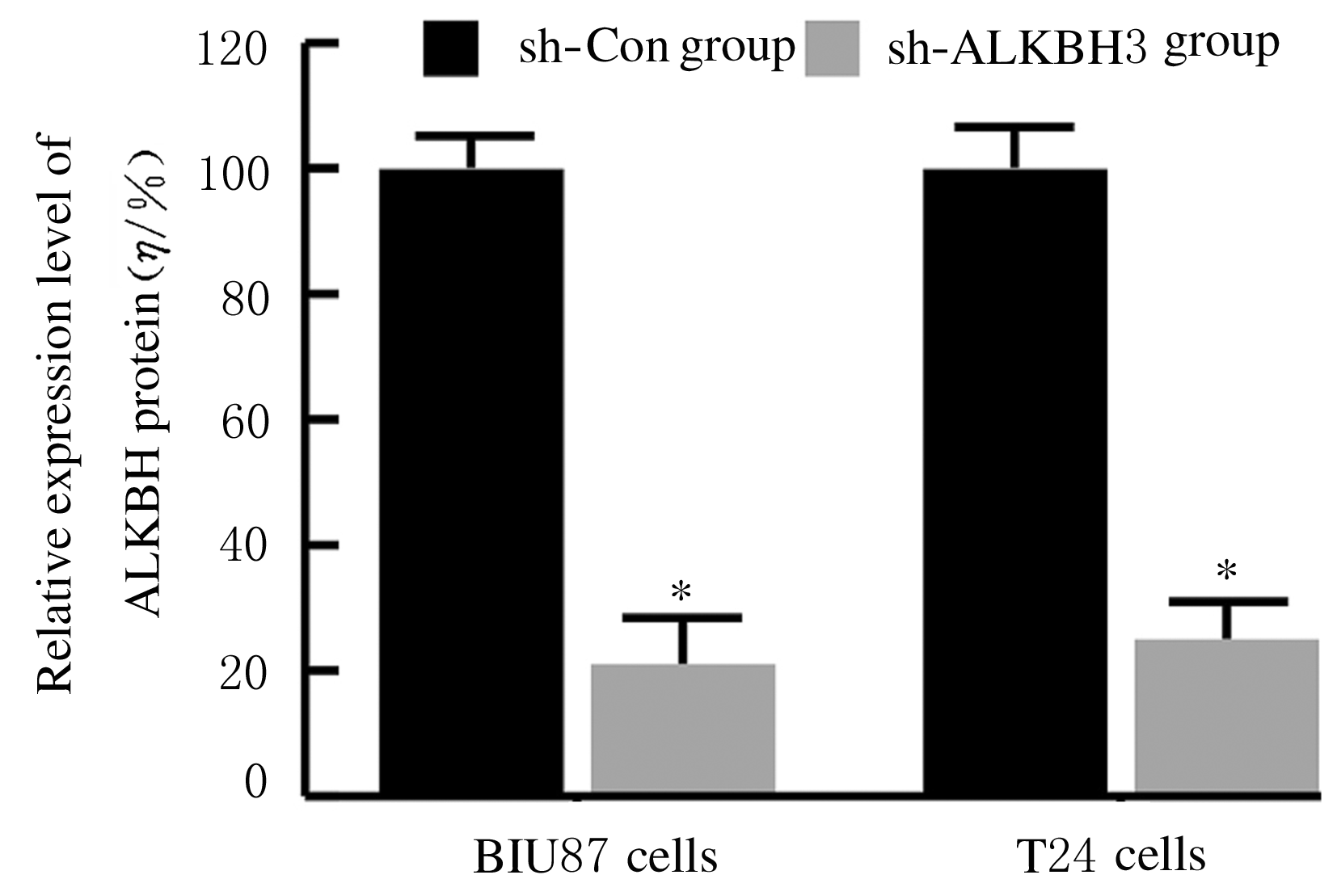
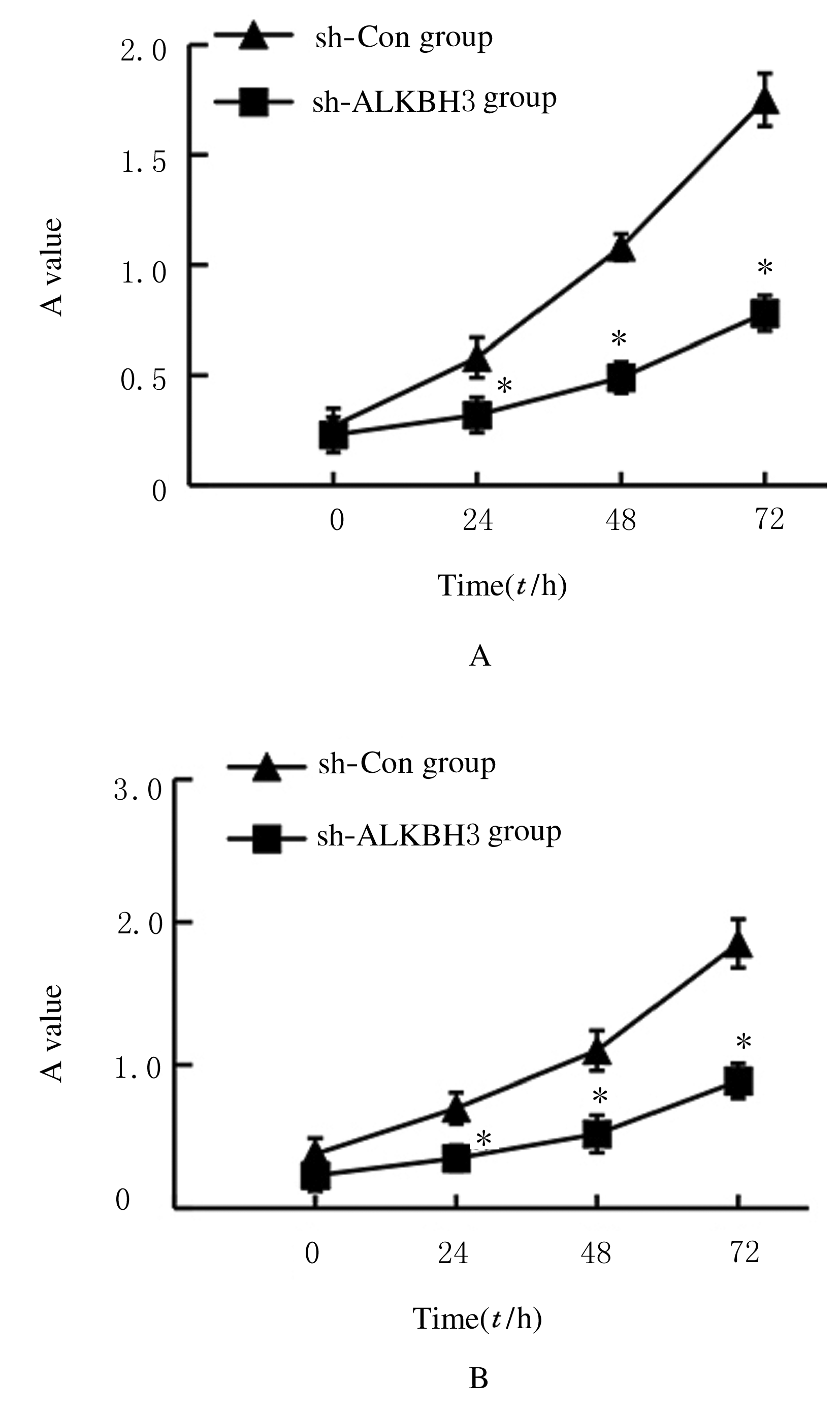
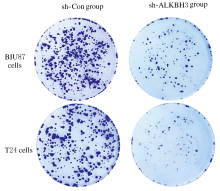
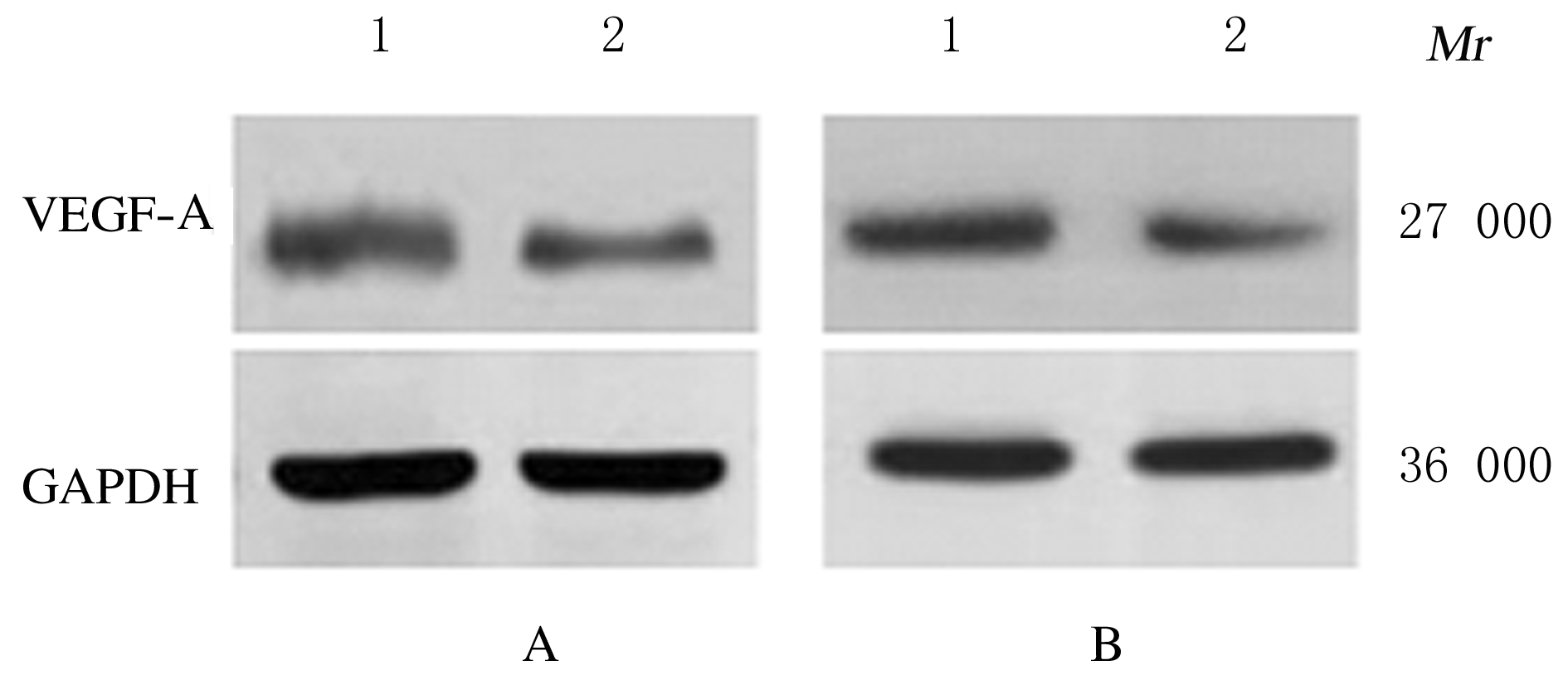
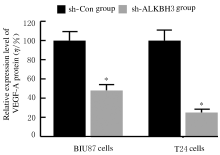
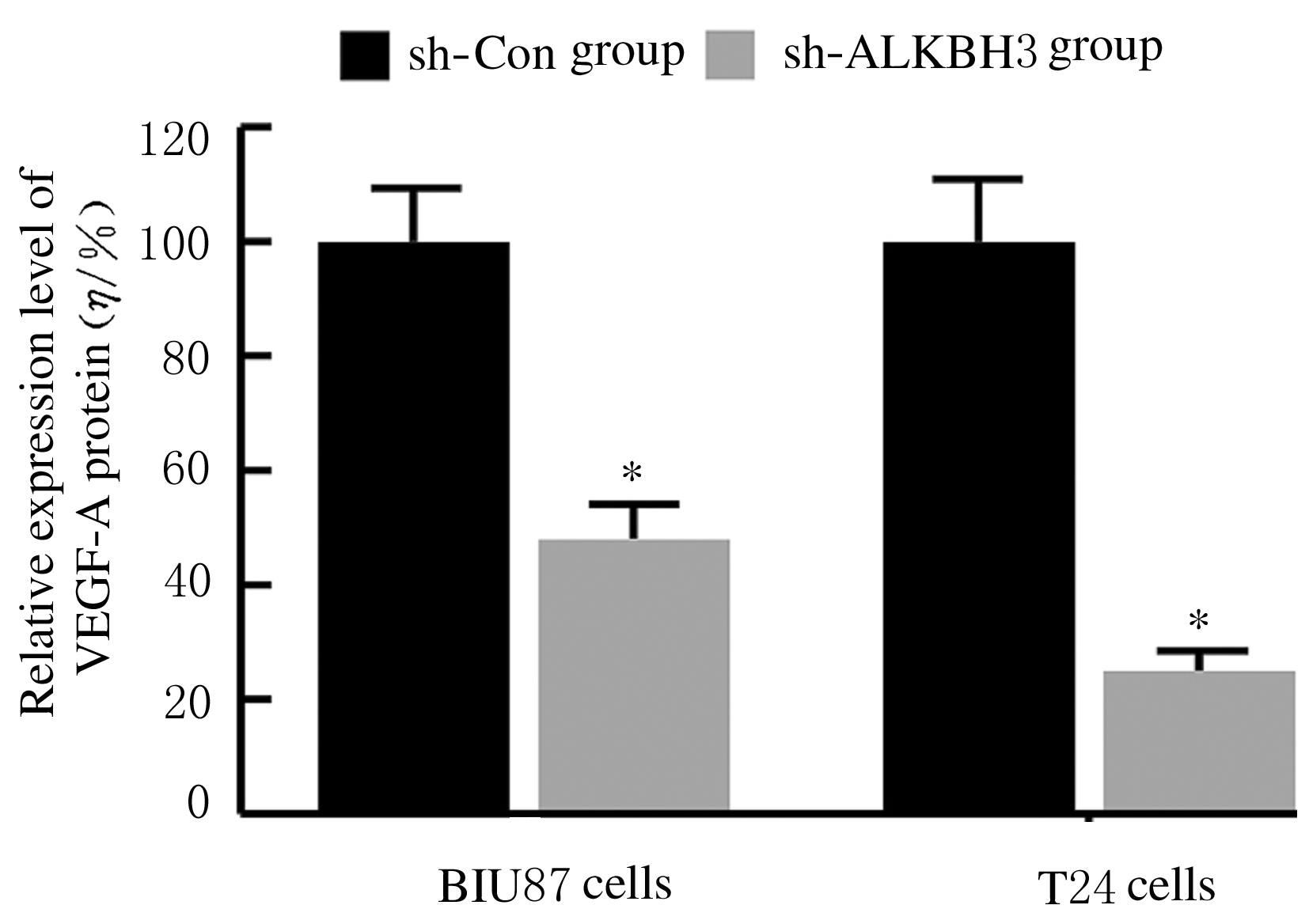
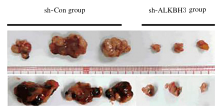
