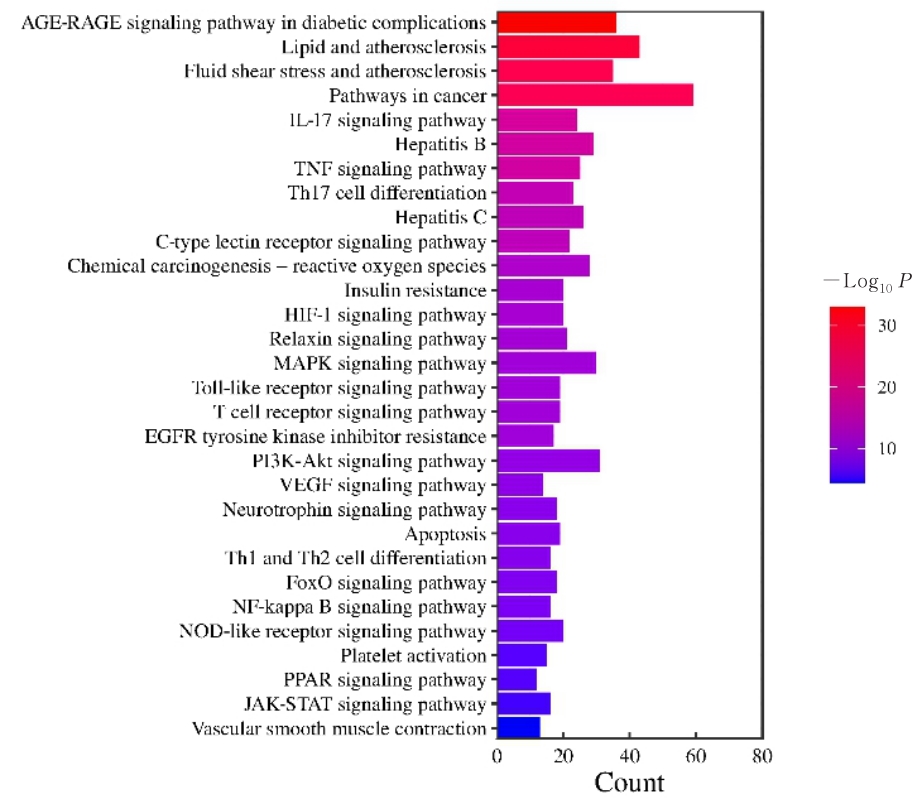
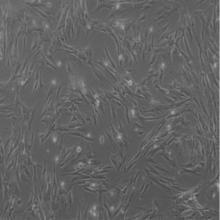
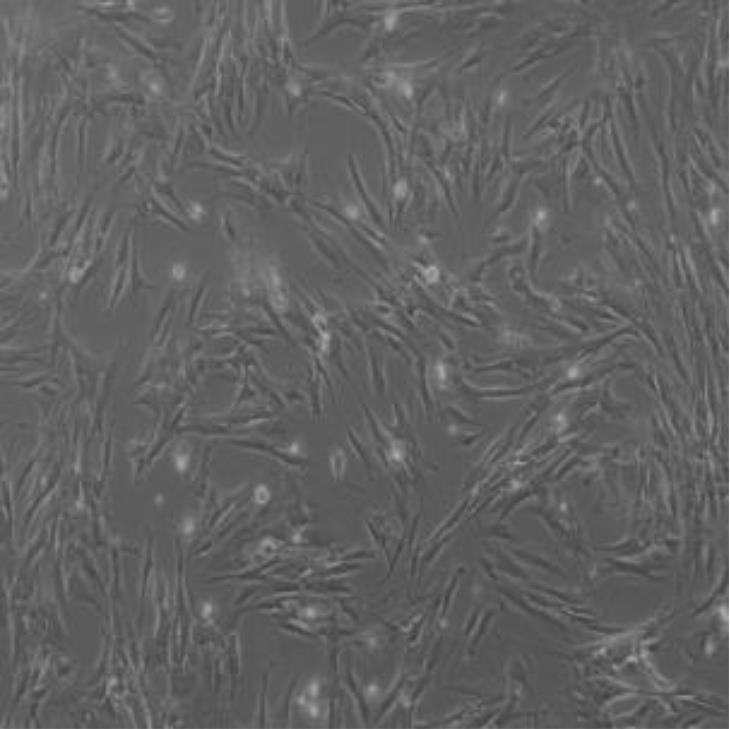
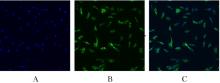
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 925-938.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240406
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro experimental verification based on anti-atherosclerosis mechanism of Xiaoban Tongmai Formula
Shan CAO1( ),Yijia ZHANG2,Yang BAI3,Fang CHEN4,Sha XIE4,Qianqian HAN5
),Yijia ZHANG2,Yang BAI3,Fang CHEN4,Sha XIE4,Qianqian HAN5
- 1.Department of Formula,School of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Zhengzhou 450046,China
2.Department of Academic Affairs,Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Zhengzhou 450046,China
3.Graduate School,Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Zhengzhou 450046,China
4.Department of Pathophysiology,School of Medical Sciences,Henan University of Chinese Medicine,Zhengzhou 450046,China
5.Basic Experimental Center,Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Zhengzhou 450046,China
-
Received:2023-06-30Online:2024-07-28Published:2024-08-01 -
Contact:Shan CAO E-mail:caoshan2000@163.com
CLC Number:
- R285.5
Cite this article
Shan CAO,Yijia ZHANG,Yang BAI,Fang CHEN,Sha XIE,Qianqian HAN. Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro experimental verification based on anti-atherosclerosis mechanism of Xiaoban Tongmai Formula[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 925-938.
share this article
Tab.1
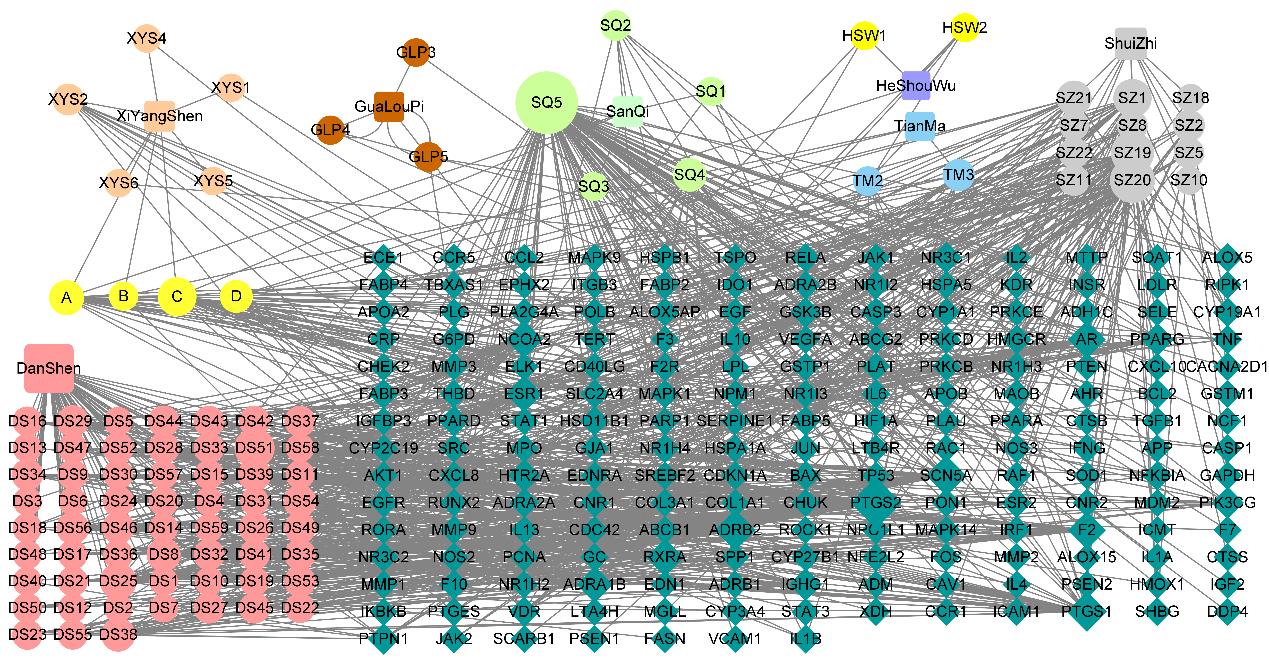
Important components of Xiaoban Tongmai Formula and corresponding targets"
| Herb | Ingredient | Name | Representative target |
|---|---|---|---|
Salvia miltiorrhiza | Miltirone | DS49 | MAPK9,ANG,SOD,JUN |
| Dan-shexinkum D | DS8 | AR,NOS2,PPARG | |
| Luteolin | DS51 | AKT1,EGFR,IL-10,IL-6 | |
| Tanshinone ⅡA | DS25 | NCOA1,FOS,MYC | |
| Cryptotanshinone | DS29 | RELA,PTGS2,STAT3 | |
| Prolithospermic acid | DS41 | NOS2,PTGS1,ESR1 | |
| Pseudo-ginseng | Stigmasterol | SQ4 | PTGS2,PLAU |
| Quercetin | SQ5 | PLAT,BCN5A,TNF,CXCL8 | |
| Panax quinquefolius | Papaverine | XYS2 | APOA1,APOE,APOC1 |
| Daucosterol_qt | XYS5 | PGR,NCOA2 | |
| Trichosanthes peel | Naphthalene | GLP4 | NF-κB1,IL-6 |
