Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (3): 778-785.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240322
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles
Mendelian randomization study based on relationship between lifestyle and occurrence and development of hepatobiliary malignancies
Huaqing LIU,Qingkai CHEN,Yongxin CHEN,Runhao QIU,Xupeng DING,Fengjing SONG,Yan WANG,Baolin WANG,Hong CAO( )
)
- Department of General Surgery,Xinmin District,China-Janpan Union Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
-
Received:2023-06-29Online:2024-05-28Published:2024-07-01 -
Contact:Hong CAO E-mail:caohong1967@163.com
CLC Number:
- R735
Cite this article
Huaqing LIU,Qingkai CHEN,Yongxin CHEN,Runhao QIU,Xupeng DING,Fengjing SONG,Yan WANG,Baolin WANG,Hong CAO. Mendelian randomization study based on relationship between lifestyle and occurrence and development of hepatobiliary malignancies[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 778-785.
share this article
Tab. 1
Informations of samples"
| Exposed lifestyle | PubMed ID | Sample size |
|---|---|---|
| Percentage of carbohydrate intake | 23372041 | 33 355 |
| Percentage of fat intake | 23372041 | 33 355 |
| Percentage of protein intake | 23372041 | 33 355 |
| Coffee intake | 31046077 | 39 924 |
| Weekly alcohol consumption times | 30643251 | 630 154 |
| Leisure electronic screen exposure time | 36071172 | 526 725 |
| MVPA during leisure time | 36071172 | 608 595 |
| Sedentary behavior at work | 36071172 | 372 609 |
| Age at first smoking | 30643251 | 216 837 |
| Daily smoking quantity | 30643251 | 216 590 |
| Current smoking status | 30643251 | 378 249 |
| Past smoking status | 30643251 | 848 460 |
Tab. 2
Influence factors and outcomes of incorporated lifestyle"
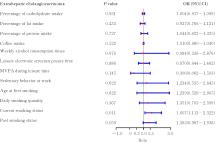
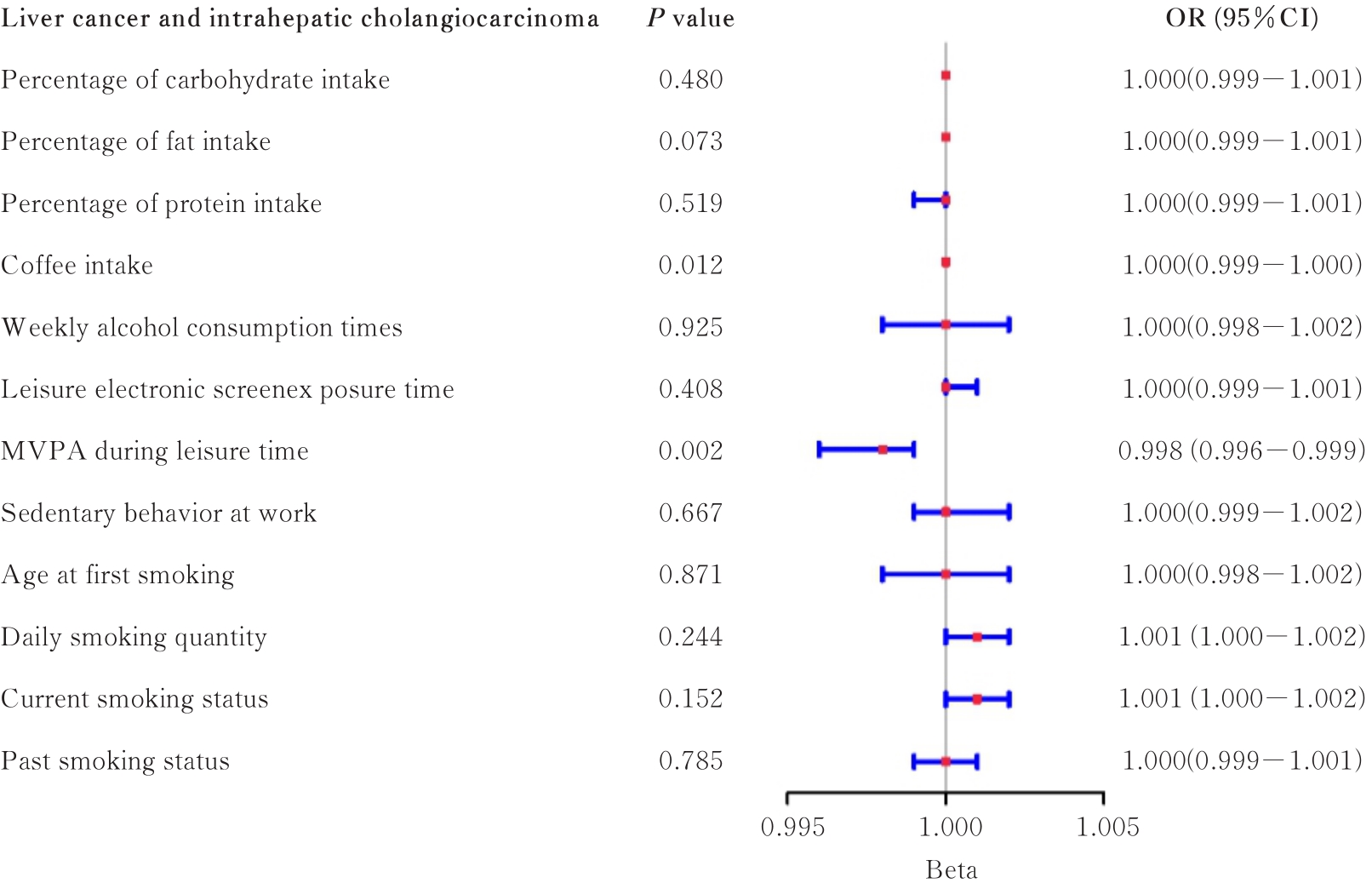
| Exposed lifestyle | Extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | Liver cancer and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of SNPs | F | R2(η/%) | Number of SNPs | F | R2(η/%) | ||
| Percentage of carbohydrate intake | 8 | 20.25—31.36 | 0.54 | 7 | 20.25—31.36 | 0.48 | |
| Percentage of fat intake | 2 | 19.99—21.60 | 0.12 | 2 | 19.99—21.60 | 0.12 | |
| Percentage of protein intake | 6 | 20.64—27.46 | 0.42 | 6 | 20.64—27.46 | 0.42 | |
| Coffee intake | 3 | 28.73—1 815.28 | 0.04 | 3 | 28.73—1 815.28 | 0.04 | |
| Weekly alcohol consumption times | 29 | 20.80—56.74 | 0.12 | 23 | 20.80—56.74 | 0.09 | |
| Leisure electronic screen exposure time | 88 | 29.34—66.76 | 0.62 | 79 | 29.34—66.76 | 0.57 | |
| MVPA during leisure time | 12 | 30.12—44.31 | 0.07 | 8 | 30.12—44.31 | 0.05 | |
| Sedentary behavior at work | 7 | 29.87—39.69 | 0.06 | 6 | 29.87—38.32 | 0.05 | |
| Age at first smoking | 22 | 21.04—31.29 | 0.24 | 14 | 21.22—31.29 | 0.15 | |
| Daily smoking quantity | 30 | 20.82—503.45 | 0.60 | 26 | 21.04—503.45 | 0.55 | |
| Current smoking status | 20 | 20.79—57.59 | 0.14 | 14 | 20.79—57.59 | 0.10 | |
