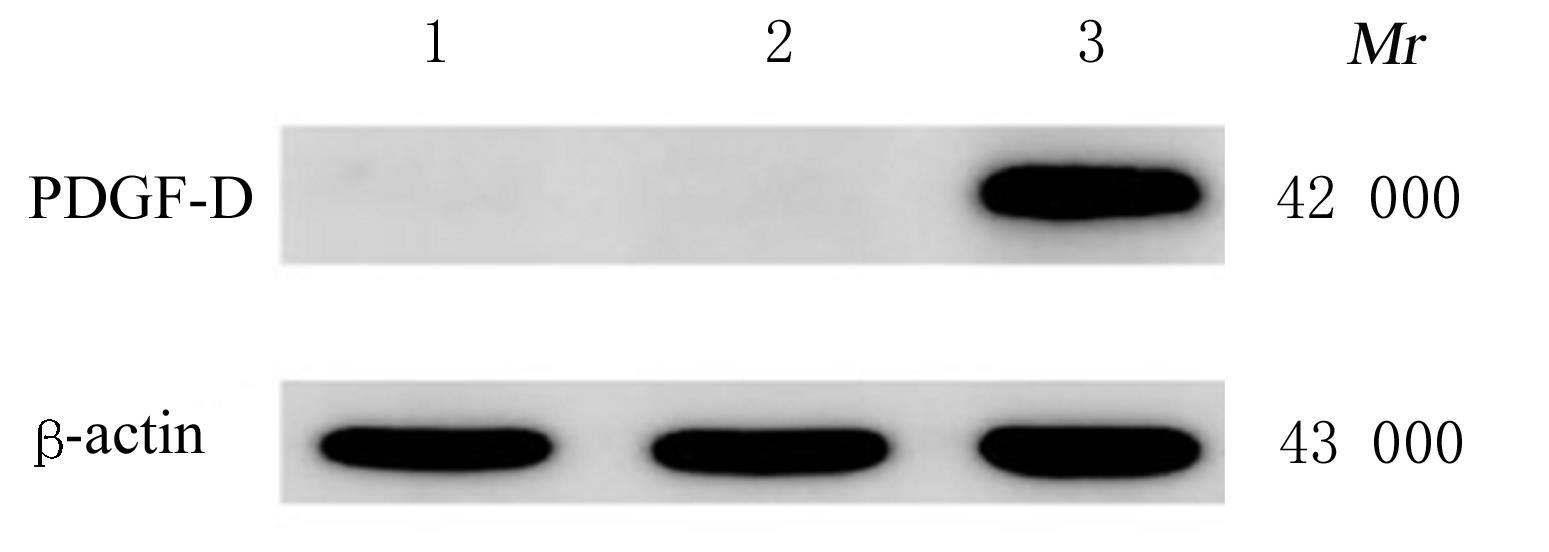
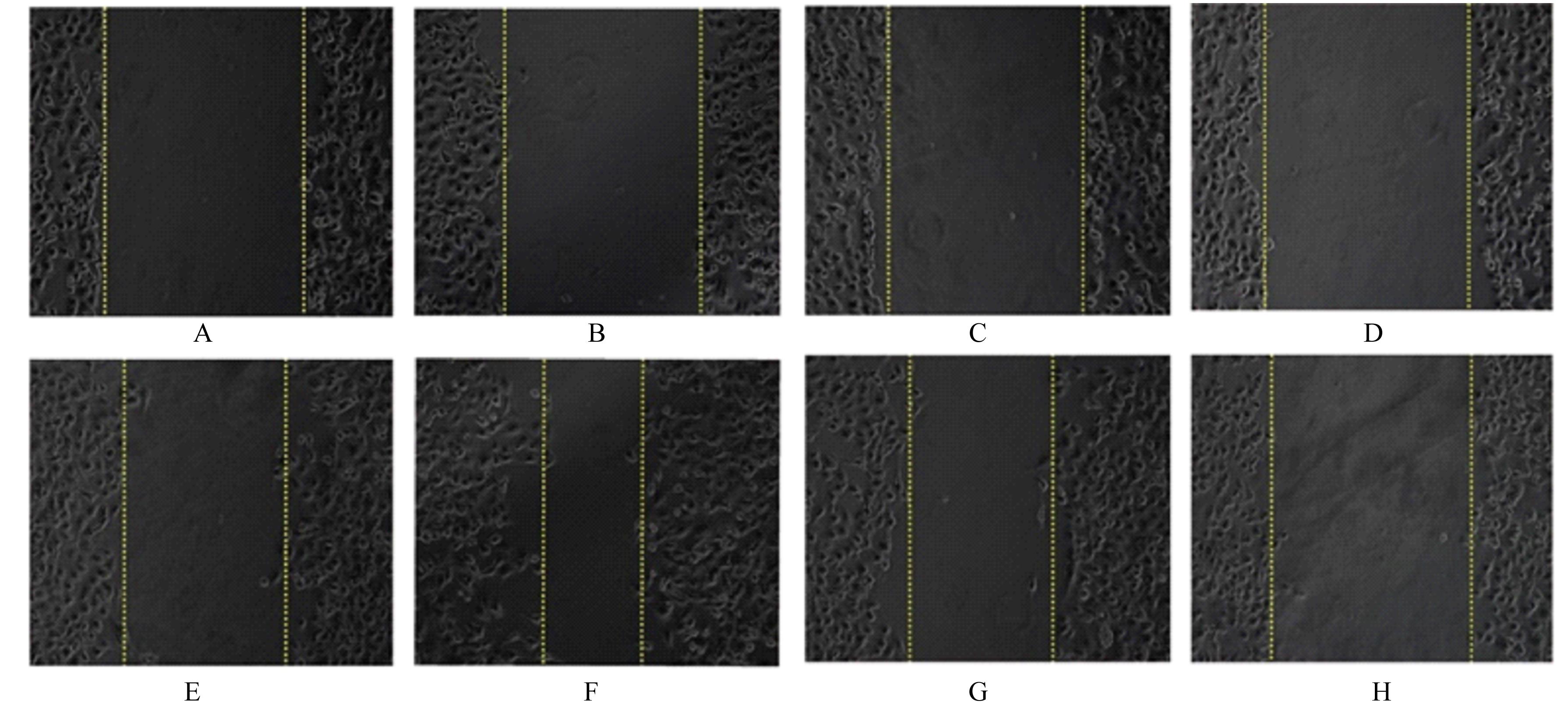
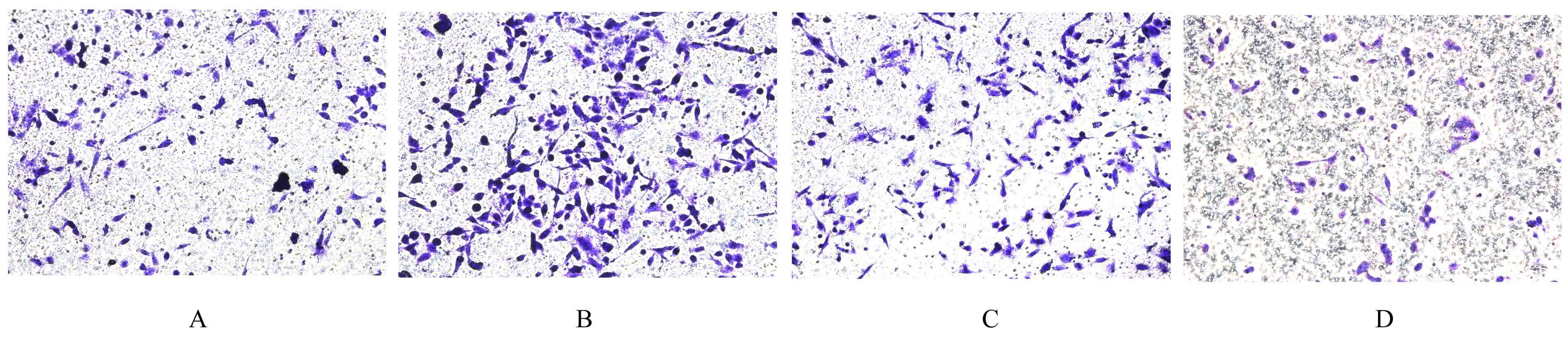
| [1] |
Yang JIANG,Zhaowen PENG,Shujing YI,Hailing YOU,Gaofei FENG,Chuanbo LIU,Kaiwen HU.
