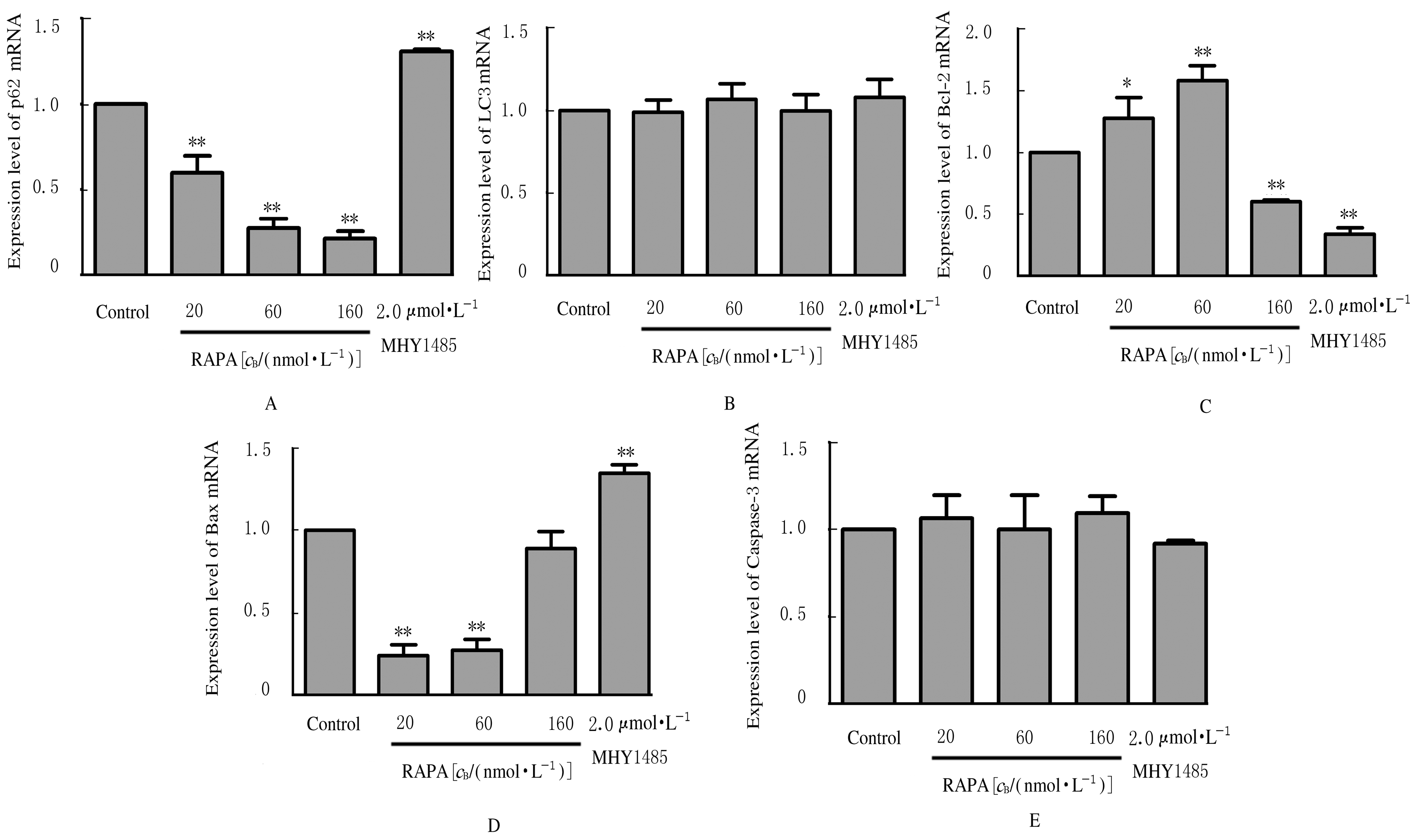
| 1 | DIAB D L, WATTS N B. Postmenopausal osteoporosis[J].Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes, 2013, 20(6): 501-509. |
| 2 | LAVOIE B, LIAN J B, MAWE G M. Regulation of bone metabolism by serotonin[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2017, 1033: 35-46. |
| 3 | DRAKE M T, CLARKE B L, LEWIECKI E M. The pathophysiology and treatment of osteoporosis[J]. Clin Ther, 2015, 37(8): 1837-1850. |
| 4 | GUI X, CHEN H, CAI H, et al. Leptin promotes pulmonary fibrosis development by inhibiting autophagy via PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 498(3): 660-666. |
| 5 | YURUBE T, ITO M, KAKIUCHI Y, et al. Autophagy and mTOR signaling during intervertebral disc aging and degeneration[J].JOR Spine,2020,3(1):e1082. |
| 6 | HE H, ZENG Q, HUANG G, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation exerts neuroprotective effects following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting autophagy via the PI3K/Akt pathway[J]. Brain Res, 2019, 1707: 124-132. |
| 7 | ZHAO J, WU J, XU B, et al. Kaempferol promotes bone formation in part via the mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2019, 20(6): 5197-5207. |
| 8 | LIANG G, LIU M, WANG Q, et al. Itraconazole exerts its anti-melanoma effect by suppressing Hedgehog, Wnt, and PI3K/mTOR signaling pathways[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(17): 28510-28525. |
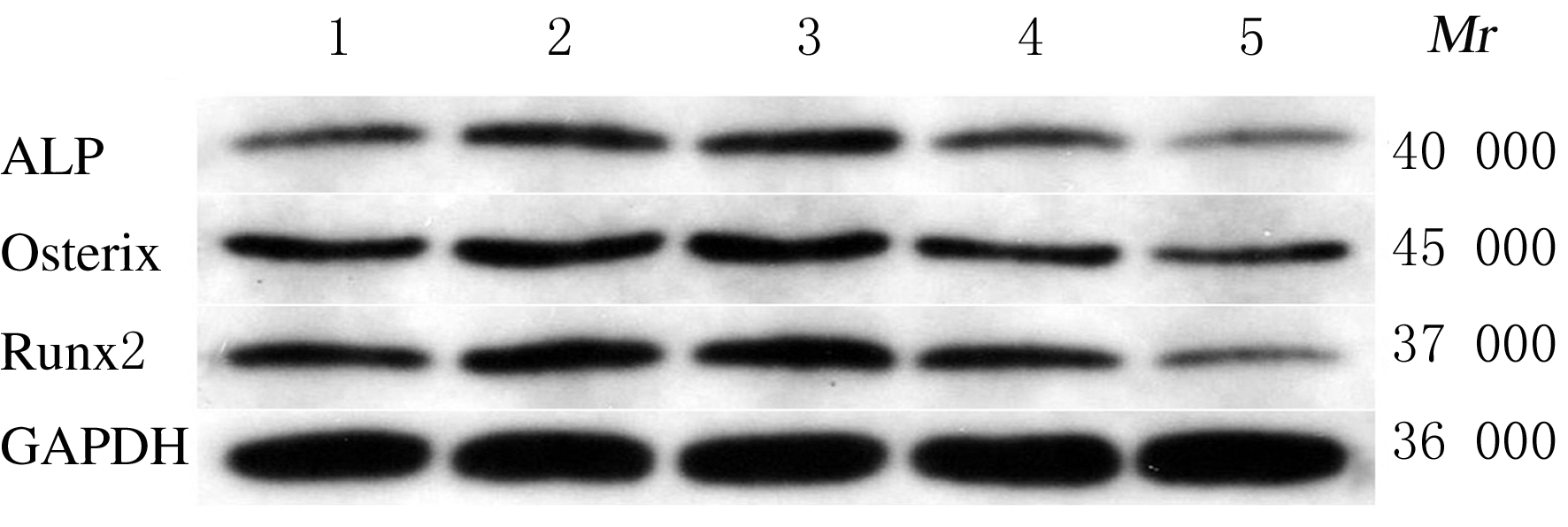
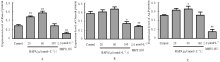