| Past smoking status | 56 | 20.75—53.17 | 0.17 | 46 | 20.75—53.17 | 0.14 | |
Tab. 3
Results of sensitivity analysis of Mendelian randomization"
| Exposed lifestyle | Extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | Liver cancer and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q | Cochrane’s Q- | MR-Egger intercept | MR-Egger intercept- | Q | Cochrane’s Q- | MR-Egger intercept | MR-Egger intercept- | |
| Percentage of carbohydrate intake | 6.751 | 0.455 | 0.040 | 0.645 | 4.285 | 0.638 | 0.00 016 | 0.342 |
| Percentage of fat intake | 1.288 | 0.256 | — | — | 0.798 | 0.372 | — | — |
| Percentage of protein in diet intake | 3.212 | 0.667 | -0.165 | 0.326 | 12.715 | 0.026 | -0.00 052 | 0.159 |
| Coffee intake | 2.536 | 0.281 | 0.312 | 0.384 | 0.123 | 0.940 | 0.00 013 | 0.794 |
| Weekly alcohol consumption time | 29.995 | 0.363 | -0.008 | 0.814 | 20.088 | 0.578 | -0.0 0010 | 0.195 |
| Leisure electronic screenex posure time | 89.132 | 0.303 | -0.022 | 0.362 | 64.966 | 0.834 | -0.00 001 | 0.885 |
| MVPA during leisure time | 18.354 | 0.049 | 0.079 | 0.467 | 2.687 | 0.912 | 0.00 001 | 0.985 |
| Sedentary behavior at work | 3.288 | 0.772 | -0.009 | 0.910 | 2.443 | 0.785 | -0.00 005 | 0.705 |
| Age at first smoking | 15.972 | 0.771 | 0.005 | 0.894 | 17.265 | 0.187 | 0.00 006 | 0.508 |
| Daily smoking quantity | 34.499 | 0.221 | 0.005 | 0.819 | 25.719 | 0.423 | -0.00 001 | 0.793 |
| Current smoking status | 11.899 | 0.890 | 0.009 | 0.790 | 13.646 | 0.399 | -0.00 004 | 0.638 |
| Past smoking status | 42.277 | 0.896 | -0.015 | 0.528 | 42.739 | 0.568 | 0.00 003 | 0.675 |
| 1 | ALJIFFRY M, ABDULELAH A, WALSH M, et al. Evidence-based approach to cholangiocarcinoma: a systematic review of the current literature[J]. J Am Coll Surg, 2009, 208(1): 134-147. |
| 2 | KOAY E J, ODISIO B C, JAVLE M, et al. Management of unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: how do we decide among the various liver-directed treatments?[J]. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr, 2017, 6(2): 105-116. |
| 3 | BRINDLEY P J, BACHINI M, ILYAS S I, et al. Cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2021, 7: 65. |
| 4 | OSATAPHAN S, MAHANKASUWAN T, SAENGBOONMEE C. Obesity and cholangiocarcinoma: a review of epidemiological and molecular associations[J]. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci, 2021, 28(12): 1047-1059. |
| 5 | SONG Y H, CAI M T, LI Y H, et al. The focus clinical research in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Eur J Med Res, 2022, 27(1): 116. |
| 6 | BAUMEISTER S E, SCHLESINGER S, ALEKSANDROVA K, et al. Association between physical activity and risk of hepatobiliary cancers: a multinational cohort study[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 70(5): 885-892. |
| 7 | KUBO S, SHINKAWA H, ASAOKA Y, et al. Liver cancer study group of Japan clinical practice guidelines for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Liver Cancer, 2022, 11(4): 290-314. |
