Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3): 599-607.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230307
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Improvement effect of β-sitosterol on cognitive function in Alzheimer’s disease model mice and its mechanism
Xingye WANG1,2,Xiangri KONG3,Mengli JIN4,Bingmei WANG4,Mingquan LI2( )
)
- 1.Laboratory of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine,School of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
2.Department of Neurology,Third Affiliated Hospital,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130118,China
3.Department of Endocrinology,School of Chinese Medicine,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
4.Department of Physiology,School of Clinical Medicine,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
-
Received:2022-08-21Online:2023-05-28Published:2023-06-20 -
Contact:Mingquan LI E-mail:limingquan0001@126.com
CLC Number:
- R742
Cite this article
Xingye WANG,Xiangri KONG,Mengli JIN,Bingmei WANG,Mingquan LI. Improvement effect of β-sitosterol on cognitive function in Alzheimer’s disease model mice and its mechanism[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 599-607.
share this article
Tab.2
Number of autonomic activity and scores of nesting behavior of mice in various groups"
| Group | Number of autonomic activity | Score of nesting behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 110.33±10.24 | 3.17±0.58 |
| Sham operation | 107.50±15.10 | 3.00±0.74 |
| AD | 110.50±14.49 | 1.67±0.78* |
| Donepezil hydrochloride | 109.83±13.81 | 2.75±0.87△ |
| Low dose of β-sitosterol | 107.17±14.41 | 2.67±0.89△ |
| High dose of β-sitosterol | 103.00±14.86 | 2.25±1.06 |
| *P<0.01 vs control group; △P<0.05 vs AD group. | ||
Tab.3
Indentification time of new object and DR of mice in various groups"
| Group | Idenfification time of new object (t/s) | DR |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 57.56±11.78 | 0.65±0.14 |
| Sham operation | 54.30±10.96 | 0.64±0.15 |
| AD | 34.47±7.94* | 0.36±0.11* |
| Donepezil hydrochloride | 50.88±11.30△△ | 0.48±0.15 |
| Low dose of β-sitosterol | 39.37±10.68 | 0.51±0.14△ |
| High dose of β-sitosterol | 44.53±4.01△△ | 0.45±0.10 |
| *P<0.01 vs control group; △P<0.05, △△P<0.01 vs AD group. | ||
Tab. 4
Escape latencies and number of crossing platform of mice in various groups"
| Group | n | Escape latency(t/s) | Number of crossing platform | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (t/d) 1 | 3 | 5 | |||
