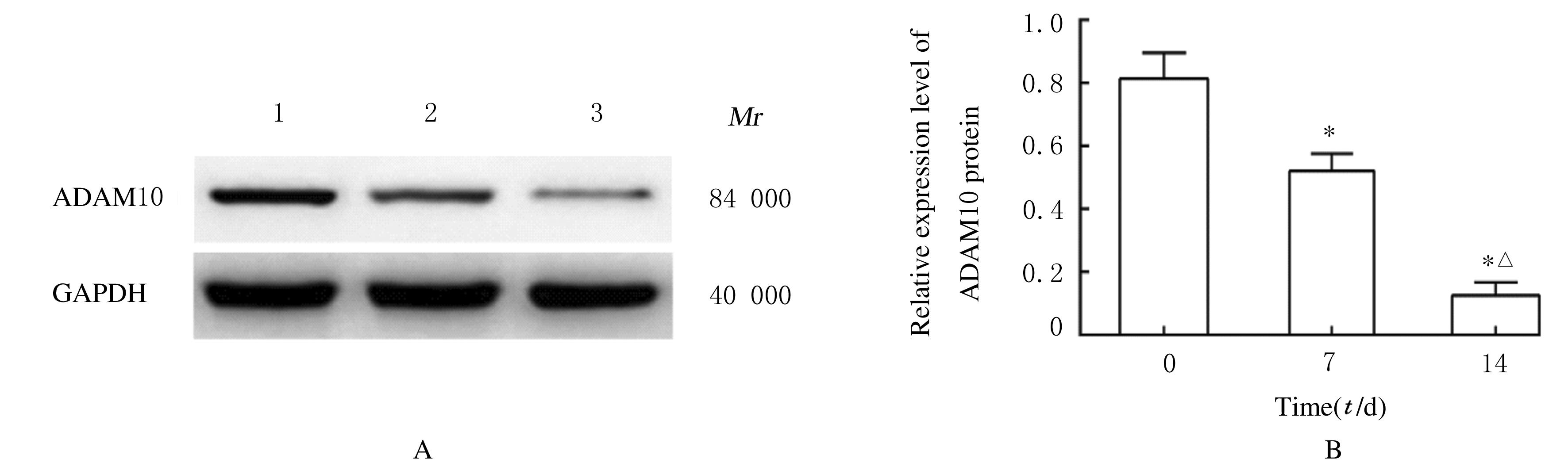
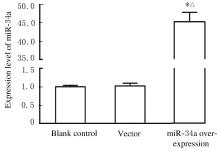
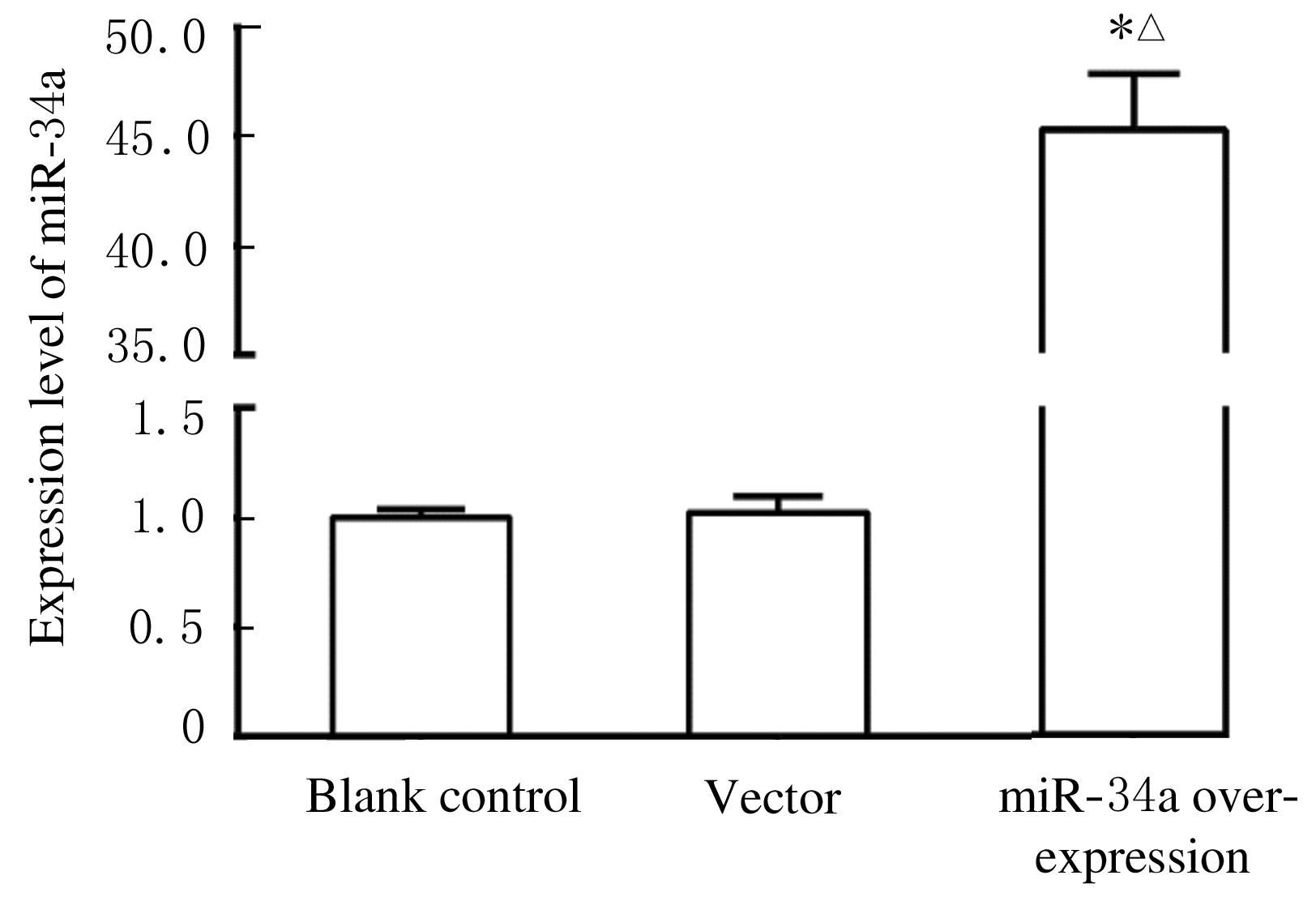
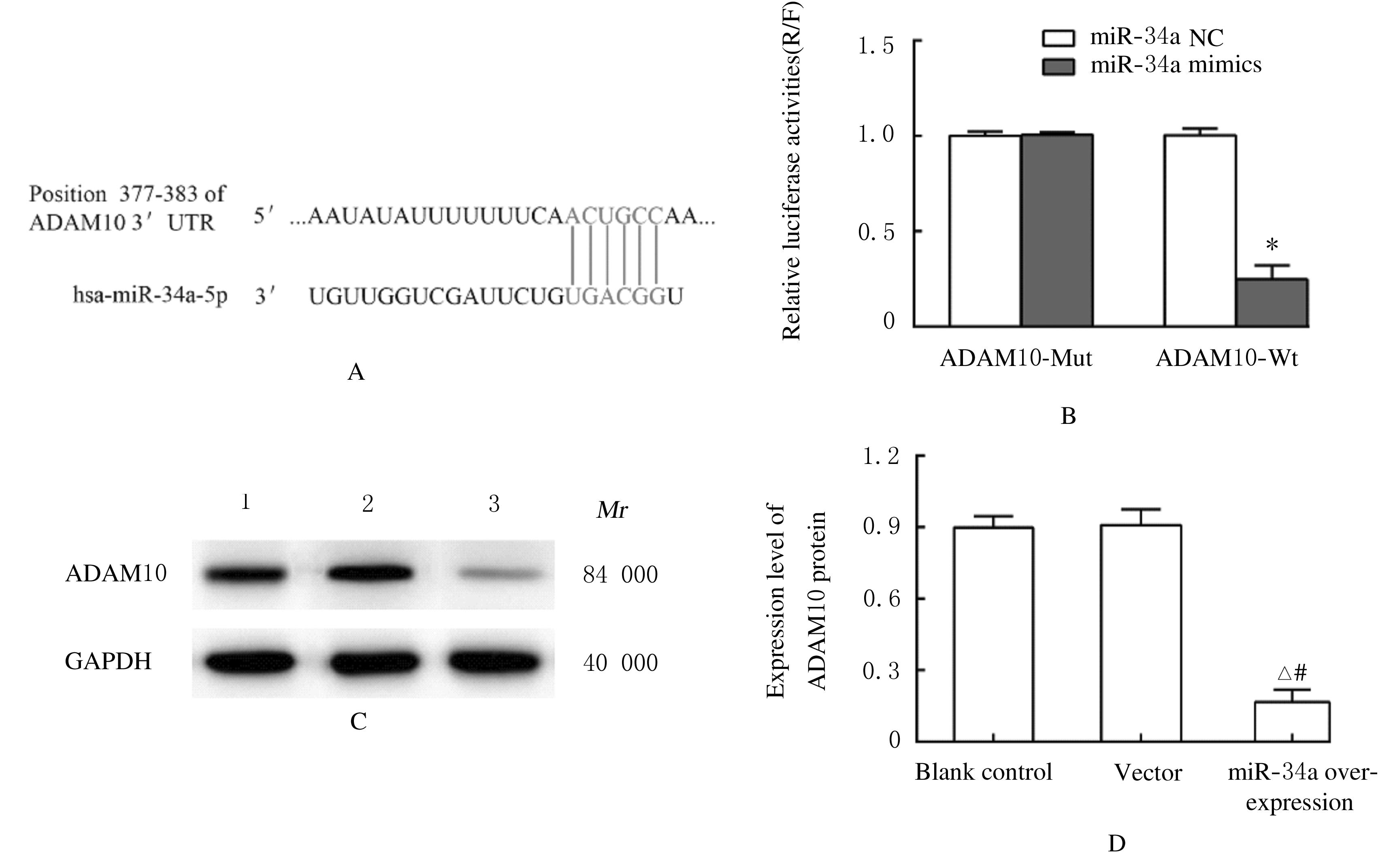
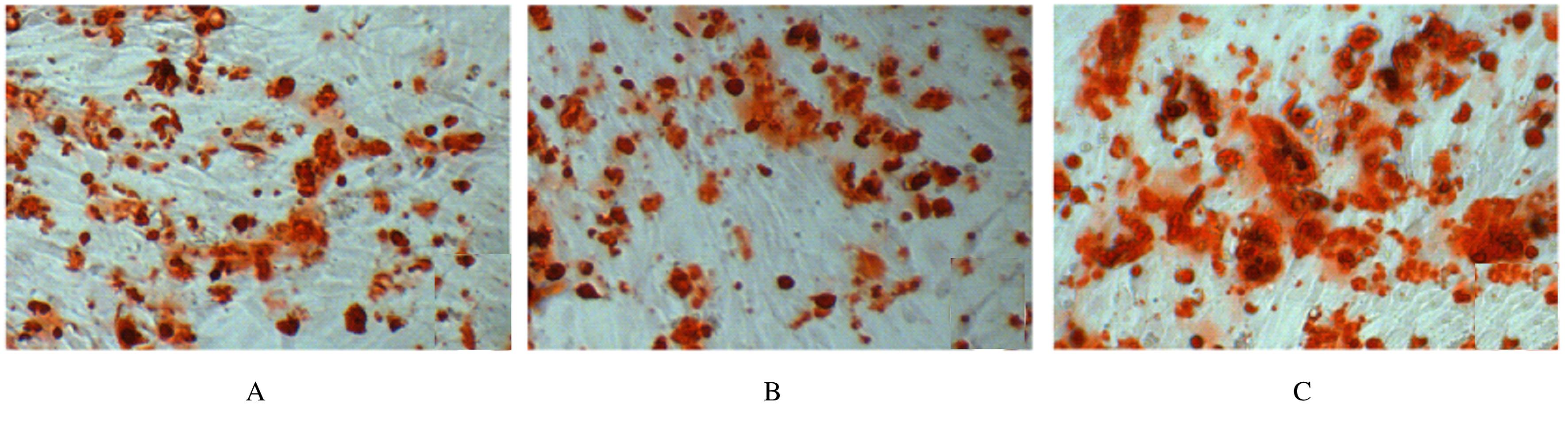
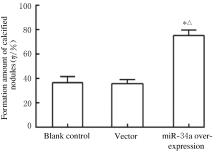