| Methyl Palmitate | GLP3 | NPR1,NPR2,NPR3,AR | |
Hirudo | Cholesterol | SZ4 | PPARA,PPARG,PRKCG |
| Adenosine | SZ2 | DDP4,SRC,MAPK1 | |
| Methyl 14-methylpentadecanoate | SZ11 | JAK2,APOE,IDH1 | |
| Methyl 11-methylhexadecanoate | SZ8 | CA2,CA1,VDR,FABP4 | |
| Polygonum multiflorum | Tetrahydroxytaxadiene | HSW1 | ESR1,PGR,VDR |
| Fetidine | HSW2 | HTR2A,DRD2 | |
| Gastrodia elata | p-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol | TM2 | PTGS2,PPARG,IL-1B |
| M-Hydroxybenzoic Acid | TM3 | PPARG,MAPK9,IL-1B | |
Drug share ingredient | Ginsenoside rh2 | A | BAX,TNF,NF-κBIA,IL-1B |
| 20-Hexadecanoylingenol | B | APOC2,PRKCA | |
| Beta-sitosterol | C | PIK3CG,PTGS1,PTGS2 | |
| Gamma-sitosterol | D | NFKB1,WNT4,BAX,AR |
Tab.2
Partial targets of anti-AS"
| Gene | Corresponding protein |
|---|---|
| AKT1 | RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase |
| APOB | Apolipoprotein B-100 |
| CASP-1/-3/-9 | Caspase-1/-3/-9 |
| CXCL8 | Interleukin-8 |
| FOS | Protein c-Fos |
| HIF1A | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha |
| ICAM-1/-2/-3 | Intercellular adhesion molecule 1/2/3 |
| IL-6/IL-1β | Interleukin-8 |
| JAK1/2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 |
| MAPK1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MTOR | Threonine-protein kinase mTOR |
| NFKB1/2 | Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit |
| NOD1/2 | Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain- containing protein 1/2 |
| NOS1/2/3 | Nitric oxide synthase |
| RELA | Nuclear factor kappa B p65 |
| PLAT | Tissue-type plasminogen activator |
| STAT1/2/3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| VEGFA | Vascular endothelial growth factor A |
Tab.5
Proliferation activities of ox-LDL-induced HA-VSMCs in various groups after treated with different doses of XBTMF"
| Group | Proliferation activity |
|---|---|
| Blank | 0.57±0.03 |
| Model | 0.81±0.05* |
| Rosuvastatin | 0.63±0.04△ |
| XBTMF(mg·L-1 ) | |
| 0.025 | 0.66±0.03△ |
| 0.050 | 0.57±0.05△ |
| 0.100 | 0.45±0.03△# |
| 0.200 | 0.83±0.05# |
| 0.400 | 0.81±0.06# |
| 0.800 | 0.80±0.02# |
Tab.6
Levels of inflammatory factors in HA-VSMCs culture supernatant in various groups [n=5,xˉ±s,ρB/(ng·L-1)]"
