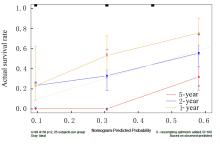
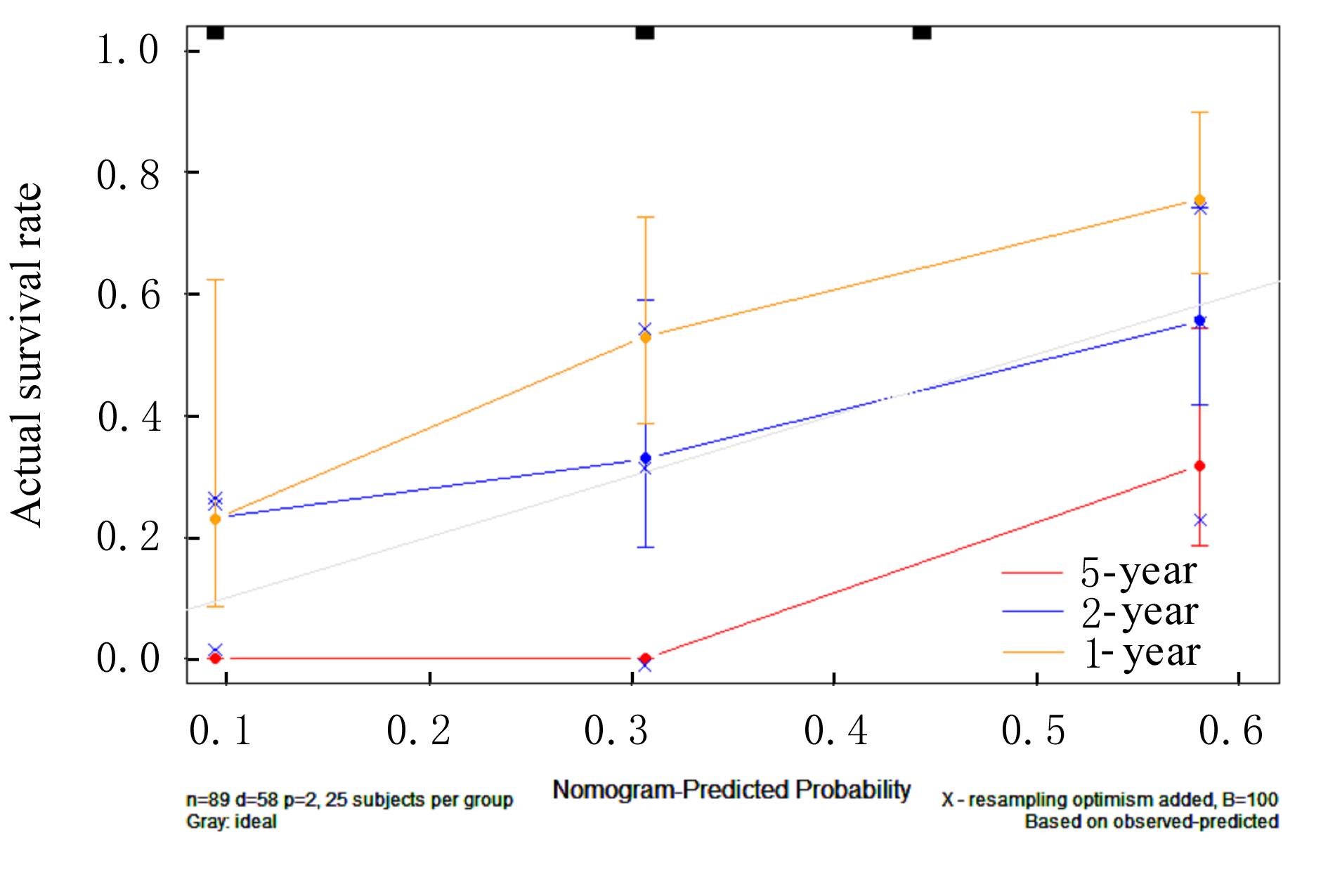
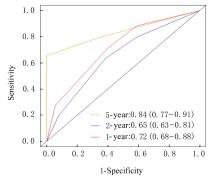
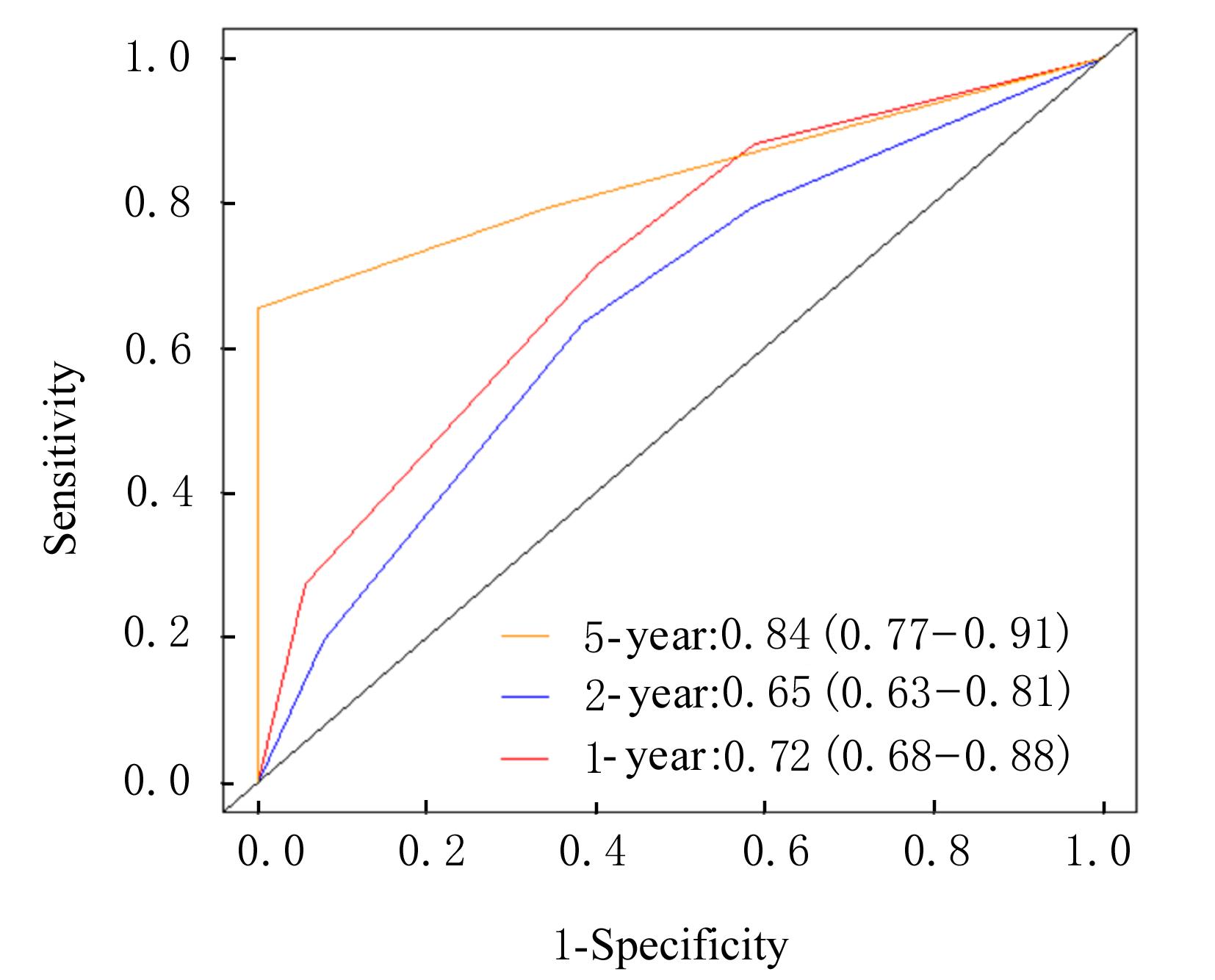
| 1 |
HOYOS S, NAVAS M C, RESTREPO J C, et al. Current controversies in cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis,2018,1864(4 Pt B): 1461-1467.
|
| 2 |
BERGQUIST A, EVON SETH. Epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol, 2015, 29(2): 221-232.
|
| 3 |
RIZVI S, KHAN S A, HALLEMEIER C L, et al. Cholangiocarcinoma - evolving concepts and therapeutic strategies[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2018,15(2): 95-111.
|
| 4 |
VALLE J W, BORBATH I, KHAN S A, et al. Biliary cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up[J]. Ann Oncol, 2016, 27(): v28-v37.
|
| 5 |
RAZUMILAVA N, GORES G J.Cholangiocarcinoma[J].Lancet, 2014, 383(9935): 2168-2179.
|
| 6 |
RIZVI S, GORES G J. Emerging molecular therapeutic targets for cholangiocarcinoma[J].J Hepatol,2017,67(3):632-644.
|
| 7 |
PUHALLA H, GRUENBERGER T, POKORNY H, et al. Resection of hilar cholangiocarcinomas: pivotal prognostic factors and impact of tumor sclerosis[J]. World J Surg, 2003, 27(6): 680-684.
