Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (2): 469-476.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210228
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of ulinastatin pretreatment on postoperative recipients’ renal function in operation of donation after controllable cardiac death
Yangyang SONG1,Tingting LIN1,Qianyan HE2,Huanqiu LIU1( ),Yanhua FENG1(
),Yanhua FENG1( )
)
- 1.Department of Anesthesiology,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
2.Department of Neurology,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
-
Received:2020-05-22Online:2021-03-28Published:2021-03-25 -
Contact:Huanqiu LIU,Yanhua FENG E-mail:chunqiu2002@163.com;fengyanhua77@163.com
CLC Number:
- R617
Cite this article
Yangyang SONG,Tingting LIN,Qianyan HE,Huanqiu LIU,Yanhua FENG. Effect of ulinastatin pretreatment on postoperative recipients’ renal function in operation of donation after controllable cardiac death[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 469-476.
share this article
Tab. 1
Comparison of donor data among three groups"
| Items | Age (year) | Gender [male,n(η/%] | BMI (kg·m-2) | MAP (P/mmHg) | HR (beat·min-1) | Na+ [cB/(mmol·L-1)] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 49.53±6.94 | 22(73.3) | 23.56±2.23 | 99.10±8.31 | 92.43±8.42 | 140.65±6.95 |
| U1 | 46.13±9.16 | 24(80.0) | 24.23±1.99 | 100.78±9.20 | 88.33±8.91 | 141.94±4.23 |
| U2 | 45.33±11.63 | 22(73.3) | 23.55±1.70 | 99.54±7.43 | 89.10±11.38 | 142.17±10.30 |
| χ2/F | 1.675 | 0.481 | 1.157 | 0.326 | 1.529 | 0.349 |
| P | 0.193 | 0.786 | 0.319 | 0.723 | 0.222 | 0.706 |
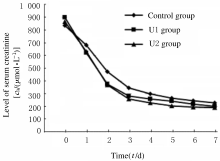
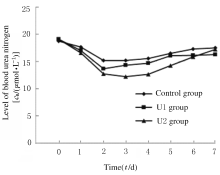
| Group | Serum creatinine [cB/ (mmol·L-1)] | Blood urea nitrogen [cB/ (mmol·L-1)] | CPR [Yes,n(η/%)] | Cause of death[n(η/%)] | ||
| Trauma | Cerebral hemorrhage | Others | ||||
| Control | 91.50(78.75,101.18) | 4.83(3.80,5.86) | 2(6.7) | 13(43.3) | 14(46.7) | 3 (10.0) |
| U1 | 91.75(65.83,104.68) | 3.68(2.98,6.15) | 1(3.3) | 15(50.0) | 12(40.0) | 3 (10.0) |
| U2 | 86.10(68.00,108.78) | 4.19(3.75,7.02) | 2(6.7) | 14(46.7) | 13(43.3) | 3 (10.0) |