| Group | MCP-1 | IL-6 | IL-8 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 266.80±18.04 | 36.66±0.23 | 297.95±18.06 |
| Model | 413.36±39.99** | 41.12±2.70* | 373.45±22.37* |
| Rosuvastatin | 296.06±8.42△ | 13.11±4.08△△ | 340.03±6.65 |
| XBTMF(mg·L-1) | |||
| 0.025 | 173.63±0.94△△# | 14.49±3.45△△ | 333.81±19.97 |
| 0.050 | 103.20±15.34△△# | 11.32±2.95△△ | 208.46±10.60△△# |
| 0.100 | 36.58±0.07△△# | 9.24±0.87△△ | 156.68±4.62△△# |
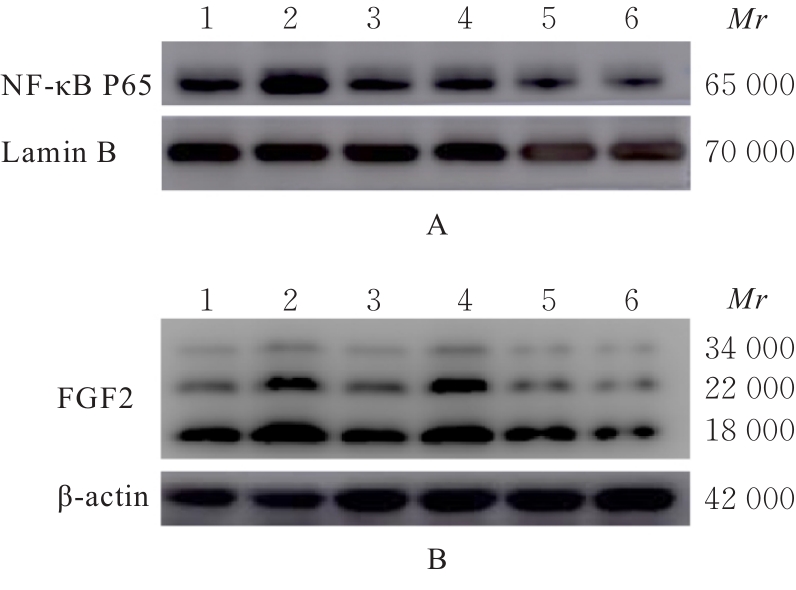
Tab.8
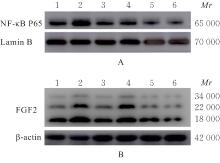
Expression levels of NF-κB p65 and FGF2 proteins in HA-VSMCs in various groups"
| Group | NF-κB p65 protein | FGF2 protein |
|---|---|---|
| Blank | 0.660±0.008 | 1.88±0.13 |
| Model | 1.200±0.002* | 3.83±0.25* |
| Rosuvastatin | 0.630±0.002△ | 1.31±0.05△ |
| XBTMF(mg·L-1) | ||
| 0.025 | 0.710±0.003△ | 2.41±0.11△# |
| 0.050 | 0.360±0.001△# | 1.26±0.03△ |
| 0.100 | 0.250±0.002△# | 0.58±0.03△# |
| 1 | GROOTAERT M O J, BENNETT M R. Vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis: time for a reassessment[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2021, 117(11): 2326-2339. |
| 2 | GUIJARRO C, COSÍN-SALES J. LDL cholesterol and atherosclerosis: the evidence[J]. Clin Investig Arterioscler, 2021, 33(): 25-32. |
| 3 | KATTOOR A J, POTHINENI N V K, PALAGIRI D, et al. Oxidative stress in atherosclerosis[J]. Curr Atheroscler Rep, 2017, 19(11): 42. |
| 4 | DEROISSART J, PORSCH F, KOLLER T, et al. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory therapies in atherosclerosis[J]. Handb Exp Pharmacol, 2022, 270: 359-404. |
| 5 | 庞树朝, 张军平, 陈美玲, 等. 中医药治疗动脉粥样硬化新进展[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2017, 32(1): 214-217. |
| 6 | 中国医师协会中西医结合分会心血管专业委员会, 中中医药学会心血管病分会. 动脉粥样硬化中西医防治专家共识(2021年)[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2022, 42(3): 287-293. |
| 7 | 张艺嘉, 樊 珂, 崔小数, 等. 中医药治疗动脉粥样硬化临床研究进展[J]. 中医学报, 2020, 35(9): 1908-1912. |
| 8 | 吴晶魁, 杨 乔, 李洋洋, 等. 水蛭通过p38MAPK信号通路对早期动脉粥样硬化大鼠VSMCs的影响[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2017, 42(16): 3191-3197. |
| 9 | 王 群, 杨关林, 贾连群, 等. 基于网络药理学探讨何首乌治疗动脉粥样硬化作用机制[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2019, 21(9): 136-139. |
| 10 | 郑云霞, 孟 萌. 中药丹参治疗冠心病的药理成分及作用分析[J]. 双足与保健, 2018, 27(17): 190-191. |
| 11 | 任超,王萍,闫东明,等.三七总皂苷对AS小鼠的治疗作用[J].中国药理学通报,2018,34(9):1289-1295. |