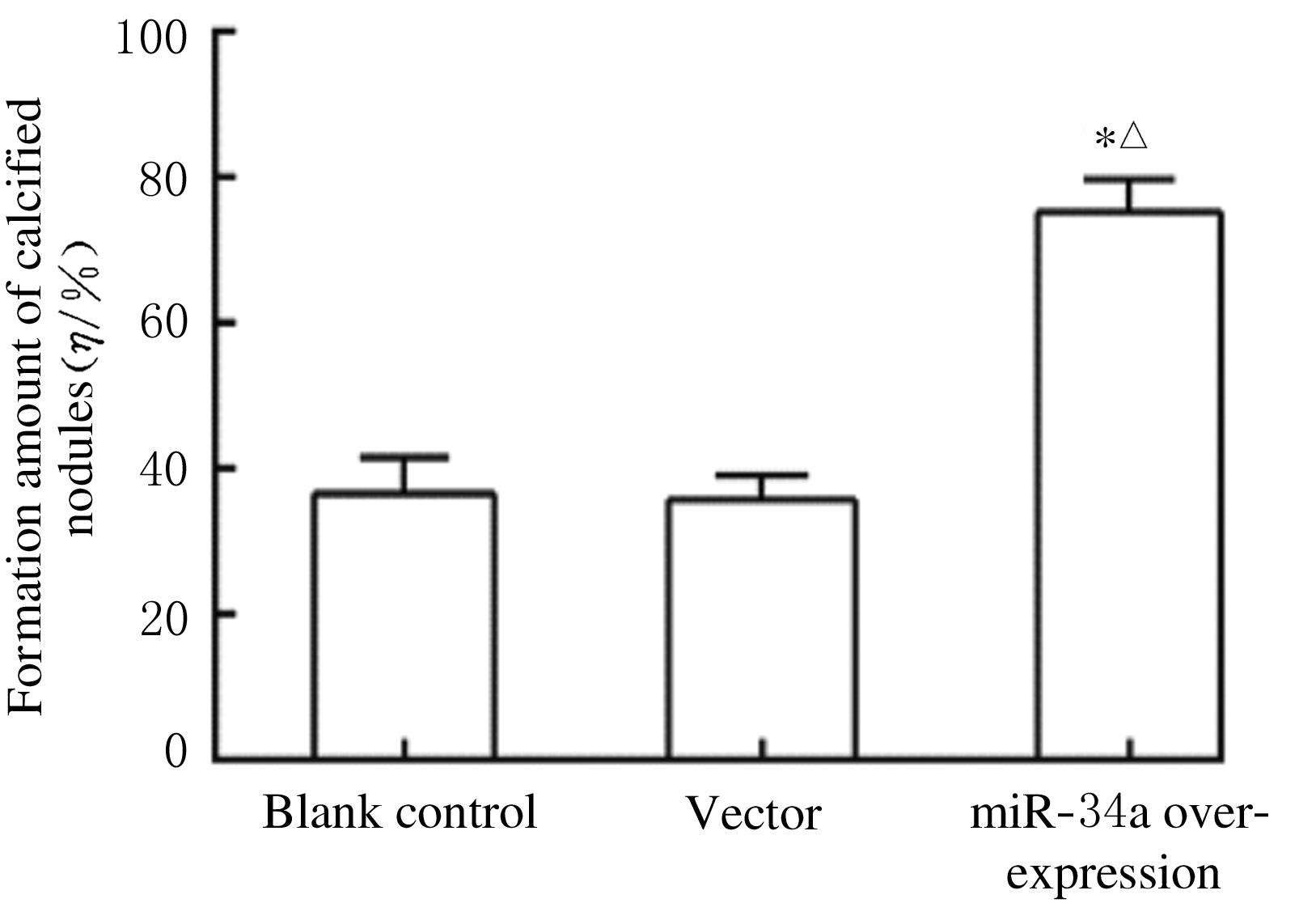
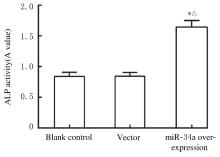
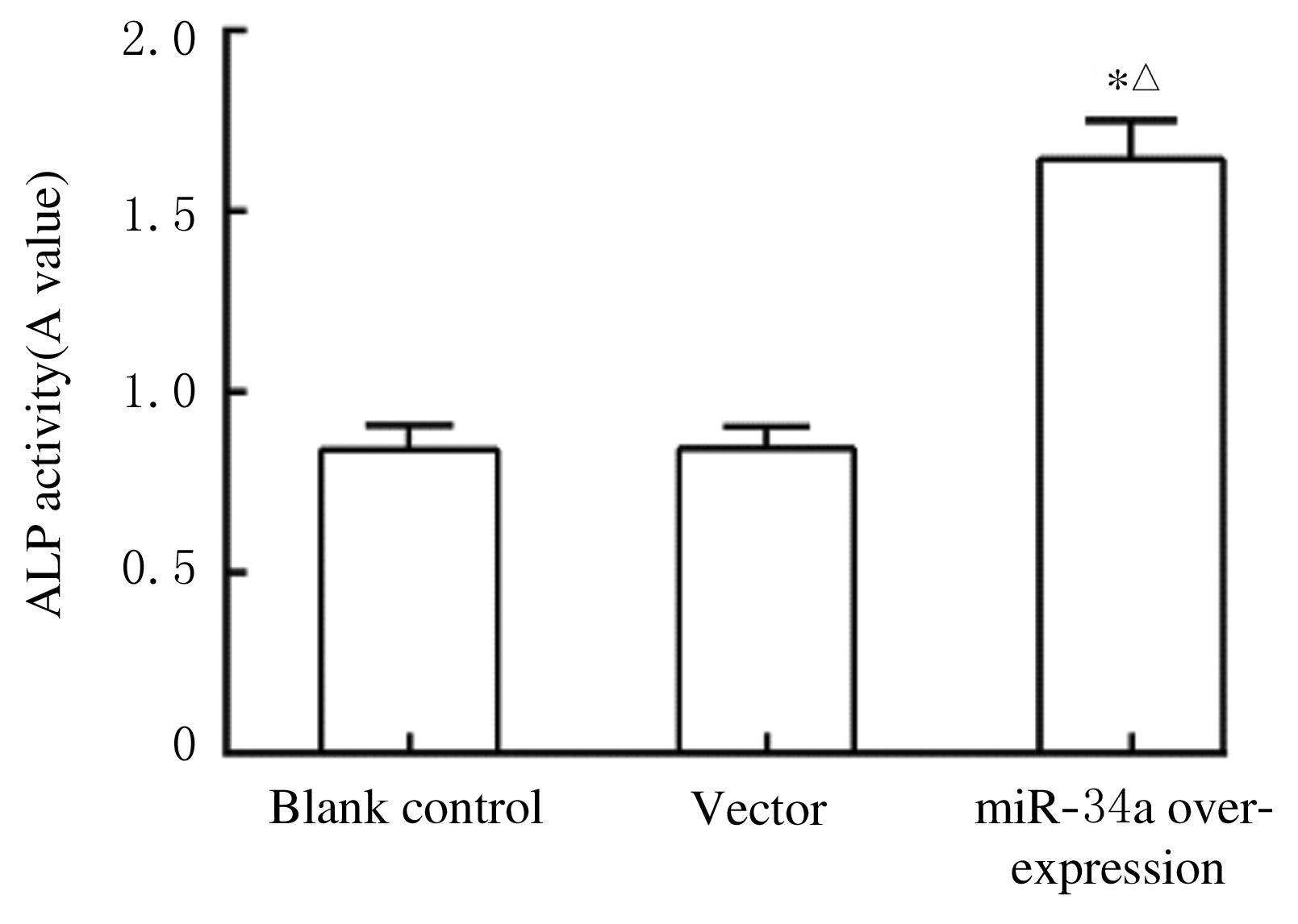
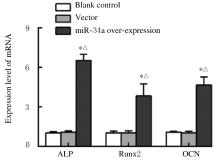
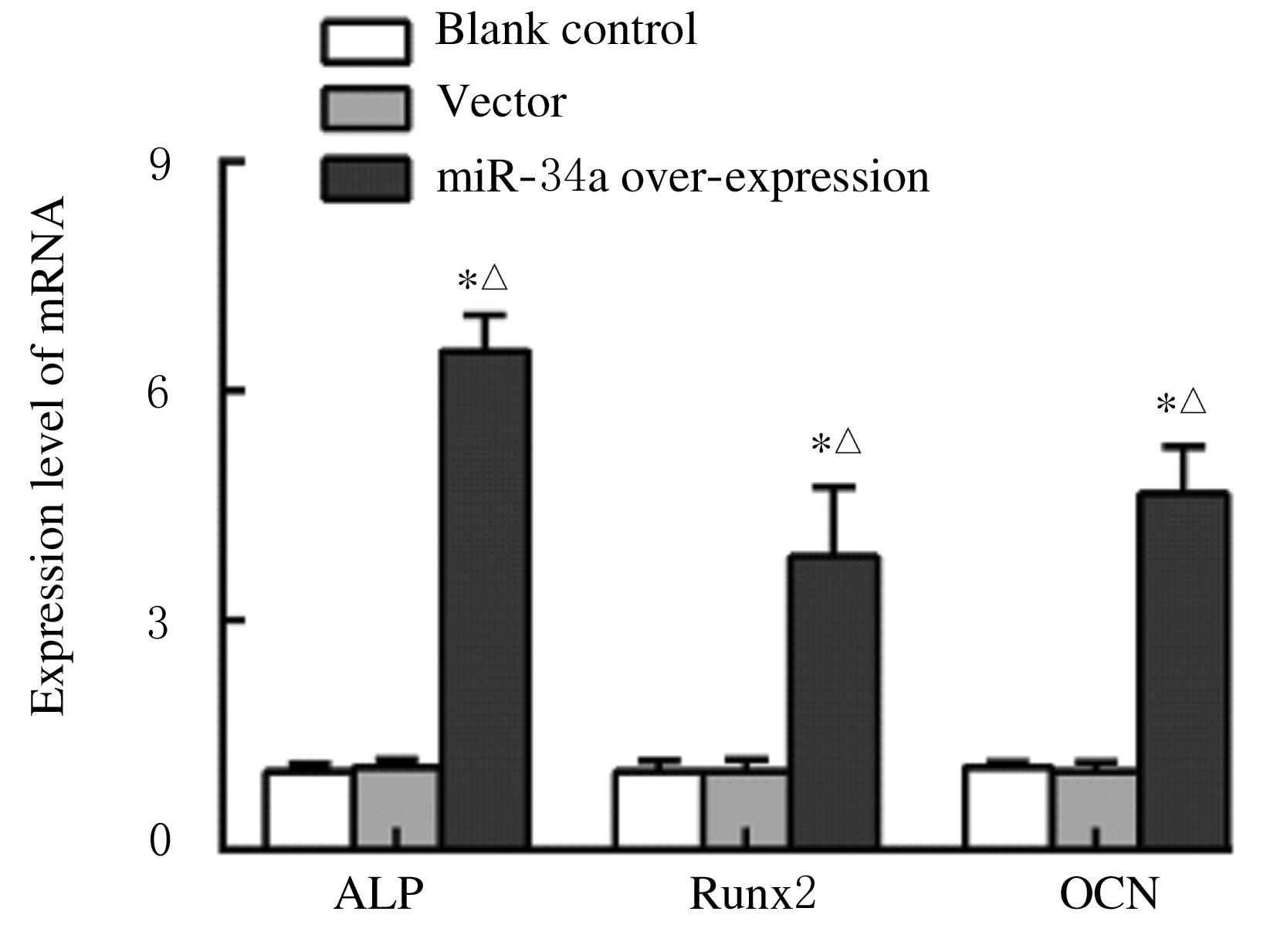