|
| 8 |
EATON J E, TALWALKAR J A, LAZARIDIS K N, et al. Pathogenesis of primary sclerosing cholangitis and advances in diagnosis and management[J]. Gastroenterology, 2013, 145(3): 521-536.
|
| 9 |
LENDVAI G, SZEKERCZÉS T, ILLYÉS I, et al. Cholangiocarcinoma: classification, histopathology and molecular carcinogenesis[J]. Pathol Oncol Res, 2020, 26(1): 3-15.
|
| 10 |
PAPOUTSOGLOU P, LOUIS C, COULOUARN C. Transforming growth factor-beta (TGFβ) signaling pathway in cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Cells, 2019, 8(9): E960.
|
| 11 |
MOHR R, ÖZDIRIK B, KNORR J, et al. In vivo models for cholangiocarcinoma-what can we learn for human disease?[J].Int J Mol Sci,2020,21(14): E4993.
|
| 12 |
LEE A J, CHUN Y S. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: the AJCC/UICC 8th edition updates[J]. Chin Clin Oncol, 2018, 7(5): 52.
|
| 13 |
SIMILE M M, BAGELLA P, VIDILI G, et al. Targeted therapies in cholangiocarcinoma: emerging evidence from clinical trials[J]. Medicina (Kaunas), 2019, 55(2): 42.
|
| 14 |
BANALES J M, MARIN J J G, LAMARCA A, et al. Cholangiocarcinoma 2020: the next horizon in mechanisms and management[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 17(9): 557-588.
|
| 15 |
PASTORE M, LORI G, GENTILINI A, et al. Multifaceted aspects of metabolic plasticity in human cholangiocarcinoma: an overview of current perspectives[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(3): E596.
|
| 16 |
BRIVIO S, CADAMURO M, FABRIS L, et al. Molecular mechanisms driving cholangiocarcinoma invasiveness: an overview[J]. Gene Expr, 2018,18(1): 31-50.
|
| 17 |
SUZUKI S, SHIMODA M, SHIMAZAKI J, et al. Number of positive lymph nodes and lymphatic invasion are significant prognostic factors after pancreaticoduodenectomy for distal cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Clin Exp Gastroenterol, 2019, 12: 255-262.
|
| 18 |
LIAO P, CAO L, CHEN H, et al. Analysis of metastasis and survival between extrahepatic and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a large population-based study[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2021, 100(16): e25635.
|
| 19 |
SATO K, GLASER S, ALVARO D, et al. Cholangiocarcinoma: novel therapeutic targets[J]. Expert Opin Ther Targets, 2020, 24(4): 345-357.
|
| 20 |
WASEEM D, TUSHAR P. Intrahepatic, perihilar and distal cholangiocarcinoma: management and outcomes[J]. Ann Hepatol, 2017, 16(1): 133-139.
|
| 21 |
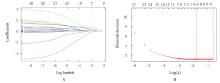
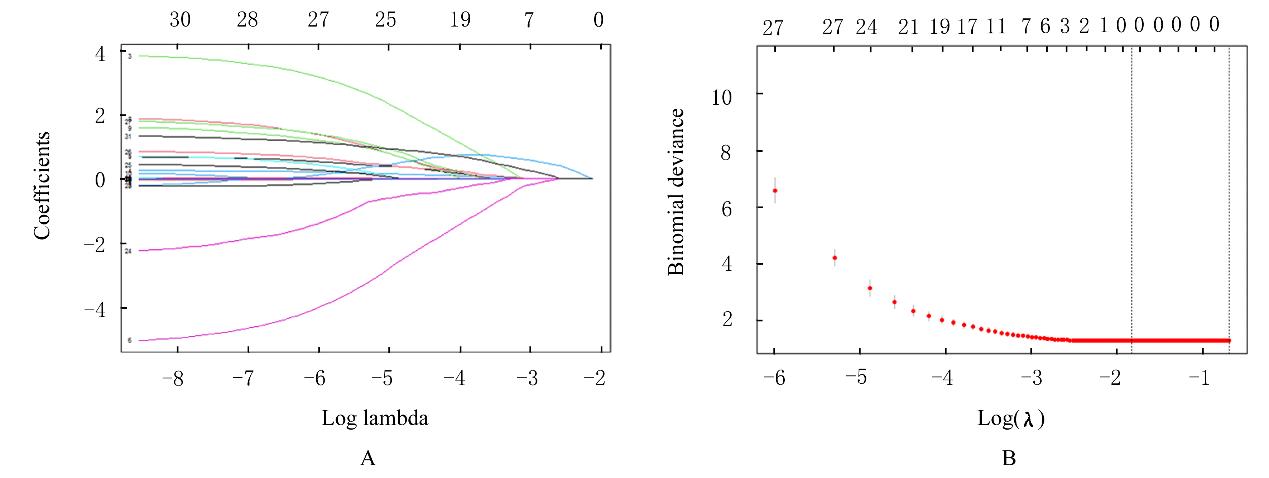
KLOSA J, SIMON N, WESTERMARK P O, et al. Seagull: lasso, group lasso and sparse-group lasso regularization for linear regression models via proximal gradient descent[J].BMC Bioinformatics, 2020,21(1): 407.
