| 1 |
LU W, JIANG G R, GROUP S H H C. Hemoperfusion in maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. Blood Purif, 2022: 1-9.
|
| 2 |
林 文. 维持性血液透析患者死亡危险因素分析[J]. 中国处方药, 2022, 20(7): 142-144.
|
| 3 |
李 明, 李灿明, 叶增纯, 等. 维持性血液透析患者死亡及其危险因素的单中心分析[J]. 中山大学学报(医学科学版), 2020, 41(4): 620-626.
|
| 4 |
LI Q, ZHANG S, WU Q J, et al. Serum total indoxyl sulfate levels and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in maintenance hemodialysis patients: a prospective cohort study[J]. BMC Nephrol, 2022, 23(1): 231.
|
| 5 |
郭佳佳, 马胜银, 刘莉华, 等. 维持性血液透析患者发生心血管疾病的相关危险因素分析[J]. 中华全科医学, 2022, 20(6): 978-981.
|
| 6 |
GUO J C, NUNLEY K A, COSTACOU T, et al. Greater progression of coronary artery calcification is associated with clinically relevant cognitive impairment in type 1 diabetes[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2019, 280: 58-65.
|
| 7 |
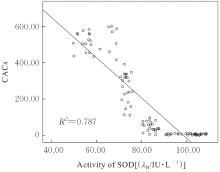
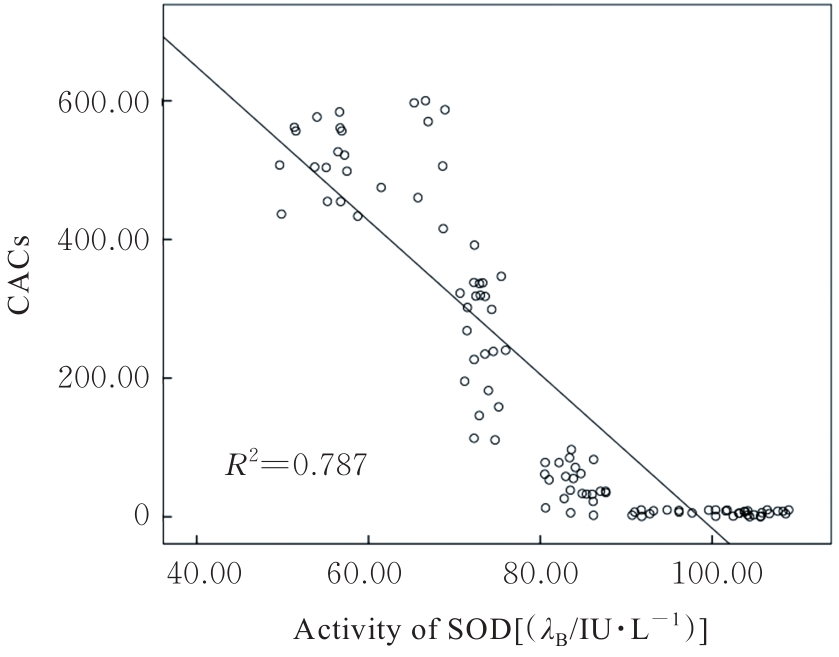
HA L, SHI J B, YU H Y, et al. Association between serum cartilage oligomeric matrix protein and coronary artery calcification in maintenance hemodialysis patients[J]. J Geriatr Cardiol, 2020, 17(2): 67-73.
|
| 8 |
CHEN D T, LIANG M H, JIN C, et al. Expression of inflammatory factors and oxidative stress markers in serum of patients with coronary heart disease and correlation with coronary artery calcium score[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2020, 20(3): 2127-2133.
|
| 9 |
KUNUTSOR S K, BAKKER S J L, DULLAART R P F. Soluble vascular cell adhesion molecules may be protective of future cardiovascular disease risk: findings from the PREVEND prospective cohort study[J]. J Atheroscler Thromb, 2017, 24(8): 804-818.
