| [1] |
Xiaochen HUANG,Hao LI,Baohua WANG,Kai LI.
Protective effect of lidocaine on PC12 cells in Parkinson’s disease model and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 638-647.
|
| [2] |
Yang ZHOU,Xuguang MI,Wenxing PU,Wentao WANG,Meng JING,Fankai MENG.
Ameliorative effect of melatonin on oxidative stress of human neuroblastoma SHSY5Y cells induced by hydrogen peroxide and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 340-347.
|
| [3] |
Suxian CHEN,Zehui GU,Yangfei MA,Qi TAN,Qi LI,Yadi WANG.
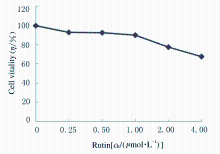
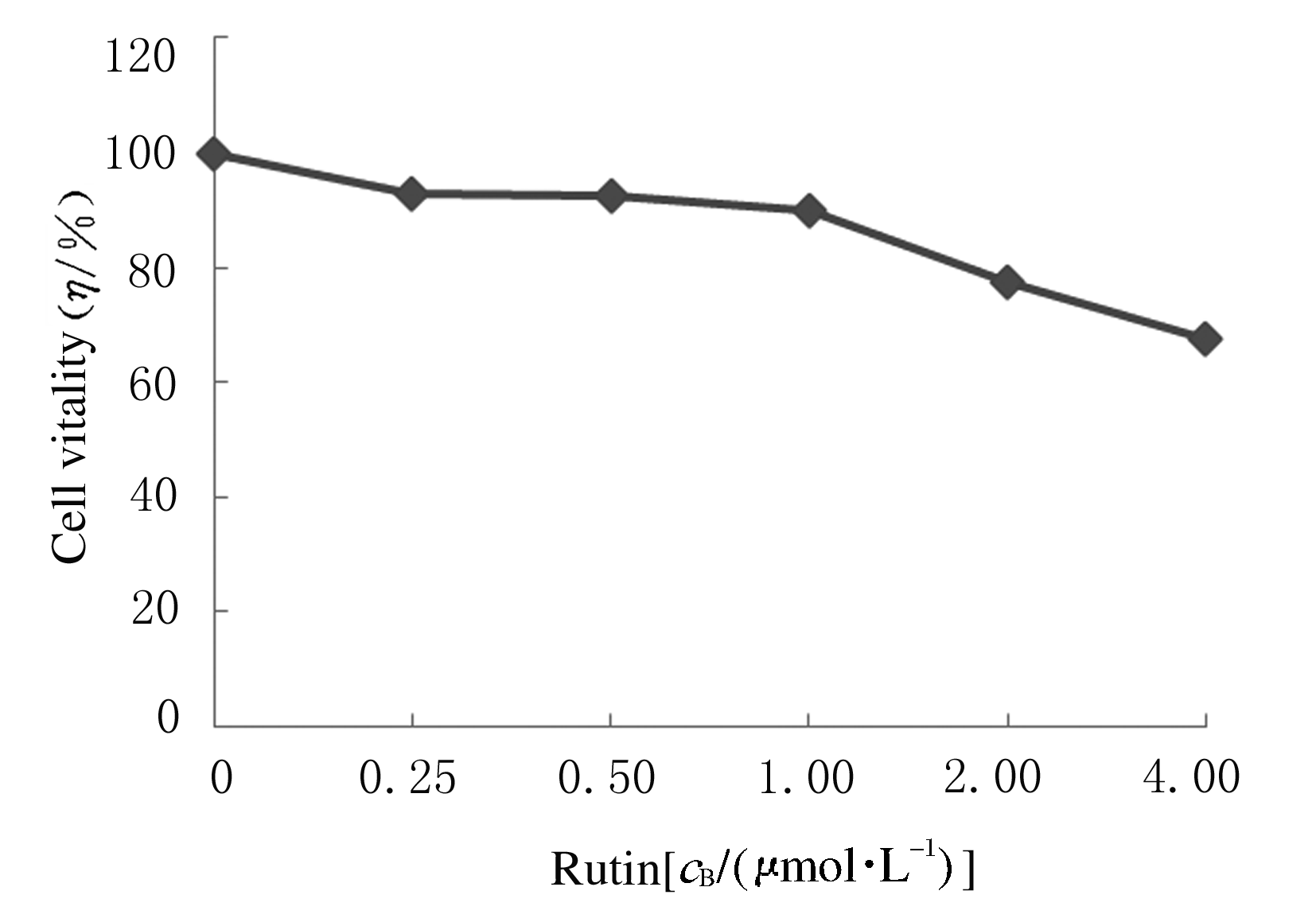
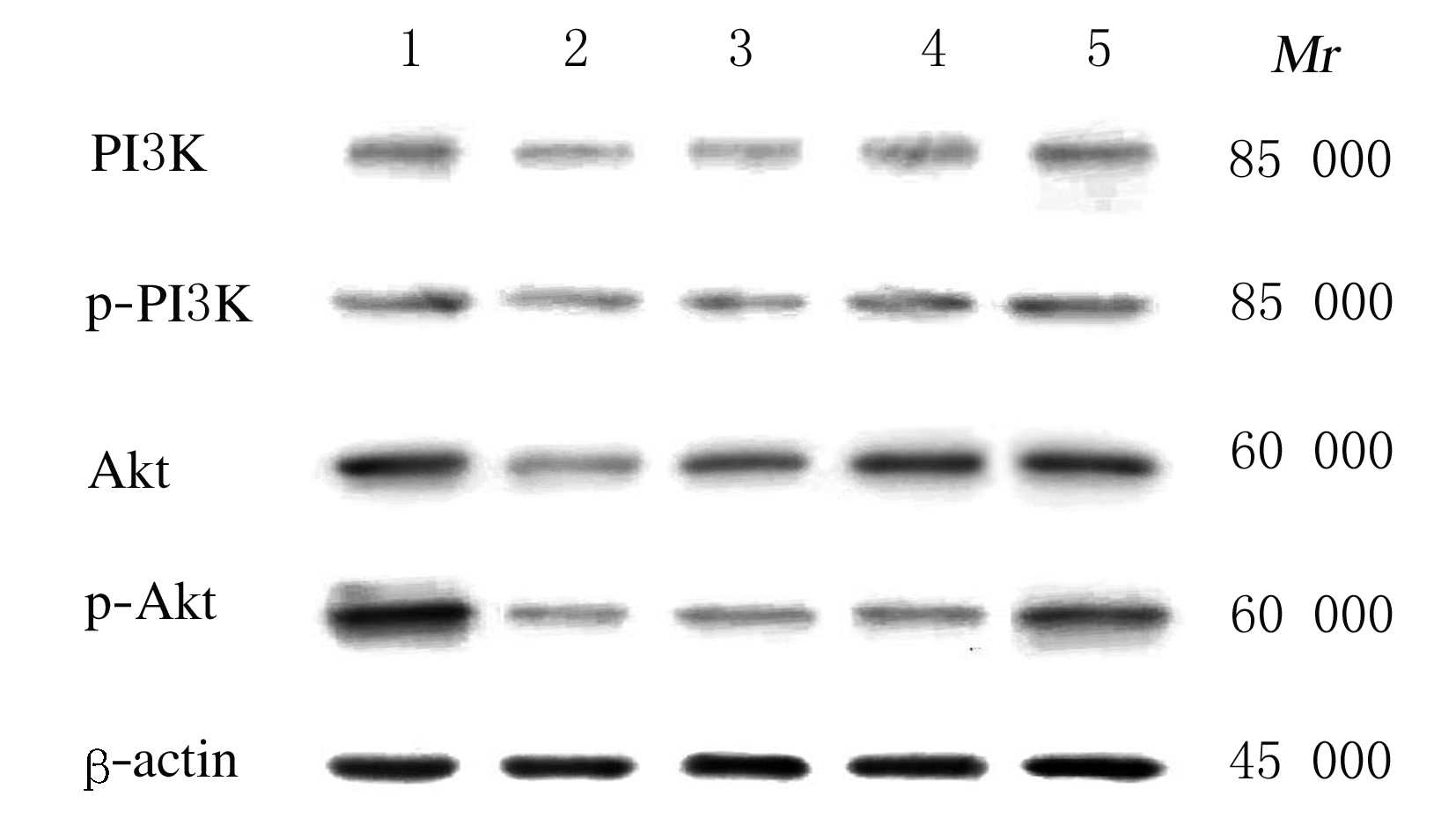
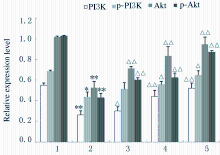
Promotion effect of rutin on apoptosis of human colon cancer SW480 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 356-363.