|
| 22 |
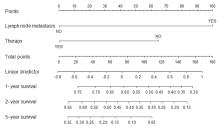
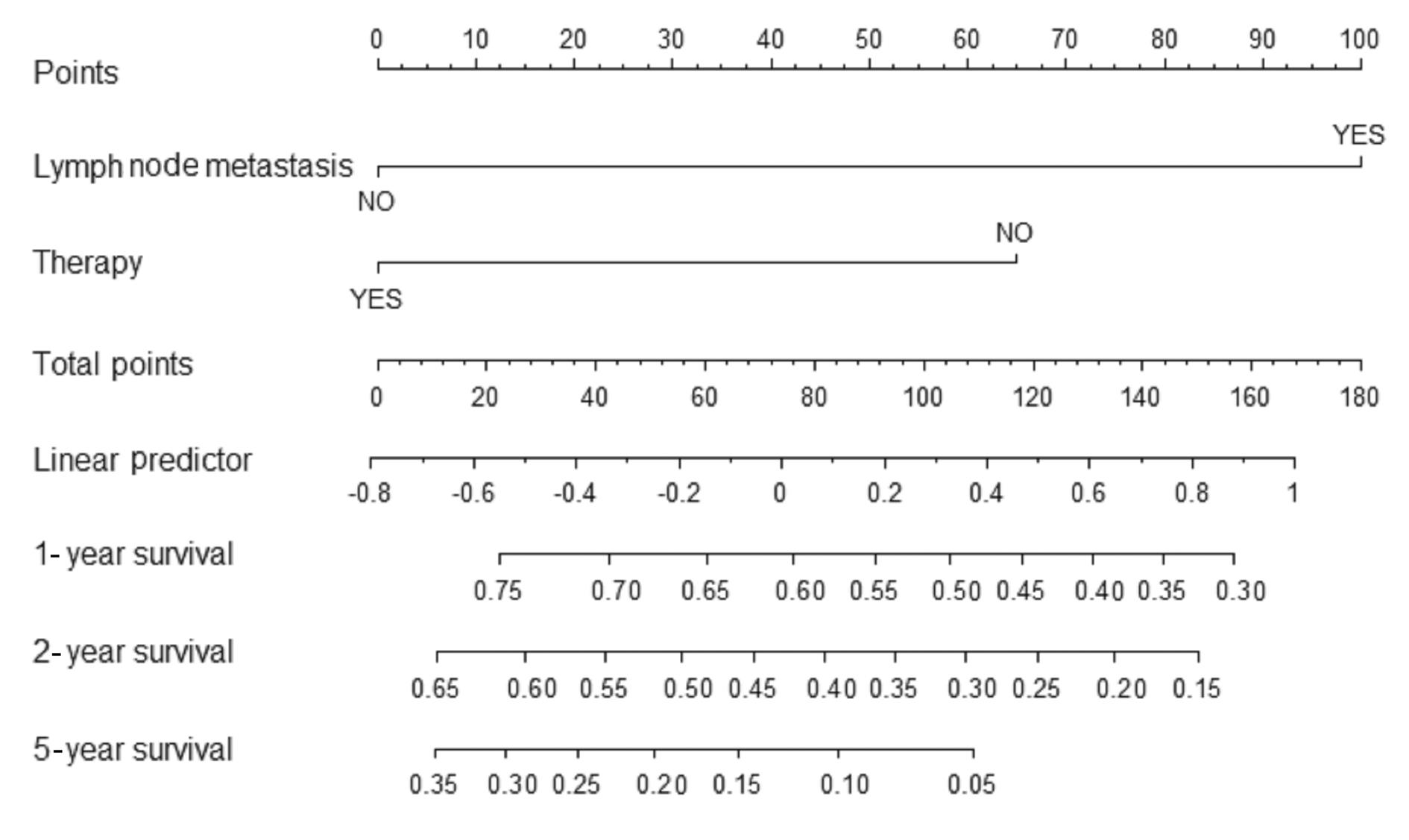
PARK S Y. Nomogram: an analogue tool to deliver digital knowledge[J]. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2018, 155(4): 1793.
|
 ),Hongyang LI1(
),Hongyang LI1( )
)