| Control | 12 | 80.73±5.10 | 47.47±12.57 | 35.81±11.81 | 2.70±0.65 |
| Sham operation | 12 | 81.36±4.51 | 54.06±13.00 | 41.14±7.79 | 2.80±0.97 |
| AD | 11 | 81.33±4.93 | 75.14±8.35* | 67.80±5.60* | 5.90±1.60* |
| Donepezil hydrochloride | 12 | 80.23±3.75 | 62.12±11.56△ | 47.81±7.65△△ | 3.10±1.30△△ |
| Low dose of β-sitosterol | 12 | 77.10±5.95 | 61.91±9.87△ | 52.79±12.06△△ | 3.40±1.80△△ |
| High dose of β-sitosterol | 12 | 80.19±4.96 | 56.57±10.40△△ | 55.62±7.39△△ | 4.00±1.21△△ |
| *P<0.01 vs control group; △P<0.05, △△P<0.01 vs AD group. | |||||
Tab.5
SOD activities and GSH levels in hippocampus tissue of mice in various groups"
| Group | SOD[λB/(U·mL-1)] | GSH[cB/(μmol·L-1)] |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 56.97±5.51 | 123.47±27.99 |
| Sham operation | 54.77±6.30 | 123.71±22.85 |
| AD | 37.41±9.94* | 70.59±9.64* |
| Donepezil hydrochloride | 44.18±14.76 | 88.30±10.95 |
| Low dose of β-sitosterol | 40.15±7.89 | 93.70±16.22 |
| High dose of β-sitosterol | 53.56±8.13△ | 109.59±13.59△ |
| *P<0.01 vs control group; △P<0.01 vs AD group. | ||
Tab.6
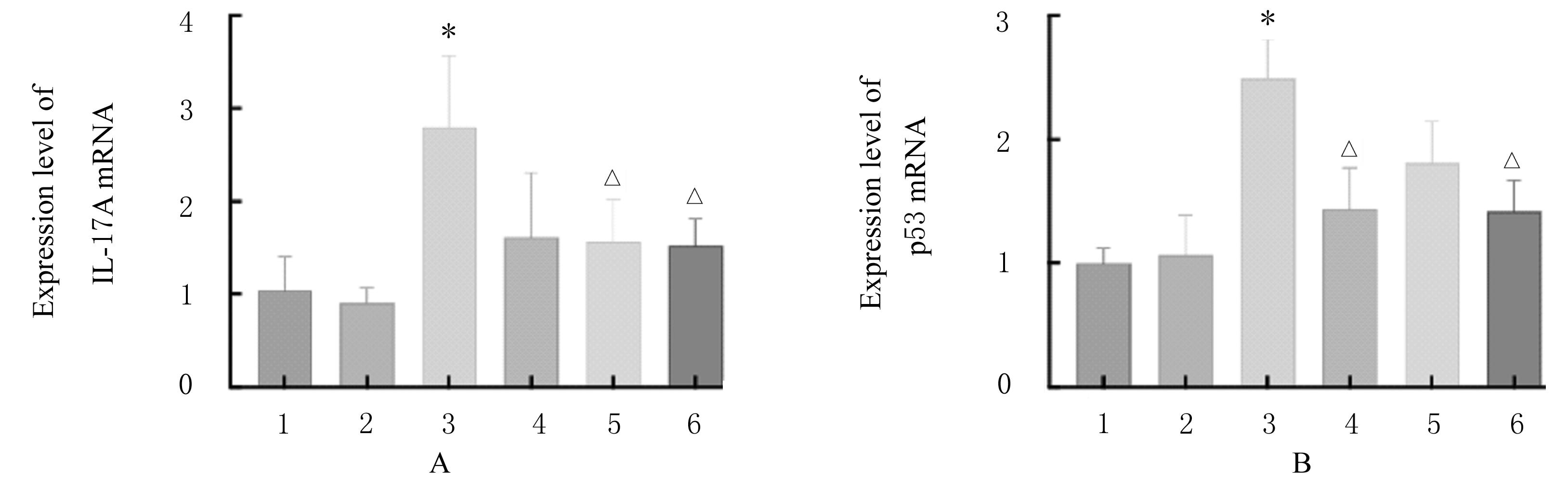
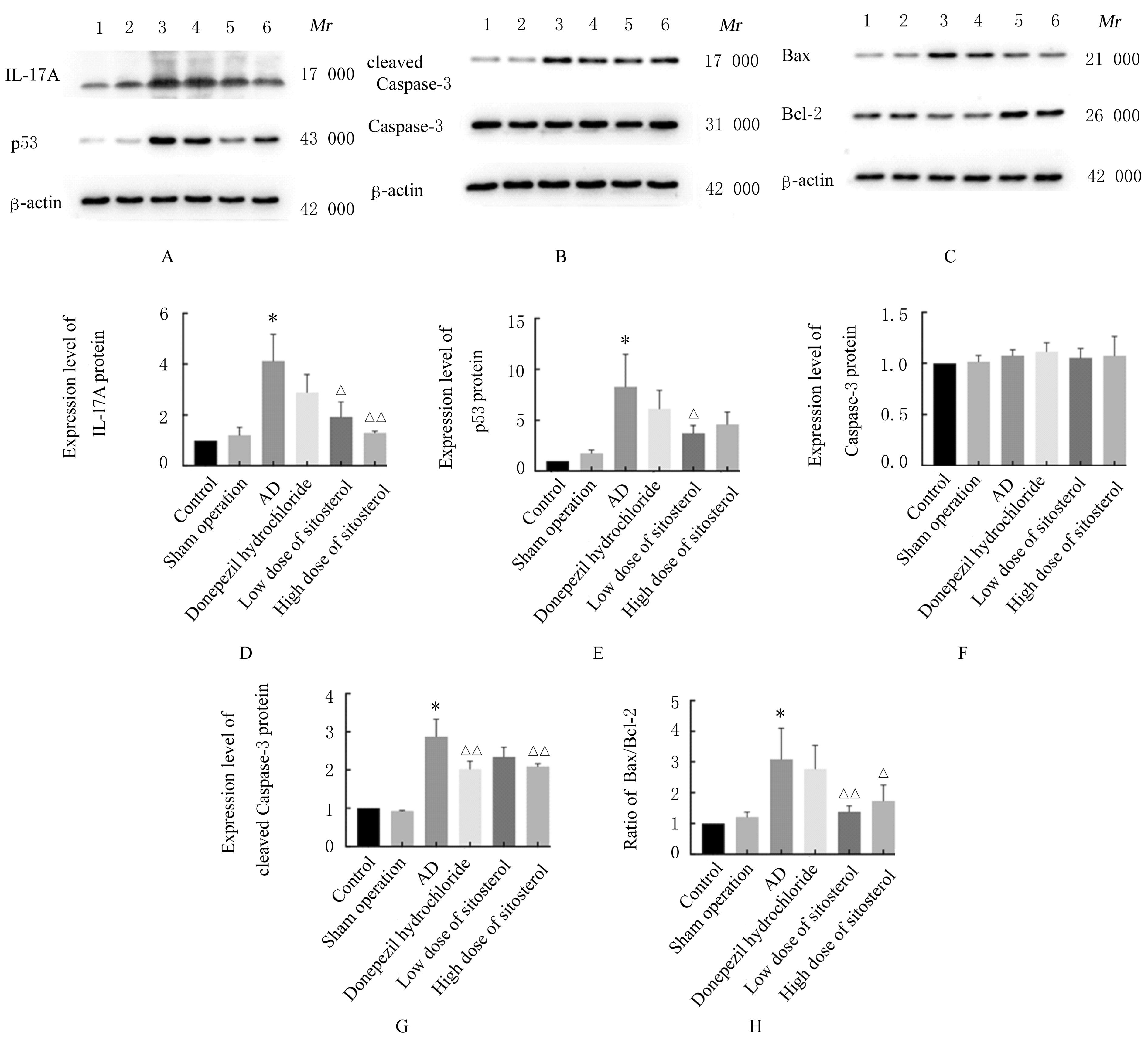
Levels of TNF-α and IL-17A in hippocampus tissue of mice in various groups [n=3,x±s,ρB/(ng·L-1)]"
| Group | TNF-α | IL-17A |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 467.63±36.50 | 192.98±57.22 |
| Sham operation | 495.21±54.06 | 218.30±62.85 |
| AD | 571.12±52.05* | 489.49±45.26* |
| Donepezil hydrochloride | 547.58±32.65 | 454.13±92.60 |
| Low dose of β-sitosterol | 507.49±41.57△ | 415.89±64.78 |
| High dose of β-sitosterol | 525.28±39.31 | 381.97±94.82△ |
| 1 | BRIGAS H C, RIBEIRO M, COELHO J E,et al.IL-17 triggers the onset of cognitive and synaptic deficits in early stages of Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Cell Rep, 2021, 36(9): 109574. |
| 2 | 张 钰, 马 兰. β淀粉样蛋白寡聚体参与阿尔茨海默病发病机制的研究进展[J].中华老年多器官疾病杂志, 2021, 20(8): 628-631. |
| 3 | AMOR S, PEFEROEN L A, VOGEL D Y, et al. Inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases: an update[J]. Immunology, 2014, 142(2): 151-166. |
| 4 | TANG Y, LE W D. Differential roles of M1 and M2 microglia in neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2016, 53(2): 1181-1194. |
| 5 | DUGGER B N, DICKSON D W. Pathology of neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2017, 9(7): a028035. |
| 6 | KWEON J H, KIM S, LEE S B. The cellular basis of dendrite pathology in neurodegenerative diseases[J]. BMB Rep, 2017, 50(1):5-11. |