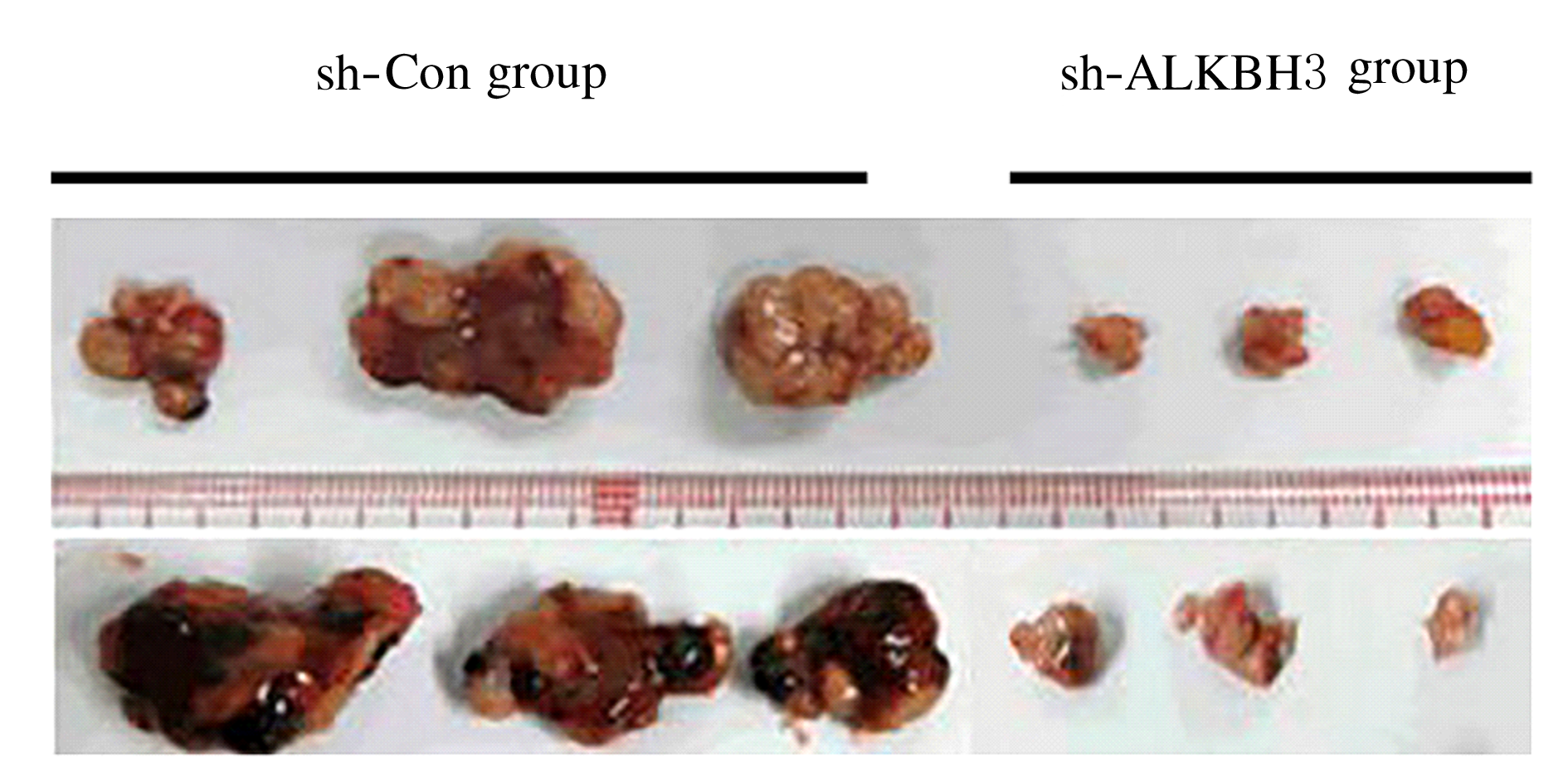
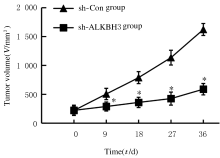
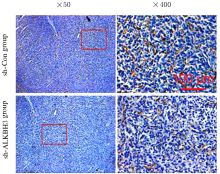
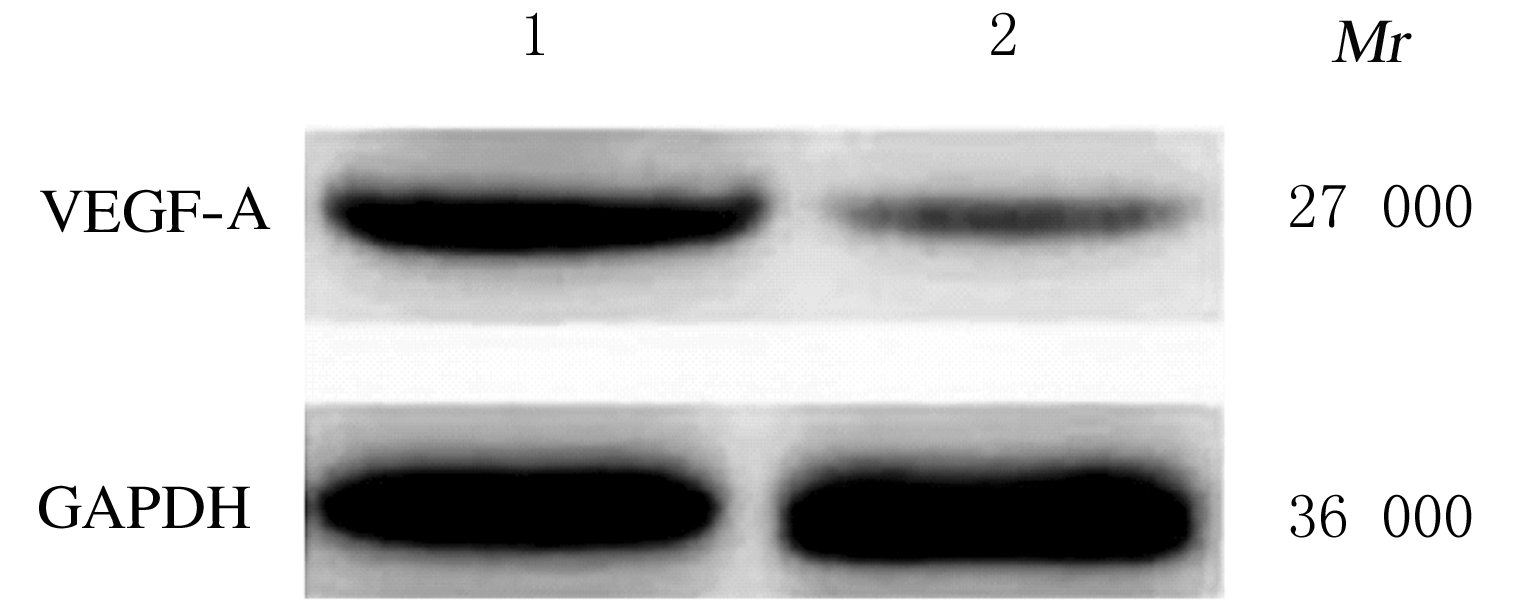
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (2): 397-406.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210220
