| [1] |
Linru WANG,Jing ZHANG,Dongchan ZHAO,Jinjun WANG,Wenxian HU.
Effect of silencing FOXO1 gene on autophagy and apoptosis of human aortic vascular smooth muscle cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 431-441.
|
| [2] |
Ruipeng ZHANG,Jie LI.
Resistance and regeneration effects of lncRNA GPRC5D-AS1 on muscle atrophy of myocytes in mice induced by dexamethasone and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1457-1465.
|
| [3] |
Lijun SUN,Jie FENG,Xiaoming LIU,Guangwei REN,Lin RUAN.
Expression of ADAM10 in vascular tissue at stenosis of human arteriovenous fistula and its effect on proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 482-491.
|
| [4] |
Renyi YANG,Shuwang PENG,Yongheng WANG,Yuxuan DONG,Shanshan DUAN.
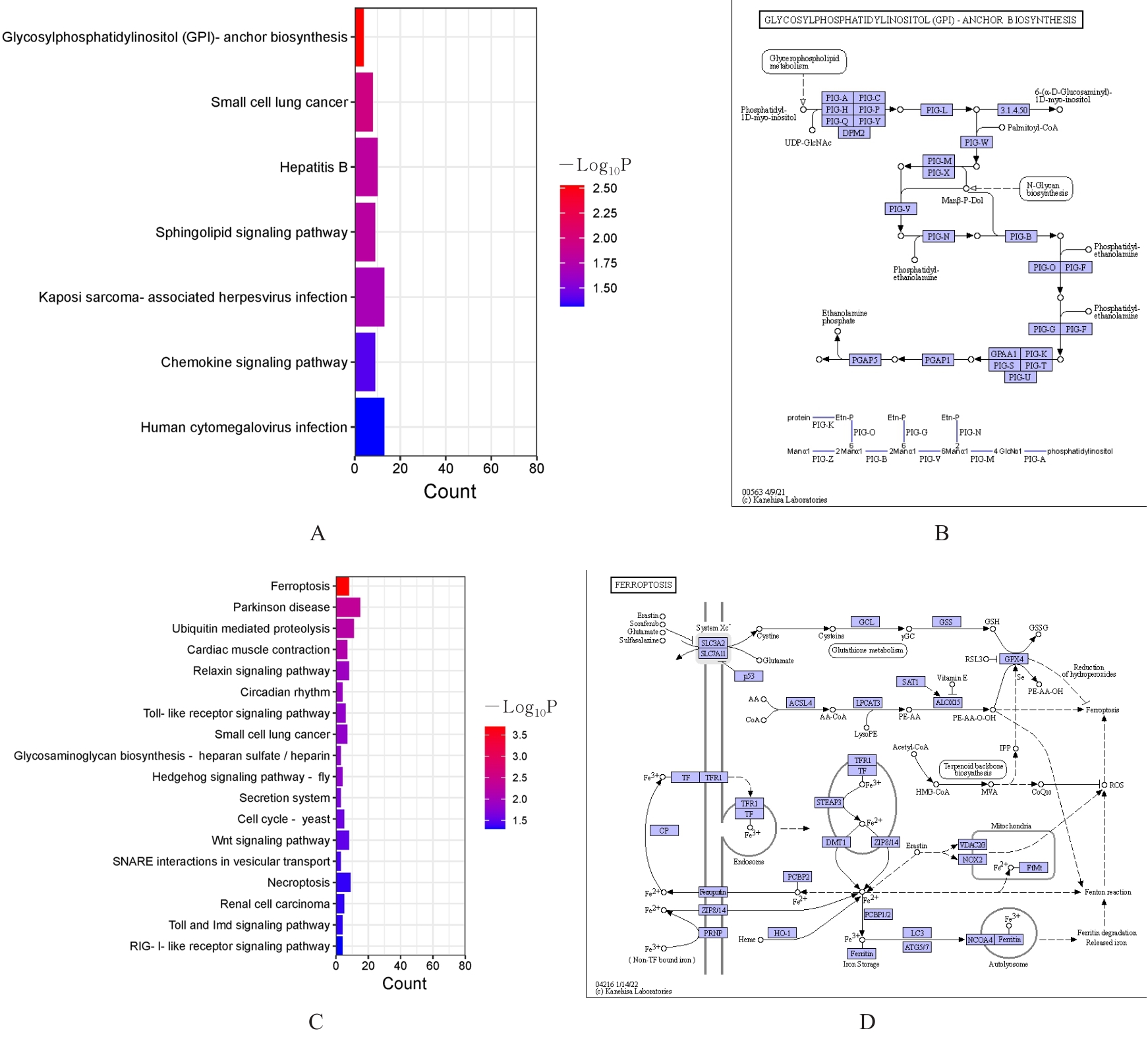
Construction of ferroptosis prognostic risk model of thyroid cancer and bioinformatics analysis on its potential mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 402-413.
