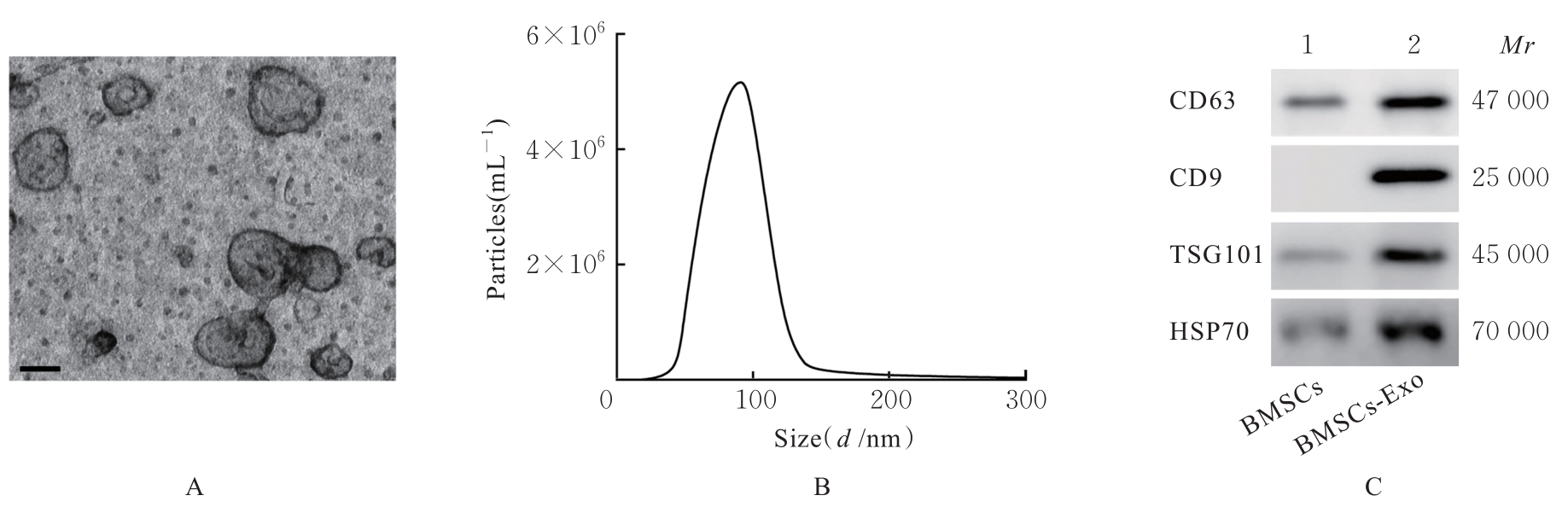
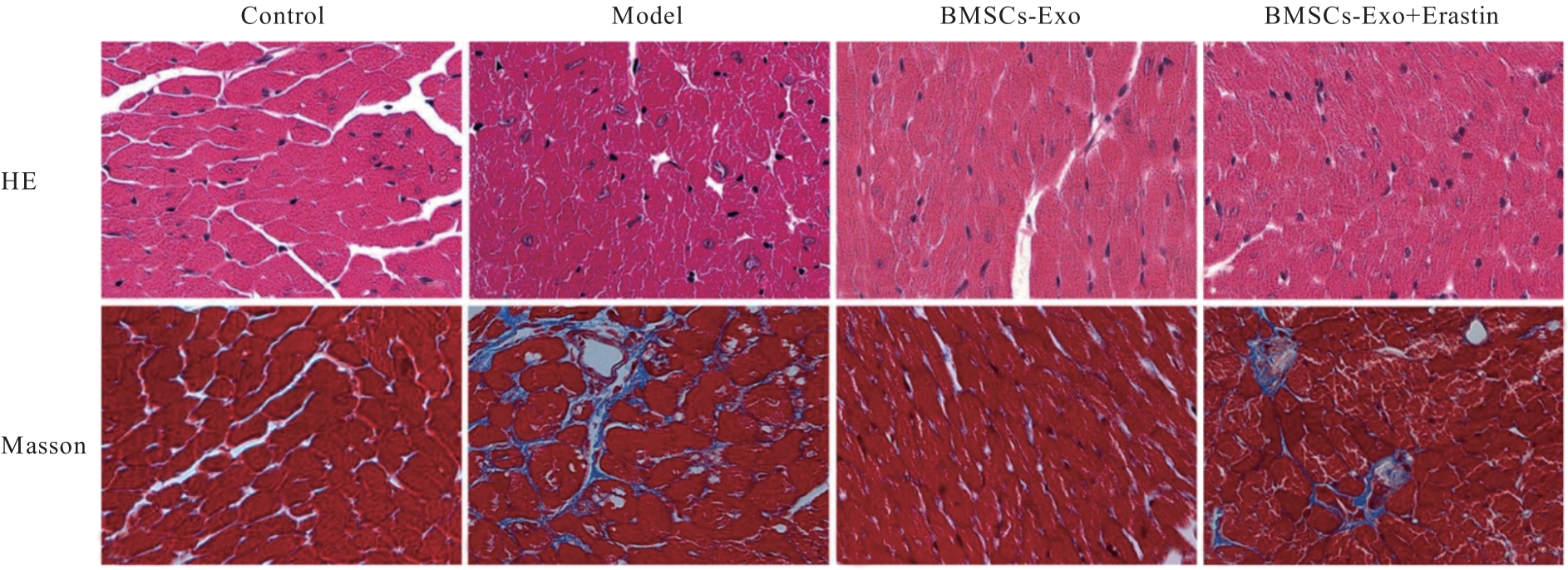
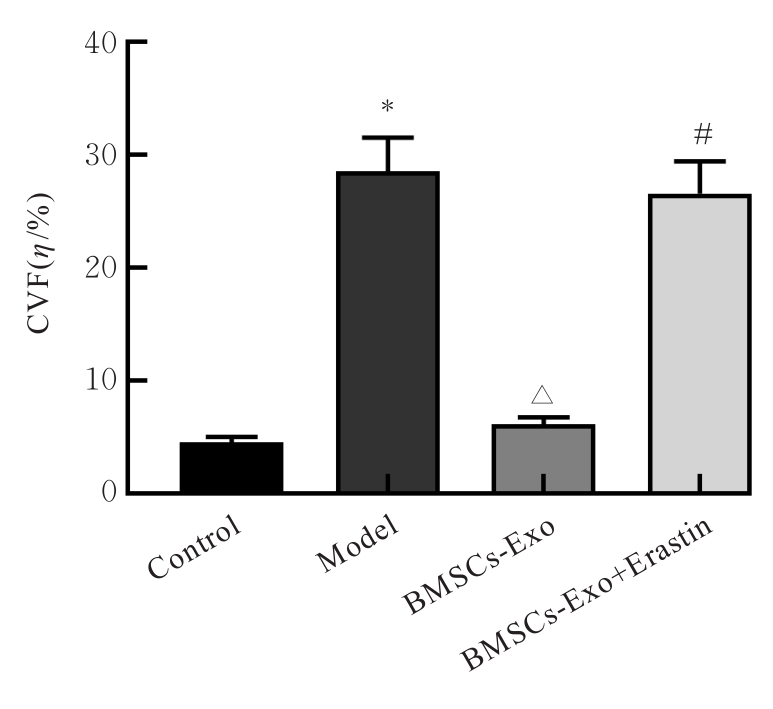
| 1 |
LEE H J, LEE H, KIM S M, et al. Diffuse myocardial fibrosis and diastolic function in aortic stenosis[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging, 2020, 13(12): 2561-2572.
|
| 2 |
KARAMITSOS T D, ARVANITAKI A, KARVOUNIS H, et al. Myocardial tissue characterization and fibrosis by imaging[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging, 2020, 13(5): 1221-1234.
|
| 3 |
HERON C, DUMESNIL A, HOUSSARI M, et al. Regulation and impact of cardiac lymphangiogenesis in pressure-overload-induced heart failure[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2023, 119(2): 492-505.
|
| 4 |
HOANG D M, PHAM P T, BACH T Q, et al. Stem cell-based therapy for human diseases[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2022, 7(1): 272.
|
| 5 |
MATSUZAKA Y, YASHIRO R. Therapeutic strategy of mesenchymal-stem-cell-derived extracellular vesicles as regenerative medicine[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(12): 6480.
|
| 6 |
HA D H, KIM H K, LEE J, et al. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-derived exosomes for immunomodulatory therapeutics and skin regeneration[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(5): 1157.
|
| 7 |
KALLURI R, LEBLEU V S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes[J]. Science, 2020, 367(6478): eaau6977.
|
| 8 |
XU R Q, ZHANG F C, CHAI R J, et al. Exosomes derived from pro-inflammatory bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells reduce inflammation and myocardial injury via mediating macrophage polarization[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2019, 23(11): 7617-7631.
