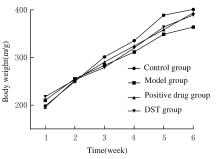
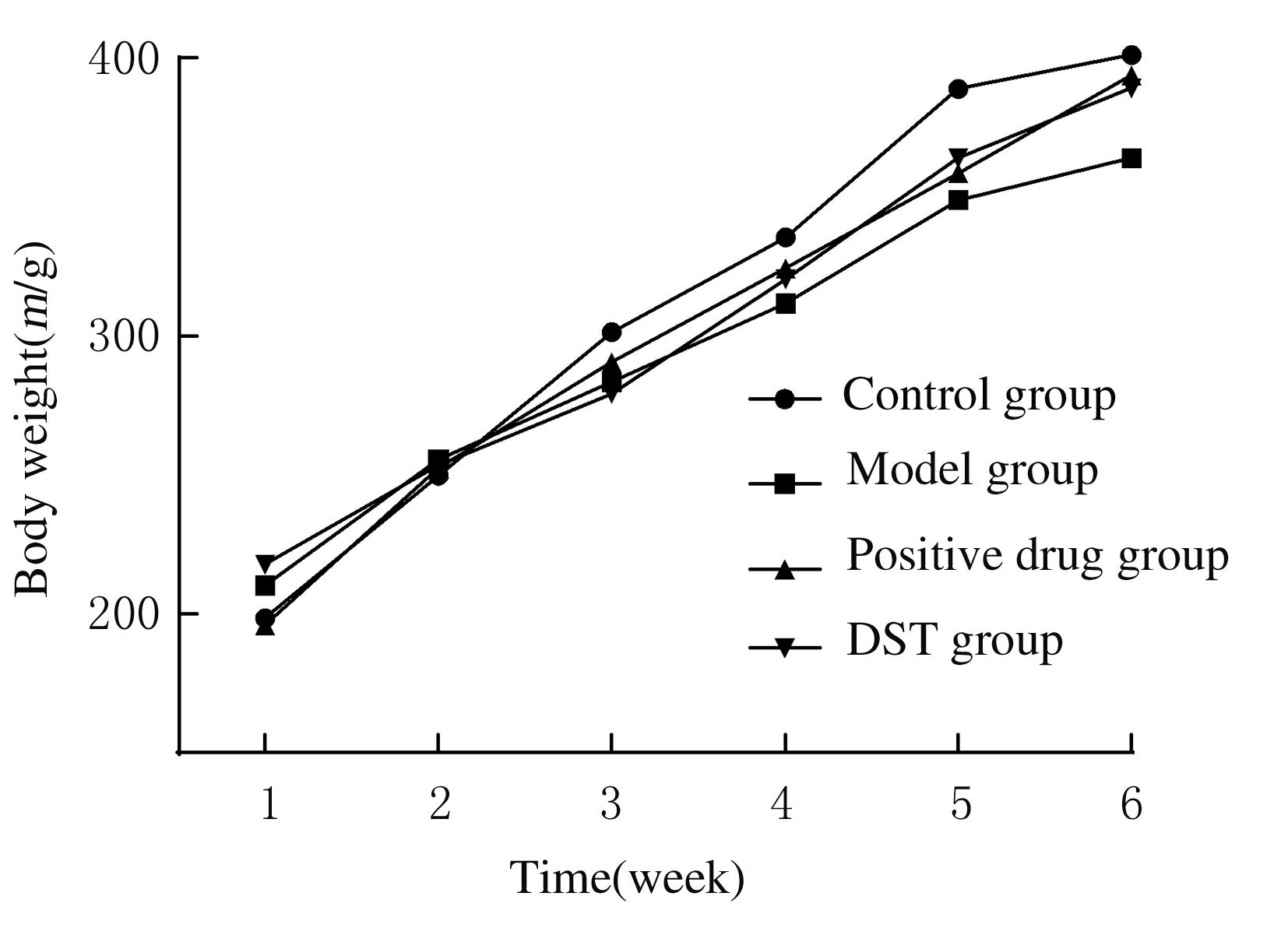
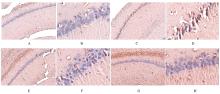
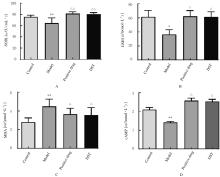
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (4): 865-873.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210407
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
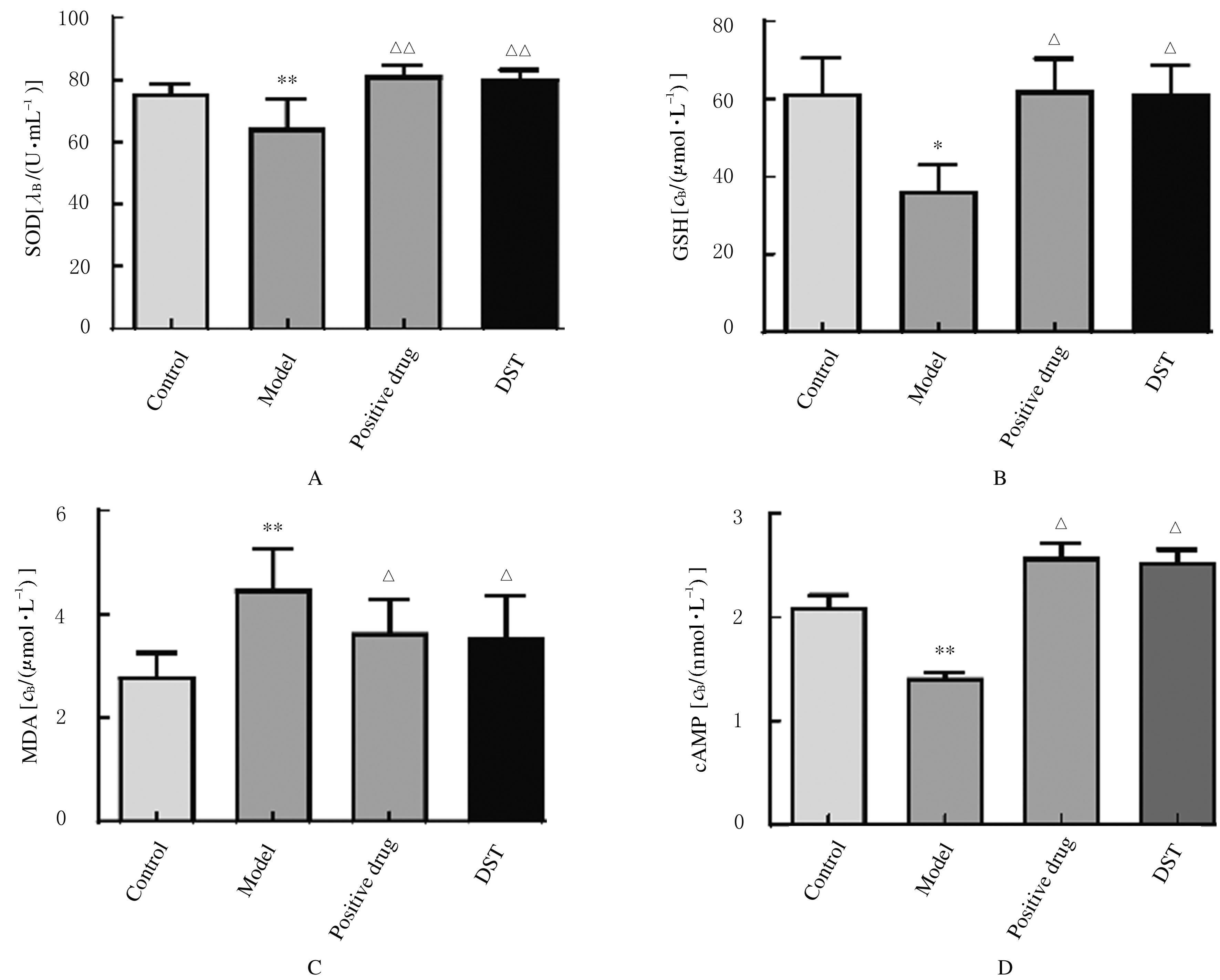
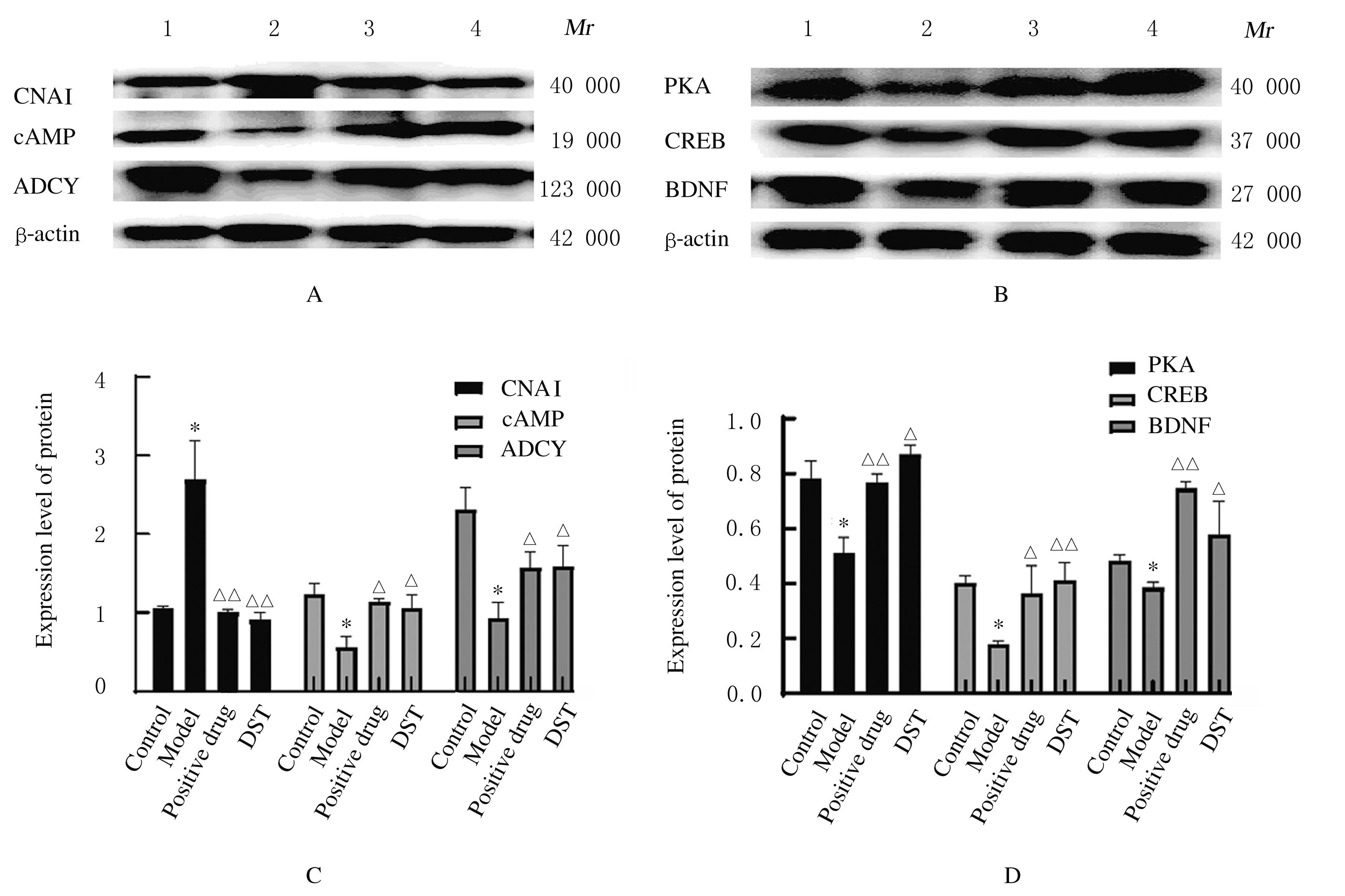
Effect of Dushen Tang on cognitive dysfunction of aging model rats based on cAMP/PKA/CREB signal pathway
Jifeng WANG1,Xiaoran LIU1,Xin SUI1,Mo KAN1,Hui LI2,Wenjun GUO1,Qing YANG1,Zhuang ZHANG1,Sitong MING1,Na LI1( ),Xiaobo QU1(
),Xiaobo QU1( )
)
- 1.Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
2.Department of General Surgery,Qianwei Hospital of Jilin Province,Changchun 130012,China
-
Received:2020-12-25Online:2021-07-28Published:2021-07-22 -
Contact:Na LI,Xiaobo QU E-mail:lhaln@hotmail.com;quxiaobo0504@hotmail.com
CLC Number:
- R285.5
Cite this article
Jifeng WANG,Xiaoran LIU,Xin SUI,Mo KAN,Hui LI,Wenjun GUO,Qing YANG,Zhuang ZHANG,Sitong MING,Na LI,Xiaobo QU. Effect of Dushen Tang on cognitive dysfunction of aging model rats based on cAMP/PKA/CREB signal pathway[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 865-873.
share this article
| 1 | 宋承吉. 《十药神书》与独参汤[J]. 人参研究, 2005, 17(2): 2-3. |
| 2 | YANG D W, YANG X F, YAN H, et al. UPLC-MS/MS determination of twelve ginsenosides in shenfu Tang and dushen Tang[J]. Int J Anal Chem, 2019, 2019: 6217125. |
