Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (4): 905-914.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220409
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
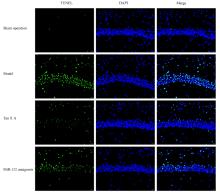
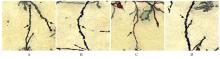
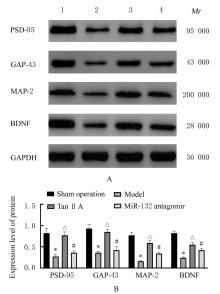
Effects of tanshinone ⅡA on miR-132 expression in hippocampus tissue of neonatal rats with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy and its mechanism
Yang ZHANG( ),Meiyue CHEN,Ying CUI,Na LIU
),Meiyue CHEN,Ying CUI,Na LIU
- Department of Pediatrics,Second Department of First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130031,China
-
Received:2021-10-17Online:2022-07-28Published:2022-07-26 -
Contact:Yang ZHANG E-mail:513396998@qq.com
CLC Number:
- R-332
Cite this article
Yang ZHANG,Meiyue CHEN,Ying CUI,Na LIU. Effects of tanshinone ⅡA on miR-132 expression in hippocampus tissue of neonatal rats with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy and its mechanism[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 905-914.
share this article
Tab.1
Levels of noradrenaline, dopamine,and 5-hydroxytryptamine in hippocampus tissue of rats in various groups [n=10,x±s, ρB/(μg·L-1)]"
| Group | Noradrenaline | Dopamine | 5-Hydroxytryptamine |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sham operation | 16.23±1.77 | 0.38±0.05 | 31.23±2.14 |
| Model | 8.94±0.85* | 0.14±0.03* | 19.82±1.35* |
| Tan ⅡA | 14.82±1.23△ | 0.33±0.07△ | 28.77±2.01△ |
| MiR-132 antagomir | 9.11±0.91# | 0.18±0.04# | 20.05±1.28# |
| 1 | QIN X, CHENG J, ZHONG Y, et al. Mechanism and treatment related to oxidative stress in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy[J]. Front Mol Neurosci, 2019, 12(1): 88. |
| 2 | LI B, DASGUPTA C, HUANG L, et al. MiRNA-210 induces microglial activation and regulates microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2020, 17(9): 976-991. |
| 3 | RODRIGUEZ M, VALEZ V, CIMARRA C, et al. Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy and mitochondrial dysfunction: facts, unknowns, and challenges[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2020, 33(4): 247-262. |
| 4 | SHIM G H. Which factors predict outcomes of neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy following therapeutic hypothermia?[J]. Clin Exp Pediatr, 2021, 64(4): 169-171. |
| 5 | ZHAO M, ZHU P, FUJINO M, et al. Oxidative stress in hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2016, 17(12): 2078-2092. |
| 6 | WASSINK G, DAVIDSON J O, DHILLON S K,et al. Therapeutic hypothermia in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy[J]. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep, 2019, 19(2): 2. |
| 7 | BI Z, WANG Y, ZHANG W. A comprehensive review of tanshinone ⅡA and its derivatives in fibrosis treatment[J].Biomed Pharmacother,2021,137(2):111404. |
| 8 | WANG L, XIONG X, ZHANG X, et al. Sodium tanshinone ⅡA sulfonate protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting autophagy and inflammation[J]. Neuroscience, 2020, 441(1): 46-57. |
| 9 | LAI Z, HE J, ZHOU C, et al. Tanshinones: an update in the medicinal chemistry in recent 5 years[J]. Curr Med Chem, 2021, 28(14): 2807-2827. |
| 10 | FANG C, XIE L, LIU C, et al. Tanshinone ⅡA improves hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy through TLR4 mediated nf-kappaB signal pathway[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2018, 18(2): 1899-1908. |
| 11 | ZUO X, LU J, MANAENKO A, et al. MicroRNA-132 attenuates cerebral injury by protecting blood-brain-barrier in MCAO mice[J]. Exp Neurol, 2019, 316(4): 12-19. |
| 12 | FENG B, MENG L, LUAN L, et al. Upregulation of extracellular vesicles-encapsulated miR-132 released from mesenchymal stem cells attenuates ischemic neuronal injury by inhibiting Smad2/c-jun pathway via Acvr2b suppression[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8(3): 568304. |
| 13 | FEI S, CAO L, LI S. microRNA-139-5p alleviates neurological deficit in hypoxic-ischemic brain damage via HDAC4 depletion and BCL-2 activation[J]. Brain Res Bull, 2021, 169(5): 73-80. |
| 14 | ZHANG B, CHEN X, LV Y, et al. Cdh1 overexpression improves emotion and cognitive-related behaviors via regulating hippocampal neuroplasticity in global cerebral ischemia rats[J]. Neurochem Int, 2019, 124(3): 225-237. |
| 15 | SIVAGURU M, KHAW YM, INOUE M. A confocal reflection super-resolution technique to image golgi-cox stained neurons[J]. J Microsc, 2019, 275(2): 115-130. |
| 16 | HAGBERG H, DAVID EDWARDS A, GROENENDAAL F. Perinatal brain damage: the term infant[J]. Neurobiol Dis, 2016, 92(Pt A): 102-112. |
| 17 | GUO K, YIN G, ZI XH, et al. Effect of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors on expression of 5-HT1AR and neurotransmitters in rats with vascular dementia[J]. Genet Mol Res, 2016, 15(4): 15049031. |
| 18 | LIN R, WU Y, TAO J, et al. Electroacupuncture improves cognitive function through Rho GTPases and enhances dendritic spine plasticity in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2016, 13(3): 2655-2660. |