| 12 | 甄庆强, 张 洁, 雷 震, 等. 瓜蒌皮提取物对同型半胱氨酸诱导动脉粥样硬化的保护作用[J]. 东南大学学报(医学版), 2018, 37(2): 239-243. |
| 13 | 于进.天麻酚性成分抗AS的实验研究[D].昆明:云南中医药大学,2019. |
| 14 | 荆文光, 符 江, 刘玉梅, 等. 水蛭的化学成分[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2014, 20(19): 120-123. |
| 15 | 李国强, 李韵仪, 李 桃, 等. 水蛭的化学成分研究[J]. 天津中医药, 2018, 35(9): 703-705. |
| 16 | 许石钟. 水蛭经炮制后的化学成分变化研究[J]. 陕西中医, 2018, 39(7): 980-982. |
| 17 | 朱 迪, 曹烨民. 动脉粥样硬化抗炎治疗的研究进展[J]. 中国现代医学杂志, 2023, 33(5): 50-55. |
| 18 | WOLF D, LEY K. Immunity and inflammation in atherosclerosis[J]. Circ Res, 2019, 124(2): 315-327. |
| 19 | BÄCK M, YURDAGUL A Jr, TABAS I, et al. Inflammation and its resolution in atherosclerosis: mediators and therapeutic opportunities[J]. Nat Rev Cardiol, 2019, 16(7): 389-406. |
| 20 | 李思瑞, 冯泽清, 吴玉章. C1632通过MAPK和NF-κB抑制巨噬细胞M1型极化[J]. 免疫学杂志, 2022, 38(3): 185-192. |
| 21 | ZHOU X, XU S N, YUAN S T, et al. Multiple functions of autophagy in vascular calcification[J]. Cell Biosci, 2021, 11(1): 159. |
| 22 | BENNETT M R, SINHA S, OWENS G K. Vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis[J]. Circ Res, 2016, 118(4): 692-702. |
| 23 | MARCOVECCHIO P M, THOMAS G D, MIKULSKI Z, et al. Scavenger receptor CD36 directs nonclassical monocyte patrolling along the endothelium during early atherogenesis[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2017, 37(11): 2043-2052. |
| 24 | DONG X Z, HU H J, FANG Z D, et al. CTRP6 inhibits PDGF-BB-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2018, 103: 844-850. |
| 25 | NEWBY A C, GEORGE S J. Proposed roles for growth factors in mediating smooth muscle proliferation in vascular pathologies[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 1993, 27(7): 1173-1183. |
| 26 | ZHANG S G, ZHANG S H, LIANG X, et al. Guanxinping ameliorates atherosclerosis via MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway in ApoE-/- mice[J]. Perfusion, 2023, 38(3): 557-566. |
| 27 | ZEBOUDJ L, GIRAUD A, GUYONNET L, et al. Selective EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) deletion in myeloid cells limits atherosclerosis-brief report[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2018, 38(1): 114-119. |
| 28 | VLACIL A K, SCHUETT J, RUPPERT V, et al. Deficiency of Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing proteins (NOD) 1 and 2 reduces atherosclerosis[J]. Basic Res Cardiol, 2020, 115(4): 47. |