| 3 | LI S L, LAI S F, SONG J Z, et al. Decocting-induced chemical transformations and global quality of Du-Shen-Tang, the decoction of ginseng evaluated by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS based chemical profiling approach[J]. J Pharm Biomed Anal, 2010, 53(4): 946-957. |
| 4 | CHOI S H, LEE R, NAM S M, et al. Ginseng gintonin, aging societies, and geriatric brain diseases[J]. Integr Med Res, 2021, 10(1): 100450. |
| 5 | KIM H J, JUNG S W, KIM S Y, et al. Panax ginseng as an adjuvant treatment for Alzheimer’s disease[J]. J Ginseng Res, 2018, 42(4): 401-411. |
| 6 | 苏向东, 陆启丽, 高琴琴, 等. 独参汤化学成分的研究[J]. 人参研究, 2013, 25(4):12-16. |
| 7 | 凌继祖. 氧化应激在间歇性低氧幼鼠认知障碍和海马损伤中的机制研究[D].兰州: 兰州大学, 2020. |
| 8 | AKHTER K F, MUMIN M A, LUI E M K, et al. Fabrication of fluorescent labeled ginseng polysaccharide nanoparticles for bioimaging and their immunomodulatory activity on macrophage cell lines[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2018, 109: 254-262. |
| 9 | ZHANG Y, YANG X M, WANG S, et al. Ginsenoside Rg3 prevents cognitive impairment by improving mitochondrial dysfunction in the rat model of Alzheimer’s disease[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2019, 67(36): 10048-10058. |
| 10 | BUDNI J, GARCEZ M L, MINA F, et al. The oral administration of D-galactose induces abnormalities within the mitochondrial respiratory chain in the brain of rats[J]. Metab Brain Dis, 2017, 32(3): 811-817. |
| 11 | 李红波, 王小琴, 熊 飞, 等.六味地黄丸对D-半乳糖致衰老大鼠抗氧化功能影响的实验研究[J].中国中医药科技,2019,26(1):31-33. |
