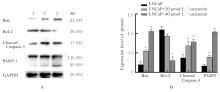
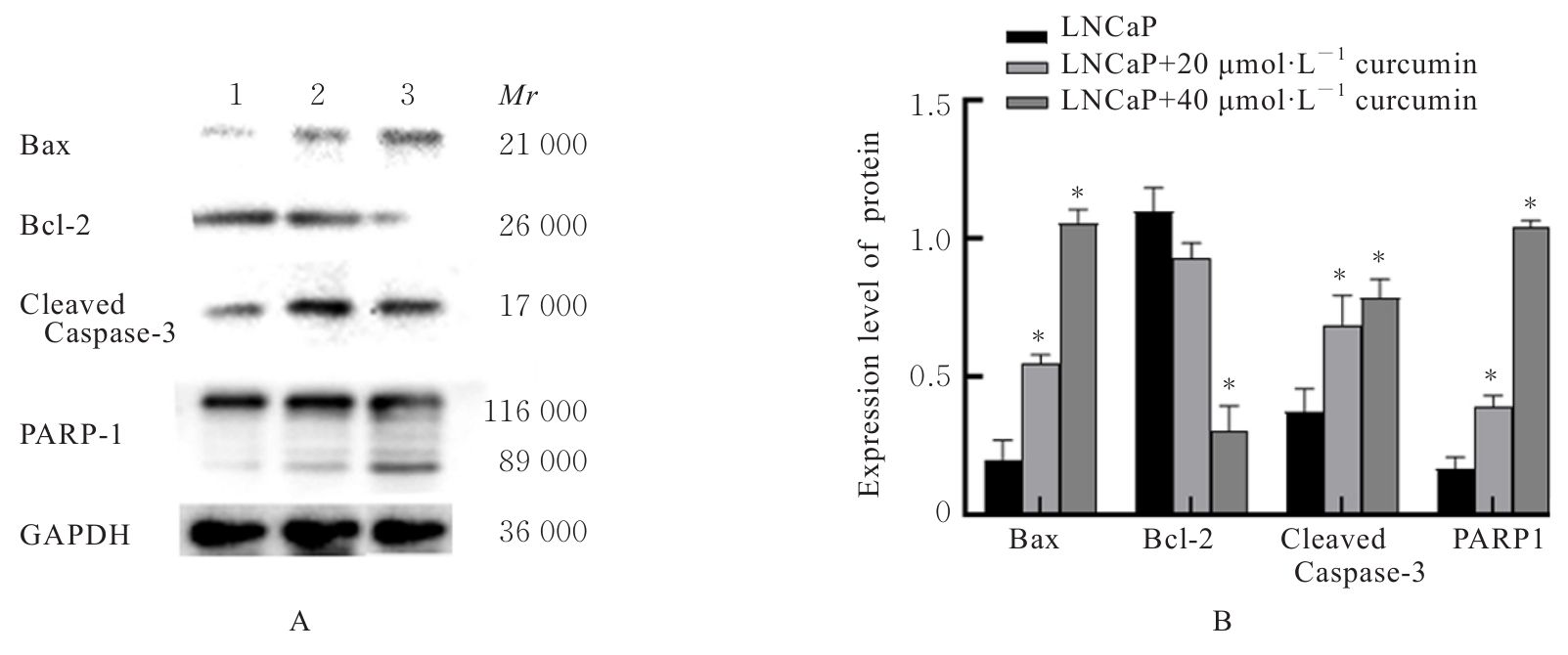
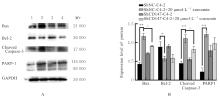
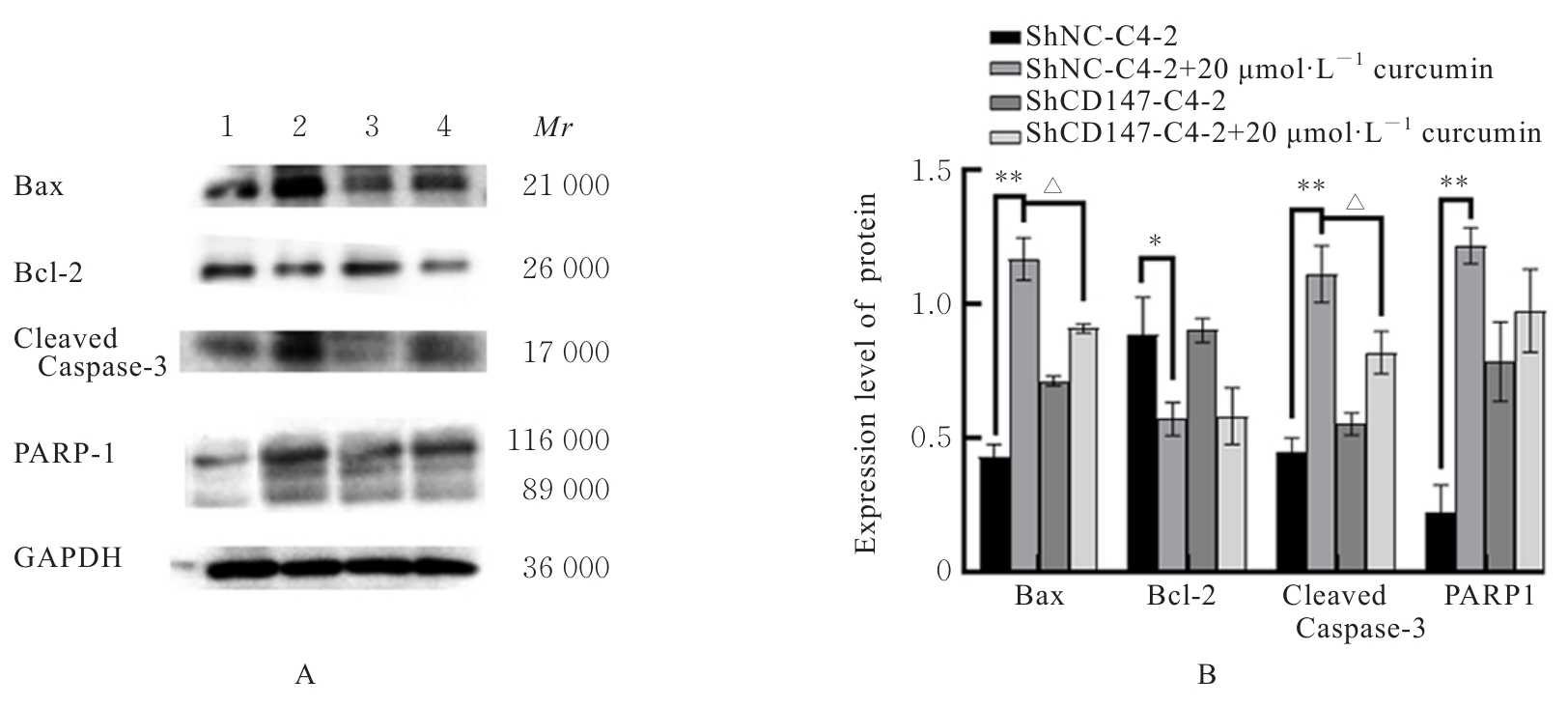
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 1572-1586.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240611
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles
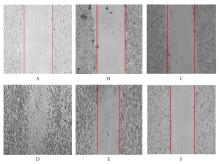
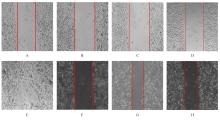
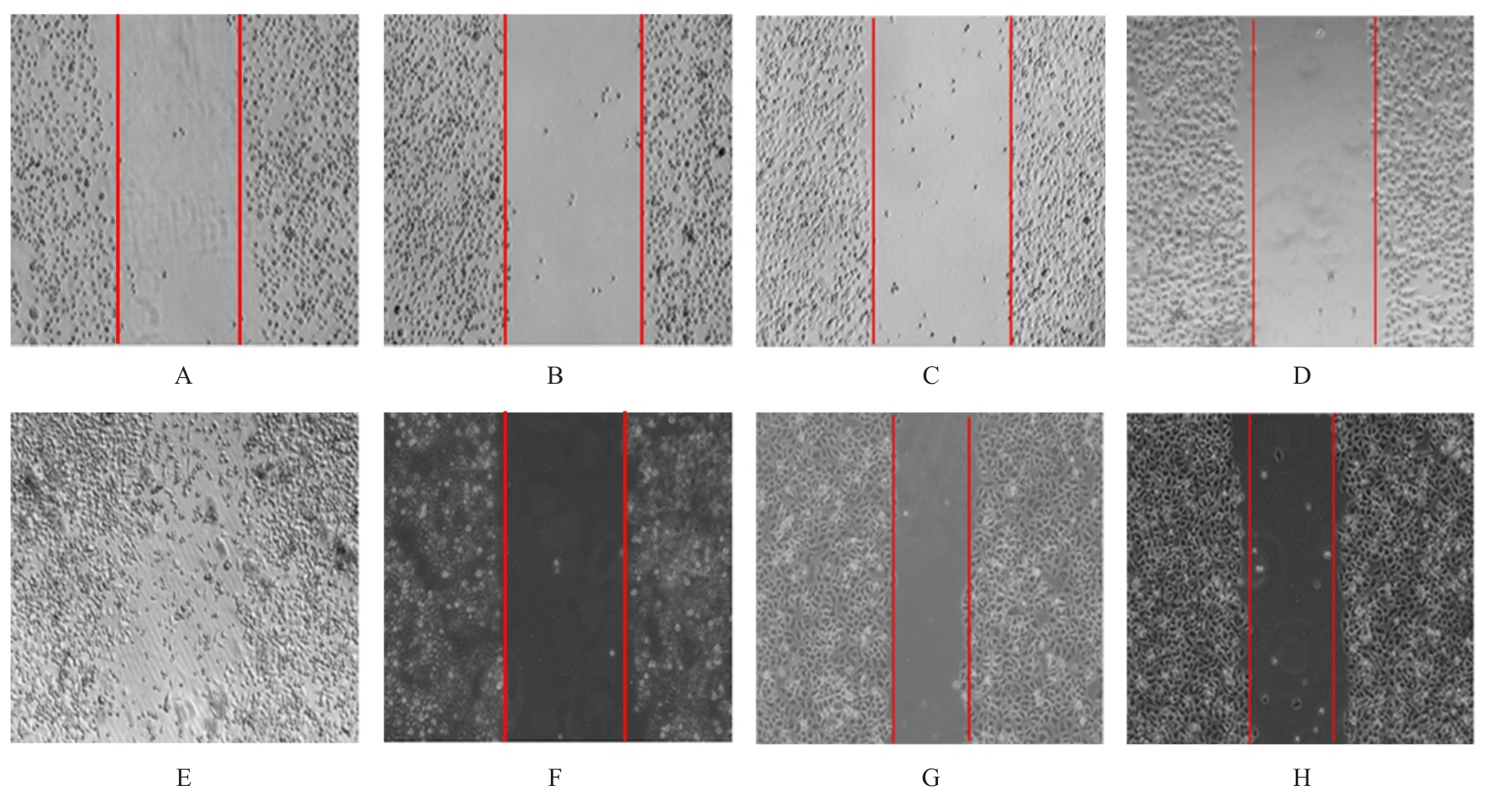
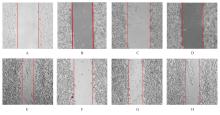
Effect of silencing CD147 gene on proliferation, migration, invasion, and inducing apoptosis of prostate cancer cells inhibited by curcumin
Xin WANG1,Jierui ZHAO2,Yumiao GUO3,Shutong CHEN1,Zonghao HOU1,Ruowen ZHANG1( )
)
- 1.Department of Pathogenic Biology,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Beihua University,Jilin 132000,China
2.Department of Orthopedics,Affiliated Hospital,Traditional Chinese Medicine,Macao University of Science and Technology,Zhuhai 519000,China
3.Department of Biochemistry,School of Medical Sciences,Yanbian University,Yanji 133000,China
-
Received:2023-12-02Online:2024-11-28Published:2024-12-10 -
Contact:Ruowen ZHANG E-mail:zrwa1828@163.com
CLC Number:
- R735.25
Cite this article
Xin WANG,Jierui ZHAO,Yumiao GUO,Shutong CHEN,Zonghao HOU,Ruowen ZHANG. Effect of silencing CD147 gene on proliferation, migration, invasion, and inducing apoptosis of prostate cancer cells inhibited by curcumin[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1572-1586.
