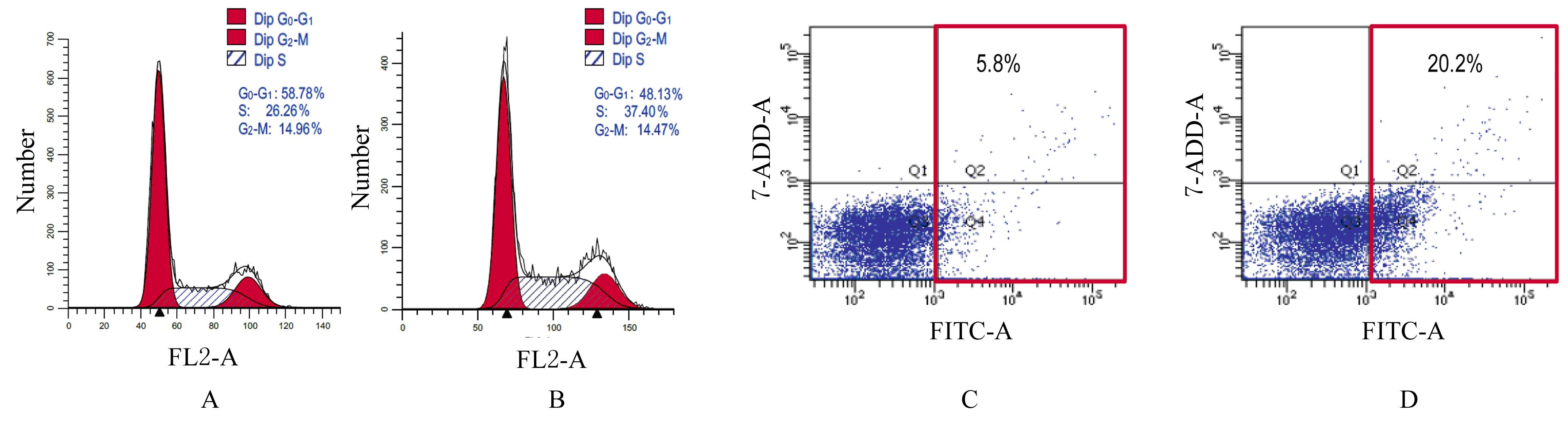
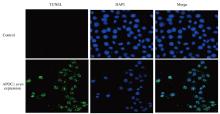
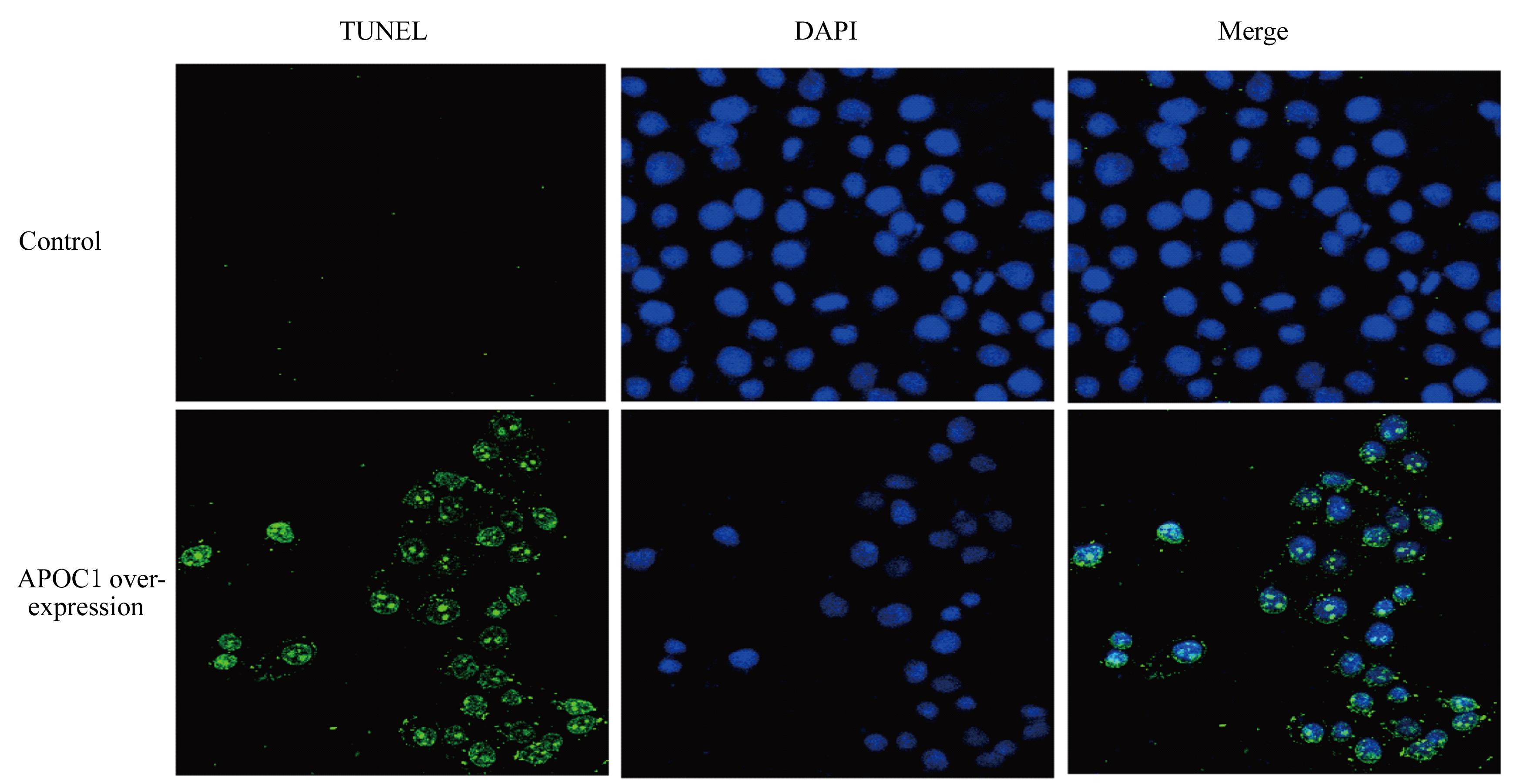
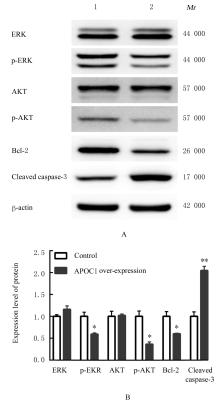
| [1] |
Xiaoni WANG,Tao GUO,Qiyun LUO,Lifeng GUAN.