| 12 | 段懿涵, 盛 瑜, 徐 健, 等. 姬松茸多糖对D-半乳糖诱导的衰老模型小鼠的抗衰老作用及其Keap1/Nrf2/ARE信号转导途径机制[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2020, 46(2): 346-351, 435. |
| 13 | 刘 颖, 王宇瑄, 陈 勤, 等. 健脑益智胶囊对衰老小鼠大脑学习记忆功能减退的作用机制研究[J].中国医院药学杂志, 2020, 40(17): 1840-1845. |
| 14 | 梅 健, 王艳丽, 雷 莹, 等. 衰老相关认知障碍的研究进展[J].海南医学, 2020, 31(15): 2014-2017. |
| 15 | 许梦然, 王迦琦, 高婧雯, 等. 北柴胡多糖对D-半乳糖致衰老模型小鼠的保护作用及其机制[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2020, 46(6): 1215-1220, 1350. |
| 16 | 黄清松, 李红枝, 郑 敏, 等.姬松茸粗多糖提高脑老化小鼠学习记忆能力的作用及其机制[J].吉林大学学报(医学版), 2014, 40(1):70-73. |
| 17 | MA C L, LI L, YANG G M, et al. Neuroprotective effect of gastrodin in methamphetamine-induced apoptosis through regulating cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway in cortical neuron[J]. Hum Exp Toxicol, 2020, 39(8): 1118-1129. |
| 18 | 郑彩霞. PKA/CREB信号通路在电针改善脑缺血大鼠学习记忆功能中作用机制的研究[D].武汉: 华中科技大学, 2017. |
| 19 | 平 鑫. 基于cAMP-PKA-CREB通路探讨化浊解毒疏肝方对癫痫大鼠学习记忆的影响[D]. 保定: 河北大学, 2020. |
| 20 | 赵 凡, 尚志远,瞿 融. 黄芩含药血清对神经干细胞分化钠离子通道基因及cAMP/PKA信号通路的影响[J].中医杂志, 2020, 61(16): 1444-1448. |
| 21 | 于琰同, 张风霞. 复健片对大脑中动脉闭塞模型大鼠cAMP/PKA信号通路mRNA及神经营养因子表达的影响[J].四川中医, 2020, 38(7): 69-73. |
| 22 | 尹传红, 闫宇辉. 高压氧通过激活CREB/BDNF信号通路减轻阿尔茨海默病小鼠海马神经元突触损伤[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2020, 36(6): 1063-1070. |
| 23 | SANDERS O, RAJAGOPAL L. Phosphodiesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review of clinical trials and epidemiology with a mechanistic rationale[J]. J Alzheimers Dis Rep, 2020,4(1): 185-215. |
| 24 | 伍向民, 王晓敏, 黄开勇, 等. 5-羟色胺转运体敲除小鼠行为学与其海马PKA/CREB/BDNF信号通路水平变化的研究[J].广西医科大学学报, 2020, 37(5): 827-831. |