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
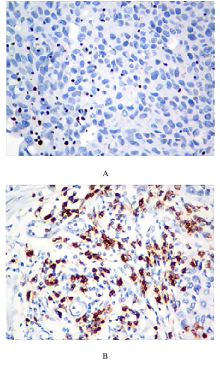
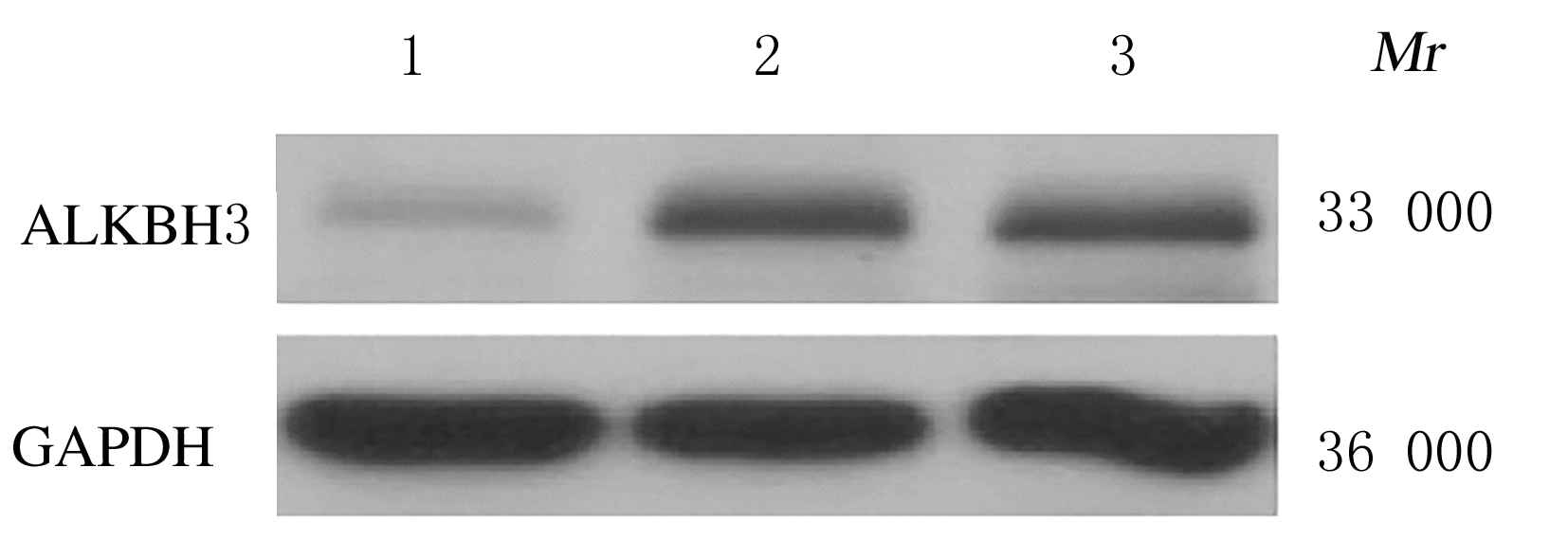
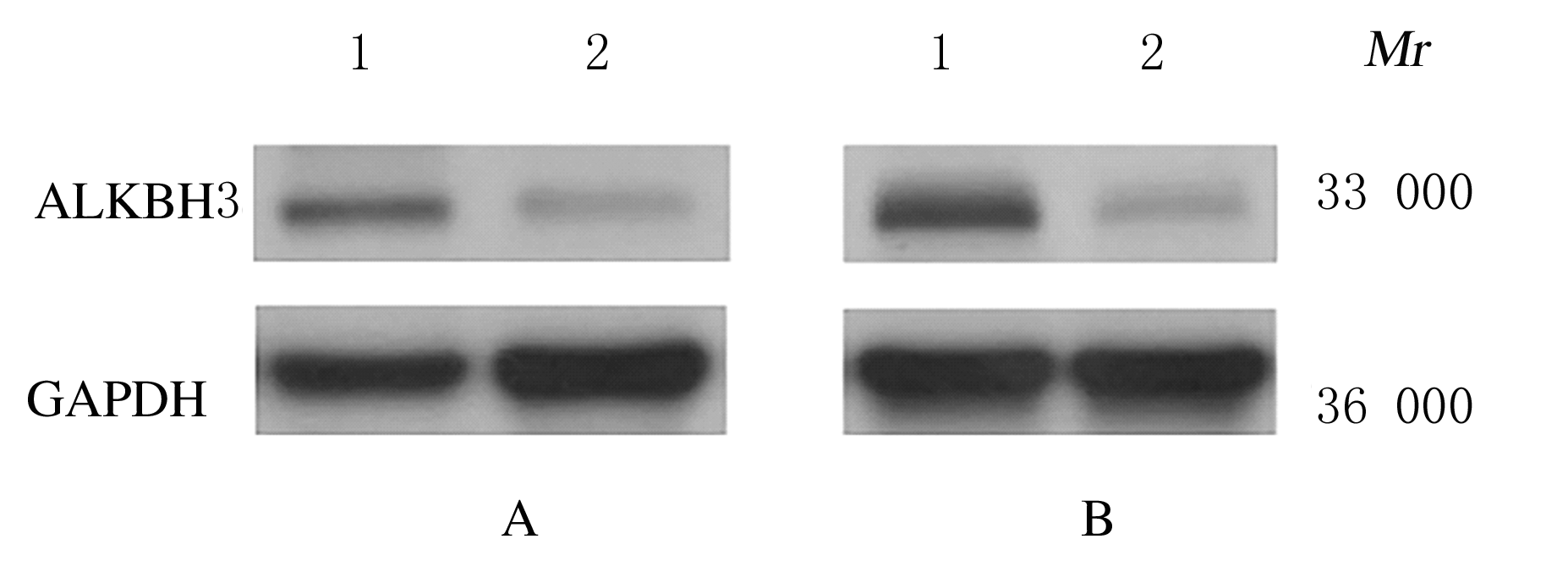
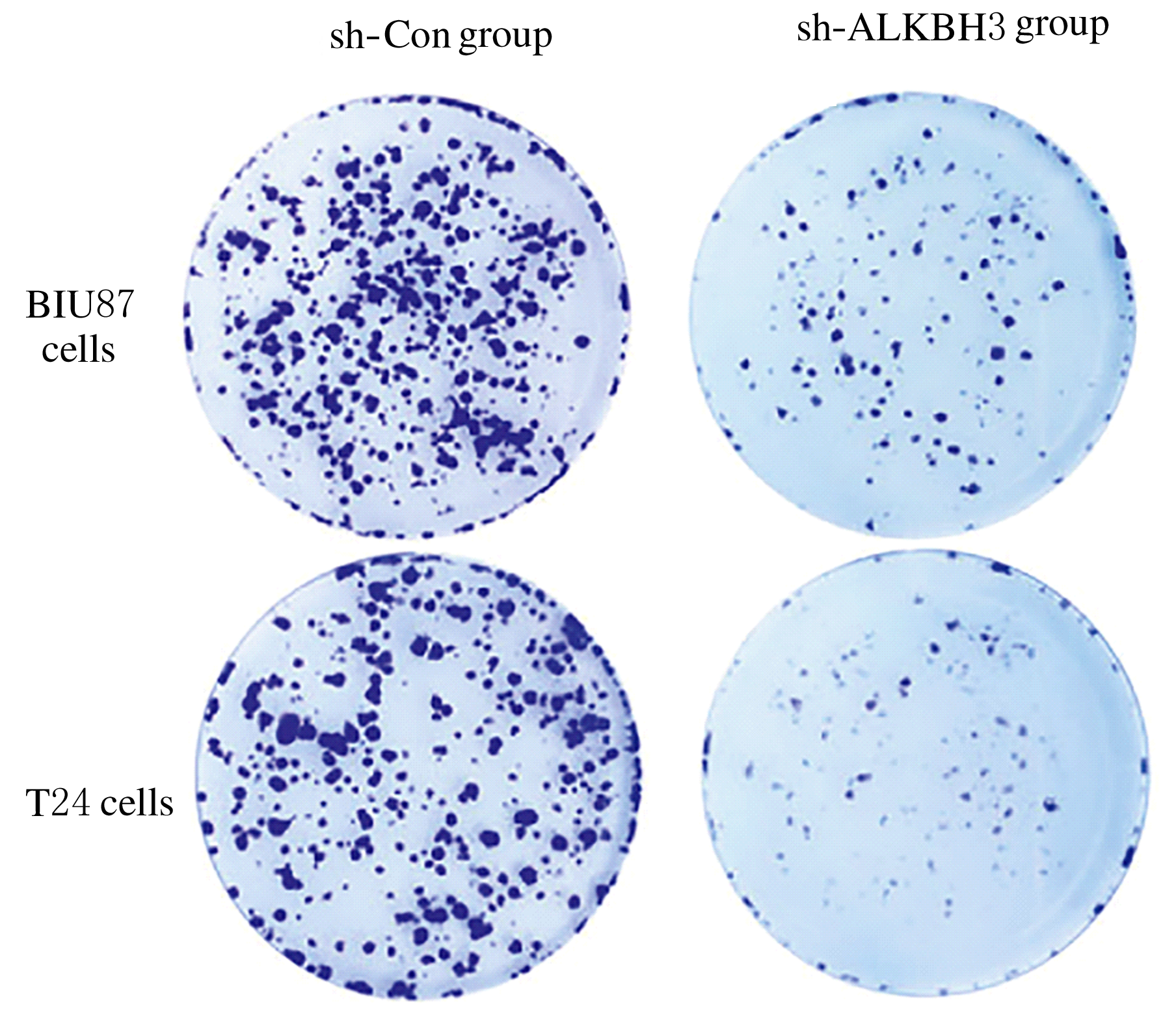
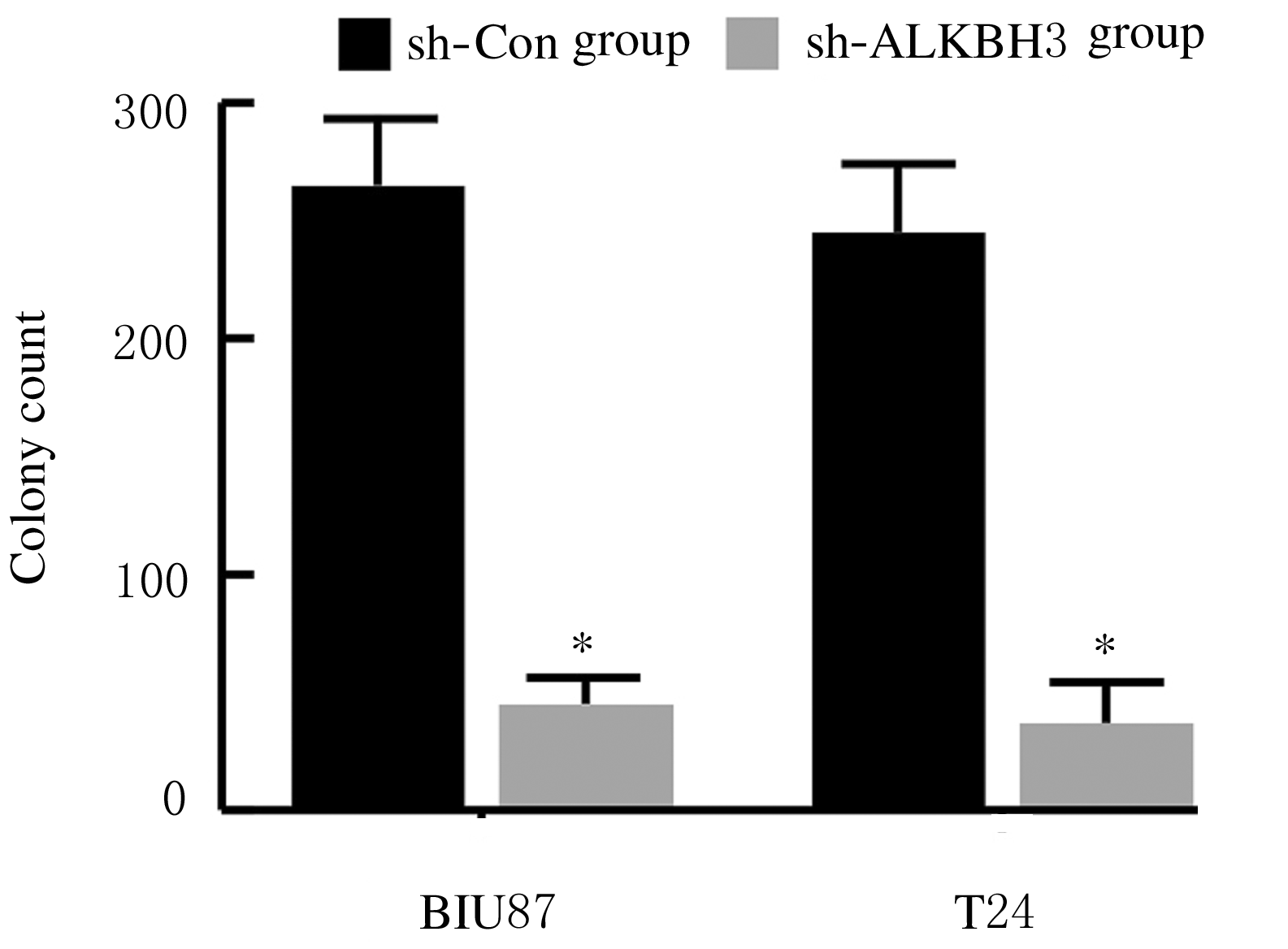
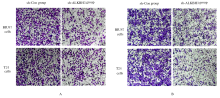
