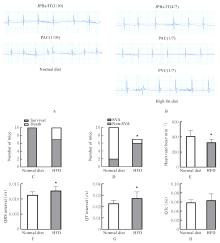
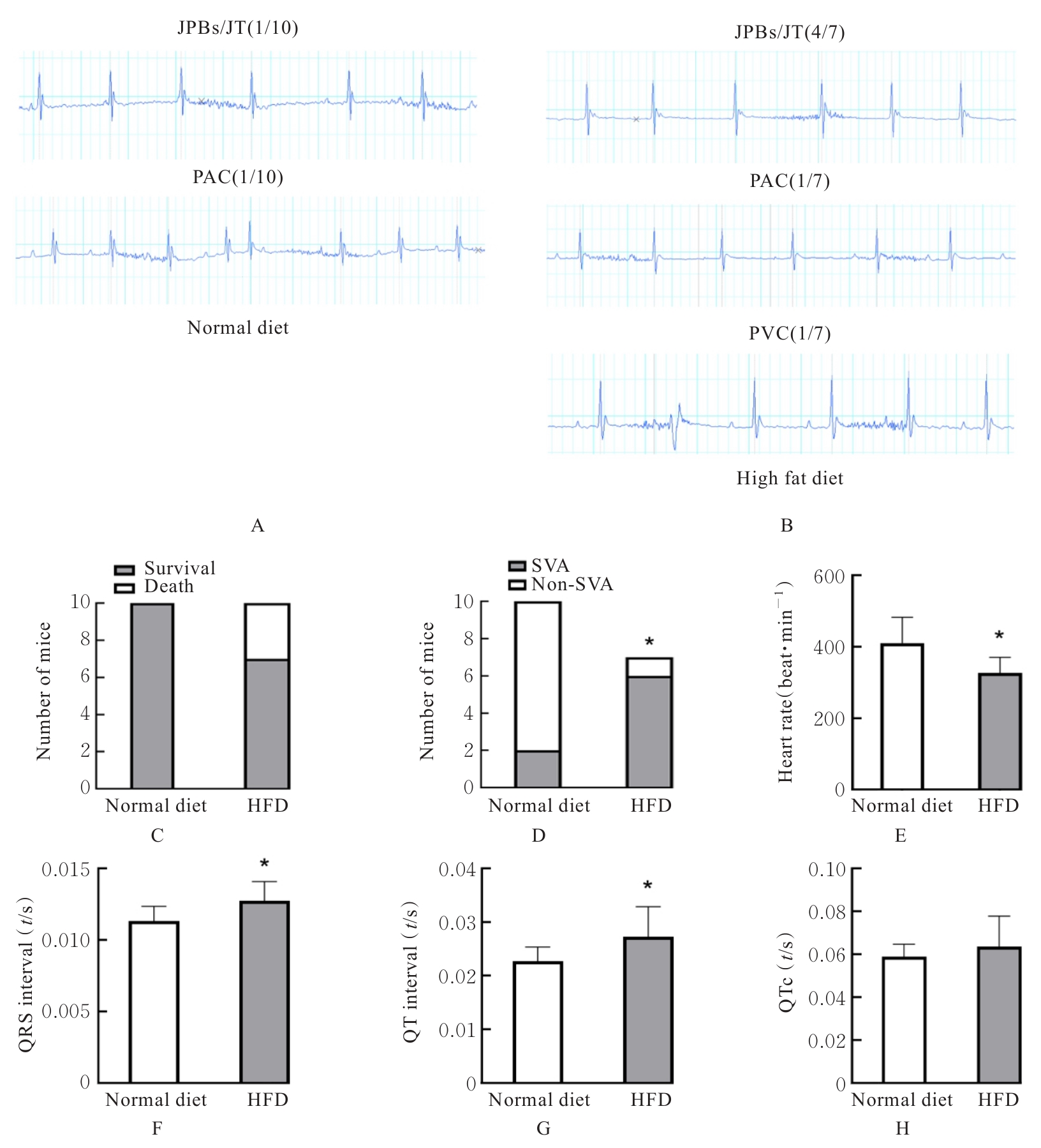
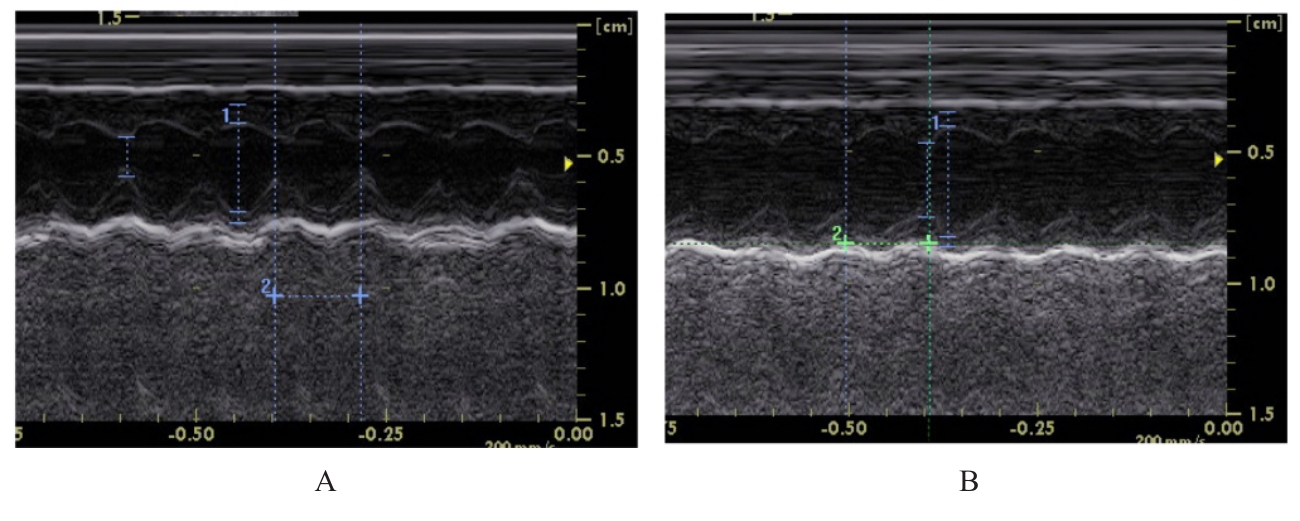
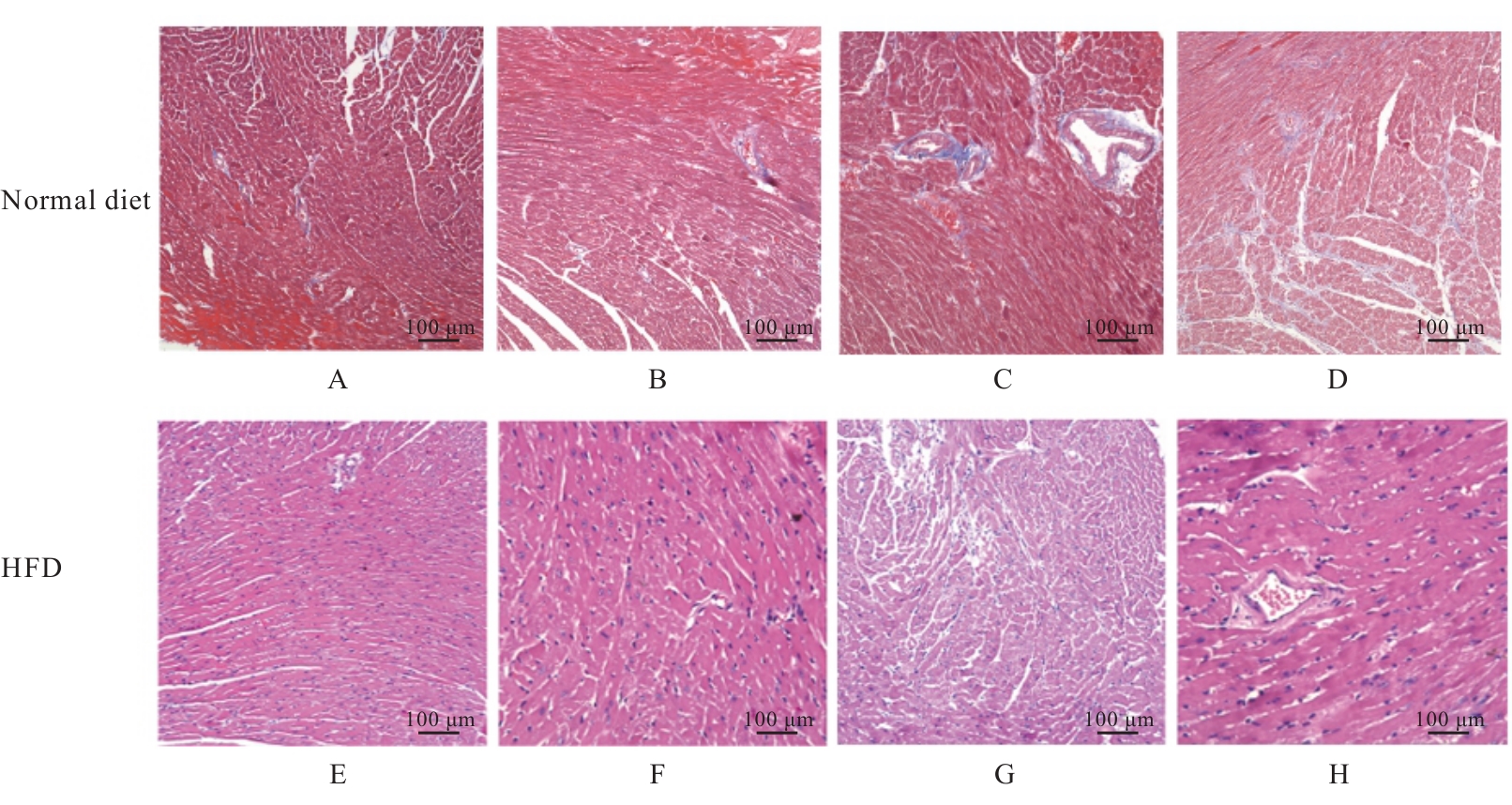
| [1] |
ZELJKOVIĆ I, ĐULA K, BABACANLI A, et al. High prevalence of hyperlipidaemia in patients with AV re-entry tachycardia and AV nodal re-entry tachycardia[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 11502.
|
| [2] |
MCCULLY B H, HASAN W, STREIFF C T, et al. Sympathetic cardiac hyperinnervation and atrial autonomic imbalance in diet-induced obesity promote cardiac arrhythmias[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2013, 305(10): H1530-H1537.
|
| [3] |
ZARZOSO M, MIRONOV S, GUERRERO-SERNA G, et al. Ventricular remodelling in rabbits with sustained high-fat diet[J]. Acta Physiol (Oxf), 2014, 211(1): 36-47.
|
| [4] |
AUBIN M C, CARDIN S, COMTOIS P, et al. A high-fat diet increases risk of ventricular arrhythmia in female rats: enhanced arrhythmic risk in the absence of obesity or hyperlipidemia[J]. J Appl Physiol (1985), 2010, 108(4): 933-940.
|
| [5] |
RAHIMI K, MAJONI W, MERHI A, et al. Effect of statins on ventricular tachyarrhythmia, cardiac arrest, and sudden cardiac death: a meta-analysis of published and unpublished evidence from randomized trials[J]. Eur Heart J, 2012, 33(13): 1571-1581.
|
| [6] |
CHOLESTEROL Treatment Trialists’ Collaboration. Efficacy and safety of statin therapy in older people: a meta-analysis of individual participant data from 28 randomised controlled trials[J]. Lancet, 2019, 393(10170): 407-415.