| 29 | HANG M, LI F, WANG X, et al. MiR-145 alleviates Hcy-induced VSMCs proliferation, migration, and phenotypic switch through repression of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway[J]. Histochem Cell Biol,2020,153:357-366. |
| 30 | 李文倩. 齐墩果酸经FGF2/JNK/PON2通路抑制ox-LDL诱导的大鼠血管平滑肌细胞增殖[D]. 青岛: 青岛大学, 2018. |
| 31 | 梁文静. 糖尿病及血管新生因子对动脉粥样硬化斑块不稳定性的影响及作用机制[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2018. |
| 32 | LEE J G, KAY E P. NF-κB is the transcription factor for FGF-2 that causes endothelial mesenchymal transformation in cornea[J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2012, 53(3): 1530-1538. |
| 33 | 朱 莹. FGF/FGFR3与非经典NF-κB信号通路的交互作用及其在多发性骨髓瘤细胞增殖中的意义[D]. 重庆: 第三军医大学, 2013. |
| [1] | Hua CHEN,Na SHA,Ning LIU,Yang LI,Haijun HU. Effect of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on biological behavior of human liposarcoma SW872 cells through YAP [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1000-1008. |
| [2] | Yongjing YANG,Tianyang KE,Shixin LIU,Xue WANG,Dequan XU,Tingting LIU,Ling ZHAO. Synergistic sensitization of apatinib mesylate and radiotherapy on hepatocarcinoma cells invitro [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1009-1015. |
| [3] | Chaojie GUO,Jiajia ZHANG,Jie ZENG,Huiyu WANG, AIERFATI·Aimaier,Jiang XU. Expressions of PLOD1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue and cells and their significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1035-1043. |
| [4] | Xinchen ZHOU,Shuhan DONG,Zhuo ZHANG,Mingmei SHEN,Xiangjun WANG,Ying LI,Limei LIU. Network pharmacology analysis based on potential mechanism of dandelion-mulberry leaf in treatment of acute myeloid leukemia [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1087-1097. |
| [5] | Xiaoyu WANG,Bing LI,Guohui LIU. Research progress in application of inflammatory markers in diagnosis and treatment of coronary heart disease [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1173-1181. |
| [6] | Guoxing YU,Xin ZHANG,Hengwei DU,Bingjie CUI,Na GAO,Cuilan LIU,Jing DU. Effect of urolithin C on proliferation, apoptosis and autophagy of human acute myeloid leukemia HL-60 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 908-916. |
