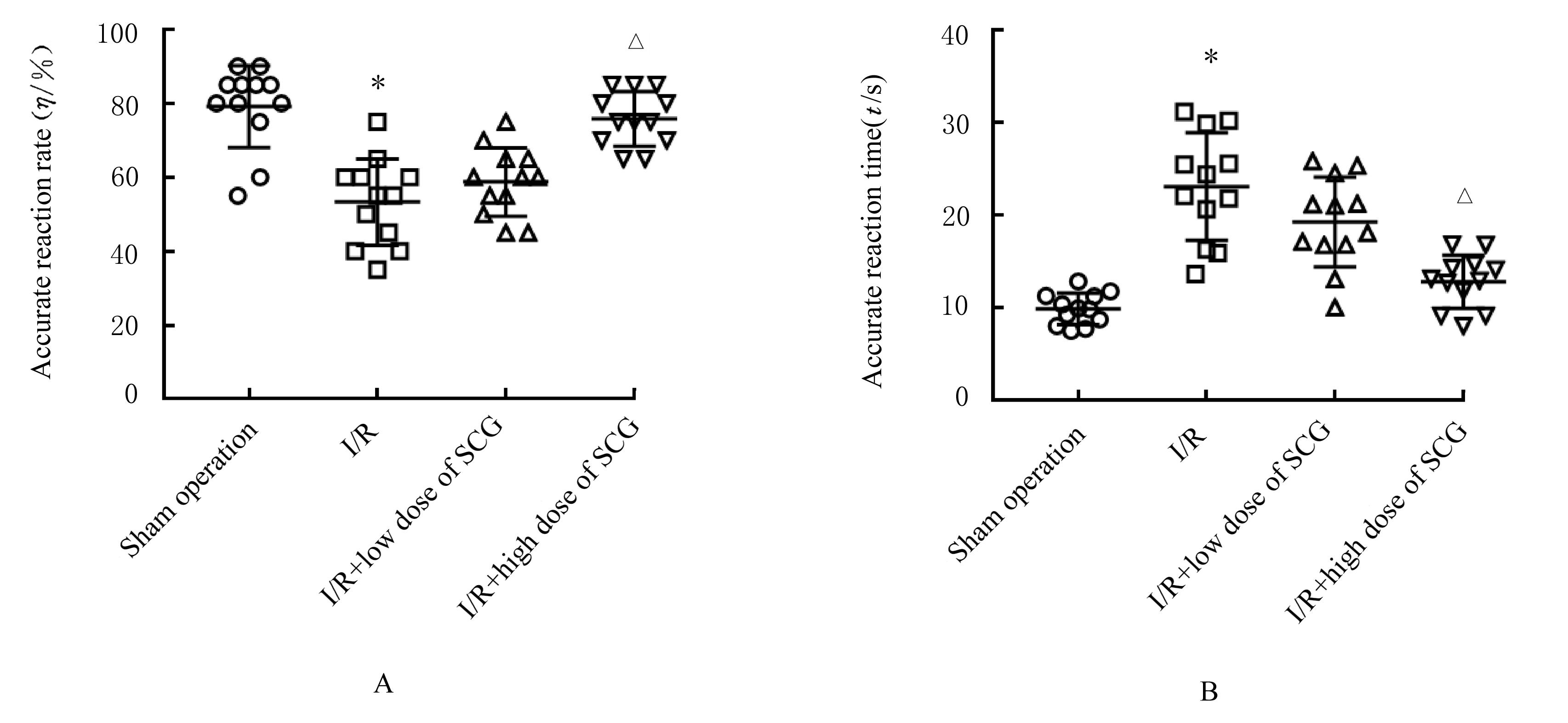
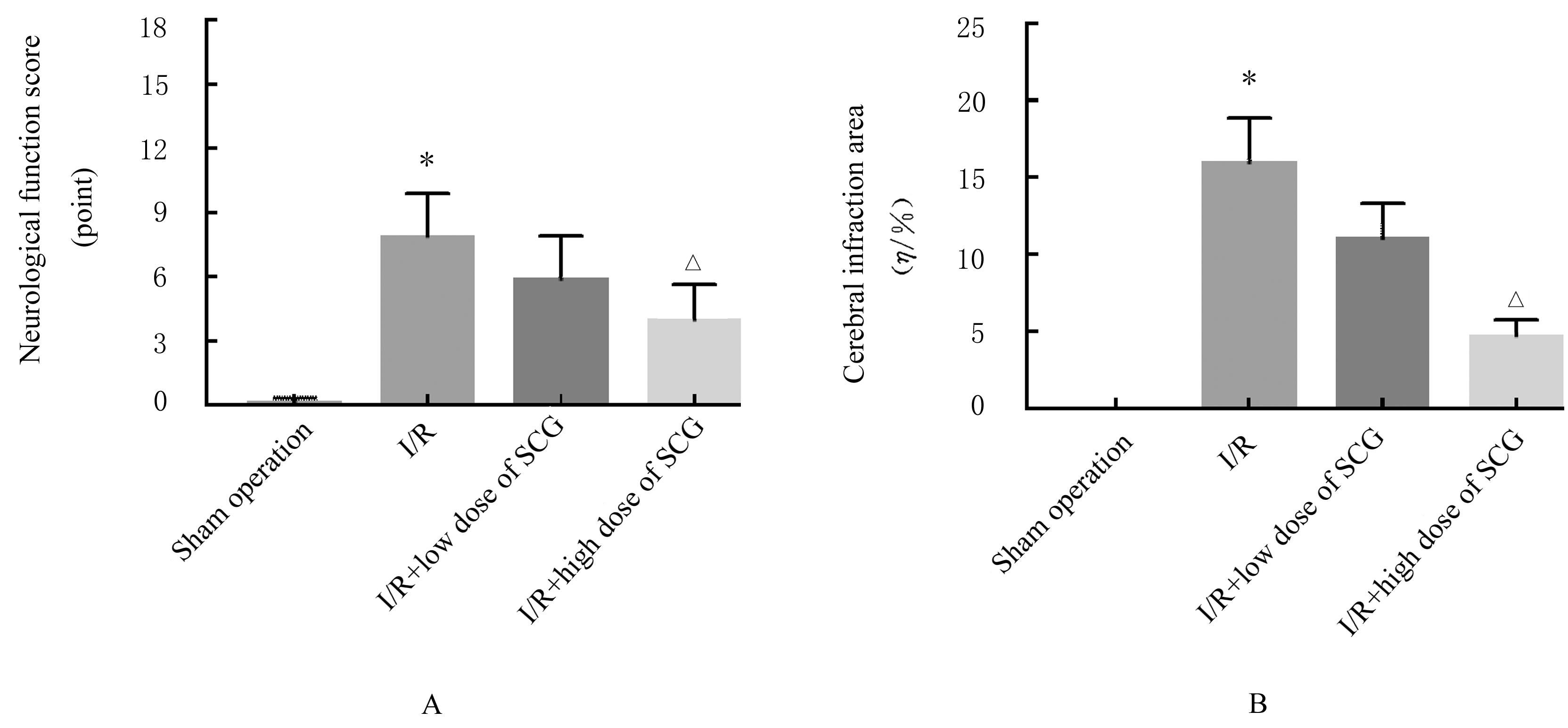
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (5): 1182-1191.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230511
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles
Improvement effect of sodium cromoglycate on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats and its mechanism
Xian ZHU,Xinxu CHEN,Yibin CHEN,Changxuan LI,Jie LIU,Tan WANG( )
)
- Department of Neurology,First Affiliated Hospital,Hainan Medical College,Haikou 570102,China
-
Received:2022-08-10Online:2023-09-28Published:2023-10-26 -
Contact:Tan WANG E-mail:1821007419@qq.com
CLC Number:
- R364.6
Cite this article
Xian ZHU,Xinxu CHEN,Yibin CHEN,Changxuan LI,Jie LIU,Tan WANG. Improvement effect of sodium cromoglycate on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats and its mechanism[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1182-1191.