Effect of usnic acid on biological behaviors of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts and JNK/MAPK signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1445-1451.
|
| [2] |
Aihua REN,Xinda JU,Aofei LIU,Yongchao LIU,Yanfeng LIU.
Effect of ganoderic acid A on proliferation and apoptosis of human non-small cell lung cancer PC-9 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1466-1472.
|
| [3] |
Manying OU,Chunxia HU,Yueping LI.
Effect of expression of microtubule inhibitory assembly protein 1 in placenta tissue of pre-eclampsia patients on trophoblast cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1519-1527.
|
| [4] |
Lu FU, Yanjue YE, Jiangying LI, Ziyi TANG, Li YIN.
Expressions of Sirtuins protein in testis tissue and GC-2 cells in male reproductive system damage model mice induced by bisphenol A and their significances
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1107-1116.
|
| [5] |
Xing LIU,Jiali LIU,Liangui NIE,Maojun LIU,Junxiong ZHAO,Liuyang WANG,Jun YANG.
Improvement effect of SO2 on myocardial fibrosis after acute myocardial ischemic injury in rats and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1125-1133.
|
| [6] |
Dandan WANG,Ning ZHOU,Dongqin LIU,Jie ZHAO,Chao LIANG,Juanjuan DAI,Yan WU.
Effect of miR-491-5p over-expression on proliferation and migration of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma HONE-1 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1134-1139.
|
| [7] |
Na NI,Hongliang DONG,Haiyang GAO,Weiwei CHEN,Xinyu MENG,Bingjie CUI,Jing DU.
Construction of human lncRNA-GACAT2 over-expression vector and its effect on proliferation and stemness of lung cancer cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1147-1153.
|
| [8] |
Yong GUO,Shengyan WANG,Jingjing YI,Sen CUI.
Effect of salidroside on apoptosis of CD71+ nucleated red blood cells in bone marrow in high altitude polycythemia model rats
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1174-1181.
|
| [9] |
Qi WU,Jianfeng CHEN,Hao LI,Feng WEN.
Effect of paeonol on proliferation, migration, and CXCR4/STAT3 pathway of human osteosarcoma MG-63 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1202-1209.
|
| [10] |
Wenjun DENG,Liantao HU,Binnan ZHAO,Xinyu DONG,Xuebin LI,Jie LI,Xinyan YANG,Xiaoli GUO,Yue LI,Yikun QU,Weiqun WANG.
Effect of CXC chemokine ligand 10 on proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1227-1233.
|
| [11] |
Yuesheng ZHAO,Zubin LI,Haiou LIU,Kunlin TAO,Qihai ZHAO,Na LI.
Inhibitory effect of silencing CDKL1 gene on proliferation and invasion of breast cancer MCF-7 cells by regulating PTEN/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1234-1242.
|
| [12] |
Yuanying SONG,Jing KAN,Kun PENG,Yue LI.
Effect of honeysuckle extract on proliferation and apoptosis of airway smooth muscle cells in asthmatic model mice
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 1001-1007.
|
| [13] |
Meng LIU,Xiaodong HUANG,Zheng HAN,Qingxi ZHU,Jie TAN,Xia TIAN.
Effect of cadherin-17 on proliferation and apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells and its PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway regulatory mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 1008-1017.
|
| [14] |
Xuying WANG,Mingzhen JING,Jin YU,Rong FU,Ru YANG.
Effects of miR-181a-5p and BACH2 expressions on apoptosis and invasion of leukemic CCRF-CEM cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 840-849.
|
| [15] |
Guan LIU,Guizhou TAO,Hongxin WANG.
Effect of baicalin on myocardial hypertrophy and apoptosis induced by abdominal aorta ligation in rats and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 850-857.
|
 )
)