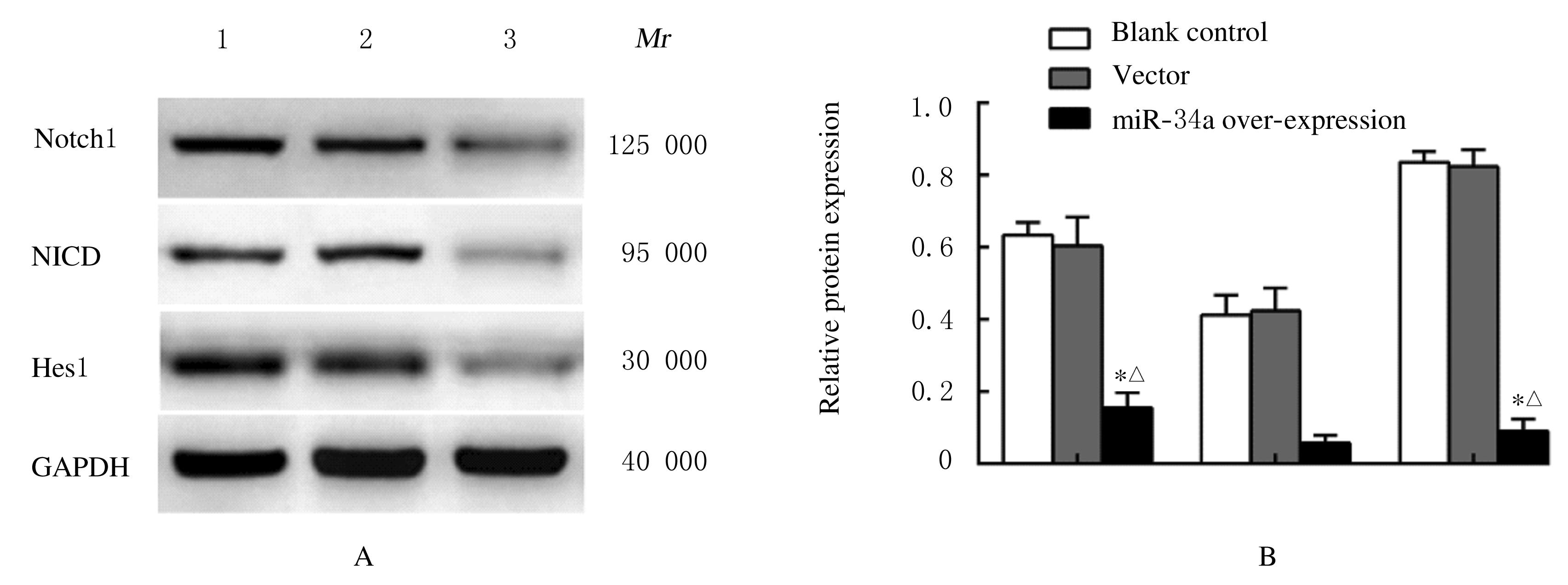
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (6): 1362-1370.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210604
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Promotion effect of miR-34a on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells and its mechanism
Xia DONG1,Xunxia WANG1( ),Fang YANG2
),Fang YANG2
- 1.Department of Stomatology,Haici Medical Group,Qingdao Ctiy,Shangdong Province,Qingdao 266000,China
2.Stomatology Center,Qingdao Municipal Hospital,Shangdong Province,Qingdao 266000,China
-
Received:2021-03-09Online:2021-11-28Published:2021-12-14 -
Contact:Xunxia WANG E-mail:wangqianyang876@163.com
CLC Number:
- R780.2
Cite this article
Xia DONG,Xunxia WANG,Fang YANG. Promotion effect of miR-34a on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells and its mechanism[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1362-1370.
