Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (6): 1462-1468.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210616
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
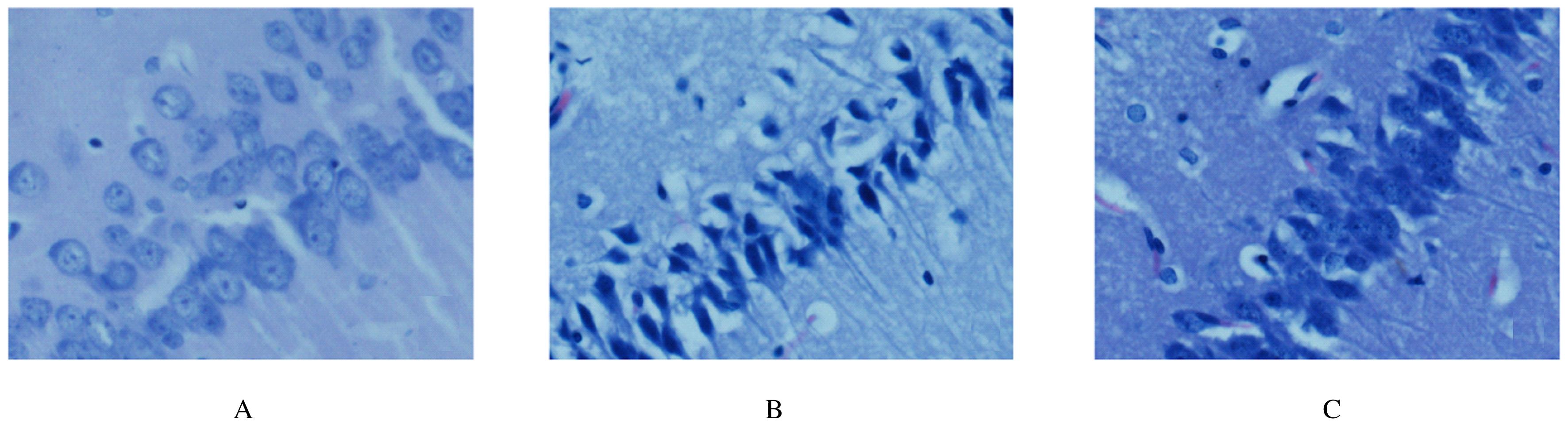
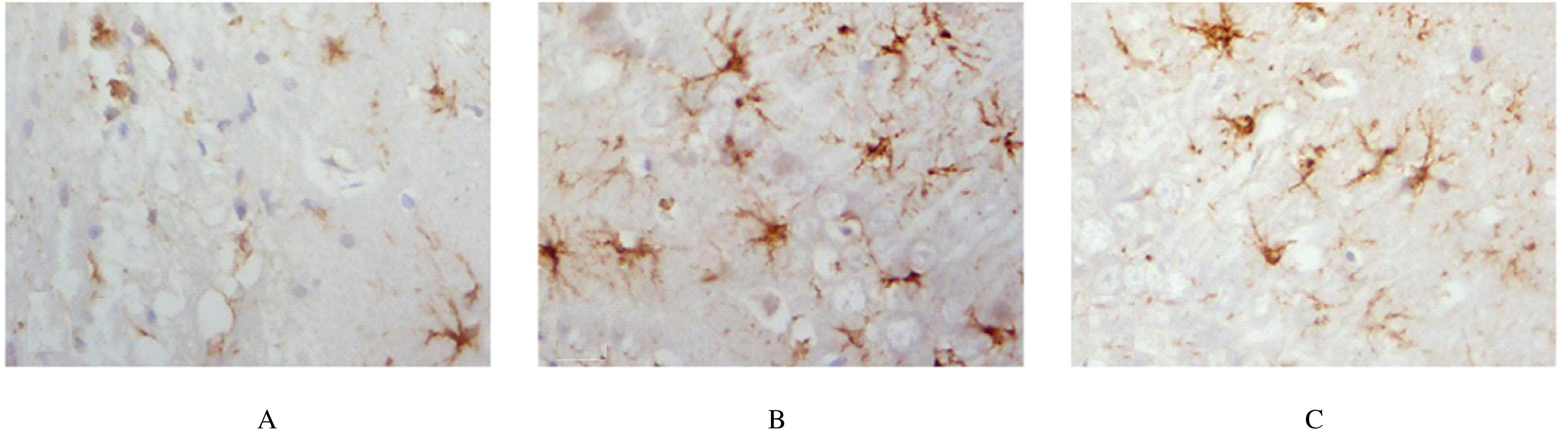
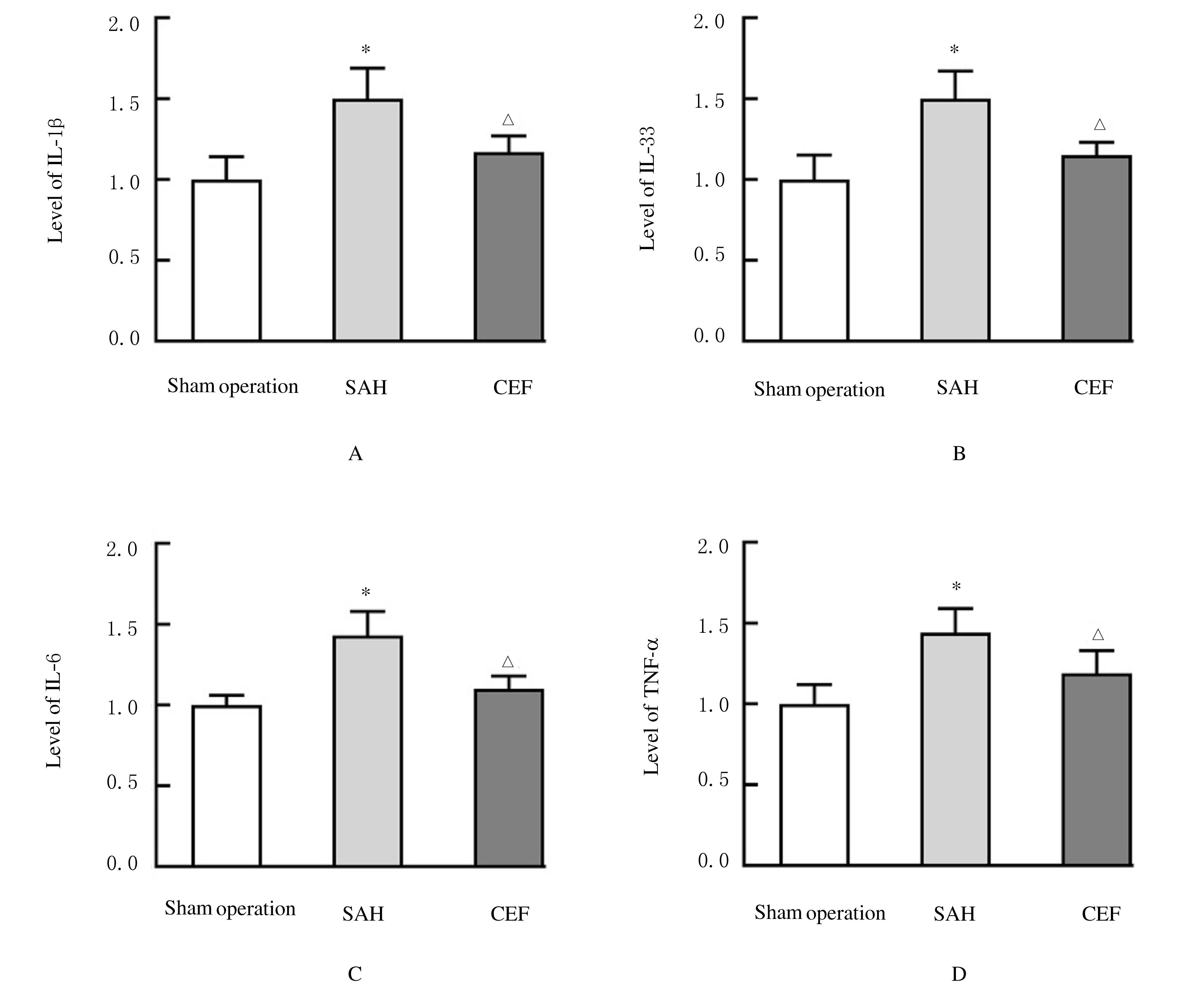
Effects of ceftriaxone on activation of astrocytes and inflammation reaction in rats with subarachnoid hemorrhage
Zehua GONG1,2,Junjie LIU1,2,Jiwei XU2,Jianmin LI1,2( )
)
- 1.Experimental Center,College of Clinical Medicine,North China University of Science and Technology,Tangshan 063000,China
2.Department of Neurosurgery,Affiliated Hospital of North China University of Science and Technology,Tangshan 063000,China
-
Received:2021-03-25Online:2021-11-28Published:2021-12-14 -
Contact:Jianmin LI E-mail:2360796486@qq.com
CLC Number:
- R743.35
Cite this article
Zehua GONG,Junjie LIU,Jiwei XU,Jianmin LI. Effects of ceftriaxone on activation of astrocytes and inflammation reaction in rats with subarachnoid hemorrhage[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1462-1468.
