Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (1): 180-186.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20210125
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
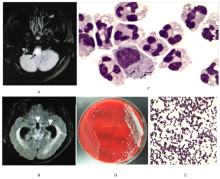
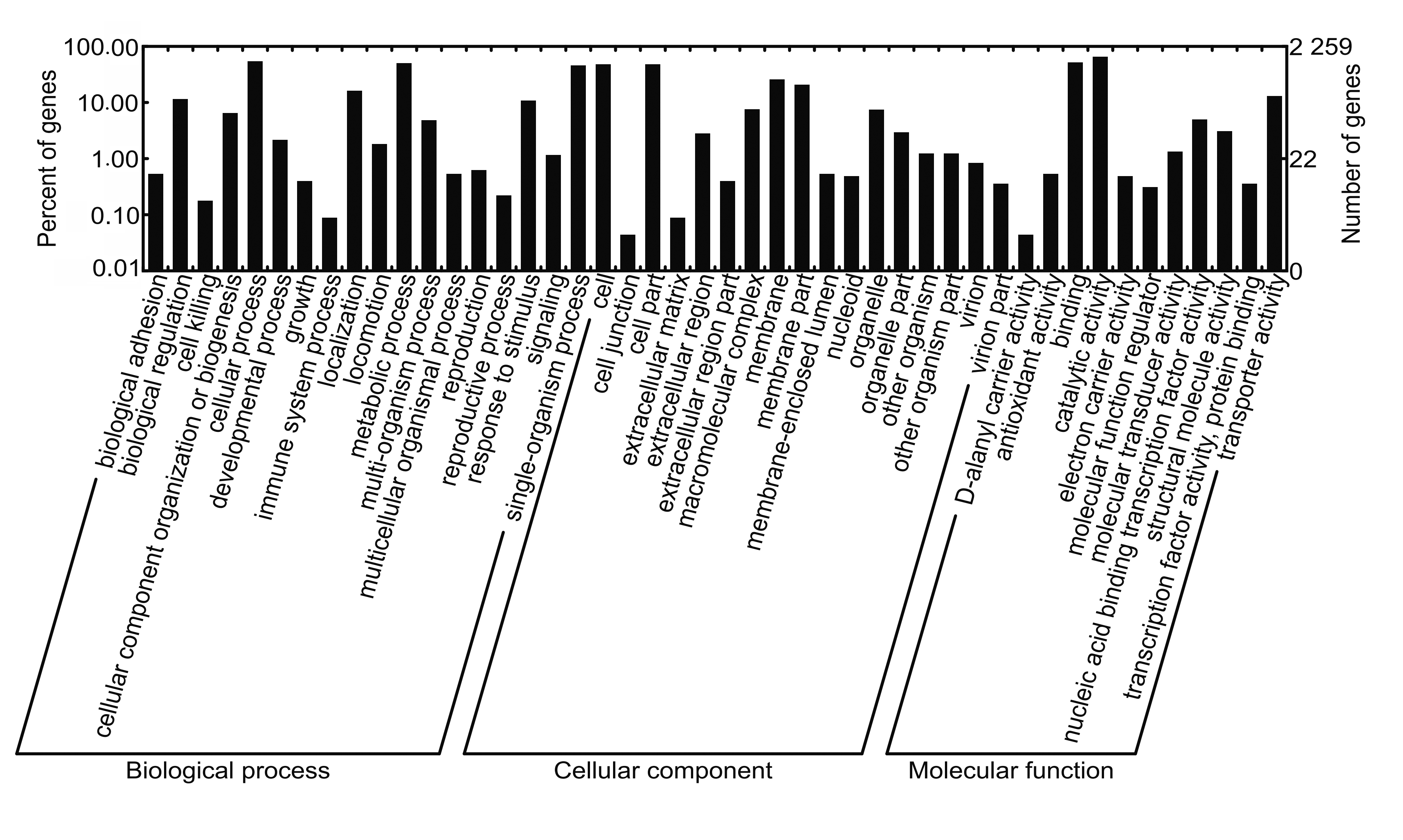
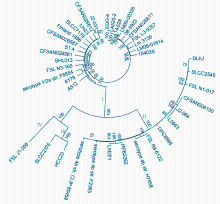
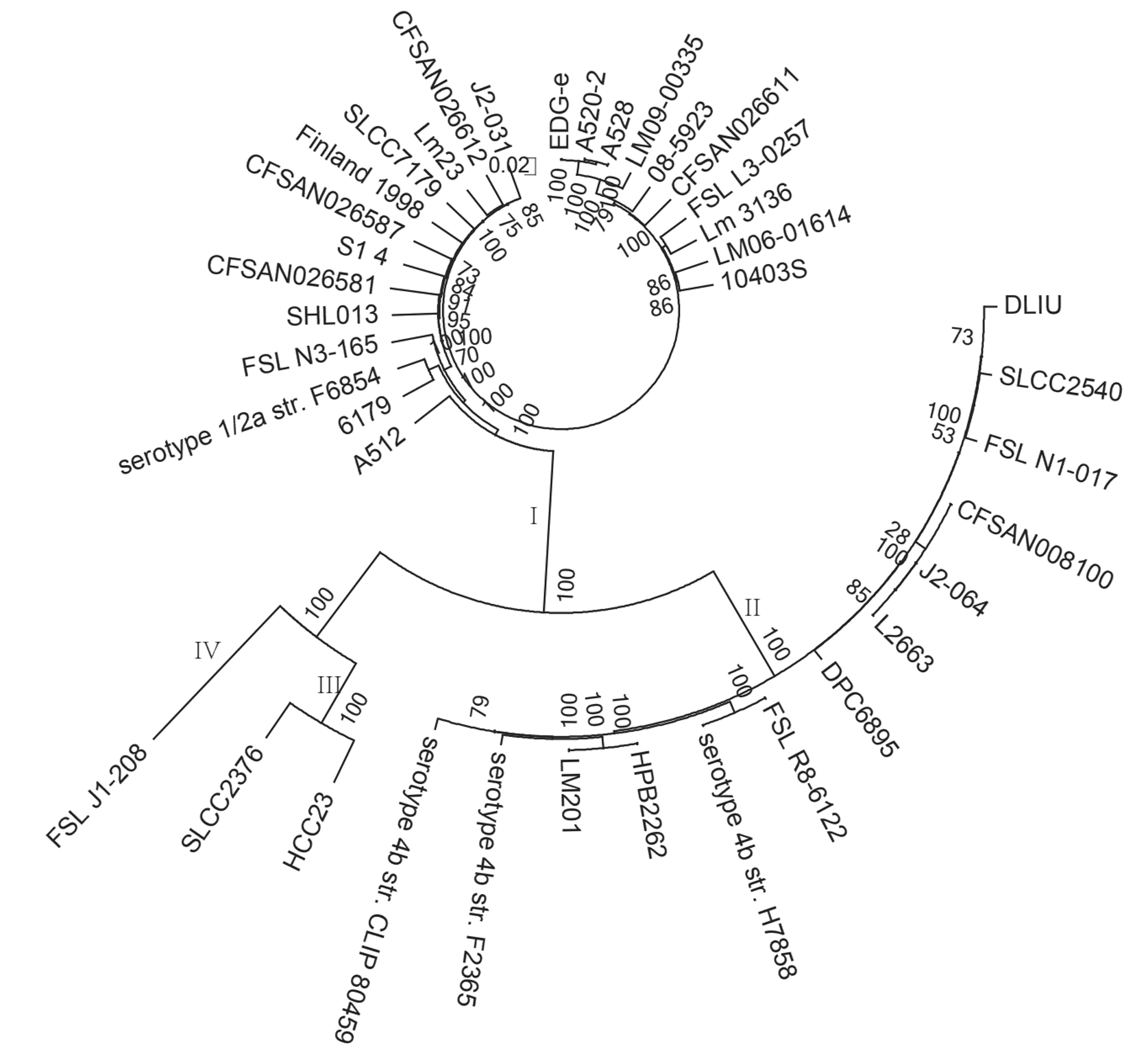
Genomic evolution and drug resistance analysis of human-derived Listeria monocytogenes
Guang YAO,Yuying LU,Qinghua ZHANG,Haixia ZHU,Yiwei CHEN,Dong SUN,Zhen ZHUANG,Feng ZHANG,Ding LIU,Zhi SONG( )
)
- Department of Neurology,Third Xiangya Hospital,Central South University,Changsha 410008,China
-
Received:2020-05-09Online:2021-01-28Published:2021-01-27 -
Contact:Zhi SONG E-mail:docsong@126.com
CLC Number:
- R446.5
Cite this article
Guang YAO,Yuying LU,Qinghua ZHANG,Haixia ZHU,Yiwei CHEN,Dong SUN,Zhen ZHUANG,Feng ZHANG,Ding LIU,Zhi SONG. Genomic evolution and drug resistance analysis of human-derived Listeria monocytogenes[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 180-186.