| 19 | MAGEE JC, GRIENBERGER C. Synaptic plasticity forms and functions[J]. Annu Rev Neurosci, 2020, 43(5): 95-117. |
| 20 | LALERT L, JI-AU W, SRIKAM S, et al. Alterations in synaptic plasticity and oxidative stress following long-term paracetamol treatment in rat brain[J]. Neurotox Res, 2020, 37(2): 455-468. |
| 21 | CHEN X, WANG X, TANG L, et al. Nhe5 deficiency enhances learning and memory via upregulating Bdnf/TrkB signaling in mice[J]. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet, 2017, 174(8): 828-838. |
| 22 | ZHU X, WANG P, LIU H, et al. Changes and significance of SYP and GAP-43 expression in the hippocampus of CIH rats[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2019, 16(3): 394-402. |
| 23 | RABER J, TORRES ERS, AKINYEKE T, et al. Detrimental effects of helium ion irradiation on cognitive performance and cortical levels of MAP-2 in B6D2F1 mice[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19(4): 1247. |
| 24 | ZHANG Y, LAN R, WANG J, et al. Acupuncture reduced apoptosis and up-regulated BDNF and GDNF expression in hippocampus following hypoxia-ischemia in neonatal rats[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2015, 172(4): 124-132. |
| [1] | Manying WANG,Baoyu FU,Xiaohao XU,Xiangzhu LI,Hong CHEN,Liwei SUN,Daqing ZHAO. Anti-fatigue effect of ginseng adventitious root protein in mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 18-25. |
| [2] | Na HAN,Fanping LIU,Yanqing TIAN,Zhiqing ZHENG,Weiming LANG,Qian WANG,Yatao LIU,Jianguang ZHU. Regulatory effect of miRNA-27a on immune function in experimental pulmonary tuberculosis rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 104-110. |
| [3] | Mengjie LI,Jinfang XIE,Shuo YIN,Xia LIU. Expressions of MMP-3 and CCN2 in dental pulp tissue of rats with dental pulp injury and their significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 89-95. |
| [4] | YANG Fan, LI Lihua. Effect of vitamin D receptor activation on hepatic fibrosis induced by bile duct ligation in mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 722-727. |
| [5] | HUANG Jiangyong, LI Chanxiu, ZHENG Zhichao, WANG Hongjuan, GUO Lyuhua, WU Zhe, LUO Tao. Effect of probiotics on expression of IL-17 in periodontal tissue of estrogen-deficient mice induced by ovariectomy and its significance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 733-738. |
| [6] | GAO Ruimin, KANG Lingling, HOU Fangzhen. Protective effect of paeonol on myocardial injury in rats with heart failure and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 765-770. |
| [7] | QIN Chao, DAI Xi, YANG Xiaoqiong, WANG Rongli, WANG Xing, LI Guoping. Intervention effect of honokiol on inflammatory response in lung tissue of asthma mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 214-220. |
| [8] | TONG Siya, YANG Qian, ZHANG Mijuan, LI Wei, WANG Tao. Repair effect of cannabinoid on myelin sheath of demyelination model mice induced by cuprizone [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(01): 35-39. |
| [9] | LYU Yanan, FAN Wei, HU Zheng. Construction of immunodeficient mouse models with long-term expression of human cytokines based on piggyBac transposon system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(01): 176-181. |
| [10] | LIU Heng, SUN Fan, XU Qianqian, GAO Yanjun, MA Zheng, DOU Zhijie. Effects of baicalin on cognitive function and expression levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and endostatin in cerebral small vessel disease model rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(05): 1080-1085. |
| [11] | WANG Ruibin, ZHAO Yanjie, SONG Qingkun, SHENG Minjia. Inhibitory effect of metformin on inflammatory responseof Kupffer cells of liver in diabetic mice and its improvement on phagocytic function [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(01): 39-44. |
| [12] | JIANG Ren, FENG Zhiying, LI Ping, LI Hong, LI Shuangyue. Effect of sciatic nervepulsed radiofrequency glial activation levels in spinal dorsal horn in chronic constriction injury rat models and its analgesia effect [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(01): 45-50. |
| [13] | . Research progress in establishment and application of humanized mouse models with human red blood cell reconstitution [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(04): 859-863. |
| [14] | SHI Jing, TAN Xiaobo, YANG Jie, HAO Jiaying, YANG Weili, LI Na. Influence of astaxanthin in refractive status and pathohistology of myopia models caused by concave lens of guinea pigs [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(05): 932-936. |
| [15] | YANG Jie, MA Yinghui, CUI Xiucheng, WANG Hongmei, DONG Weili, TAN Xiaobo. Hypoglycemic effect of panaxnotoginseng polysaccharides in diabetic model ratsand its therapeutic effect on diabetic retinopathy and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(04): 734-738. |
|
||