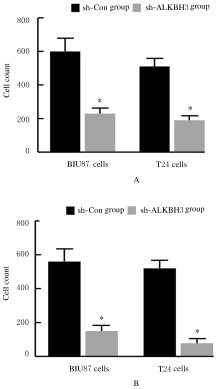
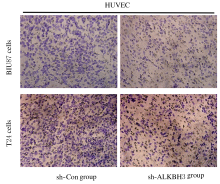
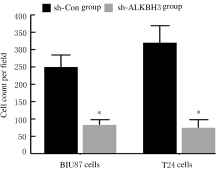
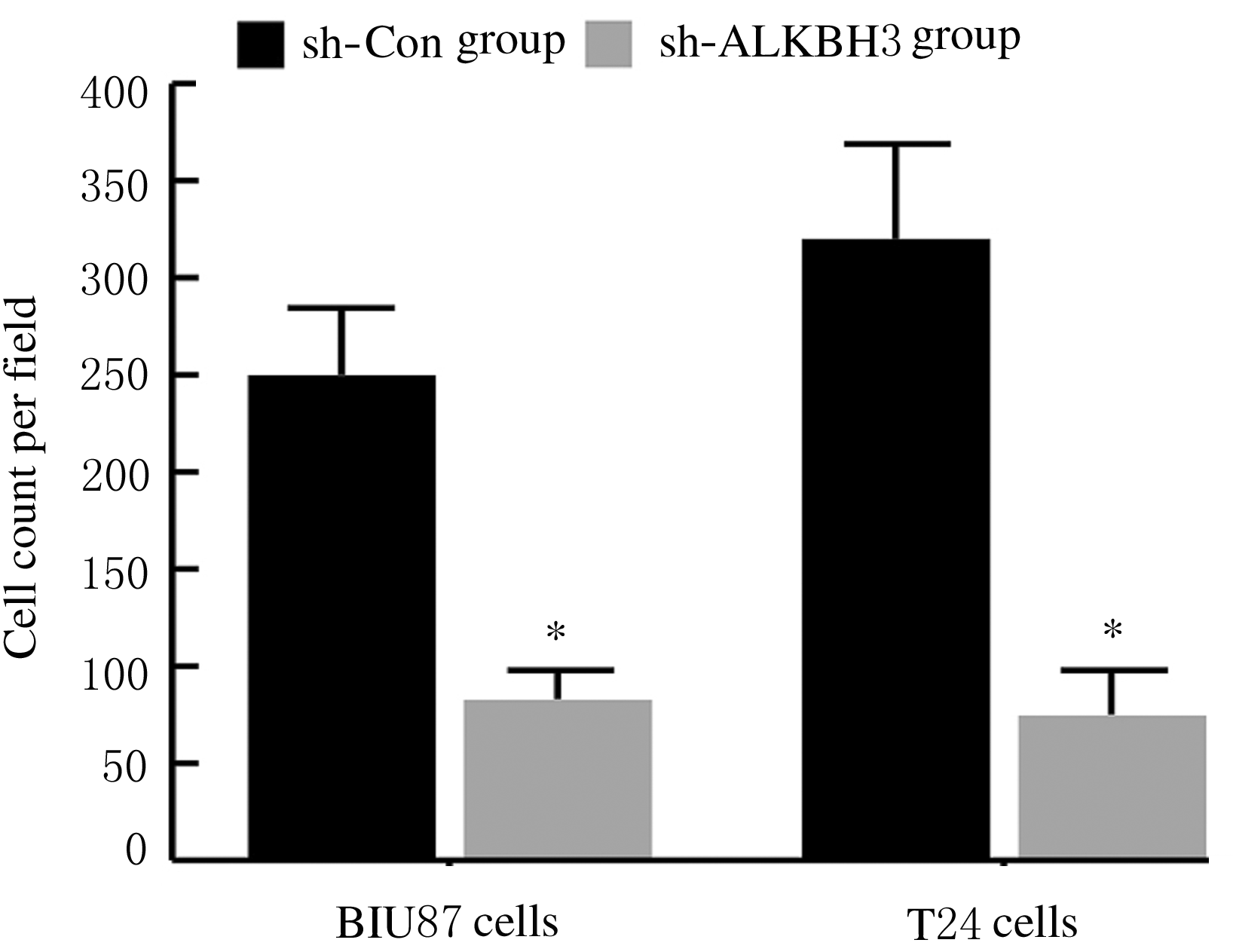
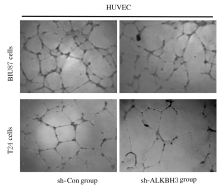
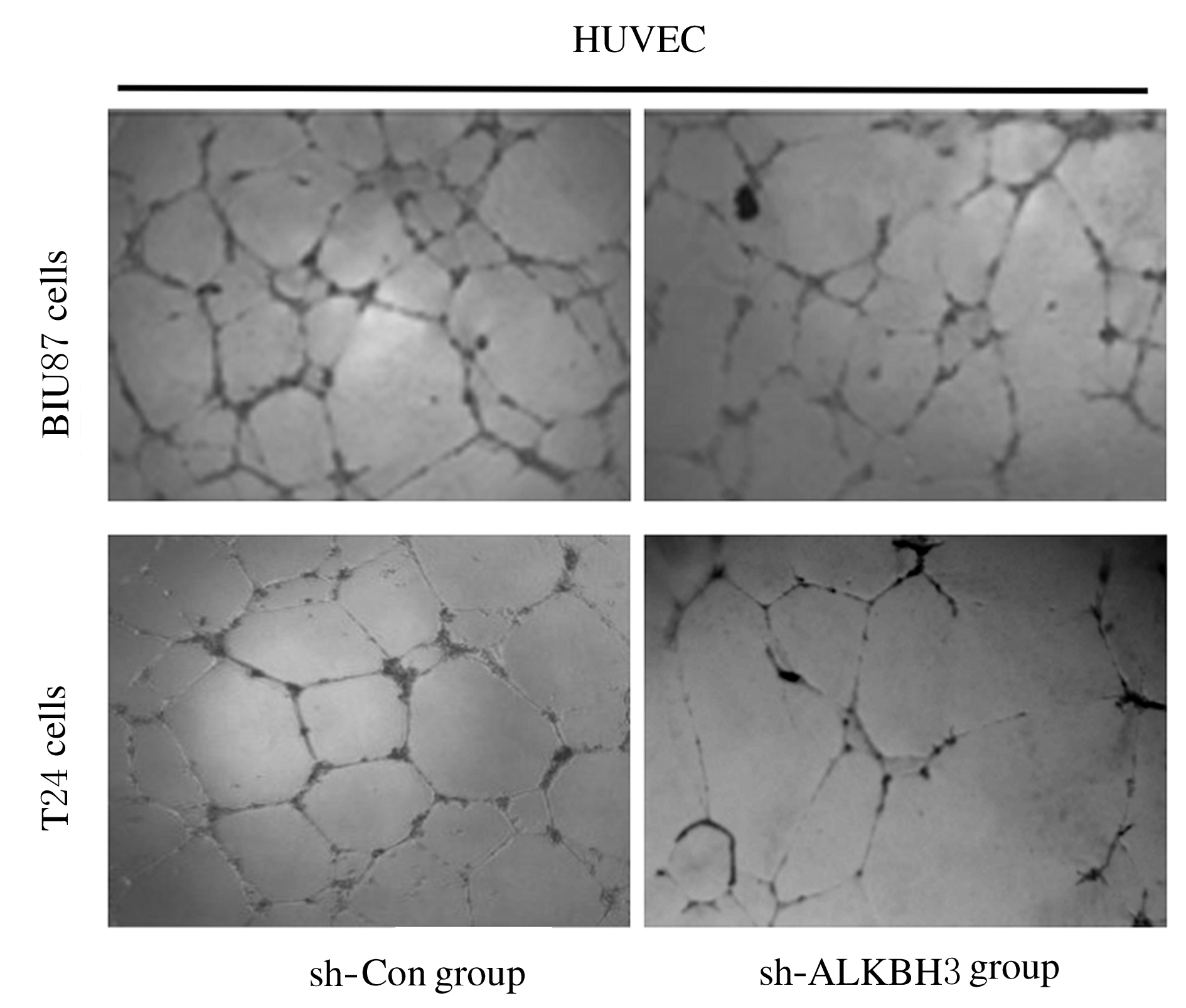
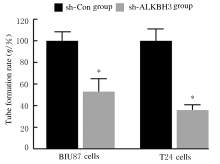