share this article
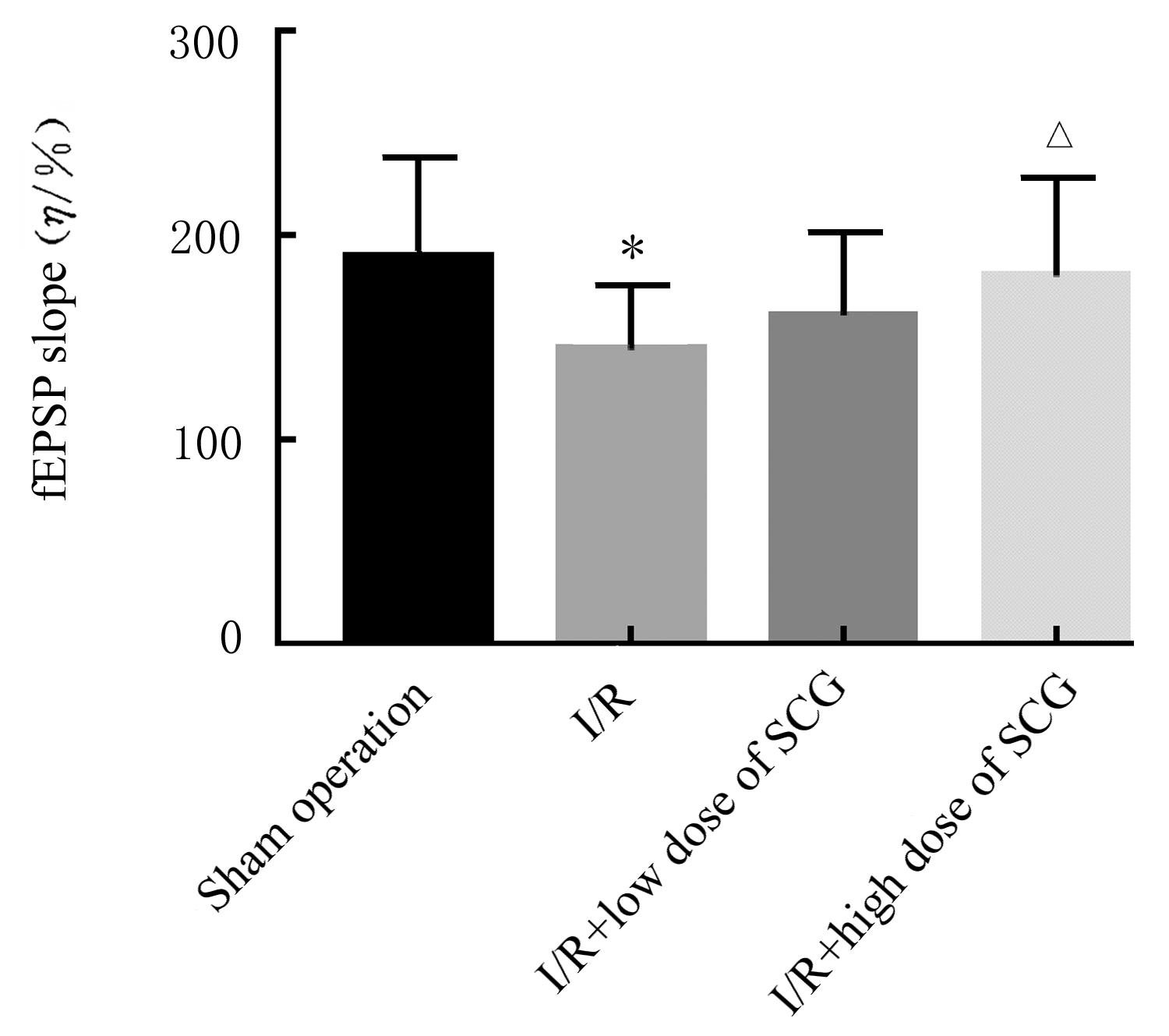
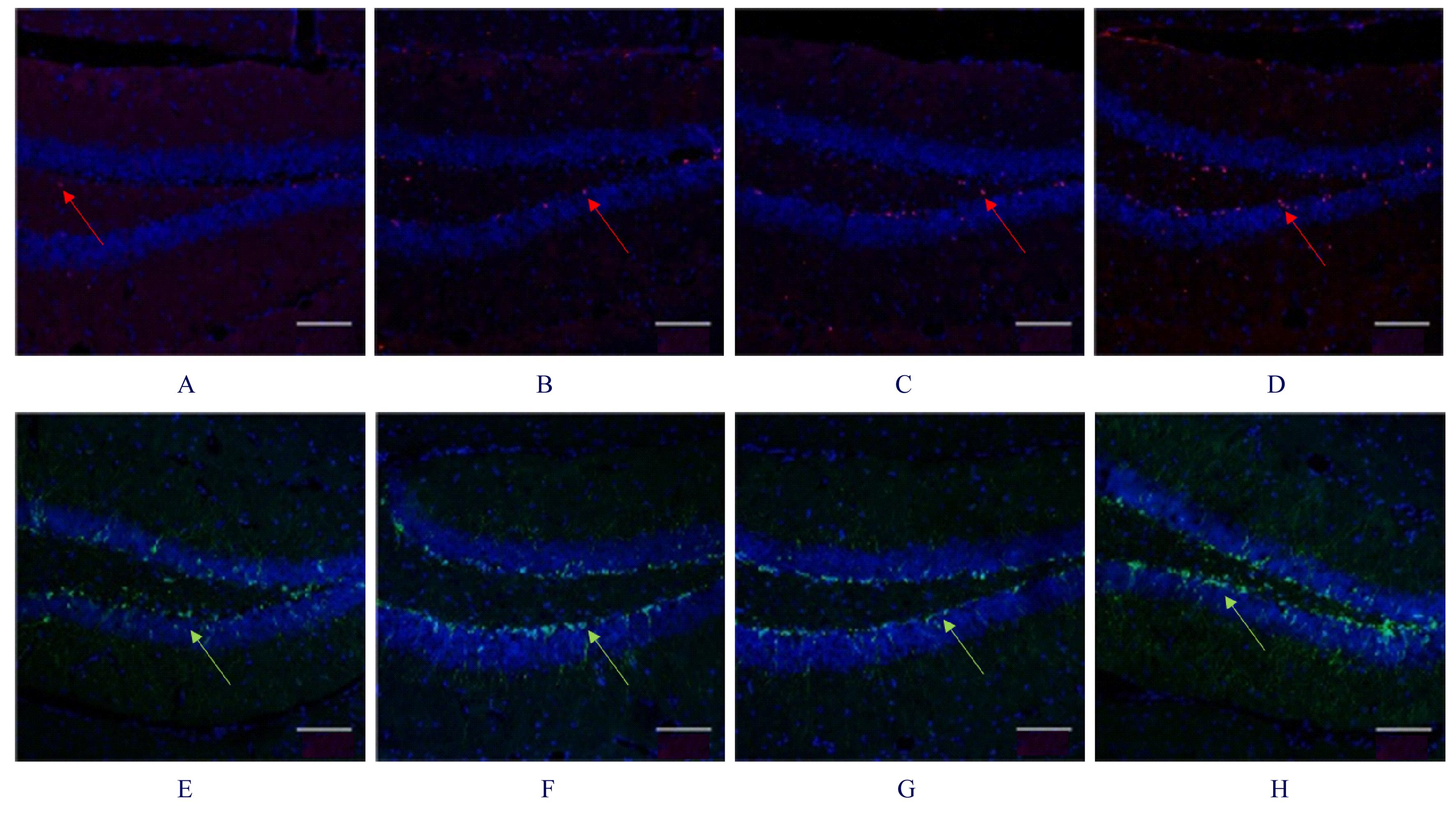
Tab. 1
Number of BrdU positive cells and expression levels of DCX protein in dentate gyrus of hippocampus in brain tissue of rats in various groups"
| Group | Number of BrdU positive cells | Expression level of DCX protein | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sham operation | 7.33±1.53 | 497.86±38.62 | |
| I/R | 10.00±2.65 | 594.94±54.67 | |
| I/R+low dose of SCG | 13.00±3.61 | 667.37±44.45 | |
| I/R+high dose of SCG | 20.33±2.08* | 936.61±55.13* |
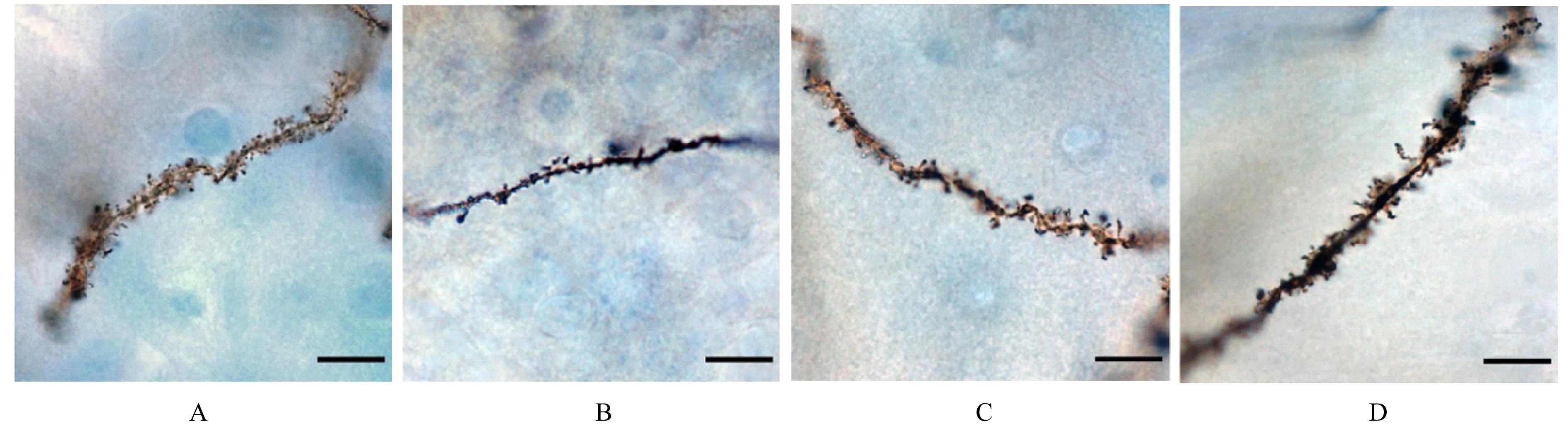
Tab. 2
Expression levels of BDNF,TrkB, NT-3, and TrkC proteins in hippocampus tissue of brain of rats in various groups (n=3,x±s)"
| Group | BDNF | TrkB | NT-3 | TrkC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sham operation | 0.23±0.04 | 0.26±0.06 | 0.08±0.01 | 0.22±0.02 |
| I/R | 0.30±0.03 | 0.37±0.05 | 0.14±0.03* | 0.20±0.04 |
| I/R+low dose of SCG | 0.36±0.05 | 0.39±0.07 | 0.17±0.03 | 0.26±0.01 |
| I/R+high dose of SCG | 0.82±0.07△ | 1.02±0.14△ | 0.62±0.07△ | 0.41±0.03△ |
| 1 | ZHAO L R, WILLING A. Enhancing endogenous capacity to repair a stroke-damaged brain: an evolving field for stroke research[J]. Prog Neurobiol, 2018, 163/164: 5-26. |
| 2 | 王欢欢, 王 刚, 仲婷婷, 等. 脑原位缺血预处理通过Nrf2/HO-1信号通路减轻大鼠缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2021, 41(7): 1477-1481. |
| 3 | 殷秀梅, 杨丽红, 韩佳炜, 等. 电针人中穴对脑梗死大鼠内源性神经干细胞分化的影响[J]. 天津中医药, 2023, 40(3): 325-333. |
| 4 | JIN Y X, SILVERMAN A J, VANNUCCI S J. Mast cell stabilization limits hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the immature rat[J].Dev Neurosci,2007,29(4/5):373-384. |
| 5 | SEGOVIA-OROPEZA M, SANTIAGO-CASTAÑEDA C, OROZCO-SUÁREZ S A, et al. Sodium cromoglycate decreases sensorimotor impairment and hippocampal alterations induced by severe traumatic brain injury in rats[J]. J Neurotrauma, 2020, 37(23): 2595-2603. |