share this article
| 1 | SCHATLO B, FUNG C, STIENEN M N, et al. Incidence and outcome of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: the Swiss study on subarachnoid hemorrhage (Swiss SOS)[J].Stroke,2021,52(1): 344-347. |
| 2 | WANG C, JIA Q, SUN C, et al. Calcium sensing receptor contribute to early brain injury through the CaMKII/NLRP3 pathway after subarachnoid hemorrhage in mice[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2020, 530(4): 651-657. |
| 3 | LIU W, LI R, YIN J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate the early brain injury of subarachnoid hemorrhage partly by suppression of Notch1-dependent neuroinflammation: involvement of Botch[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2019, 16(1): 8. |
| 4 | HEINZ R, BRANDENBURG S, NIEMINEN-KELHÄ M, et al. Microglia as target for anti-inflammatory approaches to prevent secondary brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH)[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2021, 18(1): 36. |
| 5 | HAMAO N, ITO I, KONISHI S, et al. Comparison of ceftriaxone plus macrolide and ampicillin/sulbactam plus macrolide in treatment for patients with community-acquired pneumonia without risk factors for aspiration: an open-label, quasi-randomized, controlled trial[J]. BMC Pulm Med, 2020, 20(1): 160. |
| 6 | THÖNE-REINEKE C, NEUMANN C, NAMSOLLECK P, et al. The beta-lactam antibiotic, ceftriaxone, dramatically improves survival, increases glutamate uptake and induces neurotrophins in stroke[J]. J Hypertens, 2008, 26(12): 2426-2435. |
| 7 | KAUR B, PRAKASH A. Ceftriaxone attenuates glutamate-mediated neuro-inflammation and restores BDNF in MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease in rats[J]. Pathophysiology, 2017, 24(2): 71-79. |
| 8 | BARRY K J, GOGJIAN M A, STEIN B M. Small animal model for investigation of subarachnoid hemorrhage and cerebral vasospasm[J]. Stroke, 1979, 10(5): 538-541. |
| 9 | GARCIA J H, WAGNER S, LIU K F, et al. Neurological deficit and extent of neuronal necrosis attributable to middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats[J]. Stroke, 1995, 26(4): 627-635. |
| 10 | FENG D, WANG W, DONG Y, et al. Ceftriaxone alleviates early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage by increasing excitatory amino acid transporter 2 expression via the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Neuroscience, 2014, 268: 21-32. |
| 11 | WANG Y, KONG X Q, WU F,et al.SOCS1/JAK2/STAT3 axis regulates early brain injury induced by subarachnoid hemorrhage via inflammatory responses[J].Neural Regen Res,2021,16(12): 2453-2464. |
| 12 | LUO X, LI L N, ZHENG W, et al. HLY78 protects blood-brain barrier integrity through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway following subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats[J]. Brain Res Bull, 2020, 162: 107-114. |
| 13 | LIU C M, TIAN Z K, ZHANG Y J, et al. Effects of gastrodin against lead-induced brain injury in mice associated with the wnt/Nrf2 pathway[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12(6): 1805. |
| 14 | WANG X, LI S, MA J, et al. Effect of gastrodin on early brain injury and neurological outcome after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats[J]. Neurosci Bull, 2019, 35(3): 461-470. |
| 15 | LIANG H, KE D Q, CHEN Z Y, et al. Target inhibition of caspase-8 alleviates brain damage after subarachnoid hemorrhage[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2020, 15(7): 1283. |
| 16 | LIN C, LECCA D, YANG L, et al. 3,6'-dithiopomalidomide reduces neural loss, inflammation, behavioral deficits in brain injury and microglial activation [J]. Elife, 2020, 9: e54726-54759. |
| 17 | LIU M, XU Z P, WANG L, et al. Cottonseed oil alleviates ischemic stroke injury by inhibiting the inflammatory activation of microglia and astrocyte[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2020, 17(1): 270. |
