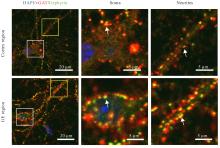
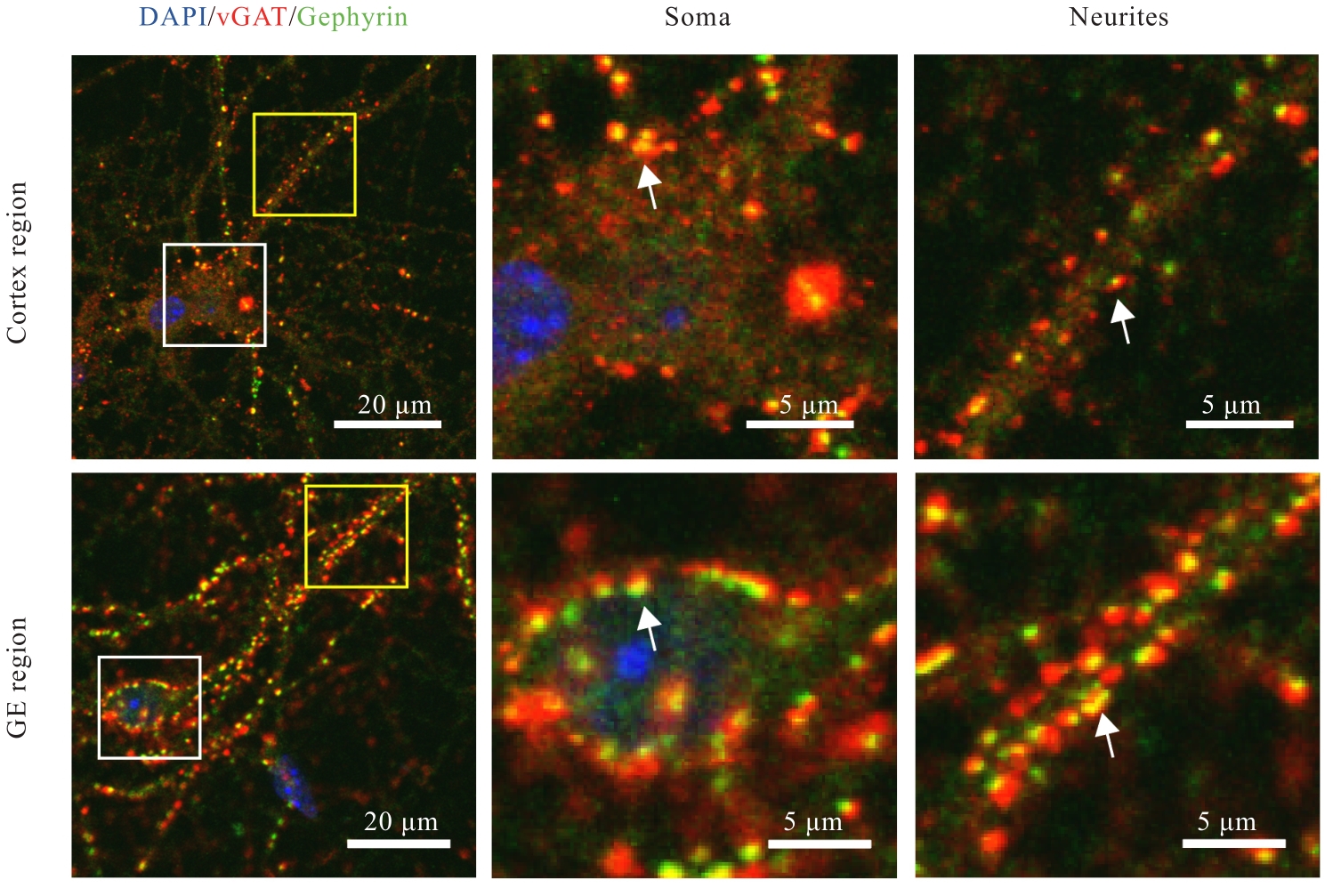
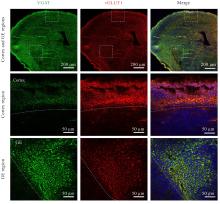
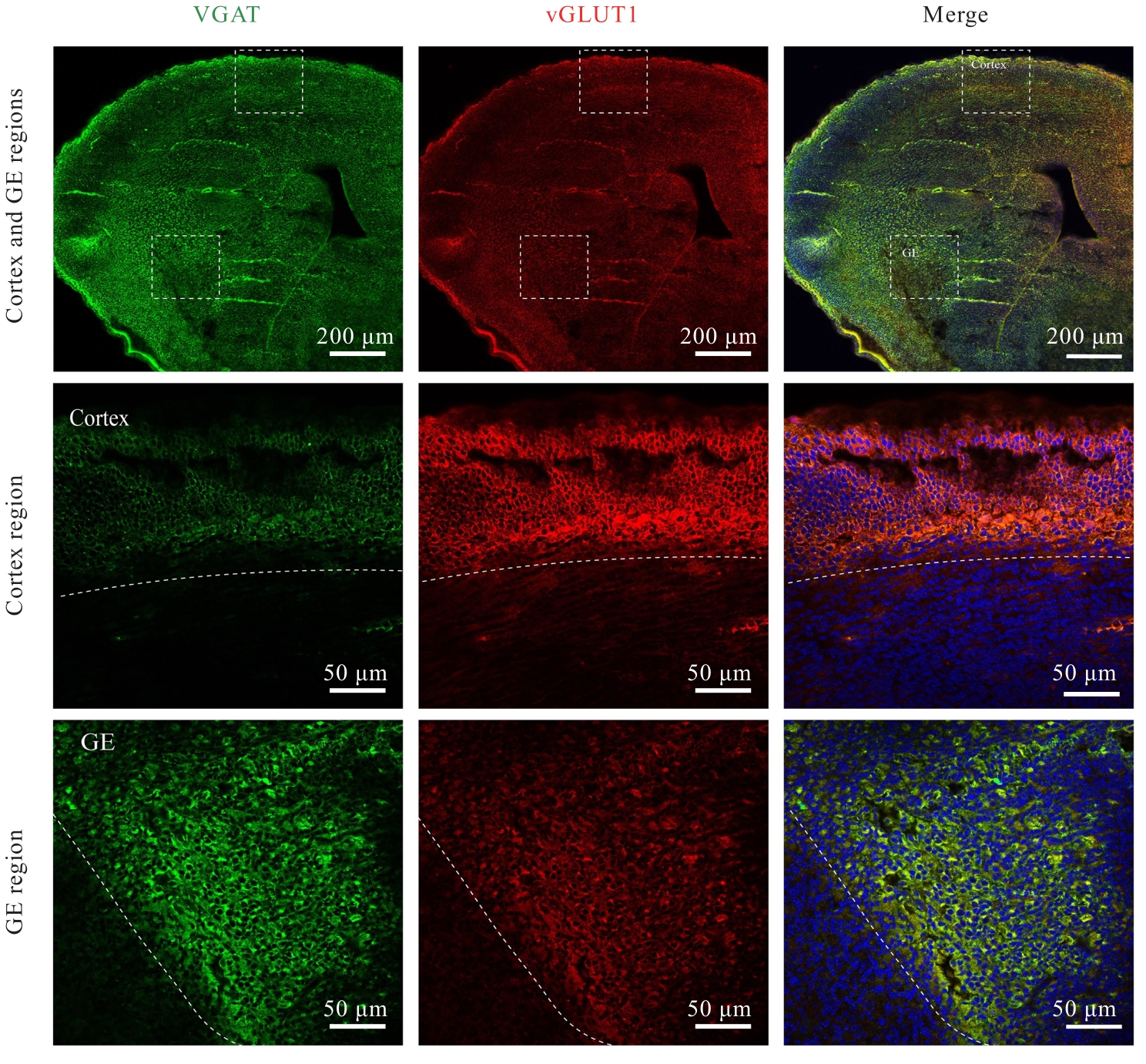
| 1 |
DU X C, LI J S, LI M H, et al. Research progress on the role of type I vesicular glutamate transporter (VGLUT1) in nervous system diseases[J]. Cell Biosci, 2020, 10: 26.
|
| 2 |
COLEY A A, GAO W J. PSD95: a synaptic protein implicated in schizophrenia or autism?[J]. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry, 2018, 82: 187-194.
|
| 3 |
MCEACHERN E P, COLEY A A, YANG S S, et al. PSD-95 deficiency alters GABAergic inhibition in the prefrontal cortex[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2020, 179: 108277.
|
| 4 |
COLEY A A, GAO W J. PSD-95 deficiency disrupts PFC-associated function and behavior during neurodevelopment[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 9486.
|
| 5 |
ALONSO-MARTÍNEZ C, RUBIO-TEVES M, PORRERO C, et al. Cerebellar and basal Ganglia inputs define three main nuclei in the mouse ventral motor thalamus[J]. Front Neuroanat, 2023, 17: 1242839.