| 7 | STEPHENSON J, NUTMA E, VAN DER VALK P, et al. Inflammation in CNS neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Immunology, 2018, 154(2): 204-219. |
| 8 | 薛 愉, 邹和建, 郑颂国. IL-17与自身免疫性疾病相关研究进展[J].中华微生物学和免疫学杂志,2007,27(9): 866-870. |
| 9 | OGITA N, OKUSHIMA Y, TOKIZAWA M, et al. Identifying the target genes of suppressor of gamma response 1, a master transcription factor controlling DNA damage response in Arabidopsis[J].Plant J, 2018, 94(3): 439-453. |
| 10 | ABATE G, FRISONI G B, BOURDON J C, et al. The pleiotropic role of p53 in functional/dysfunctional neurons: focus on pathogenesis and diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease[J].Alzheimers Res Ther,2020,12(1): 160. |
| 11 | 陈元堃, 曾 奥, 罗振辉, 等. β-谷甾醇药理作用研究进展[J]. 广东药科大学学报, 2021, 37(1): 148-153. |
| 12 | 刘雅谦, 李 琳, 孙万成, 等. 植物甾醇的抗炎性研究进展[J]. 中国油脂, 2022, 47(5): 93-99. |
| 13 | SHI C, WU F M, ZHU X C, et al. Incorporation of beta-sitosterol into the membrane increases resistance to oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation via estrogen receptor-mediated PI3K/GSK3beta signaling[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2013, 1830(3): 2538-2544. |
| 14 | 赵 帅, 陈冬梅, 虎 娜, 等. β-谷甾醇通过PI3K/AKT通路影响颗粒细胞增殖及凋亡[J]. 宁夏医科大学学报, 2021, 43(4): 339-344. |
| 15 | SHI C, WU F, XU J. Incorporation of β-sitosterol into mitochondrial membrane enhances mitochondrial function by promoting inner mitochondrial membrane fluidity[J]. J Bioenerg Biomembr,2013,45(3): 301-305. |
| 16 | ZHANG J, KE K F, LIU Z, et al. Th17 cell-mediated neuroinflammation is involved in neurodegeneration of aβ1-42-induced Alzheimer’s disease model rats[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(10): e75786. |
| 17 | 闵 喆, 王淑楠, 吴 军,等. Tg-SwDI小鼠的筑巢行为研究[J]. 神经损伤与功能重建, 2014, 9(1): 1-5. |
| 18 | SIVAKUMARAN M H, MACKENZIE A K, CALLAN I R, et al. The discrimination ratio derived from novel object recognition tasks as a measure of recognition memory sensitivity, not bias[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 11579. |
| 19 | 白鑫宇, 刘 萍, 杨 帆, 等. 补阴益智汤配方颗粒对东莨菪碱所致小鼠学习记忆损伤的保护作用[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2017, 23(12): 138-144. |
| 20 | CHEN J M, JIANG G X, LI Q W, et al. Increased serum levels of interleukin-18, -23 and -17 in Chinese patients with Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord, 2014, 38(5/6): 321-329. |
| 21 | CRISTIANO C, VOLPICELLI F, LIPPIELLO P,et al.Neutralization of IL-17 rescues amyloid-β-induced neuroinflammation and memory impairment[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2019, 176(18): 3544-3557. |