| 9 | KARNER C M, LEE S Y, LONG F X. Bmp induces osteoblast differentiation through both Smad4 and mTORC1 signaling[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2017, 37(4). DOI:10.1128/mcb.00253-16. |
| 10 | ETNYRE D, STONE A L, FONG J T, et al. Targeting c-Met in melanoma: mechanism of resistance and efficacy of novel combinatorial inhibitor therapy[J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2014, 15(9): 1129-1141. |
| 11 | NIKONOROVA I A, AL-BAGHDADI R J T, MIREK E T, et al. Obesity challenges the hepatoprotective function of the integrated stress response to asparaginase exposure in mice[J]. J Biol Chem, 2017, 292(16): 6786-6798. |
| 12 | TOMLINSON I. The Mendelian colorectal cancer syndromes[J]. Ann Clin Biochem, 2015, 52(pt 6): 690-692. |
| 13 | ZHAO H L, YANG L Q, CUI H J. SIRT1 regulates autophagy and diploidization in parthenogenetic haploid embryonic stem cells[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2015, 464(4): 1163-1170. |
| 14 | ZHAO D, YANG J, YANG L. Insights for oxidative stress and mTOR signaling in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury under diabetes[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2017, 2017: 6437467. |
| 15 | PERUMAL E, PAUL V, GOVINDARAJAN V,et al. A brief review on experimental fluorosis[J]. Toxicol Lett, 2013, 223(2): 236-251. |
| 16 | WANG Y, ZHANG H. Regulation of autophagy by mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2019, 1206: 67-83. |