|
| [7] |
ZHANG H X, ZHANG C S, HUANG R Z, et al. Oral administration of MnCl2 attenuated hyperlipidemia-related cardiac remodeling in ApoE-/- mice[J]. J Pharmacol Sci, 2021, 145(2): 167-174.
|
| [8] |
CHAN Y K, BRAR M S, KIRJAVAINEN P V, et al. High fat diet induced atherosclerosis is accompanied with low colonic bacterial diversity and altered abundances that correlates with plaque size, plasma A-FABP and cholesterol: a pilot study of high fat diet and its intervention with Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) or telmisartan in ApoE-/- mice[J]. BMC Microbiol, 2016, 16(1): 264.
|
| [9] |
LIN H, AN Y P, TANG H R, et al. Alterations of bile acids and gut microbiota in obesity induced by high fat diet in rat model[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2019, 67(13): 3624-3632.
|
| [10] |
WESTMAN P C, LIPINSKI M J, LUGER D, et al. Inflammation as a driver of adverse left ventricular remodeling after acute myocardial infarction[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2016, 67(17): 2050-2060.
|
| [11] |
SUETOMI T, WILLEFORD A, BRAND C S, et al. Inflammation and NLRP3 inflammasome activation initiated in response to pressure overload by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase Ⅱ δ signaling in cardiomyocytes are essential for adverse cardiac remodeling[J]. Circulation, 2018, 138(22): 2530-2544.
|
| [12] |
VOIOSU A M, WIESE S, VOIOSU T A, et al. Total bile acid levels are associated with left atrial volume and cardiac output in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 30(4): 392-397.
|
| [13] |
GAO X X, YE M Y, LIU Y, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy in a Chinese population[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 16307.
|
| [14] |
ZHANG S H, REDDICK R L, PIEDRAHITA J A, et al. Spontaneous hypercholesterolemia and arterial lesions in mice lacking apolipoprotein E[J]. Science, 1992, 258(5081): 468-471.
|
| [15] |
GOLDBERG I J, SHARMA G, FISHER E A. Atherosclerosis: making a U turn[J]. Annu Rev Med, 2020, 71: 191-201.
|
| [16] |
MILAD N, WHITE Z, TEHRANI A Y, et al. Increased plasma lipid levels exacerbate muscle pathology in the mdx mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Skelet Muscle, 2017, 7(1): 19.
|
| [17] |
RADYMSKA-WAWRZYNIAK K, SZEMBER-NYRKA B, RYBKA A. Effect of the bile and bile acids on the motility of the innervated rabbit colon[J]. Pol Arch Weter, 1987, 27(4): 85-98.
|
| [18] |
徐艳红, 王兴德, 杨嘉君, 等. 急性脑梗死患者心率减速力变化及临床意义[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2016, 51(6): 766-769.
|
| [19] |
WILLIAMSON C, GORELIK J, EATON B M, et al. The bile acid taurocholate impairs rat cardiomyocyte function: a proposed mechanism for intra-uterine fetal death in obstetric cholestasis[J]. Clin Sci (Lond), 2001, 100(4): 363-369.
|
| [20] |
GORELIK J, HARDING S E, SHEVCHUK A I, et al. Taurocholate induces changes in rat cardiomyocyte contraction and calcium dynamics[J]. Clin Sci (Lond), 2002, 103(2): 191-200.
|
| [21] |
GORELIK J, SHEVCHUK A I, DIAKONOV I, et al. Dexamethasone and ursodeoxycholic acid protect against the arrhythmogenic effect of taurocholate in an in vitro study of rat cardiomyocytes[J]. BJOG, 2003, 110(5): 467-474.
|
| [22] |
NATTEL S, MAGUY A, LE BOUTER S, et al. Arrhythmogenic ion-channel remodeling in the heart: heart failure, myocardial infarction, and atrial fibrillation[J]. Physiol Rev, 2007, 87(2): 425-456.
|
 )
)