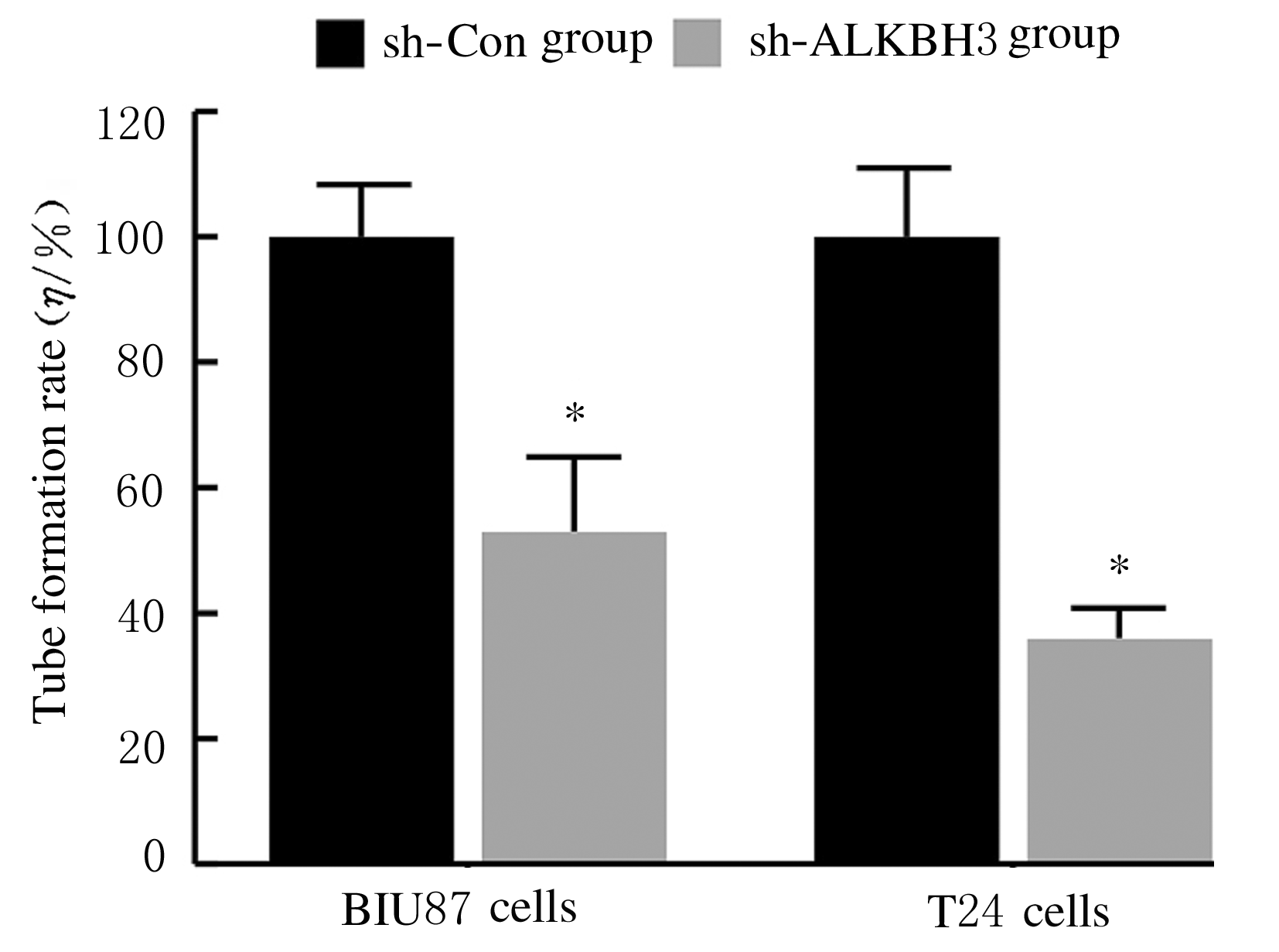
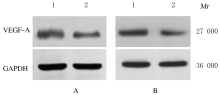
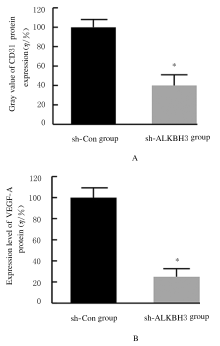
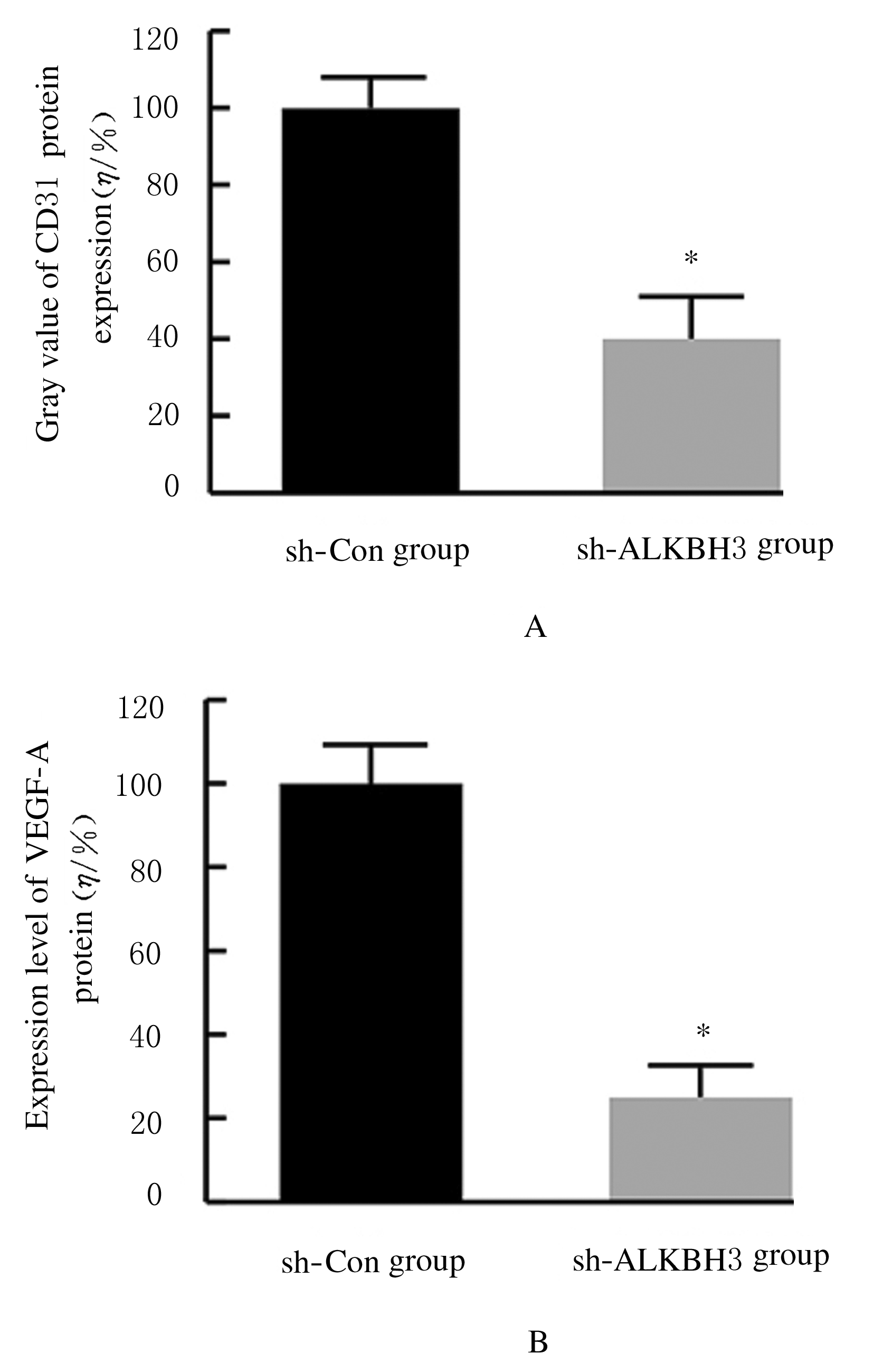
Inhibitory effect of ALKBH3 knockdown on growth, migration and tumor angiogenesis of bladder cancer cells and its mechanism
Qi ZHAO( ),Changhai HE,Zhi WANG,Xuefeng WANG,Xiaofei LIU
),Changhai HE,Zhi WANG,Xuefeng WANG,Xiaofei LIU
- Department of Urinary Surgery,Nanyang First People’s Hospital,Nanyang 473010,Henan Province,China
-
Received:2020-06-16Online:2021-03-28Published:2021-03-25 -
Contact:Qi ZHAO E-mail:zhaoqi1256@tom.com
CLC Number:
- R737.14
Cite this article
Qi ZHAO,Changhai HE,Zhi WANG,Xuefeng WANG,Xiaofei LIU. Inhibitory effect of ALKBH3 knockdown on growth, migration and tumor angiogenesis of bladder cancer cells and its mechanism[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 397-406.