share this article
| 1 | 杜婷婷, 刘 娜, 张 彤. 影响牙周膜干细胞生物学特性的生物学因素[J]. 中华老年口腔医学杂志, 2017, 15(1): 46-50. |
| 2 | RAMENZONI L L, RUSSO G, MOCCIA M D, et al. Periodontal bacterial supernatants modify differentiation, migration and inflammatory cytokine expression in human periodontal ligament stem cells[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(7): e0219181. |
| 3 | GU X, LI M, JIN Y, et al. Identification and integrated analysis of differentially expressed lncRNAs and circRNAs reveal the potential ceRNA networks during PDLSC osteogenic differentiation[J]. BMC Genet, 2017, 18(1): 100. |
| 4 | MOKHBERIAN N, BOLANDI Z, EFTEKHARY M, et al. Inhibition of miR-34a reduces cellular senescence in human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells through the activation of SIRT1[J]. Life Sci, 2020, 257: 118055. |
| 5 | LINDSEY R C, XING W R, POURTEYMOOR S,et al.Novel role for claudin-11 in the regulation of osteoblasts via modulation of ADAM10-mediated notch signaling[J]. J Bone Miner Res, 2019, 34(10): 1910-1922. |
| 6 | YANG F, CHEN Q S, YANG M, et al. Macrophage-derived MMP-8 determines smooth muscle cell differentiation from adventitia stem/progenitor cells and promotes neointima hyperplasia[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2020, 116(1): 211-225. |
| 7 | LIU N X, ZHOU M, ZHANG Q, et al. Effect of substrate stiffness on proliferation and differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells[J]. Cell Prolif, 2018, 51(5): e12478. |
| 8 | 贾凌璐, 文 勇, 徐 欣. 体外培养环境影响牙周膜干细胞生物学特性的研究进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2018, 45(3): 255-260. |
| 9 | SEO B M, MIURA M, GRONTHOS S, et al. Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human periodontal ligament[J].Lancet,2004,364(9429):149-155. |
| 10 | GEOFFROY A, KEREK R, POURIÉ G, et al. Late maternal folate supplementation rescues from methyl donor deficiency-associated brain defects by restoring let-7 and miR-34 pathways[J].Mol Neurobiol,2017,54(7): 5017-5033. |
| 11 | CHOI Y J, LIN C P, RISSO D, et al. Deficiency of microRNA miR-34a expands cell fate potential in pluripotent stem cells[J]. Science,2017, 355(6325): eaag1927. |
| 12 | ZENG H B, DONG L Q, XU C, et al. Artesunate promotes osteoblast differentiation through miR-34a/DKK1 axis[J]. Acta Histochem, 2020, 122(7): 151601. |
| 13 | YAN X, ZHANG D, WU W, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells promote hepatocarcinogenesis via lncRNA-MUF interaction with ANXA2 and miR-34a[J]. Cancer Res, 2017, 77(23): 6704-6716. |
| 14 | MIZUNO S, YODA M, SHIMODA M, et al. Inhibition of ADAM10 in satellite cells accelerates muscle regeneration following muscle injury[J]. J Orthop Res, 2018, 36(8): 2259-2265. |
| 15 | SUN S Q, REN L J, LIU J, et al. Sevoflurane inhibits migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by regulating microRNA-34a/ADAM10 axis[J]. Neoplasma, 2019, 66(6): 887-895. |
| 16 | 程孟文, 周 毅. MiR-34a在牙周膜细胞成骨向分化中的作用[J]. 口腔医学研究, 2017, 33(9): 928-932. |
| 17 | 封 艳, 粱学萍, 赵 今, 等. 人牙周膜干细胞与牙周膜细胞生物学特性的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(28): 4510-4516. |
| 18 | 张 文, 方 明, 鲍东昱, 等. DAPT对牙周膜干细胞体外增殖及成骨分化的影响[J]. 口腔生物医学, 2018, 9(1): 7-11. |
| 19 | BAGHERI L, PELLATI A, RIZZO P, et al. Notch pathway is active during osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced by pulsed electromagnetic fields[J]. J Tissue Eng Regen Med, 2018, 12(2): 304-315. |
| 20 | 王 林, 王 熙, 季 楠, 等. 机械激活性离子通道压电蛋白piezo1通过notch信号通路介导牙周膜干细胞成骨分化作用机制研究[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2020, 38(6): 628-636. |
| [1] | Xinying ZOU,Shuang GAO,Hong ZHAO,Xin LIU,Yuanhang ZHAO,Jiazhuo SONG,Linlin YAN,Zhimin ZHANG. Effect of TGF-β3-loaded methacrylated heparin on osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 954-961. |
