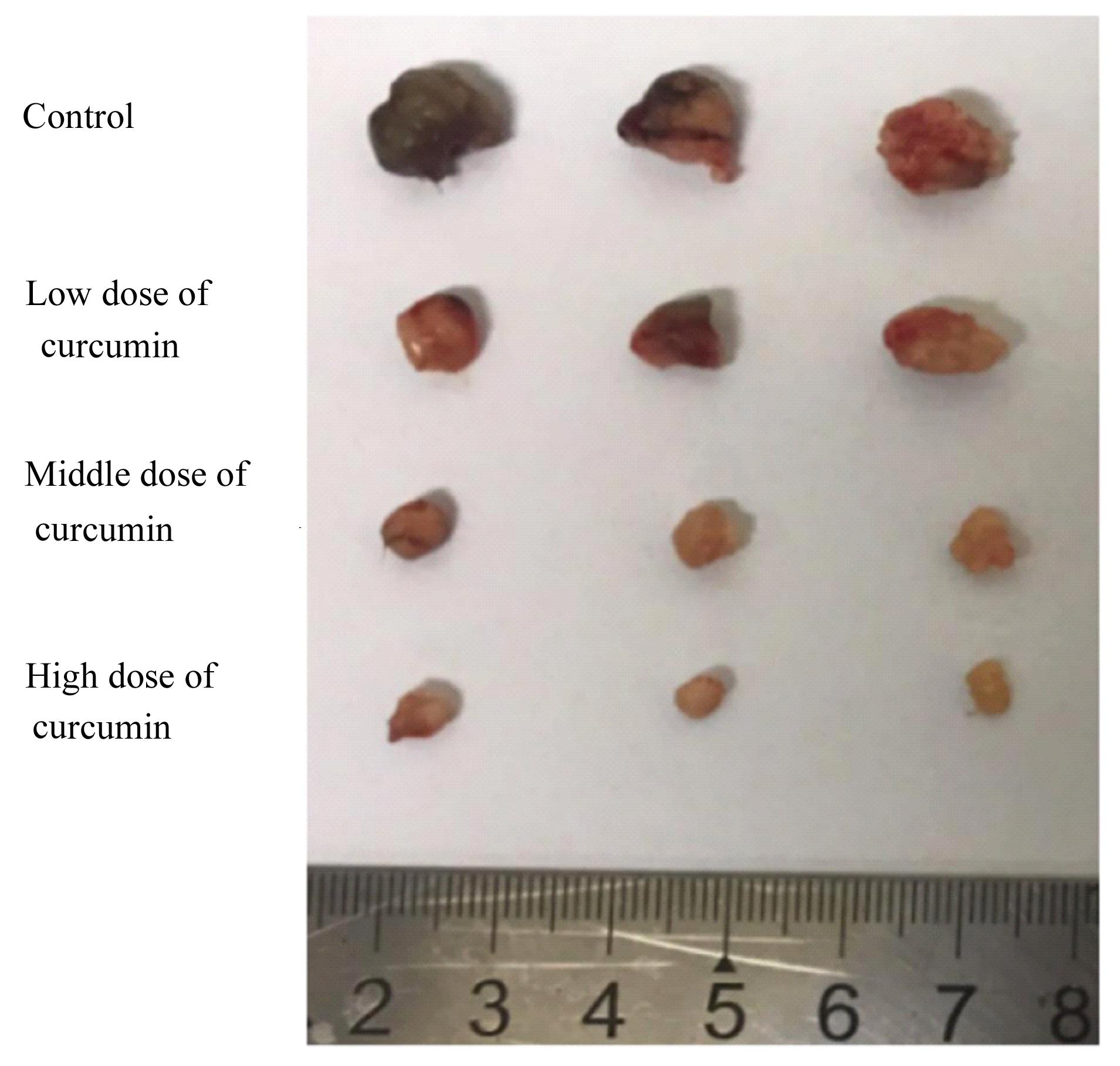
| 1 |
李 婧, 梁何俊, 隋 鑫, 等. Ⅱ/Ⅲ期胃癌术后患者预后预测模型的建立[J].郑州大学学报(医学版),2022,57(2):220-227.
|
| 2 |
SUN W H, JIANG C Q, JI Y, et al. Long noncoding RNAs: new regulators of resistance to systemic therapies for gastric cancer[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2021, 2021: 8853269.
|
| 3 |
高 磊, 俞 阳, 李晓梅, 等. 化疗与免疫检查点抑制剂联用对肿瘤的作用研究进展[J].解放军医学杂志,2022,47(11):1152-1158.
|
| 4 |
DI VITA M, ZANGHÌ A, CAVALLARO A, et al. Gastric GIST and prognostic models. Which is the best to predict survival after surgery? [J]. Ann Ital Chir, 2019, 90: 31-40.
|
| 5 |
CUI L, WANG X Q, ZHANG D K. TLRs as a promise target along with immune checkpoint against gastric cancer[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 8: 611444.
|
| 6 |
LI H Y, YANG M, LI Z, et al. Curcumin inhibits angiotensin Ⅱ-induced inflammation and proliferation of rat vascular smooth muscle cells by elevating PPAR-γ activity and reducing oxidative stress[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2017, 39(5): 1307-1316.