share this article
| 1 | PAN Y, LIU G, ZHOU F, et al. DNA methylation profiles in cancer diagnosis and therapeutics[J]. Clin Exp Med, 2018,18(1): 1-14. |
| 2 | UEDA Y, OOSHIO I, FUSAMAE Y, et al. AlkB homolog 3-mediated tRNA demethylation promotes protein synthesis in cancer cells[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 42271. |
| 3 | STEFANSSON O A, HERMANOWICZ S, HORST JVAN D E R, et al. CpG promoter methylation of the ALKBH3 alkylation repair gene in breast cancer[J]. BMC Cancer, 2017, 17: 469. |
| 4 | DANGO S, MOSAMMAPARAST N, SOWA M E, et al. DNA unwinding by ASCC3 helicase is coupled to ALKBH3-dependent DNA alkylation repair and cancer cell proliferation[J]. Mol Cell, 2011, 44(3): 373-384. |
| 5 | PILŽYS T, MARCINKOWSKI M, KUKWA W, et al.ALKBH overexpression in head and neck cancer: potential target for novel anticancer therapy[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 13249. |
| 6 | WOO H H, CHAMBERS S K. Human ALKBH3-induced m(1)A demethylation increases the CSF-1 mRNA stability in breast and ovarian cancer cells[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech,2019,1862(1): 35-46. |
| 7 | CHEN Z, QI M, SHEN B, et al. Transfer RNA demethylase ALKBH3 promotes cancer progression via induction of tRNA-derived small RNAs[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2019,47(5): 2533-2545. |
| 8 | SHIMADA K, FUJII T, TSUJIKAWA K, et al. ALKBH3 contributes to survival and angiogenesis of human urothelial carcinoma cells through NADPH oxidase and tweak/Fn14/VEGF signals[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2012, 18(19): 5247-5255. |
| 9 | WONG M C S, FUNG F D H, LEUNG C, et al. The global epidemiology of bladder cancer: a joinpoint regression analysis of its incidence and mortality trends and projection[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 1129. |
| 10 | DEGEORGE K C, HOLT H R, HODGES S C. Bladder cancer: diagnosis and treatment[J]. Am Fam Physician, 2017, 96(8): 507-514. |
| 11 | WOLDU S L, BAGRODIA A, LOTAN Y. Guideline of guidelines: non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer[J]. BJU Int, 2017,119(3): 371-380. |
| 12 | NADAL R, BELLMUNT J. Management of metastatic bladder cancer[J]. Cancer Treat Rev, 2019, 76: 10-21. |
| 13 | ALTORKI N K, MARKOWITZ G J, GAO D C, et al. The lung microenvironment: an important regulator of tumour growth and metastasis[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2019, 19(1): 9-31. |
| 14 | HINSHAW D C, SHEVDE L A. The tumor microenvironment innately modulates cancer progression[J]. Cancer Res, 2019, 79(18): 4557-4566. |
| 15 | ZHAO Y, ADJEI A A. Targeting angiogenesis in cancer therapy: moving beyond vascular endothelial growth factor[J]. Oncologist, 2015, 20(6):660-673. |
| 16 | MAISHI N, HIDA K. Tumor endothelial cells accelerate tumor metastasis[J]. Cancer Sci, 2017, 108(10):1921-1926. |
| 17 | MELINCOVICI C S, BOŞCA A B, ŞUŞMAN S, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) - key factor in normal and pathological angiogenesis[J]. Rom J Morphol Embryol, 2018, 59(2):455-467. |
| 18 | GAO J, HU H, WANG X. Clinically relevant concentrations of lidocaine inhibit tumor angiogenesis through suppressing VEGF/VEGFR2 signaling[J]. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol, 2019, 83(6):1007-1015. |
| 19 |
ITATAN Y, KAWADA K, YAMAMOTO T, et al. Resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy in cancer-alterations to anti-VEGF pathway[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018.DOI:10.3390/ijms 19041232.
doi: 10.3390/ijms 19041232 |
| 20 | PERROT-APPLANAT M, DI BENEDETTO M. Autocrine functions of VEGF in breast tumor cells: adhesion, survival, migration and invasion[J]. Cell Adh Migr, 2012, 6(6): 547-553. |
| 21 | WANG L, ZHAO F, XIAO Z, et al. Exosomal microRNA-205 is involved in proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells via regulating VEGFA[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2019, 19: 281. |
| [1] | Runhong MU,Xinzhu LIU,Rui LIN,Yupeng LI,Luyao WANG,Chunyu WANG,Xiao GUO. Effect of PRDX6 over-expression of proliferation, invasion and migration of liver cancer cells and its molecular mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 559-565. |
| [2] | Cuilan LIU,Jianjun LI,He JIANG,Jing LIU,Dan WANG,Chen LI,Di ZHAO. Effect of urolithin B on biological behaviors of human glioblastome U118 MG cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 566-574. |
| [3] | Bo MA,Jiangang LI,Jun WANG,Junli HOU,Liang LI. Promotion effect of miR-106b on invasion and migration of colon cancer cells through targeting TGF-β/Smad pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 630-636. |
| [4] | Xiaohui LI,Ziwei QU,Xin LU,Qingbin MENG,Huatao CHEN,Jun REN,Chengpei TAN. Regulatory effect of exosomes carrying miR-196b-5p derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on biological characteristics of colon cancer cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 660-668. |
| [5] | Bo WANG,Yan YANG,Rui FEI,Niancai JING,Zhaodong LI,Yi LU,Hongyu XIAO,Yue ZHANG. Inhibitory effect of Shuganhuazheng Formula on growth of triple negative breast cancer of subcutaneous transplantation in mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 299-306. |
| [6] | Nuan WANG,Lijuan YANG,Juanjuan DAI,Aili WANG,Yan WU,Chengxia LIU. Promotion effects of MARCH1 on migration and invasion of human gastric cancer cells through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 352-359. |
| [7] | Jing WANG,Jing LIU,Xujing WEI,Yafei DU,Guiying FANG,Lin LI. Effects of oridonin on proliferation, migration, invasion and expression of lncRNA CCAT1 of endometrial carcinoma HEC-1B cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 384-389. |
| [8] | Chunying ZHANG,Guangwei YIN,Mingda YOU,Hong CHEN,Yaojie HU,Yanbing LI,Chunyou CHEN. Inhibitory effects of siRNA targeting silencing TAK1 gene on proliferation and migration of thyroid cancer cells and p38 MAPK signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 110-117. |
| [9] | Lu LIU,Tianfu ZHANG,Xiaofeng WANG,Chenfei KONG. Regulatory effects of syndecan-1 on migration, invasion and cell cycle of tongue squamous cell carcinoma CAL27 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 59-65. |
| [10] | GE Jing, XIE Lei, LI Lin, WEI Xujing, CHEN Ran, WANG Na. Expression of integrin-linked kinase in endometrial carcinoma tissue and its effects on migration and invasion abilities of cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 1011-1015. |
| [11] | WEI Xujing, LI Lin, ZHANG Hongzhen, WANG Jing, XU Jing. Effects of LncRNA CCAT1 on proliferation,invasion and migration of endometrial cancer cells through TGF-β1/smad signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 1016-1022. |
| [12] | ZHOU Ning, WU Rui, MA Zhenkai, CHEN Weiwei, LI Xuelin, GONG Kaikai, YANG Lijuan, DAI Juanjuan, WU Yan. Effects of down-regulation of ADAR1 expression on proliferation, migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human lung cancer cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 669-674. |
| [13] | BU Yi, ZHANG Shuo, QIAN Xudong, WANG Hongmei, DOU Zhijie. Expression of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in ischemic brain tissue of cerebral infarction model rats and its relationship with angiogenesis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 759-764. |
| [14] | QIN Qiaohong, ZHANG Nan, ZHAO Shujun, LI Hongyu. Expressions of miR-216a-5p and WASL in endometrial carcinoma tissue and their molecular mechanisms of regulating proliferation, migration and invasion of endometrial carcinoma cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 844-850. |
| [15] | XU Jianguo, CAO Hongtao, ZHANG Zilong, JI Baoyan, WANG Chunqiu, LI Shengdong, LIU Guoqing. Effects of LincRNA-p21 knockdown on growth and metastasis of gastric cancer cells and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 266-273. |
|