|
| [5] |
Qiaoling YANG,Lu FU,Yu SHI,Yanjue YE,Rifeng LU,Yong LIU,Li YIN.
Inhibitory effect of rosiglitazone on ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells in mice with acute renal injury induced by lipopolysaccharide and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 351-359.
|
| [6] |
Xuechun DU,Baosheng LI,Shuwei QIAO,Yanzhen OU,Zhen LI,Weiyan MENG.
Effect of Porphyromonas gingivalis-LPS on expression levels of ferroptosis-related factors in macrophages
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1148-1155.
|
| [7] |
Xinying ZOU,Shuang GAO,Hong ZHAO,Xin LIU,Yuanhang ZHAO,Jiazhuo SONG,Linlin YAN,Zhimin ZHANG.
Effect of TGF-β3-loaded methacrylated heparin on osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 954-961.
|
| [8] |
Xuanchen LIU,Xiaoying TIE,Yulin LIU, WangNing.
Effect of polygonum multiflorum extract on osteoporosis and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in agravic mice
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1386-1396.
|
| [9] |
Xia DONG,Xunxia WANG,Fang YANG.
Promotion effect of miR-34a on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1362-1370.
|
| [10] |
GUO Weiwei, QIN Yue, YANG Haibo, MI Zhanhu.
Promotion effect of LncRNA MALAT1 on osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells through miR-34c/SATB2 axis
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 963-971.
|
| [11] |
WANG Lan, ZHU Guoshuang, SUN Long, WANG Xiaoqin.
Improvement effect of Shenyuan Granule on vascular calcification in db/db diabetic nephropathy mice and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(03): 431-438.
|
| [12] |
BI Hongdong, XIE Yaqin, CUI Haipeng, LIU Kai, SUN Xiaoxu, WANG Tu, ZHAO Juan.
Effects of urantide on expressions of type Ⅳcollagenin thoracic aorta and VSMC of atherosclerotic rats
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(02): 342-346.
|
| [13] |
BI Xueting, SHEN Yuqin, XU Xiaowei, LI Wenjie, WANG Zhuoran, LIN Chongtao.
Effects of oligodeoxynucleotide YW002 on proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis and early osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(02): 273-279.
|
| [14] |
FENG Wenlei, ZHANG Meng, XU Fangjie, YIN Shuanghong, WANG Yanjie, CHEN Xueling, WU Xiangwei.
Effects of endothelial progenitor cells conditioned medium on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and their mechanisms
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(02): 218-224.
|
| [15] |
ZHAO Juan|WANG Hong,YU Quan-xin|SHI Yan|LI Xiang-jun|REN Li-qun .
Effect of urantide on proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells in rats
[J]. J4, 2011, 37(6): 1079-1082.
|
 ),Mao YANG1,Di YANG1,Chenglin GUO1,Wenjun ZHU4,Yaqin YU4,Qin LU4,Jinzhi LUO4,Chunqin WU4,Zhaohui FANG1,2,3
),Mao YANG1,Di YANG1,Chenglin GUO1,Wenjun ZHU4,Yaqin YU4,Qin LU4,Jinzhi LUO4,Chunqin WU4,Zhaohui FANG1,2,3