| 22 | JAZVINŠĆAK JEMBREK M, SLADE N, HOF P R, et al. The interactions of p53 with tau and Aß as potential therapeutic targets for Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Prog Neurobiol, 2018, 168(104-127. |
| 23 | 邹 瑜, 钟纯正, 郭春宣, 等. miR-130b通过调控p53抑制局灶性脑缺血大鼠神经细胞凋亡[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2020, 40(3): 602-605. |
| 24 | DEZOR M, DORSZEWSKA J, FLORCZAK J, et al. Expression of 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1 (OGG1) and the level of p53 and TNF-αlpha proteins in peripheral lymphocytes of patients with Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Folia Neuropathol, 2011, 49(2): 123-131. |
| 25 | 陈小玉, 罗连响, 潘韵琪, 等. 组织透明化技术在神经退行性疾病中的应用研究进展[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2022, 47(3): 305-313. |
| 26 | 郝淼淼, 田海燕, 刘 晗, 等. 水通道蛋白4低表达通过抑制类淋巴系统功能对AD模型615-619小鼠脑组织磷酸化Tau蛋白表达的影响[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2022, 57(5). |
| 27 | NAKANISHI A, MINAMI A, KITAGISHI Y, et al. BRCA1 and p53 tumor suppressor molecules in Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2015, 16(2): 2879-2892. |
| 28 | 杨俊峰, 刘 强. 免疫与神经系统遗传病[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2022(4): 273-277. |
| [1] | Hongyuan TIAN,Caiyun YIN,Li WANG,Peiyun HU,Chenyang ZHANG,Qiuyue LI,Qingzhao ZHENG,Yali QI,Fang FANG,Zhicheng WANG. Effects of hydroxyurea combined with radiation on cell cycle and apoptosis of cells after silencing ATRX [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 590-598. |
| [2] | Shengyu YAN,Changhua LIU,Zhijie XU,Yating DING,Yafeng XIE,Qiao ZHANG,Wanying LIU. Effect of lncRNA PAX8-AS1 on proliferation, apoptosis and invasion of colorectal cancer cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 656-664. |
| [3] | Shuya ZHANG,Hongying SUN,Jian MAO,Chengxi MENG,Gelong BA. Expression of circ_EFCAB2 in epileptic cell model and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 691-696. |
| [4] | Kai WANG,Han HUANG. Effects of atorvastatin on proliferation, apoptosis, and migration of human tongue squamous cell carcinoma CAL-27 cells and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 324-331. |
| [5] | Yifei SUN,Dinuo LI,Yubin WANG. Inhibitory effect of curcumin on proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer MGC-803 cells by down-regulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway protein expression [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 332-340. |