| 25 | ZHOU L, MA S L, YEUNG P K, et al. Anxiety and depression with neurogenesis defects in exchange protein directly activated by cAMP 2-deficient mice are ameliorated by a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, Prozac[J]. Transl Psychiatry, 2016, 6(9): e881. |
| 26 | 郝继伟, 李莺歌, 王 来, 等. BDNF在APP/PS1转基因小鼠皮层和海马内的表达及其对学习记忆能力的影响[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2019, 35(5): 858-864. |
| 27 | GONG J J, ZHOU F, WANG S X X, et al. Caveolin-3 protects diabetic hearts from acute myocardial infarction/reperfusion injury through β2AR, cAMP/PKA, and BDNF/TrkB signaling pathways[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2020, 12(14): 14300-14313. |
| [1] | Qian LI,Jingyi YUAN,Jiaqi ZHOU,Min ZHAO,Ke WANG. Pulmonary imaging changes as first manifestation of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 796-800. |
| [2] | Ping HU,Nan JIANG,Yinghua LI,Hongguang ZHAO. Analysis on characteristics of 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging of patient with primary small cell osteosarcoma of coccyx:A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 216-221. |
| [3] | Jiayi LI,Xiaojing JIA,Shaojie JIA,Yan MA,Yuxiu SHEN,Xin LIU,Hongyan QU,Ge BAI,Na CHENG. Effect of dual anti-platelet therapy with aspirin and clopidogrel on bleeding regression and prognosis of acute ischemic stroke patients complicated with cerebral microbleeds [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1531-1537. |
| [4] | Qian LI,Jiaqi ZHOU,Jingyi YUAN,Min ZHAO,Xin DI,Ke WANG. Spindle cell carcinoma of lung: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1557-1561. |