| 8 | LAN Q Y, ZHANG Y J, LIAO G C, et al. The association between dietary vitamin A and carotenes and the risk of primary liver cancer: a case-control study[J]. Nutrients, 2016, 8(10): 624. |
| 9 | SCHERÜBL H. Alcohol use and gastrointestinal cancer risk[J]. Visc Med, 2020, 36(3): 175-181. |
| 10 | CHO I R, YI S W, CHOI J S, et al. Comparison of risk factors for cholangiocarcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective cohort study in Korean adults[J]. Cancers, 2022, 14(7): 1709. |
| 11 | HOU L, JIANG J M, LIU B Q, et al. Is exposure to tobacco associated with extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma epidemics? A retrospective proportional mortality study in China[J]. BMC Cancer, 2019, 19(1): 348. |
| 12 | MADRID-VALERO J J, GREGORY A M. Behaviour genetics and sleep: a narrative review of the last decade of quantitative and molecular genetic research in humans[J]. Sleep Med Rev, 2023, 69: 101769. |
| 13 | MOHAMMADI-SHEMIRANI P, SOOD T, PARÉ G. From’omics to multi-omics technologies: the discovery of novel causal mediators[J]. Curr Atheroscler Rep, 2023, 25(2): 55-65. |
| 14 | 丁佳豪, 章梦琦, 郝明霞, 等. 孟德尔随机化研究精神分裂症与自杀或故意自残的因果关系[J]. 中华精神科杂志, 2023, 56(1): 32-39. |
| 15 | 刘宇兴, 苗雨阳, 赵明辉, 等. 双样本孟德尔随机化研究精神疾病和阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停的关系[J]. 中华老年医学杂志, 2022, 41(10): 1146-1149. |
| 16 | 张晓宇, 刘天一, 朱文豪, 等. 孟德尔随机化研究及其在脑卒中病因探索中应用进展[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2022, 42(23): 5885-5888. |
| 17 | 吴思佳, 李洪凯, 薛付忠, 等. 血压表型、脂质成分与2型糖尿病的跨种族孟德尔随机化研究[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2023, 9(1): 19-25. |
| 18 | LIU H L, WU W, XIANG W, et al. Lifestyle factors, metabolic factors and socioeconomic status for pelvic organ prolapse: a Mendelian randomization study[J]. Eur J Med Res, 2023, 28(1): 183. |
| 19 | SKRIVANKOVA V W, RICHMOND R C, WOOLF B A R, et al. Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology using Mendelian randomization: the STROBE-MR statement[J]. JAMA, 2021, 326(16): 1614-1621. |
| 20 | SAKAUE S, KANAI M, TANIGAWA Y, et al. A cross-population atlas of genetic associations for 220 human phenotypes[J]. Nat Genet, 2021, 53(10): 1415-1424. |
| 21 | CHU A Y, WORKALEMAHU T, PAYNTER N P, et al. Novel locus including FGF21 is associated with dietary macronutrient intake[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2013, 22(9): 1895-1902. |
| 22 | ZHONG V W, KUANG A L, DANNING R D, et al. A genome-wide association study of bitter and sweet beverage consumption[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2019, 28(14): 2449-2457. |
| 23 | LIU M Z, JIANG Y, WEDOW R, et al. Association studies of up to 1.2 million individuals yield new insights into the genetic etiology of tobacco and alcohol use[J]. Nat Genet, 2019, 51(2): 237-244. |
| 24 | WANG Z, EMMERICH A, PILLON N J, et al. Genome-wide association analyses of physical activity and sedentary behavior provide insights into underlying mechanisms and roles in disease prevention[J]. Nat Genet, 2022, 54(9): 1332-1344. |