Argon-helium knife cryoablation in treatment of pulmonary mucoepidermoid carcinoma: A case report and literature review
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 1040-1044.
|
| [2] |
Guowu WANG,Yuan YAO,Yu ZHANG,Na XU,Fang LIU.
Inhibitory effect of miR-152 on proliferation and invasion of endometrial carcinoma cells by reducing low-density lipoprotein receptor expression
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 591-599.
|
| [3] |
Guanhu LI,Qingxu LANG,Chunyan LIU,Qin LIU,Mengrou GENG,Xiaoqian LI,Zhenqi WANG.
Inhibitory effect of valproic acid combined with X-ray irradiation on proliferation of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 622-629.
|
| [4] |
Peiyu YAN,Aichen ZHANG,Hong ZHANG,Yang LI,Mengmeng ZHANG,Mengze LUO,Ying PAN.
Therapeutic effect of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on premature ovarian failure model rats and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 648-656.
|
| [5] |
Cuilan LIU,Fengai HU,Jing LIU,Dan WANG,Changyun QIU,Dunjiang LIU,Di ZHAO.
Effect of adiponectin receptor agonist AdiopRon on biological behaviors of glioma cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 702-710.
|
| [6] |
Zhuangzhi WU,Xiaoning HE,Siqi CHEN.
Inhibitory effect of miR-124-3p on proliferation and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 718-727.
|
| [7] |
Xiaoyan LI,Wei ZHANG,Jie HE.
Promotion effect of REG1A on proliferation and migration of lung adenocarcinoma cells by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 444-453.
|
| [8] |
Guangsong XU,Haibing JIANG,Jing PAN,Guoqing LI.
Inhibitory effects of betulinic acid on migration and invasion of gastric cancer MGC-803 cells and their mechanisms
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 122-128.
|
| [9] |
Chaofeng ZHOU,Shifan ZHOU,Qing TIAN,Sai WANG,Honglin LI,Chunzheng MA.
Effect of lncRNA-NORAD overexpression on biological behaviors of esophageal cancer Eca-109 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 33-43.
|
| [10] |
Zetai WANG,Dandan LOU,Yan PENG,Daoqi ZHU,Aiwu LI,Fengying GONG,Ying LYU,Qin FAN.
Establishment of zebrafish xenograft model of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and inhibitory effect of curcumin on CNE-2 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 9-17.
|
| [11] |
Runhong MU,Yijiu AI,Yupeng LI,Rui LIN,Siping YE,Fang MA,Xiao GUO.
Expression of recombinant human IL-17A in gastric cancer tissue and its effects on proliferation, invasion, migration and apoptosis of gastric cancer BGC-823 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1510-1517.
|
| [12] |
Naigao TANG,Genjian ZHENG.
Effects of miR-762 on proliferation and apoptosis of human tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells by targeting NCOR1 expression
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1099-1107.
|
| [13] |
Yajie CAO,Xiaohong BAO,Shuzhen LI,Haiying GENG,Zengxiaorui CAI,Chunmei DAI,Ning LI.
Effects of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor inhibitor NVP-AEW541 on proliferation, migration and invasion of ESCC cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1131-1138.
|
| [14] |
Lisong CHEN,Hui FANG,Hefei WANG,Chengyuan HE,Xiaodong GAI,Chun LI.
Effects of Notch1 signaling pathway on invasion and cisplatin resistance of lung adenocarcinoma cells and their mechanisms
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1171-1177.
|
| [15] |
Chen WANG,Jun TIAN,Hailing CHENG.
Effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation and apoptosis of cervical cancer HeLa cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1187-1193.
|
 )
)