| [5] | Tianyi WANG,Yufeng ZHU,Miao SUN,Wei WANG. Application of three-dimensional reconstruction combined with indocyanine green intraoperative navigation in diagnosis and treatment of liver cancer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 1014-1021. |
| [6] | Yu WANG, Lan ZHAO, Bohong KAN, Huiyan SHI. Improvement effect of Sanjiao acupuncture on learning and memory abilities of rapid aging model mice by activating SDF-1α/CXCR4 pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 545-550. |
| [7] | Dong CHEN, Zhiyao LI, Haitao CHEN, Zhirui CHUAN, Yingxian ZHANG, Xin JIN, Shicong TANG, Xiaomao LUO. Diagnostic values of three-dimensional transrectal ultrasound and MRI in diagnosis of T substages and circumferential resection margin of patients with middle and lower rectal cancer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 753-760. |
| [8] | Dong CHEN,Zhiyao LI,Haitao CHEN,Zhirui CHUAN,Yingxian ZHANG,Xin JIN,Shicong TANG,Xiaomao LUO. Diagnostic value of three-dimensional transrectal ultrasound in preoperative N-staging of middle and lower rectal cancer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 497-504. |
| [9] | Dong CHEN,Haitao CHEN,Zhiyao LI,Fengming RANG,Xi ZHANG,Zhirui CHUAN,Shicong TANG,Xiaomao LUO. Effects of three-dimensional transrectal ultrasound and MRI in evaluation of extramural vascular invasion degrees of middle and lower rectal cancer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 203-209. |