|
| 10 |
GROSS M D, BIELINSKI S J, SUAREZ-LOPEZ J R, et al. Circulating soluble intercellular adhesion molecule 1 and subclinical atherosclerosis: the Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults Study[J]. Clin Chem, 2012, 58(2): 411-420.
|
| 11 |
CANNATA-ANDÍA J B, MARTÍN-CARRO B, MARTÍN-VÍRGALA J, et al. Chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorders: pathogenesis and management[J]. Calcif Tissue Int, 2021, 108(4): 410-422.
|
| 12 |
邵丽娜, 李 晔, 樊 伟, 等. 维持性血液透析糖尿病肾病患者冠状动脉钙化的危险因素分析[J]. 中国医药导报, 2021, 18(20): 55-58.
|
| 13 |
王旭方, 殷 蕾, 朱羿霖, 等. 腹膜透析与血液透析患者冠状动脉钙化差异分析[J]. 中国中西医结合肾病杂志, 2018, 19(7): 619-621.
|
| 14 |
ISAKA Y, HAMANO T, FUJII H, et al. Optimal phosphate control related to coronary artery calcification in dialysis patients[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2021, 32(3): 723-735.
|
| 15 |
CHEN Y B, ZHAO X Y, WU H. Arterial stiffness: a focus on vascular calcification and its link to bone mineralization[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2020, 40(5): 1078-1093.
|
| 16 |
BOURNE L E, PATEL J J, DAVIES B K, et al. N-acetylcysteine (NAC) differentially affects arterial medial calcification and bone formation: the role of l-cysteine and hydrogen sulphide[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2022, 237(1): 1070-1086.
|
| 17 |
HADRI K E L, SMITH R, DUPLUS E, et al. Inflammation, oxidative stress, senescence in atherosclerosis: thioredoxine-1 as an emerging therapeutic target[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 23(1): 77.
|
| 18 |
李 佳, 魏善斋, 孙 杰, 等. 维持性血液透析患者促红细胞生成素抵抗与炎症反应和氧化应激反应的关系[J]. 山东医药, 2018, 58(28): 65-67.
|
| 19 |
李 颖, 张五星, 周 伟, 等. 维持性血液透析患者血清超氧化物歧化酶与冠状动脉钙化的关系[J]. 山东医药, 2017, 57(17): 70-72.
|
| 20 |
林 浩, 袁得强, 陈 飞, 等. SGLT2抑制剂在冠心病中的作用机制的研究进展[J]. 同济大学学报(医学版), 2023, 44(6): 925-932.
|
| 21 |
JEROTIC D, MATIC M, SUVAKOV S, et al. Association of Nrf2, SOD2 and GPX1 polymorphisms with biomarkers of oxidative distress and survival in end-stage renal disease patients[J]. Toxins, 2019, 11(7): 431.