|
| 7 |
ALQURASHI N, HASHIMI S M, ALOWAIDI F,et al. Dual mTOR/PI3K inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 arrests colorectal cancer cell growth and displays differential inhibition of 4E-BP1[J]. Oncol Rep, 2018,40(2): 1083-1092.
|
| 8 |
XIE J, FU L P, JIN L. Immunotherapy of gastric cancer: Past, future perspective and challenges[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2021, 218: 153322.
|
| 9 |
BAHRAMI A, FERNS G A. Effect of curcumin and its derivates on gastric cancer: molecular mechanisms[J]. Nutr Cancer, 2021, 73(9): 1553-1569.
|
| 10 |
叶卫华, 袁虎方. 膜联蛋白A7水平在胃癌患者癌组织及外周血液中的变化及其临床意义[J]. 中国普通外科杂志, 2019, 28(10): 1261-1268.
|
| 11 |
陈金湖, 叶 青.黄峰局部进展期胃癌围手术期治疗的发展历程和研究进展[J].中华胃肠外科杂志,2019,22(2):196-200.
|
| 12 |
陈海滔, 徐 超, 姚庆华. 姜黄素通过调节Wnt/β-catenin信号通路抑制结肠癌细胞上皮间质转化[J]. 肿瘤学杂志, 2017, 23(1): 35-39.
|
| 13 |
YUAN H F, LI Y, YE W H, et al. Downregulation of annexin A7 decreases proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer cells by reducing matrix metalloproteinase 1 and 9 expression[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2019, 11(5): 2754-2764.
|
| 14 |
贺东黎. 姜黄素通过ATK/FoxM1信号通路调控胃癌干细胞增殖及凋亡[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(32): 4731-4737.
|
| 15 |
GHAFOURI-FARD S, ABAK A, TONDRO ANAMAG F, et al. The emerging role of non-coding RNAs in the regulation of PI3K/AKT pathway in the carcinogenesis process[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2021, 137: 111279.
|
| 16 |
崔健昆, 耿乃志, 孟凡吉, 等. 去甲氧基姜黄素通过PI3K-Akt-mTOR信号通路调控细胞自噬对心肌缺血再灌注损伤大鼠的保护作用研究[J]. 中医药学报, 2020, 48(8): 19-24.
|
| 17 |
WANG C, YANG Z, XU E, et al. Apolipoprotein C-II induces EMT to promote gastric cancer peritoneal metastasis via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway[J]. Clin Transl Med, 2021, 11(8): e522.
|
| 18 |
LIN J X, XIE X S, WENG X F, et al. UFM1 suppresses invasive activities of gastric cancer cells by attenuating the expression of PDK1 through PI3K/AKT signaling[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 38(1): 410.
|
| 19 |
XIAO M, LIN C H, YANG Z X, et al. Compound TDB (Tricyclic decyl benzoxazole) induces autophagy-dependent apoptosis in the gastric cancer cell line MGC-803 by regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2021, 13(1): 73-87.
|
| 20 |
WANG H H, MAO J, HUANG Y H, et al. Prognostic roles of miR-124-3p and its target ANXA7 and their effects on cell migration and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Int J Clin Exp Pathol,2020,13(3):357-370.
|
| 21 |
杜锐玲. 叶黄素通过PI3K/AKT信号通路调控胃癌干细胞增殖与凋亡[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2019, 23(29): 4593-4598.
|
| 22 |
沈 玲, 罗 波. 晚期胃癌二线使用EOX和FOLFIRI方案化疗的疗效及安全性评价[J]. 西安交通大学学报(医学版), 2018, 39(4): 546-550.
|
| 23 |
李 琼, 贺延苓, 张志敏. 姜黄素的抗癌生物学机制研究进展[J]. 药物生物技术, 2021, 28(2): 217-220.
|
| 24 |
李柯楠, 刘会勤, 丛 宁, 等. PI3K/mTOR双靶点抑制剂PI-103在体外对喉鳞癌细胞的作用[J]. 复旦学报(医学版), 2019, 46(3): 350-356.
|
| 25 |
ZHANG C, ZHANG M Q, GE S, et al. Reduced m6A modification predicts malignant phenotypes and augmented Wnt/PI3K-Akt signaling in gastric cancer[J]. Cancer Med, 2019, 8(10): 4766-4781.
|
| 26 |
念家云, 王笑民, 富 琦, 等. 基于PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号传导通路的抗癌中药单体的研究概况[J]. 中国药房, 2019, 30(20): 2870-2875.
|
| 27 |
江孝蓉, 王正根. PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路及PI3K/mTOR双重抑制剂在胃癌中的研究进展[J]. 西南军医, 2018, 20(3): 375-379.
|
| 28 |
刘 琦, 郝朗松, 张东兴, 等. PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路抑制剂在转移性结直肠癌中的研究进展[J]. 医学综述, 2019, 25(14): 2721-2725.
|
| 29 |
CHRISTENSEN T D, PALSHOF J A, LARSEN F O,et al. Associations between primary tumor RAS, BRAF and PIK3CA mutation status and metastatic site in patients with chemo-resistant metastatic colorectal cancer[J]. Acta Oncol, 2018, 57(8): 1057-1062.
|
| 30 |
TOWNSEND A, TEBBUTT N, KARAPETIS C,et al.Phase ⅠB/Ⅱ study of second-line therapy with panitumumab, irinotecan, and everolimus (PIE) in KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 24(16): 3838-3844.
|
 )
)