| χ2/F | 0.339 | 3.079 | — | — | ||
| P | 0.844 | 0.214 | 0.999 | 0.996 | ||
Tab. 2
Comparison of recipient data among three groups"
| Group | n | Gender [male,n(η/%] | Age (year) | BMI (kg·m-2) | Warm ischemia time (t/min) | Cold ischemia time (t/h) | Preoperative dialysis (year) | Operation time(t/min) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 57 | 36(63.2) | 43.95±9.53 | 22.79±2.93 | 3.47±0.69 | 6.34±3.17 | 2.5(1.5,4.5) | 117.40±16.60 | ||
| U1 | 59 | 37(62.7) | 42.08±11.36 | 22.4±2.76 | 3.53±0.48 | 7.12±3.28 | 2.0(1.0,3.0) | 119.68±17.41 | ||
| U2 | 58 | 35(60.3) | 45.10±10.76 | 23.06±2.57 | 3.34±0.47 | 7.26±3.26 | 2.0(1.0,3.0) | 117.02±17.01 | ||
| χ2/F | 0.112 | 1.212 | 0.821 | 1.786 | 1.355 | 3.378 | 0.418 | |||
| P | 0.945 | 0.300 | 0.442 | 0.171 | 0.261 | 0.185 | 0.659 | |||
| group | n | Dialysis methods[n(η/%)] | Renal arterial anastomosis[n(η/%)] | |||||||
| Peritoneal dialysis | Hemodialysis | No | RA with IIA | RA with EIA | RA with IIA and EIA | |||||
| Control | 57 | 5(8.8) | 50(87.7) | 2(3.5) | 2(3.5) | 55(96.5) | 0(0.0) | |||
| U1 | 59 | 9(15.3) | 50(84.7) | 0(0.0) | 4(6.8) | 54(91.5) | 1(1.7) | |||
| U2 | 58 | 10(17.2) | 47(81.0) | 1(1.7) | 5(8.6) | 52(89.7) | 1(1.7) | |||
| χ2/F | — | — | ||||||||
| P | 0.421 | 0.705 | ||||||||
Tab. 3
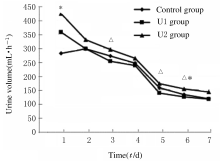
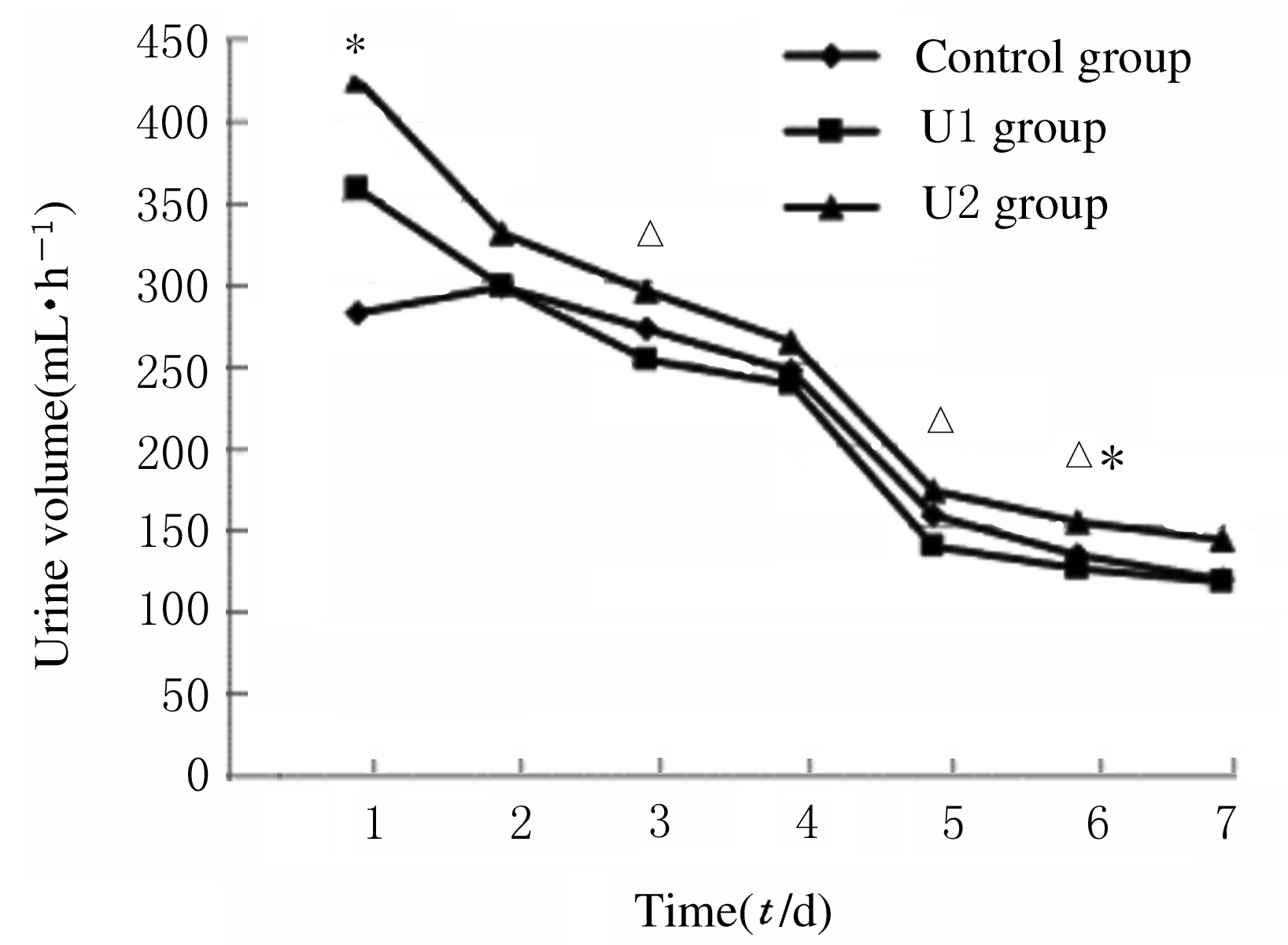
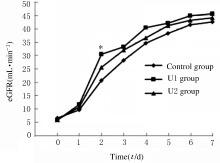
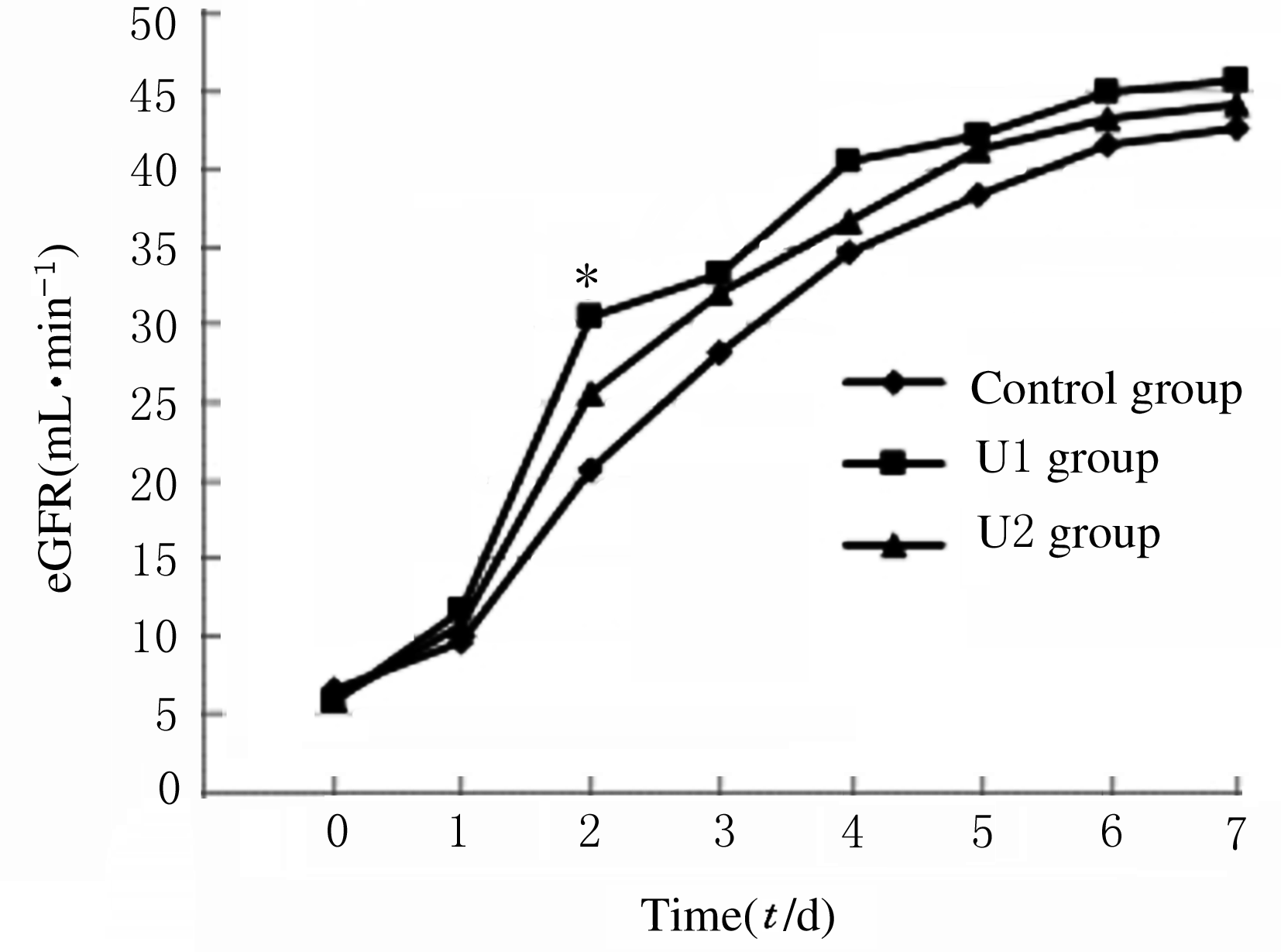
MAP of recipients at different time points in three groups"
| Group | n | MAP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before anesthesia | After anesthesia | Renal artery opening | End of the surgery | ||
| Control | 30 | 111.98±10.83 | 96.72±7.49 | 103.91±7.37 | 102.91±7.41 |
| U1 | 59 | 111.12±10.85 | 96.53±7.96 | 102.73±7.77 | 102.79±7.83 |
| U2 | 58 | 111.22±10.67 | 96.26±8.26 | 103.86±8.03 | 101.31±13.39 |
| F | 0.110 | 0.049 | 0.438 | 0.469 | |
| P | 0.896 | 0.952 | 0.646 | 0.626 | |
| 1 | WOLFE R A, ASHBY V B, MILFORD E L, et al. Comparison of mortality in all patients on dialysis, patients on dialysis awaiting transplantation, and recipients of a first cadaveric transplant [J]. N Engl J Med, 1999, 341 (23): 1725-1730. |