| 17 | KIM J, KUNDU M, VIOLLET B, et al. AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1[J].Nat Cell Biol,2011,13(2):132-141. |
| 18 | D’ARCY M S. Cell death: a review of the major forms of apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy[J]. Cell Biol Int, 2019, 43(6): 582-592. |
| 19 | XIA Y, LIU J. An overview on chronic arsenism via drinking water in PR China[J]. Toxicology, 2004, 198(1/3): 25-29. |
| 20 | GUPTA N, GUPTA N, CHHABRA P. Image diagnosis: dental and skeletal fluorosis[J]. Perm J, 2016, 20(1): e105-e106. |
| 21 | APARICIO I M, MARTIN MU?OZ P, SALIDO G M, et al. The autophagy-related protein LC3 is processed in stallion spermatozoa during short-and long-term storage and the related stressful conditions[J]. Animal, 2016, 10(7): 1182-1191. |
| 22 | GóMEZ-SáNCHEZ R, YAKHINE-DIOP S M, RODRíGUEZ-ARRIBAS M, et al. mRNA and protein dataset of autophagy markers (LC3 and p62) in several cell lines[J]. Data Brief, 2016, 7: 641-647. |
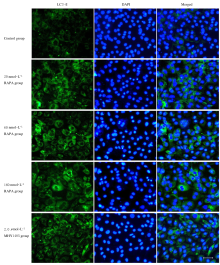
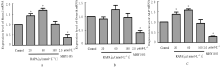
| 23 | YIN X, ZHOU C, LI J, et al. Autophagy in bone homeostasis and the onset of osteoporosis[J]. Bone Res, 2019, 7: 28. |
| 24 | FANG F, WEI X, HU M, et al. A mouse model of craniofacial bone lesion of tuberous sclerosis complex[J]. Musculoskelet Regen, 2015, 1(1):e814. |
| 25 | YANG H, WEN Y, ZHANG M, et al. MTORC1 coordinates the autophagy and apoptosis signaling in articular chondrocytes in osteoarthritic temporomandibular joint[J]. Autophagy, 2020, 16(2): 271-288. |
 )
)