|
| 22 |
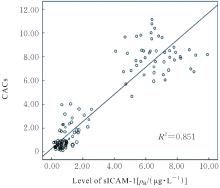
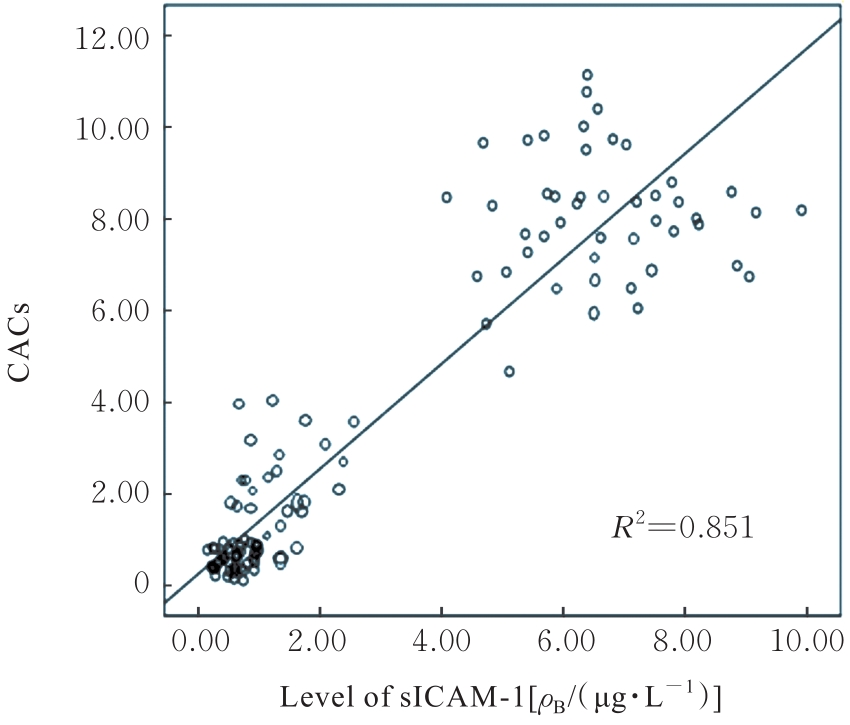
林 彬, 徐 敬, 王佳祥, 等. CRP、sICAM-1、Lp-PLA2、RBP4与AS的相关性及对冠心病的诊断价值[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2019, 11(2): 227-229.
|
| 23 |
辛艳峰, 吴振华, 郭莉清, 等. 稳定型冠心病患者vWF、ET-1、sICAM-1水平对急性心肌梗死发病风险的联合预测价值[J]. 解放军医药杂志, 2022, 34(2): 74-78.
|
| 24 |
崇显瑾, 余青原, 杨历新. 2型糖尿病肾病患者血清中miR-126和sVCAM-1的表达关系及意义[J]. 河北医药, 2019, 41(3): 334-337, 342.
|
| 25 |
梁颖兰, 张 琼. 血液透析联合血液灌流对糖尿病肾病维持性血液透析患者血清vWf、VEGF、sVCAM-1水平的影响[J]. 贵州医药, 2018, 42(7): 785-787.
|
| 26 |
侯 睿, 胡 炜, 董 佩, 等. 糖尿病肾病患者血清ICAM-1 VCAM-1及CTRP9表达水平与冠脉血管钙化的关系[J]. 河北医学, 2022, 28(8): 1279-1285.
|
| 27 |
姜立萍, 黄 雯. 维持性血液透析患者血浆血管细胞黏附分子-1的变化和意义[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2012, 41(2): 45-47.
|
| 28 |
李娅琳. 冠心病病人外周血miR-126与sVCAM-1的表达及其相关性研究[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2020, 18(3): 470-473.
|
| 29 |
秦秀男, 秦 溱, 冉 珂, 等. 七氟醚预处理通过线粒体NAD+-SIRT3通路减轻大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 中南大学学报(医学版), 2022, 47(8): 1108-1119.
|
| 30 |
ROSA A C, BRUNI N, MEINERI G, et al. Strategies to expand the therapeutic potential of superoxide dismutase by exploiting delivery approaches[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2021, 168: 846-865.
|
| 31 |
POZNYAK A, GRECHKO A V, POGGIO P, et al. The diabetes mellitus-atherosclerosis connection: the role of lipid and glucose metabolism and chronic inflammation[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(5): 1835.
|
| 32 |
TRONCOSO M F, ORTIZ-QUINTERO J, GARRIDO-MORENO V, et al. VCAM-1 as a predictor biomarker in cardiovascular disease[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2021, 1867(9): 166170.
|
| 33 |
商志鸿, 贺晓鸣, 杨育林, 等. 活血化瘀中药组方对血瘀型颈动脉粥样硬化病人血脂和血清sICAM-1、sVCAM-1 表达的影响[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2018, 16(14): 1965-1967.
|
| 34 |
程 虹. 中晚期慢性肾脏病患者血管钙化管理[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2023, 43(3): 218-224.
|
 )
)