| 2 | SCHNITZLER M A, LENTINE K L, BURROUGHS T E. The cost effectiveness of deceased organ donation[J]. Transplantation, 2005, 80 (11):1636-1637. |
| 3 | 明英姿,叶启发,邵明杰,等. 心脏死亡供者肾移植48例临床分析 [J]. 中南大学学报(医学版), 2012, 37(6): 598-605. |
| 4 | ZHANG L, ZENG L, GAO X, et al. Transformation of organ donation in China [J].Transpl Int,2015,28(4):410-415. |
| 5 | ZHAO Y, CAI H, ZHOU P, et al. Protective effect of ulinastatin on hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury through autophagy activation in Chang liver cells [J]. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120 (9): 14960-14970. |
| 6 | 巩 晶,陈乙铭,高成杰. 注射用乌司他丁在肾移植手术患者肾脏缺血再灌注损伤后对IL-1、TNF-α及尿量的影响 [J]. 广东医学, 2018, 39(51): 207-208,211. |
| 7 | 刘永贤,欧阳文. 活体肾移植供体应用乌司他丁对受体肾功能影响的研究 [J]. 器官移植, 2013, 4(5): 279-283. |
| 8 | SEO C H, JU J I, KIM M H, et al. Risk factors and long-term outcomes of delayed graft function in deceased donor renal transplantation [J]. Ann Surg Treat Res, 2015, 89 (4): 208-214. |
| 9 | 连 鑫,周洪澜,王伟刚,等. 肾移植术后移植肾功能延迟恢复的病因诊断及治疗 [J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2010, 14(2): 285-287. |
| 10 | SCHROPPEL B, LEGENDRE C. Delayed kidney graft function: from mechanism to translation [J]. Kidney Int, 2014, 86 (2): 251-258. |
| 11 | FUQUAY R, RENNER B, KULIK L, et al. Renal ischemia-reperfusion injury amplifies the humoral immune response[J].J Am Soc Nephrol,2013,24(7): 1063-1072. |
| 12 | PRATT J R, BASHEER S A, SACKS S H. Local synthesis of complement component C3 regulates acute renal transplant rejection [J]. Nat Med, 2002, 8(6): 582-587. |
| 13 | WAN X, XIE X, GENDOO Y, et al. Ulinastatin administration is associated with a lower incidence of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery: a propensity score matched study [J]. Crit Care, 2016, 20: 42. |
| 14 | LI X, LI X, CHI X, et al. Ulinastatin ameliorates acute kidney injury following liver transplantation in rats and humans [J]. Exp Ther Med, 2015, 9 (2): 411-416. |