| 25 | CAI J H, WEI Z X, CHEN M, et al. Socioeconomic status, individual behaviors and risk for mental disorders: a Mendelian randomization study[J]. Eur Psychiatry, 2022, 65(1): e28. |
| 26 | BURGESS S, BUTTERWORTH A, THOMPSON S G. Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data[J]. Genet Epidemiol, 2013, 37(7): 658-665. |
| 27 | BEHRENS G, MATTHEWS C E, MOORE S C, et al. The association between frequency of vigorous physical activity and hepatobiliary cancers in the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study[J]. Eur J Epidemiol, 2013, 28(1): 55-66. |
| 28 | MCGEE E E, JACKSON S S, PETRICK J L, et al. Smoking, alcohol, and biliary tract cancer risk: a pooling project of 26 prospective studies[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2019, 111(12): 1263-1278. |
| 29 | 林志文, 刘红枝, 曾永毅, 等. 肝内胆管癌新辅助治疗的热点与进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2023, 39(9): 2031-2038. |
| 30 | GUO W, GE X Y, LU J, et al. Diet and risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, cirrhosis, and liver cancer: a large prospective cohort study in UK biobank[J]. Nutrients, 2022, 14(24): 5335. |
| 31 | MAKIUCHI T, SOBUE T, KITAMURA T, et al. The relationship between vegetable/fruit consumption and gallbladder/bile duct cancer: a population-based cohort study in Japan[J]. Int J Cancer, 2017, 140(5): 1009-1019. |
| 32 | MAKIUCHI T, SOBUE T, KITAMURA T, et al. Association between green tea/coffee consumption and biliary tract cancer: a population-based cohort study in Japan[J]. Cancer Sci, 2016, 107(1): 76-83. |
| 33 | PETRICK J L, FREEDMAN N D, GRAUBARD B I, et al. Coffee consumption and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma by sex: the liver cancer pooling project[J]. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 2015, 24(9): 1398-1406. |
| 34 | YIN X, HE X K, WU L Y, et al. Chlorogenic acid, the main antioxidant in coffee, reduces radiation-induced apoptosis and DNA damage via NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) activation in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2022, 2022: 4566949. |
| 35 | MAKIUCHI T, SOBUE T, KITAMURA T, et al. Smoking, alcohol consumption, and risks for biliary tract cancer and intrahepatic bile duct cancer[J]. J Epidemiol, 2019, 29(5): 180-186. |
| [1] | Haiyao PANG,Jun MENG. Research progress in relationship between 14-3-3ɛ protein and occurrence and development of tumor [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 572-578. |
| [2] | Huijuan SONG,Zhenhua XU,Dongning HE. Effect of apolipoprotein C1 expression on proliferation and apoptosis of human liver cancer HepG2 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 128-135. |
| [3] | Tianyi WANG,Yufeng ZHU,Miao SUN,Wei WANG. Application of three-dimensional reconstruction combined with indocyanine green intraoperative navigation in diagnosis and treatment of liver cancer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 1014-1021. |