| [2] | Chunxu LIU,Hongxia SUN,Bo HU,Enping JIANG. Inhibitory effects of Schisandrin B on cardiac fibroblast proliferation and its PI3K/Akt/P27kip1 signaling pathway mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 52-58. |
| [3] | Xuanchen LIU,Xiaoying TIE,Yulin LIU, WangNing. Effect of polygonum multiflorum extract on osteoporosis and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in agravic mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1386-1396. |
| [4] | Xin ZHANG,Chaojuan JU,Xin JIN,Chaohui XIONG,Yan ZHAO. Protective effect of exogenous nerve growth factor on scleral tissue of guinea pigs with form-deprived myopia and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1455-1461. |
| [5] | Dayong XU,Yunpeng LI,Jingmei WEI,Ruyin LIU. Inhibitory effect of baicalin on inflammation in rats with spinal cord injury by regulating macrophage M2 polarization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 158-167. |
| [6] | GUO Weiwei, QIN Yue, YANG Haibo, MI Zhanhu. Promotion effect of LncRNA MALAT1 on osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells through miR-34c/SATB2 axis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 963-971. |
| [7] | DENG Yuening, ZHOU Daan, MA Xiande, CHEN Dan, SHI Dan, JIANG Yanan. Effects of electro-acupuncture on urodynamics and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in rats with neurogenic bladder after T10 spinal cord transection [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 221-227. |
| [8] | DUAN Yihan, SHENG Yu, XU Jian, LU Xuechun, DU Peige, AN Liping. Anti-aging effects of Agaricus blazei polysaccharide in D-galactose-induced aging model mice and Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signal transduction pathway mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 346-351. |
| [9] | ZHOU Haixia, HOU Lijian, WANG Zhengming, TIAN Yu, HAN Liang, LI Mifu. Inhibitory effect of HOXA4 on transplantationglioma of nude mice through regulating Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(03): 474-478. |
| [10] | BI Xueting, SHEN Yuqin, XU Xiaowei, LI Wenjie, WANG Zhuoran, LIN Chongtao. Effects of oligodeoxynucleotide YW002 on proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis and early osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(02): 273-279. |
| [11] | YANG Xueliang, WANG Minghua, LIU Yanbo, SUN Xuemei, ZHAO Xiahui, YANG Lijuan, XIAO Zishen. Effect of recombinant human IL-17A on growth of colon cancer cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(02): 258-261. |
| [12] | WANG Yue, LIU Chang, PIAO Xianji, ZHANG Dongyun, MENG Lingqi, WANG Hao, WANG Jiaru, LUO Yinghua, SUN Hunan, JIN Chenghao. Induction effect of tetrabromobenzotriazole on apoptosis of human colon cancer SW480 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(06): 1148-1154. |
| [13] | LI Kun, LI Jiarui, ZHANG Jiayue, DONG Danyang, ZHANG Qiang, YANG Qing, LIU Yingna, LI Na. Anti-oxidative damage effect in Schisandrin B in mice of Alzheimer's disease and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(03): 582-587. |
| [14] | QIN Beibei, LI Yaqing, LI Xiaoli, LU Lisha, ZHANG Xudong, ZHANG Mingzhi. Expressions of key molecules of Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway in NK/T-cell lymphoma tissue and their significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(02): 230-234. |
| [15] | FENG Wenlei, ZHANG Meng, XU Fangjie, YIN Shuanghong, WANG Yanjie, CHEN Xueling, WU Xiangwei. Effects of endothelial progenitor cells conditioned medium on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(02): 218-224. |