| [6] | Lianyuan WANG,Yi YANG,Huiwen CONG,Haohua WANG,Qihan BAO,Chengsheng LI,Liwen ZHOU,Zichen DING,Yanli LI,Fuyan SHI,Suzhen WANG. Bayesian quantile regression joint model analysis on risk factors of Alzheimer’s disease in people with different MMSE scores [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 395-401. |
| [7] | Junxiong ZHAO,Qian WU,Liangui NIE,Shengquan LIU,Zhentao JIANG,Jian CHEN,Ting XIAO,Jun YANG. Ameliorative effect of SO2 on myocardial fibrosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 8-14. |
| [8] | Donghui LIU,Mingxi ZHANG,Wenliang FU,Xiumei FU,Chengjun SONG,Zhihong CHEN. Effects of sericin on injury of podocytes induced by high glucose and JNK signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1403-1410. |
| [9] | Xianshun XIE,Wei WANG,Haibing JIANG. Effect of miR-431-3p on proliferation and apoptosis of gastric cancer cells and its mechanism of targeted regulation of CTDP1 gene expression [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1555-1565. |
| [10] | Bingbing WU,Aiping ZHANG,Xinke ZHAO,Yingdong LI,Kai LIU. Protective effect of ultra-filtration extract from Angelica Sinensis Radix and Hedysari Radix on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury induced by X-ray and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1139-1147. |
| [11] | Hongxia SUN,Chunxu LIU,Xuejun AN,Guanghua CUI,Jingyu WANG,Shuangxi TONG,Xiaoqiu YANG. Effect of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharide on proliferation and apoptosis of human bladder cancer T24 cells and its mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1216-1222. |
| [12] | Yuan LIAO,Kaiju WANG,Haoyan LI,Huiping CHEN,Xuanyi LI,Yong HUANG. Improvement effects of neuropeptide PACAP27 on cyclophosphamide-induced testicular injury in rats by inhibiting mitochondria-dependent apoptosis pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1266-1275. |
| [13] | Yujun YUAN,Xiuling YANG,Zhijian HU,Sumei ZHANG. Effects of traditional Chinese medicine indirubin derivative E804 on proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation of lung cancer A549 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1276-1283. |
| [14] | Qingxu LANG,Xueshuang NIU,Kaiwen YANG,Ren ZHANG,Siteng WANG, ZUMIRETIGULI·Wumaier,Zhenqi WANG. Effects of sodium butyrate combined with ionizing radiation on apoptosis of lung cancer A549 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 915-921. |
| [15] | Guanhu LI,Qingxu LANG,Chunyan LIU,Qin LIU,Mengrou GENG,Xiaoqian LI,Zhenqi WANG. Inhibitory effect of valproic acid combined with X-ray irradiation on proliferation of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 622-629. |