share this article
Tab. 1
Comparison of sequencing results of bacterial genome and drug-resistance gene annotation in database"
| XY1803 | Combined gene | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| LMXY_51 | lmrB | MFS transporter, DHA2 family, lincomycin resistance protein |
| LMXY_363 | tetA | MFS transporter, DHA1 family, tetracycline resistance protein |
| LMXY_377 | sugE | quaternary ammonium compound-resistance protein SugE |
| LMXY_378 | sugE | quaternary ammonium compound-resistance protein SugE |
| LMXY_1367 | mdtG | MFS transporter, DHA1 family, multidrug resistance protein |
| LMXY_1443 | norB, norC | MFS transporter, DHA2 family, multidrug resistance protein |
| LMXY_1747 | lmrP | MFS transporter, DHA1 family, multidrug resistance protein B |
| LMXY_2435 | TC.MATE, SLC47A, norM, mdtK, dinF | multidrug resistance protein, MATE family |
| LMXY_2511 | lmrB | MFS transporter, DHA2 family, lincomycin resistance protein |
| LMXY_2724 | mdtG | MFS transporter, DHA1 family, multidrug resistance protein |
| 1 | 陶 佳,杨佰虎,马 红,等. 单核细胞增生李斯特菌感染的临床分析[J]. 中国感染与化疗杂志, 2019, 19(4): 392-395. |
| 2 | 胡 冰,郑红艳,陈天明,等. 免疫功能正常的儿童单核细胞增生性李斯特菌脑膜炎17例[J]. 中华实用儿科临床杂志,2018, 33(22): 1735-1738. |
| 3 | GERSTEIN S, GAUTAM-GOYAL P, GOYAL S. A case of Listeria monocytogenes meningitis complicated by hydrocephalus and intraventricular hemorrhage: A review of treatment options and outcomes[J]. ID Cases, 2020, 19: e00704. |
| 4 | VISSING N H, KRISTENSEN K, MONSTER M B, et al. Listeria meningitis in danish children 2000-2017: A rare event even in a country with high rates of invasive listeriosis[J]. Pediatr Infect Dis J, 2019, 38(10): e274-e276. |
| 5 | DESAI A N, ANYOHA A, MADOFF L C, et al. Changing epidemiology of Listeria monocytogenes outbreaks, sporadic cases, and recalls globally: A review of ProMED reports from 1996 to 2018[J]. Int J Infect Dis, 2019, 84: 48-53. |
| 6 | THEISEN E, SAUER J D. Listeria monocytogenes and the Inflammasome: from cytosolic bacteriolysis to tumor immunotherapy[J]. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol,2016, 397: 133-160. |
| 7 | NESHER L, HADI C M, SALAZAR L, et al. Epidemiology of meningitis with a negative CSF Gram stain: under-utilization of available diagnostic tests[J]. Epidemiol Infect,2016, 144(1): 189-197. |
| 8 | JORDAN K, MCAULIFFE O. Listeria monocytogenes in foods[J]. Adv Food Nutr Res, 2018, 86: 181-213. |
| 9 | VILNE B, MEISTERE I, GRANTINA-IEVINA L, et al. Machine Learning approaches for epidemiological investigations of food-borne disease outbreaks[J]. Front Microbiol, 2019, 10: 1722. |
| 10 | PACIOREK M, BIENKOWSKI C, BEDNARSKA A, et al. The clinical course and outcome of Listeria monocytogenes meningitis: A retrospective single center study[J]. Neuro Endocrinol Lett, 2019, 40(2): 79-84. |
| 11 | 王晓娟,关鸿志,魏珂,等. 中枢神经系统李斯特菌感染患者的临床和脑脊液二代测序结果分析[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2018, 51(6): 451-455. |
| 12 | ALIA A, ANDRADE M J, CORDOBA J J, et al. Development of a multiplex real-time PCR to differentiate the four major Listeria monocytogenes serotypes in isolates from meat processing plants[J]. Food Microbiol, 2020, 87: 103367. |
| 13 | SHENG J, TAO T, ZHU X Y, et al. A multiplex PCR detection method for milk based on novel primers specific for Listeria monocytogenes 1/2a serotype[J]. Food Control, 2018, 86: 183-190. |
| 14 | RUHAR S, ATANU B, AMRESH P, et al. Lynn. Unraveling the mechanism of the MFS multidrug transporter using steered molecular dynamics[J]. Biophys J, 2020, 118(3): 527a. |
| 15 | VISHWAKARMA P, BANERJEE A, PASRIJA R, et al. Phylogenetic and conservation analyses of MFS transporters[J]. 3 Biotech, 2018, 8(11): 462. |
| 16 | PAGLIANO P, ARSLAN F, ASCIONE T. Epidemiology and treatment of the commonest form of listeriosis: meningitis and bacteraemia[J]. Infez Med,2017, 25(3): 210-216. |
| 17 | SHAMLOO E, HOSSEINI H, ABDIMOGHADAM M Z, et al. Importance of Listeria monocytogenes in food safety: a review of its prevalence, detection, and antibiotic resistance[J]. Iran J Vet Res,2019, 20(4): 241-254. |
| 18 | CASTELLAZZI M L, MARCHISIO P, BOSIS S. Listeria monocytogenes meningitis in immunocompetent and healthy children: a case report and a review of the literature[J]. Ital J Pediatr, 2018, 44(1): 152. |
| 19 |
LUQUE-SASTRE L, ARROYO C, FOX E M, et al. Antimicrobial resistance in Listeria species[J]. Microbiol Spectr, 2018.DOI:10.1028/microbiolspec.ARBA-0031-2017.