|
| [4] |
Leihua CUI,Yubo HOU,Chang SU,Minghe LI,Xin NIE.
Effect of N-acetylcysteine on apoptosis of MC3T3-E1 cells induced by nicotine and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 26-32.
|
| [5] |
Jie GONG,Zehua LEI,Yuanwei ZHANG,Xiong HUNANG,Bo DU,Zhixu WANG.
Improvement effect of miR-490-3p over-expression on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1495-1501.
|
| [6] |
Xinghua WANG,Hongjuan YANG,Xiuhong HU,Hongrei CUI,Baozhen XU,Danlu LI,Tao WANG,Yuwei GAO.
Effects of N-acetyl-L-cysteine on oxidative stress and vascular endothelial function in rats with hyperuricemia and their mechanisms
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1209-1214.
|
| [7] |
Dimi ZHOU,Lu GAN,Lin CHEN,Chengfang ZHOU,Liang ZENG.
Neuroprotective effect of Withaferin A on ischemic stroke rats and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 919-925.
|
| [8] |
Zhanqi ZHAO,Chengjin ZHANG,Juan TIAN.
Inhibitory effect of Ndfip1 on ferrion-induced neuronal apoptosis and its neuroprotective mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 338-343.
|
| [9] |
Ruili ZHANG,Xiaoqing YANG,Xiaoge ZHANG,Huafeng GUO,Jihong ZHU.
Effect of gestational diabetes mellitus on diaphragmatic function of newborn offsprings of rats
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 133-138.
|
| [10] |
Hongfang LI,Shao YANG,Mohan CAO,Lili YUAN,Xiaojin LI,Caixing SHI,Zhuoya WANG,Bailiu YA.
Improvement effect of curcumin on cerebral microcirculation disorder in hypercholesterolemia model rats and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 53-58.
|
| [11] |
ZHANG Cong, LIU Di, ZHANG Hanxue, ZHANG Hao, KONG Fanli, FENG Xianmin.
Protective effect of ginsenoside on hydrogen peroxide-induced HepG2 cell injury
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 985-991.
|
| [12] |
YANG Fan, LI Lihua.
Effect of vitamin D receptor activation on hepatic fibrosis induced by bile duct ligation in mice and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 722-727.
|
| [13] |
QIN Chao, DAI Xi, YANG Xiaoqiong, WANG Rongli, WANG Xing, LI Guoping.
Intervention effect of honokiol on inflammatory response in lung tissue of asthma mice and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 214-220.
|
| [14] |
GUO Xianghui, ZHENG Hui, WU Wei.
Protetive effects of anemoside B4 on kidney tissue of rats with chronic renal failure and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(01): 90-95.
|
| [15] |
LI Jinhua, JIN Ying, LI Junfeng, LI Li.
Effects of sesamin on abilities of learning and memory in AD model mice and their mechanisms
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(06): 1275-1280.
|
 )
)