share this article
| 1 | AABD WAHAB N, LAJIS N H, ABAS F, et al. Mechanism of anti-cancer activity of curcumin on androgen-dependent and androgen-independent prostate cancer[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12(3): 679. |
| 2 | ZHONG W D, HAN Z D, HE H C, et al. CD147, MMP-1, MMP-2 and MMP-9 protein expression as significant prognostic factors in human prostate cancer[J]. Oncology, 2008, 75(3/4): 230-236. |
| 3 | ZHONG W D, LIANG Y X, LIN S X, et al. Expression of CD147 is associated with prostate cancer progression[J]. Int J Cancer, 2012, 130(2): 300-308. |
| 4 | PERRONE D, ARDITO F, GIANNATEMPO G, et al. Biological and therapeutic activities, and anticancer properties of curcumin[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2015, 10(5): 1615-1623. |
| 5 | COSTEA T, NAGY P, GANEA C, et al. Molecular mechanisms and bioavailability of polyphenols in prostate cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(5): 1062. |
| 6 | DUVOIX A, BLASIUS R, DELHALLE S, et al. Chemopreventive and therapeutic effects of curcumin[J]. Cancer Lett, 2005, 223(2): 181-190. |
| 7 | 程 继,高 丹,付 国,等.姜黄素对前列腺癌PC-3细胞体外生长的影响[J]. 西部医学, 2022, 34(6): 808-812. |
| 8 | YU B B, ZHANG Y, WU K L, et al. CD147 promotes progression of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma via NF-kappa B signaling[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2019, 23(2): 954-966. |
| 9 | FANG F, LI Q, WU M Y, et al. CD147 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition of prostate cancer cells via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2020, 20(4): 3154-3160. |
| 10 | TREWARTHA D, CARTER K. Advances in prostate cancer treatment[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2013, 12(11): 823-824. |
| 11 | MELLMAN I, COUKOS G, DRANOFF G. Cancer immunotherapy comes of age[J]. Nature, 2011, 480(7378): 480-489. |
| 12 | CHEN J J, ZHANG D Q, YAN W Y, et al. Translational bioinformatics for diagnostic and prognostic prediction of prostate cancer in the next-generation sequencing era[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2013, 2013: 901578. |
| 13 | SEIDENFELD J, SAMSON D J, HASSELBLAD V, et al. Single-therapy androgen suppression in men with advanced prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2000, 132(7): 566-577. |
| 14 | TERMINI D, DEN HARTOGH D J, JAGLANIAN A, et al. Curcumin against prostate cancer: current evidence[J]. Biomolecules, 2020, 10(11): 1536. |
| 15 | VIEGAS F P D, GONTIJO V S, DE FREITAS SILVA M, et al. Curcumin, resveratrol and cannabidiol as natural key prototypes in drug design for neuroprotective agents[J]. Curr Neuropharmacol, 2022, 20(7): 1297-1328. |
| 16 | CHEN M, DU Z Y, ZHENG X, et al. Use of curcumin in diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2018, 13(4): 742-752. |
| 17 | HUANG M T, WANG Z Y, GEORGIADIS C A, et al. Inhibitory effects of curcumin on tumor initiation by benzo[a]pyrene and 7, 12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene[J]. Carcinogenesis, 1992, 13(11): 2183-2186. |
| 18 | RAVINDRAN J, PRASAD S, AGGARWAL B B. Curcumin and cancer cells: how many ways can curry kill tumor cells selectively?[J]. AAPS J, 2009, 11(3): 495-510. |
| 19 | ANAND P, SUNDARAM C, JHURANI S, et al. Curcumin and cancer: an “old-age” disease with an “age-old” solution[J]. Cancer Lett, 2008, 267(1): 133-164. |
| 20 | MOMTAZI-BOROJENI A A, HAFTCHESHMEH S M, ESMAEILI S A, et al. Curcumin: a natural modulator of immune cells in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2018, 17(2): 125-135. |
| 21 | BUYUK B, JIN S, YE K M. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition signaling pathways responsible for breast cancer metastasis[J]. Cell Mol Bioeng, 2022, 15(1): 1-13. |
| 22 | TAN T S, SHI P F, ABBAS M N, et al. Epigenetic modification regulates tumor progression and metastasis through EMT (Review)[J]. Int J Oncol, 2022, 60(6): 70. |
| 23 | ZHANG N, HÄRING M, WOLF F, et al. Dynamics and functions of E-cadherin complexes in epithelial cell and tissue morphogenesis[J]. Mar Life Sci Technol, 2023, 5(4): 585-601. |
| 24 | YE Y, LI S L, WANG Y, et al. The role of CD147 expression in prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2016, 10: 2435-2442. |
| 25 | NYALALI A M K, LEONARD A U, XU Y X, et al. CD147: an integral and potential molecule to abrogate hallmarks of cancer[J]. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 1238051. |