| [4] | Jie YANG,Wubin HE,Ni AN,Wencong KONG,Rongjian SU,Xuezhe WANG. Regulatory effect of glucose-regulating protein 78 on radiotherapy sensitivity of liver cancer cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 888-895. |
| [5] | Runhong MU, Xinzhu LIU, Rui LIN, Yupeng LI, Luyao WANG, Chunyu WANG, Xiao GUO. Effect of PRDX6 over-expression of proliferation, invasion and migration of liver cancer cells and its molecular mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 559-565. |
| [6] | Haiying ZHANG,Wenxin ZHANG,Wenjing ZHAO,Wei LI. Induction effect of gallic acid on apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG-2 cells through regulating mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 125-132. |
| [7] | CHEN Xi, BAI Lin, WANG Yingying, CAO Shuang, MU Hongping, WANG Yilin, SHI Hao, ZHANG Qian, GAO Xin, ZHANG Chengyi, ZHANG Ruowen. Inhibitory effect of tanshinone ⅡA on proliferation and migration of human liver cancer HepG2 cells and its apoptosis-promoting effect [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(03): 531-538. |
| [8] | XU Zhenhua, SU Rongjian. Inhibitory effects of zingerone combined with sorafenib on migration and invasion of human liver cancer HepG2 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(02): 228-233. |
| [9] | YU Tao, JIAO Xue, FU Changfeng, LI Qin. Selective effects of cyclamin on proliferation and apoptosis of liver cancer cells and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(02): 319-324. |
| [10] | GU Teng, WANG Jiang, CHEN Xiaoqian, LIU Kai. Hepatic angiomyolipoma: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(01): 153-155. |
| [11] | ZHU Deqiang, CHEN Xuejun. Effects of plumbagin on proliferation and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2R cells resistant to sorafenib and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2018, 44(06): 1223-1229. |
| [12] | LI Tianzhu, WANG Jiaru, ZHANG Junyi, WANG Hongquan, SHI Tiewei, ZHOU Jing, BAI Chunying, JIN Chenghao. Expression of ELK-3 protein in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue and its effects on migration and invasion abilities of HepG2 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(04): 736-740. |
| [13] | LIU Xia, QI Fengjie, DU Xiaoyuan. Effects of silencing expression of CRAF gene on invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(03): 521-525. |
| [14] | XING Shaoji, ZHENG Liansheng, WANG Diandong, ZHANG Xuan, CHI Min. Analysis on association between single nucleotide polymorphism of selenoprotein S gene and risk of liver cancer [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(03): 558-562. |
| [15] | ZHANG Yanxia, LI Yuehui, ZHANG Lihong, ZHANG Nianping, YAN Yanyan, YANG Xiaohui, FENG Xiangling. Effects of silencing HOXA13 gene on malignant phenotypes of hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 and QGY-7703 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(02): 315-320. |
|
||