| 15 | UMEADI C, KANDEEL F, AL-ABDULLAH I H. Ulinastatin is a novel protease inhibitor and neutral protease activator [J]. Transplant Proc, 2008, 40(2): 387-389. |
| 16 | CHEN C C, LIU Z M, WANG H H, et al. Effects of ulinastatin on renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2004, 25 (10): 1334-1340. |
| 17 | VANDEN HOEK T L, SHAO Z, LI C, et al. Reperfusion injury on cardiac myocytes after simulated ischemia [J]. Am J Physiol, 1996, 270 (4 pt 2): H1334-H1341. |
| 18 | HOANG T D T, BAO V Q, PHAT V H. Massive polyuria after kidney transplantation [J]. Pediatr Nephrol Berlin Ger, 2010, 25 (2): 383-384. |
| 19 | BAHL D, HADDAD Z, DATOO A, et al. Delayed graft function in kidney transplantation [J]. Curr Opin Organ Transplant, 2019, 24 (1): 82-86. |
| 20 | 高宝山,王远涛,王钢,等. 器官捐献影响移植肾功能恢复延迟的因素分析 [J]. 中华器官移植杂志, 2017, 38 (9):541-545. |
| [1] | FU Wenwen, YU Xiaofeng, XUE Yan, YU Ping, WU Xueji, XU Huali, SUI Dayun. Establishment and evaluation of rat models of myocardial ischemia reperfusion-related no-reflow under non-artificial ventilator [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(05): 1058-1062. |
| [2] | YI Xue, WU Pengyu, YANG Shuliang, HAN Yan, YANG Xuehui, ZHANG Shubo, XU Tao, GAO Yizhe, GAO Muhuo, LI Zhanqing. Influence of sulforaphane preconditioning in myocardial cold ischemia-reperfusion injury through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(05): 918-922. |
| [3] | LI Yawei, HAN Liqin, JIN Ying, ZHU Wenhe. Protective effect of Ganodermalucidumpolysaccharide sulfate on cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury in ratsand its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(04): 679-684. |
| [4] | WEI Yanhong, SONG Shuai, GENG Hui, DIAO Binbin, YANG Guangmin. Clinical significance of detection of alpha 1-microglobulin in serum of patients with chronic hepatitis B [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(01): 96-100. |
| [5] | JIANG Enping, TANG Zeli, YU Chunyan, YU Chunrong, ZHU Wei. Protective effect of schisandrin B on cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury of rats and its mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(05): 860-865. |