|
| 6 |
BOLNEO E, CHAU P Y S, NOAKES P G, et al. Investigating the role of GABA in neural development and disease using mice lacking GAD67 or VGAT genes[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(14): 7965.
|
| 7 |
OLAH S S, KAREEMO D J, BUCHTA W C, et al. Acute reorganization of postsynaptic GABAA receptors reveals the functional impact of molecular nanoarchitecture at inhibitory synapses[J]. Cell Rep, 2023, 42(11): 113331.
|
| 8 |
JUNG H, KIM S, KO J, et al. Intracellular signaling mechanisms that shape postsynaptic GABAergic synapses[J]. Curr Opin Neurobiol, 2023, 81: 102728.
|
| 9 |
HOFFMANN C, MILOVANOVIC D. Gephyrin: a scaffold that builds a phase at the inhibitory postsynapses[J]. Cell Res, 2021, 31(3): 245-246.
|
| 10 |
GASPERONI J, DWORKIN S. Neural stem/progenitor cell (NSPC) extraction and culture[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2024, 2746: 109-120.
|
| 11 |
ZHOU W H, YANG X Y, WANG H X, et al. Neuronal aerobic glycolysis exacerbates synapse loss in aging mice[J]. Exp Neurol, 2024, 371: 114590.
|
| 12 |
SOUZA S D, ROSARIO CLAUDIO J, SIM J, et al. Interleukin-10 signaling in somatosensory neurons controls CCL2 release and inflammatory response[J]. Brain Behav Immun, 2024, 116: 193-202.
|
| 13 |
GAZORPAK M, HUGENTOBLER K M, PAUL D, et al. Harnessing PROTAC technology to combat stress hormone receptor activation[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14(1): 8177.
|
| 14 |
ALEJANDRA LLANES-CUESTA M, HOI V, HA R, et al. Redox protein thioredoxin mediates neurite outgrowth in primary cultured mouse cerebral cortical neurons[J]. Neuroscience, 2024, 537: 165-173.
|
| 15 |
沈永梅, 常晓菡, 张倩文, 等. PM2.5暴露对原代皮层神经元 COX-2 启动子区甲基化水平的影响[J]. 毒理学杂志, 2022, 36(2): 152-156, 162.
|
| 16 |
石子璇, 饶 维, 姬广辉, 等. Npas4在小鼠原代神经元体外氧糖剥夺/复氧损伤中的保护作用及其可能机制[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2021, 37(8): 1409-1414.
|
| 17 |
唐凡人, 余萍萍, 王 莉, 等. 白藜芦醇预处理对大鼠皮质神经元氧糖剥夺/再复氧损伤后神经元突起生长的影响[J]. 解剖学报, 2017, 48(1): 1-6.
|
| 18 |
KANG X, ZHANG Z P, SONG C G, et al. γ-secretase inhibitor disturbs the morphological development of differentiating neurons through affecting Notch/miR-342-5p[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2022, 778: 136603.
|
| 19 |
HAMPEL H, MESULAM M M, CUELLO A C, et al. The cholinergic system in the pathophysiology and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Brain, 2018, 141(7): 1917-1933.
|
| 20 |
STILES J, JERNIGAN T L. The basics of brain development[J]. Neuropsychol Rev, 2010, 20(4): 327-348.
|
| 21 |
KEPECS A, FISHELL G. Interneuron cell types are fit to function[J]. Nature, 2014, 505(7483): 318-326.
|
| 22 |
NERY S, FISHELL G, CORBIN J G. The caudal ganglionic eminence is a source of distinct cortical and subcortical cell populations[J]. Nat Neurosci, 2002, 5(12): 1279-1287.
|
| 23 |
WICHTERLE H, TURNBULL D H, NERY S, et al. In utero fate mapping reveals distinct migratory pathways and fates of neurons born in the mammalian basal forebrain[J]. Development, 2001, 128(19): 3759-3771.
|
| 24 |
GROUP P I N, ASCOLI G A, ALONSO-NANCLARES L, et al. Petilla terminology: nomenclature of features of GABAergic interneurons of the cerebral cortex[J]. Nat Rev Neurosci, 2008, 9(7): 557-568.
|
| 25 |
HAMMOND-WEINBERGER D R, WANG Y X, GLAVIS-BLOOM A, et al. Mechanism for neurotransmitter-receptor matching[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2020, 117(8): 4368-4374.
|
 )
)