| 6 | STRBIAN D, KARJALAINEN-LINDSBERG M L, TATLISUMAK T, et al. Cerebral mast cells regulate early ischemic brain swelling and neutrophil accumulation[J].J Cereb Blood Flow Metab,2006,26(5): 605-612. |
| 7 | 朱东亚. 卒中治疗药物或治疗方法临床前评价的动物模型[J]. 中国卒中杂志, 2017, 12(8): 735-741. |
| 8 | HSU S Y, CHEN C H, MUKDA S, et al. Neuronal pnn deficiency increases oxidative stress and exacerbates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice[J]. Antioxidants, 2022, 11(3): 466. |
| 9 | CHEN Y, HONG Q L, LIU J P, et al. Effects of anterior borderzone angle grading on predicting the 90-day prognosis after recanalization of acute middle cerebral artery occlusion[J]. Front Neurol, 2021, 12: 700732. |
| 10 | 孔玉明, 李治璋, 岳蕴华. 急性缺血性脑卒中静脉溶栓患者并发卒中相关性肺炎的危险因素分析[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2021,38(8):693-695. |
| 11 | WARD R, LI W G, ABDUL Y, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition with MCC950 improves diabetes-mediated cognitive impairment and vasoneuronal remodeling after ischemia[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2019, 142: 237-250. |
| 12 | VALLE-DORADO M G, SANTANA-GÓMEZ C E, OROZCO-SUÁREZ S A, et al. The mast cell stabilizer sodium cromoglycate reduces histamine release and status epilepticus-induced neuronal damage in the rat hippocampus[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2015, 92: 49-55. |
| 13 | JIN Y X, SILVERMAN A J, VANNUCCI S J. Mast cells are early responders after hypoxia-ischemia in immature rat brain[J]. Stroke, 2009, 40(9): 3107-3112. |
| 14 | SHEN S W, DUAN C L, CHEN X H, et al. Neurogenic effect of VEGF is related to increase of astrocytes transdifferentiation into new mature neurons in rat brains after stroke[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2016, 108: 451-461. |
| 15 | SONG X Y, ZHOU B, ZHANG P P, et al. Protective effect of silibinin on learning and memory impairment in LPS-treated rats via ROS-BDNF-TrkB pathway[J]. Neurochem Res, 2016, 41(7): 1662-1672. |