| [10] | Meijuan LU,Xiande MA,Lu REN. Effect of acupuncture combined with medicine-induced autophagy on cognitive function of mice with ApoE gene knockout [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(6): 1124-1130. |
| [11] | Lingxue SHI,Shuo LIU,Xuewei ZHENG,Xiaoliang CHENG,Zhaohui CHEN,Baolin MA,Hongguo ZHANG,Jun DING. Application of magnetic resonance diffusion weighted imaging ADC and rADC in differential diagnosis of benign and malignant parotid gland tumors [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(6): 1309-1314. |
| [12] | ZHOU Dongkui, LU Mingqian, FENG Xuesong, LIU Yufei, SONG Hao, XU Liang. Follicular dendritic cell sarcoma of small intestine and ileocecal region: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 858-862. |
| [13] | ZHAO Min, JIN Xin, DI Xin, TIAN Chang, LIU Jiaying, CONG Shan, WANG Ke. Invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma of lung: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(03): 634-638. |
| [14] | DUAN Yihan, SHENG Yu, XU Jian, LU Xuechun, DU Peige, AN Liping. Anti-aging effects of Agaricus blazei polysaccharide in D-galactose-induced aging model mice and Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signal transduction pathway mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 346-351. |
| [15] | ZHAO Miao, WANG Yi, ZHANG Ying, FENG Yumei, CAO Yawen, JIANG Haisen, LI Wei. Improvement effect of curcumin on cognitive function in mice with sleep deprivation and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(06): 1373-1378. |