| 26 | JIA L, WANG H X, QU S X, et al. CD147 regulates vascular endothelial growth factor-a expression, tumorigenicity, and chemosensitivity to curcumin in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. IUBMB Life, 2008, 60(1): 57-63. |
| 27 | KANEKURA T. CD147/basigin is involved in the development of malignant tumors and T-cell-mediated immunological disorders via regulation of glycolysis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(24): 17344. |
| [1] | Fengmei XIONG,Yuxiang CAI,Zhuo LIU,Na SUN,Yang LI. Alleviatory effect of curcumin on cardiomyocyte toxicity induced by doxorubicin by regulating SIRT3/SOD2 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1339-1347. |
| [2] | Hua CHEN,Na SHA,Ning LIU,Yang LI,Haijun HU. Effect of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on biological behavior of human liposarcoma SW872 cells through YAP [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1000-1008. |
| [3] | Yongjing YANG,Tianyang KE,Shixin LIU,Xue WANG,Dequan XU,Tingting LIU,Ling ZHAO. Synergistic sensitization of apatinib mesylate and radiotherapy on hepatocarcinoma cells invitro [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1009-1015. |
| [4] | Chaojie GUO,Jiajia ZHANG,Jie ZENG,Huiyu WANG, AIERFATI·Aimaier,Jiang XU. Expressions of PLOD1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue and cells and their significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1035-1043. |
| [5] | Yilin REN,Yichen ZANG,Lele XUE,Kaige YANG,Sufang CHEN,Weinan WANG,Chenghua LUO,Weihua LIANG,Lianghai WANG,Feng LI,Jianming HU. Bioinformatics analysis based on effect of M2 macrophage-derived Siglec15 on malignant biological behaviour of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells and its experimental validation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 881-890. |
| [6] | Yuan WANG,Zhijuan WANG,Mingshu ZHANG,Yihui WANG,Qing ZHANG,Liping YE. Effects of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 on invasion and migration of lung cancer A549 and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 666-675. |
| [7] | Bo YUAN,Jiayi XIE,Siyu JIANG,Yajun MENG,Qinghua ZHU,Xiaofei LI,Xiumei FU,Lide XIE. Effect of adipose-derived stem cell-derived exosomes on migration ability of macrophages in vitro [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 718-727. |
| [8] | Shuang CHEN,Hong LI. Effect of silencing FOXK1 gene on proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer HGC-27 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 371-378. |
| [9] | Buqi NA,Chunji QUAN,Fang ZHAO,Fan YANG,Ru XIAO,Xuemei JIN,Zhenling LI. Effect of histone deacetylase inhibitor CUDC-101 on DNA damage, migration, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of prostate cancer DU145 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 400-410. |
| [10] | Yang LIU,Ming LU,Wen HONG,Kelin HUANG. Improvement effect of curcumin combined with fecal bacteria transplantation on mice with ulcerative colities induced by DSS [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 136-142. |
| [11] | Yanhong WEI,Chenxue YANG,Guangmin YANG,Shuai SONG,Ming LI,Haijiao YANG,Haifeng WEI. Inhibitory effect of downregulating HMGB2 expression on epithelial-mesenchymal transition of liver cancer LM3 cells and its AKT/mTOR signaling pathway mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 143-149. |
| [12] | Jie ZENG,Xueyan YU,Ting LUO,Jiang XU. Effect of PD-L1 on proliferation, migration, and invasion of human oral squamous carcinoma cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 18-24. |
| [13] | Jia ZHOU,Zhidong QIU,Zhe LIN,Guangfu LYU,Jiaming XU,He LIN,Kexin WANG,Yuchen WANG,Xiaowei HUANG. Effect of chelerythrine on migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human ovarian cancer SKOV3 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 25-32. |
| [14] | Yuxue SUN,Ziqiang LIU,Hao WU,Liming ZHAO,Tao GAO,Haiyan HUANG,Chaoyue LI. Inhibitory effect of berberine on migration and invasion of human glioma T98G cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 50-57. |
| [15] | Manying OU,Chunxia HU,Yueping LI. Effect of expression of microtubule inhibitory assembly protein 1 in placenta tissue of pre-eclampsia patients on trophoblast cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1519-1527. |
|
||