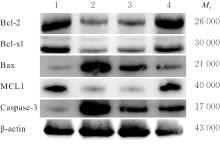
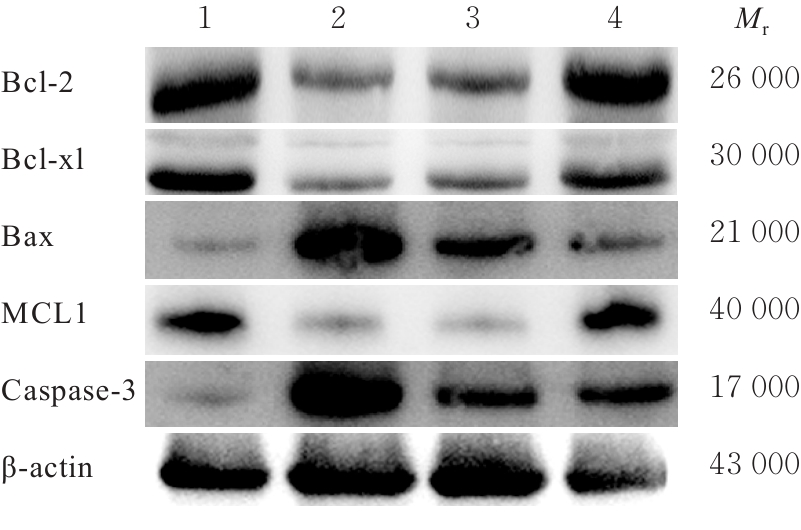
| [1] |
ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA F E. Osteoarthritis[J]. Med Clin N Am, 2020, 104(2): 293-311.
|
| [2] |
谢文慧, 张卓莉. 难治性类风湿关节炎的治疗策略[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2024, 44(12): 1006-1010.
|
| [3] |
中国医师协会风湿免疫科医师分会骨关节炎学组. 中国膝骨关节炎临床药物治疗专家共识(2023)[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2024, 63(6): 560-578.
|
| [4] |
中华中医药学会. 膝骨关节炎中西医结合诊疗指南(2023年版)[J]. 中医正骨, 2023, 35(6):1-10.
|
| [5] |
郑曲, 林星星, 张宇, 等. 基 于 Piezo1/YAP/Caspase3轴探讨针刺保护膝骨性关节炎模型大鼠股四头肌细胞的机制研究[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2025, 27(8): 2274-2283.
|
| [6] |
YANG X F, XUE P P, CHEN H R, et al. Denervation drives skeletal muscle atrophy and induces mitochondrial dysfunction, mitophagy and apoptosis via miR-142a-5p/MFN1 axis[J]. Theranostics, 2020, 10(3): 1415-1432.
|
| [7] |
李嫣晓, 陈红霞, 程梦蝶, 等.铁死亡与心肌纤维化相关信号通路的研究进展[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2024, 59(2): 195-201.
|
| [8] |
LIU X X, LI X H, ZHOU J T.Experimental study on replicating knee osteoarthritis by modified Hulth’s modeling method[J]. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi, 2005, 25(12): 1104-1108.
|
| [9] |
薛立功. 经 筋 理 论 研 究 对 经 络 学 说 形 成 的 启 迪意义[A]. //中国针灸学会经筋诊治专业委员会成立大会暨首届中华经筋医学论坛论文集[C]. 2009: 1-7.
|
| [10] |
APURBA G, SUDIP B. Biomonitoring the skeletal muscle metabolic dysfunction in knee osteoarthritis in older adults: Is Jumpstart Nutrition® Supplementation effective[J]. Caspian J Intern Med, 2023, 14(4): 590-606.
|
| [11] |
中医康复临床实践指南·膝骨关节炎制定工作组, 王尚全, 朱立国,等. 中医康复临床实践指南·膝骨关节炎[J]. 康复学报, 2020, 30(3): 177-182
|
| [12] |
林星星, 董宝强, 王树东, 等. 基于筋膜的经筋基础研究:述评与展望[J]. 中国针灸, 2023, 43(11): 1338-1342.
|
| [13] |
罗序国, 熊明洁, 江睿. 基于“宗筋主束骨而利机关”理论的中医手法治疗膝骨关节炎的临床观察[J]. 中国医学创新, 2022, 19(21): 86-90.
|
| [14] |
贺文华, 董晓慧, 汤臣建, 等. “宗筋主束骨而利机关”理论在经筋病中的临床应用概况[J]. 湖南中医杂志, 2019, 35(5): 155-157.
|
| [15] |
COLETTI C, ACOSTA G F, KESLACY S, et al. Exercise-mediated reinnervation of skeletal muscle in elderly people: an update[J]. Eur J Transl Myol, 2022, 32(1): 10416.
|
| [16] |
ZHENG D D, LIU J, PIAO H L, et al. ROS-triggered endothelial cell death mechanisms: Focus on pyroptosis, parthanatos, and ferroptosis[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 1039241.
|
| [17] |
黄吴心蕊, 田静, 贺洁宇. 原发性干燥综合征合并骨质疏松的危险因素[J].中南大学学报(医学版), 2024, 49(2): 312-318.
|
| [18] |
SOUSA-VICTOR P, GARCÍA-PRAT L, MUÑOZ-CÁNOVES P. Control of satellite cell function in muscle regeneration and its disruption in ageing[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2022, 23(3): 204-226.
|
| [19] |
KUANG S H, KURODA K, LE GRAND F, et al. Asymmetric self-renewal and commitment of satellite stem cells in muscle[J]. Cell, 2007, 129(5): 999-1010.
|
| [20] |
BACHMAN J F, CHAKKALAKAL J V. Satellite cells in the growth and maintenance of muscle[J]. Curr Top Dev Biol, 2024, 158: 1-14.
|
| [21] |
COLLINS B C, KARDON G. It takes all kinds: heterogeneity among satellite cells and fibro-adipogenic progenitors during skeletal muscle regeneration[J]. Development, 2021, 148(21): dev199861.
|
| [22] |
PIETROSEMOLI N, MELLA S, YENNEK S, et al. Comparison of multiple transcriptomes exposes unified and divergent features of quiescent and activated skeletal muscle stem cells[J]. Skeletal Muscle, 2017, 7(1): 28.
|
| [23] |
SU Y, YU Y Y, LIU C C, et al. Fate decision of satellite cell differentiation and self-renewal by miR-31-IL34 axis[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2020, 27(3): 949-965.
|
| [24] |
SONG Z W, JIN C L, YE M, et al. Lysine inhibits apoptosis in satellite cells to govern skeletal muscle growth via the JAK2-STAT3 pathway[J]. Food Funct, 2020, 11(5): 3941-3951.
|
 ),Xingxing LIN1,3,Xuefeng GUAN1,Yu ZHANG4,Chaojie WANG1,Yiyan Han1(
),Xingxing LIN1,3,Xuefeng GUAN1,Yu ZHANG4,Chaojie WANG1,Yiyan Han1( )
)