| [7] | Yingqun NI,Mao YANG,Di YANG,Chenglin GUO,Wenjun ZHU,Yaqin YU,Qin LU,Jinzhi LUO,Chunqin WU,Zhaohui FANG. Screening of key differentially expressed genes involved in osteogenic differentiation of lower limb vascular smooth muscle cells and validation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 620-627. |
| [8] | Zijia ZHU,Xia CHEN,Man CUI,Jihong WEN,Ping WANG,Dong SONG. Bioinformatics and molecular docking technology analysis on mechanism of salidroside on key differential genes of triple negative breast cancer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 759-769. |
| [9] | Shuang CHEN,Hong LI. Effect of silencing FOXK1 gene on proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer HGC-27 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 371-378. |
| [10] | Linru WANG,Jing ZHANG,Dongchan ZHAO,Jinjun WANG,Wenxian HU. Effect of silencing FOXO1 gene on autophagy and apoptosis of human aortic vascular smooth muscle cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 431-441. |
| [11] | Huijuan SONG,Zhenhua XU,Dongning HE. Effect of apolipoprotein C1 expression on proliferation and apoptosis of human liver cancer HepG2 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 128-135. |
| [12] | Yang YU,Dan TIAN,Donghe NI,Duo ZHANG. Network pharmacologry and molecular docking analysis based on mechanism of monk fruit in treatment of diabetic nephropathy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 161-167. |
| [13] | Jie ZENG,Xueyan YU,Ting LUO,Jiang XU. Effect of PD-L1 on proliferation, migration, and invasion of human oral squamous carcinoma cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 18-24. |
| [14] | Aiying CHEN,Jinwen JIANG,Hui ZHANG. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis based on mechanism of Huangqin Tang in treatment of colorectal cancer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 208-220. |
| [15] | Li LIU,Linsheng HUANG,Yongheng ZHAO,Wenjie CAO,Yongshuai QIAN,Huifan YU,Fei LI. Network pharmacological analysis on Balanophora involucrataHook.f. in treatment of hyperuricemia and its therapeutic effect on hyperuricemia cell model and hyperuricemia model mouse [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 58-70. |
|