| 16 | BUKALO O, LEE P R, FIELDS R D. BDNF mRNA abundance regulated by antidromic action potentials and AP-LTD in hippocampus[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2016, 635: 97-102. |
| 17 | GHARAMI K, DAS S. BDNF local translation in viable synaptosomes: implication in spine maturation[J]. Neurochem Int, 2014, 69: 28-34. |
| 18 | ZHU L, YANG L, ZHAO X M, et al. Xanthoceraside modulates NR2B-containing NMDA receptors at synapses and rescues learning-memory deficits in APP/PS1 transgenic mice[J]. Psychopharmacology, 2018, 235(1): 337-349. |
| 19 | ZHANG S J, WANG R L, ZHAO H P, et al. MEPO promotes neurogenesis and angiogenesis but suppresses gliogenesis in mice with acute ischemic stroke[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2019, 849: 1-10. |
| 20 | MARTI H J, BERNAUDIN M, BELLAIL A, et al. Hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial growth factor expression precedes neovascularization after cerebral ischemia[J]. Am J Pathol, 2000, 156(3): 965-976. |
| 21 | BOROS B D, GREATHOUSE K M, GENTRY E G, et al. Dendritic spines provide cognitive resilience against Alzheimer’s disease[J].Ann Neurol,2017,82(4):602-614. |
| 22 | KIM H, SEO J S, LEE S Y, et al. AIM2 inflammasome contributes to brain injury and chronic post-stroke cognitive impairment in mice[J]. Brain Behav Immun, 2020, 87: 765-776. |
| 23 | DIJKE PTEN, ARTHUR H M. Extracellular control of TGFbeta signalling in vascular development and disease[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2007,8(11): 857-869. |
| 24 | XIE Q F, CHENG J Y, PAN G Y, et al. Treadmill exercise ameliorates focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced neurological deficit by promoting dendritic modification and synaptic plasticity via upregulating caveolin-1/VEGF signaling pathways[J]. Exp Neurol, 2019, 313: 60-78. |