|
| 9 |
ZHANG L Y, WEI Q X, LIU X M, et al. Exosomal microRNA-98-5p from hypoxic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibits myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by reducing TLR4 and activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2021, 101(Pt B): 107592.
|
| 10 |
CHEN F, LI X L, ZHAO J X, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes attenuate cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis in pressure overload induced remodeling[J]. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim, 2020, 56(7): 567-576.
|
| 11 |
程 阳, 葛晨亮, 范奕好, 等. 薯蓣皂苷对异丙肾上腺素诱导的大鼠心肌纤维化的作用及机制研究[J]. 广西医科大学学报, 2022, 39(4): 526-532.
|
| 12 |
张 双, 刘淑华, 刘立杰, 等. 增强型体外反搏治疗急性心肌梗塞的疗效及其对肾素-血管紧张素-醛固酮系统的影响[J]. 川北医学院学报, 2022, 37(1): 39-42.
|
| 13 |
FANG J C, ZHANG Y X, CHEN D L, et al. Exosomes and exosomal cargos: a promising world for ventricular remodeling following myocardial infarction[J]. Int J Nanomedicine, 2022, 17: 4699-4719.
|
| 14 |
LIU X L, LI X, ZHU W W, et al. Exosomes from mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing MIF enhance myocardial repair[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2020, 235(11): 8010-8022.
|
| 15 |
WEN Z Z, MAI Z, ZHU X L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes ameliorate cardiomyocyte apoptosis in hypoxic conditions through microRNA144 by targeting the PTEN/AKT pathway[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2020, 11(1): 36.
|
| 16 |
REN Y, WU Y, HE W S, et al. Exosomes secreted from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells suppress cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through Hippo-YAP pathway in heart failure[J]. Genet Mol Biol, 2023, 46(1): e20220221.
|
| 17 |
STAAB-WEIJNITZ C A. Fighting the fiber: targeting collagen in lung fibrosis[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2022, 66(4): 363-381.
|
| 18 |
PERETTO G, MAZZONE P. Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy: one, none and a hundred thousand diseases[J]. J Pers Med, 2022, 12(8): 1256.
|
| 19 |
ASSAR D H, MOKHBATLY A A, GHAZY E W, et al. Silver nanoparticles induced hepatoxicity via the apoptotic/antiapoptotic pathway with activation of TGFβ-1 and α-SMA triggered liver fibrosis in Sprague Dawley rats[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, 2022, 29(53): 80448-80465.
|
| 20 |
JIANG X J, STOCKWELL B R, CONRAD M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2021, 22(4): 266-282.
|
| 21 |
ZHENG H Y, SHI L, TONG C C, et al. circSnx12 is involved in ferroptosis during heart failure by targeting miR-224-5p[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2021, 8: 656093.
|
| 22 |
CHEN X Q, XU S D, ZHAO C X, et al. Role of TLR4/NADPH oxidase 4 pathway in promoting cell death through autophagy and ferroptosis during heart failure[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2019, 516(1): 37-43.
|
| 23 |
WANG J Y, DENG B, LIU Q, et al. Pyroptosis and ferroptosis induced by mixed lineage kinase 3 (MLK3) signaling in cardiomyocytes are essential for myocardial fibrosis in response to pressure overload[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(7): 574.
|
| 24 |
ZHANG H L, HU B X, LI Z L, et al. PKC βⅡphosphorylates ACSL4 to amplify lipid peroxidation to induce ferroptosis[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2022, 24(1): 88-98.
|
| 25 |
FANG Y Y, CHEN X C, TAN Q Y, et al. Inhibiting ferroptosis through disrupting the NCOA4-FTH1 interaction: a new mechanism of action[J]. ACS Cent Sci, 2021, 7(6): 980-989.
|
| 26 |
WANG Y, ZHENG L X, SHANG W J, et al. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling confers ferroptosis resistance by targeting GPX4 in gastric cancer[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2022, 29(11): 2190-2202.
|
| 27 |
YE Y Z, CHEN A, LI L, et al. Repression of the antiporter SLC7A11/glutathione/glutathione peroxidase 4 axis drives ferroptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells to facilitate vascular calcification[J]. Kidney Int, 2022, 102(6): 1259-1275.
|
 ),Daofei LIN1,Yanzai LIN1
),Daofei LIN1,Yanzai LIN1