| 18 | YANG L J, LI X, WANG S Q, et al. Ceftriaxone pretreatment protects rats against cerebral ischemic injury by attenuating microglial activation-induced IL-1β expression[J]. Int J Neurosci, 2014, 124(9): 657-665. |
| 19 | FAIRLIE-CLARKE K, BARBOUR M, WILSON C, et al. Expression and function of IL-33/ST2 axis in the central nervous system under normal and diseased conditions[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 2596. |
| 20 | 颜姝雯,周 双,蔡晓菁,等.长程使用头孢曲松钠治疗原发性颅底坏死性炎症9例报道[J].同济大学学报(医学版),2021,42(5):724-728. |
| 21 | CHISTYAKOV D V, GAVRISH G E, GORIAINOV S V,et al. Oxylipin profiles as functional characteristics of acute inflammatory responses in astrocytes pre-treated with IL-4, IL-10,or LPS[J].Int J Mol Sci,2020,21(5):1780. |
| 22 | 刘俊杰, 杜 鹃, 杨雅菊, 等. 头孢曲松对蛛网膜下腔出血大鼠海马神经细胞的保护作用及其机制[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2019, 45(5): 1069-1074, 1196. |
| [1] | Feng ZHAO,Shaoqing FAN,Xiaoyan CHENG,Xiaona LI,Changsheng LI,Haojie MA. Effect of intrathecal injection of transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily A member 1 shRNA on neuropathic pain in mice with partial sciatic nerve ligation and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1485-1494. |
| [2] | Qi LIU,Xianchen ZHANG,Xiangyu LI,Yumiao LIN,Yanqi YANG,Enzhi YAN. Inhibitory effect of lithium chloride on Aβ1-42-induced astrocyte glutamate release and its protective effect on hippocampal neuronal injury [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 35-43. |
| [3] | PEI Dan, LIU Xue. Effect of inhibition of PDGFRα activation on glial cell proliferation and scar formation after brain injury in mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 1023-1028. |
| [4] | LIU Junjie, DU Juan, YANG Yaju, WANG Xue, SUN Yuting, LIU Yao, ZHAO Yaning, LI Jianmin. Protective effect of ceftriaxone on hippocampal neurons in subarachnoid hemorrhage rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(05): 1069-1074. |
| [5] | JIANG Ren, FENG Zhiying, LI Ping, LI Hong, LI Shuangyue. Effect of sciatic nervepulsed radiofrequency glial activation levels in spinal dorsal horn in chronic constriction injury rat models and its analgesia effect [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(01): 45-50. |
| [6] | LIU Linna, CHEN Jieyu, LYU Fangyi, HUA Kouzhen, CAI Damin, YIN Guoli, WANG Junjuan. Effect of fingolimod on proliferation and migration of neural stem cells and astrocytes and its protective mechanism against spinal cord injury in mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2018, 44(06): 1218-1222. |
| [7] | FAN Hairui, ZHAO Yan, FU Jinglong, ZHANG Haibo, WANG Dechao, GAO Yugang, ZHANG Lianxue. Anti-inflammatory effect of Tongfengning Capsule in rats with acute gouty arthritis and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(02): 270-274. |
| [8] | ZHAO Yaning, ZHAO Xu, GUO Xiangfei, LI Jianmin, XUE Chengjing. Improvement effect of BQ-123 on nerve function damage after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(05): 925-931. |
| [9] | ZHAO Lijun, LI Kaiji, LU Qiuling, MEN Xiuli. Protective effect of ischemia postconditioning on lung injury after limb ischemia reperfusion in rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(02): 255-259. |
| [10] | WU Bing|KANG Jin-song| WANG He-yuan,XI Xin,QIU Hai-yang|WANG Wei-wei. Establishment of rat subarachroid hemorrhage model by second injection of blood into cisterna and protective effect of nimodipine on brain [J]. J4, 2011, 37(6): 1153-1156. |
| [11] | MA Li-na, YU Hong-mei,ZHAO Wen-jing, LUO Tao, CHEN Sen, NOMOTO Hiroshi, FURUKAWA Shoei. Construction and identification of astrocyte linesexpressing NGF, BDNF, and NT3 steadily [J]. J4, 2005, 31(2): 227-230. |
| [12] | MA Li-na, ZHAO Wen-jing, LUO Tao, NOMOTO Hiroshi,FURUKAWA Shoei. Establishment of culture system of conditionalizationfor astrocytes of cerebral cortex in vitro [J]. J4, 2004, 30(5): 727-729. |
| [13] | LI Xian-hui, CHENG Yi, LIU Ya-wen , WANG Gang, LI Ji-sheng. Expression of nerve growth factor gene in astrocytescultured in 1,25-(OH)2D3 defined medium [J]. J4, 2004, 30(3): 398-400. |