| [1] | Sihan LAI,Juntong LIU,Luying TAN,Jinping LIU,Pingya LI. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on anti-ischemic stroke mechanism of Panax quinquefolium triolsaponins [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 913-922. |
| [2] | Jun ZHU,Nan ZHOU,Deming LI. Improvement effect of propofol postconditioning on focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 46-54. |
| [3] | Haixing LIAN,Wei WANG,Baisong LIN,Chen CHEN,Xuefeng SUN,Zhe LI. Application of Del Nido cardioplegic in coronary artery bypass grafting [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 1045-1050. |
| [4] | Zhihui ZHAO,Xianghua BAI,Jinling HE,Weiqin DUAN,Min LIU,Shengmao ZHANG. Inhibitory effect of sufentanil on apoptosis of myocardial cells in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 364-373. |
| [5] | Jiayi LI,Xiaojing JIA,Shaojie JIA,Yan MA,Yuxiu SHEN,Xin LIU,Hongyan QU,Ge BAI,Na CHENG. Effect of dual anti-platelet therapy with aspirin and clopidogrel on bleeding regression and prognosis of acute ischemic stroke patients complicated with cerebral microbleeds [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1531-1537. |
| [6] | Haoyang DUAN,Zhenlan LI,Fuxian LYU,Na LIU,Zhaohong YAN. Effect evaluation of isokinetic muscle strength training with different flexor and extensor muscle strength ratios in treatment of hyperextension of knee after stroke [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1538-1543. |
| [7] | Peng JI,Xiangdong GUO,Gen SUN,Qixing KOU,Xueping QU,Yajing SUN,Limin JIANG. Role of Rho/ROCK signaling pathway in occurrence of acute ischemic stroke in rats with obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1178-1186. |
| [8] | Dimi ZHOU,Lu GAN,Lin CHEN,Chengfang ZHOU,Liang ZENG. Neuroprotective effect of Withaferin A on ischemic stroke rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 919-925. |