| [6] | QU Yuan, FU Danyang, JI Yingshi. Protective effect of Danshenlinzhi on cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury in rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(02): 291-294. |
| [7] | MA Dan,XIE Xiao-na,ZOU Jing-tao,LIU Yu-jia,SUN Zhong-hua,GAO Ying. Protective effect of Injection of Milkvetch Root on kidney of diabetic rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2014, 40(02): 271-275. |
| [8] | SHI Bo,HUANG Ke-xin,YE Bao-guo,ZHANG Yan,HUANG Ke-jing. Effects of atorvastatin pretreatment on expressions of HIF-α and VEGF at different time points in myocardium tissue of rats after myocardial ischemia reperfusion [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2013, 39(6): 1159-1163. |
| [9] | . Protective effect of leptin pretreatment on myocardial ischemic reperfusion injury in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2013, 39(6): 1219-1223. |
| [10] | GUO Xin-min, JIN Hong,PAN Li-wen,CHEN Hui,LIU Wei,QUAN Xian-yue. Evaluation on changes of early renal function in patients with diabetic nephropathy with contrast-enhanced ultrasound and its clinical significance [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2013, 39(1): 156-160. |
| [11] | YAN Jin-jun,PANG Lei,DONG Su,FENG Yan-hua,MA Hai-chun. Effect of parecoxib sodium on postoperative analgesia in patients after renal transplantation and evaluation on its security [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2013, 39(1): 138-142. |
| [12] | GAO Kun,HU Mei-qin,QI Hong-gang,WENG Guo-bin,GAO Wen-bo,YAO Xu-ping. Protective effect of salidroside on renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats [J]. J4, 2012, 38(4): 687-691. |
| [13] | LV Xiang-wei,XU Tong-tong,QIN Xiao-hu. Effect of leptin pretreatment on serum IL-6 and TNF-&alpha|levels in mice with myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury [J]. J4, 2012, 38(1): 58-61. |
| [14] | ZHANG Chi, GONG Shou-Liang, MENG Tao, LI Cai, CAi Lou, LI Xiao-Kun. Effects of low dose radiation on kidney function and morphology of diabetic mice [J]. J4, 2010, 36(3): 434-438. |