doi: 10.1028/microbiolspec.ARBA-0031-2017 |
| 20 | DISSON O, LECUIT M. Targeting of the central nervous system by Listeria monocytogenes[J]. Virulence, 2012, 3(2): 213-221. |
| 21 | 王 译,亓连玉,张程璐,等. 基因治疗药物递送系统研究进展[J]. 药学进展, 2018, 42(12): 884-896. |
| [1] | Xiulan YE,Ming LI,Zhaojian WANG,Haiyan ZHAO,Jianning MA,Jing LIU,Yi ZHENG,Shunqing LI,Yu ZHANG. Effects of Cornus officinalis polysaccharide on behavior and multidrug resistance gene 1b and major vault protein expressions in hippocampus tissue of refractory epilepsy young rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 644-651. |
| [2] | Aihua REN,Wan LIU,Dawei WANG. Influence of PD-L1 knockout based on CRISPR/Cas9 technology in gefitinib resistance sensitivity of PC-9/T790M in non-small cell lung cancer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 292-298. |
| [3] | Guo HUANG,Youquan WANG,Juan CHEN. Reverse effect of miR-138-5p targeted inhibition of HIF-1α expression on cisplatin resistance of breast cancer MCF-7 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 360-368. |
| [4] | REN Aihua, WANG Dawei. Effect of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated TKI on sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer gene targeting gefitinib resistance and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(06): 1288-1293. |
| [5] | YANG Li, WANG Xuewen, ZHOU Ming, ZHANG Fan. Effect of arsenic trioxide combined with γ-secretase inhibitor MW167 on drug resistance of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2/ADM cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(01): 1-7. |
| [6] | ZHOU Haoquan, CHU Xinmin, DAI Yuanyuan, DAI Chuanlin, PAN Jiahua. Clinical characteristics and drug resistance analysis of non-fermentative bacteria infection in infants [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(05): 975-979. |
| [7] | HUI Shuang, GUO Hongqiang. Chemoresistance of multi-drug resistance malignant glioma cells mediated by DNA-PKcs and its molecular mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(05): 877-881. |
| [8] | JIANG Hui, ZHANG Tongfei, YANG He, XU Zhaonan, BI Ye, SUN Shu, ZHANG Zebing, JIA Jie. Establishment of human tongue squamous cell carcinoma cisplatin resistant cell line CAL-27/DDPand its biological evaluation [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(03): 506-511. |
| [9] | ZHANG Peng, CHE Lihe, GUO Zhimin, LOU Lixin, BAO Wanguo, LI Yuxiang. Analysis on distribution and drug resistance of pathogens in patients with urinary tract infections [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(03): 593-598. |
| [10] | WANG Huai-dong,ZHANG Xiao-tian,ZHANG Chao,GUAN Shi-hui,DONG Jun-xue,MU Jia,WANG Fang,ZHENG Jing-tong. Application of DNA sequencing technology in study on mechanism of resistance of Escherichia coli under different drug pressure [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2014, 40(01): 109-112. |
| [11] | XUE Hui-rong,WANG Li-ping,GENG Jia-nan,CUI Man-hua. Mechanism of resistance of ovarian cancer cell SKOV3/DDP reversed by HIF-1α gene silencing [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2013, 39(6): 1103-1107. |
| [12] | LI Ping|ZHANG Jie|LI Ya-rong|WANG Ke|SU Zhen-zhong . Reversal effect of Ku70-targeted siRNA on chemoresistance to cisplatin in human lung adenocarcinoma cells [J]. J4, 2012, 38(2): 240-245. |
| [13] | CUI Dian-long|XIE Bai-yi|HU Meng|XIANG Xin|BAO Chuan-en,CHEN Yu-qiang. Inhibitory effect of tetraiodothyroacetic acid on proliferation of drug- resistant human gastric cancer cell line in vivo and in vitro [J]. J4, 2012, 38(2): 281-285. |
| [14] | SHEN Yu|WANG Chun-mei,HUANG Ying|HE Xiao-fang. Relationship between changes of drug resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii strains and preferences of clinical antibiotics adoption [J]. J4, 2011, 37(5): 885-889. |
| [15] | LUO Dan,XIANG Yan-gen,PAN Jian-hua,PENG Xue-feng,DENG Wei-zhi,SHI Guo-min. Detection of |three-drug resistance related genes of mycobacterium tuberculosis by |membrance reverse dot blot hybridization [J]. J4, 2011, 37(4): 759-762. |