| [9] | Jifeng WANG,Xiaoran LIU,Xin SUI,Mo KAN,Hui LI,Wenjun GUO,Qing YANG,Zhuang ZHANG,Sitong MING,Na LI,Xiaobo QU. Effect of Dushen Tang on cognitive dysfunction of aging model rats based on cAMP/PKA/CREB signal pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 865-873. |
| [10] | Tianye ZHAO,Liting ZHOU,Xueting ZHANG,Wen QI,Xu LI,Shuyue WANG,Lin YE. Analysis on correlation between exposure to air pollutants and hospitalization risk of stroke in Changchun city of Jilin province [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 505-510. |
| [11] | Yangyang SONG,Tingting LIN,Qianyan HE,Huanqiu LIU,Yanhua FENG. Effect of ulinastatin pretreatment on postoperative recipients’ renal function in operation of donation after controllable cardiac death [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 469-476. |
| [12] | Yulei WEI,Yuhuan CUI,Bo HAN,Dawei WANG,Guigang WANG,Qian LI,Wen ZENG. Clinical effect of valve replacement combined with radiofrequency ablation and left atrial appendage closure in treatment of valvular heart disease complicated with atrial fibrillation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(6): 1298-1303. |
| [13] | Meijuan LU,Xiande MA,Lu REN. Effect of acupuncture combined with medicine-induced autophagy on cognitive function of mice with ApoE gene knockout [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(6): 1124-1130. |
| [14] | WEN Ying, WU Qiaoling, LIU Guoli. Protective effect of sufentanil post-conditioningthrough ERK1/2-mediated p70S6K signaling pathway on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injuryof rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 792-797. |
| [15] | ZHAO Miao, WANG Yi, ZHANG Ying, FENG Yumei, CAO Yawen, JIANG Haisen, LI Wei. Improvement effect of curcumin on cognitive function in mice with sleep deprivation and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(06): 1373-1378. |
|
||