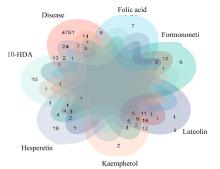
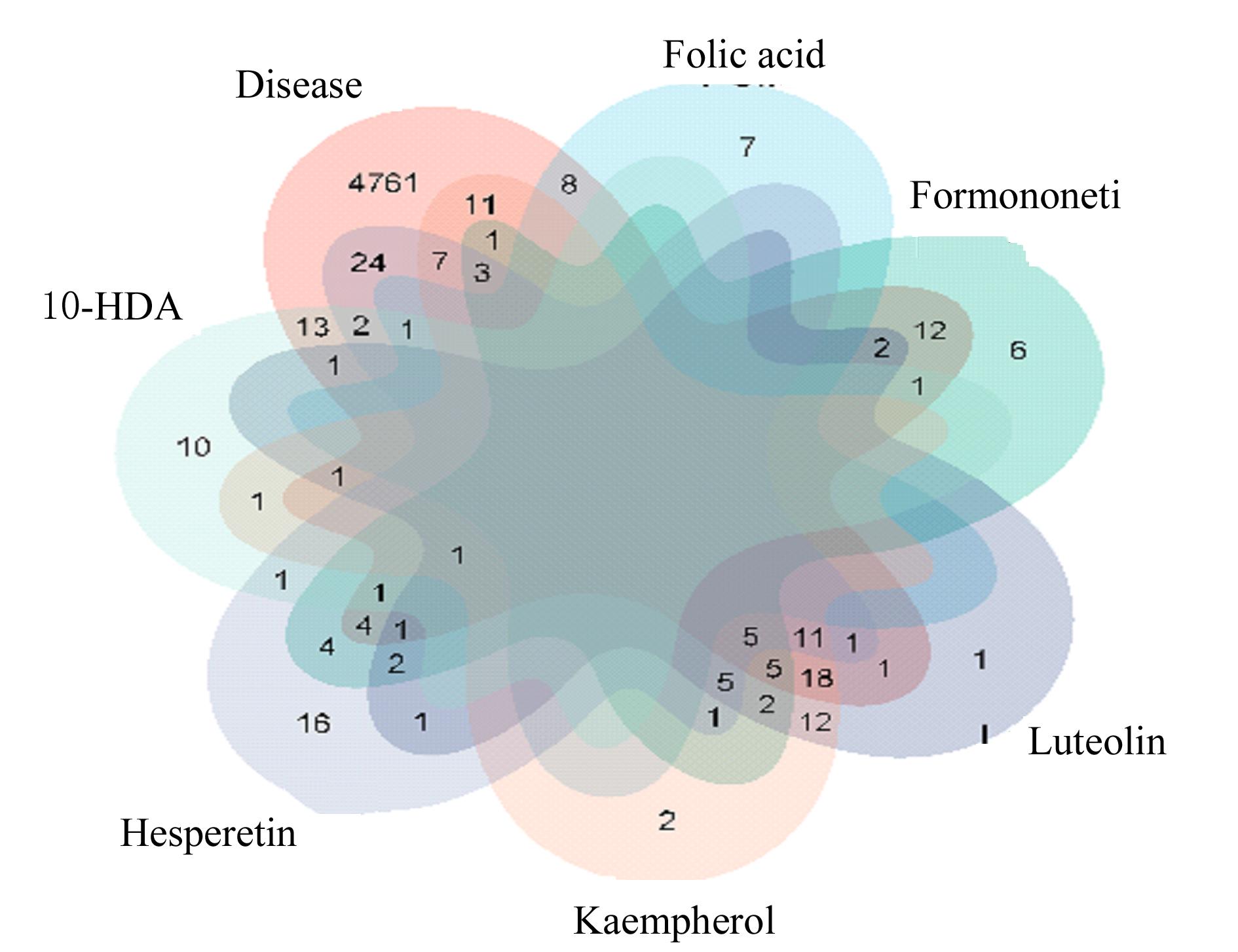
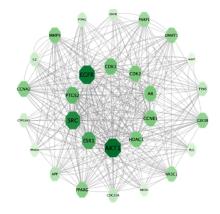
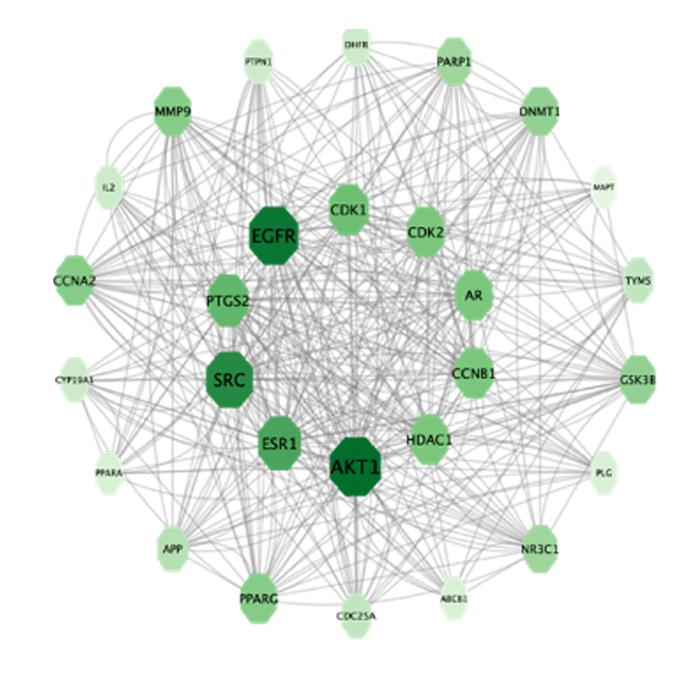
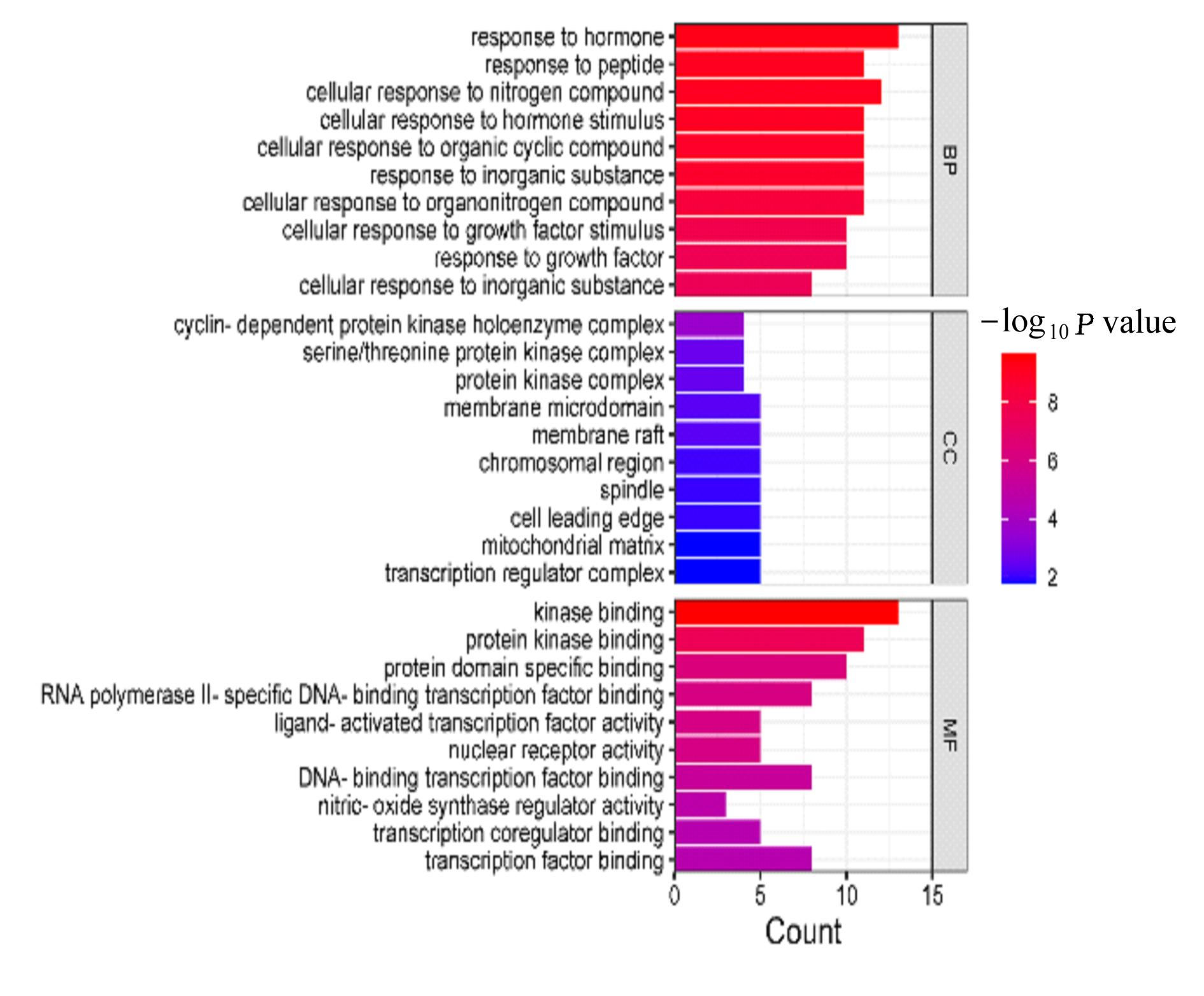
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1): 150-160.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240119
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles
Inhibitory effect of royal jelly acid on proliferation of human colon cancer SW620 cells and its network pharmacological analysis
Yaxin LIU1,Jian LIU1,Zhen LI1,Zhanhong CAO1,Haonan BAI1,Yu AN1,Xingyu FANG1,Qing YANG1,Hui LI2( ),Na LI1(
),Na LI1( )
)
- 1.Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Jilin Ginseng Academy,Changchun University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
2.Department of Anorectology,Qianwei Hospital,Jilin Province,Changchun 130012,China
-
Received:2023-02-19Online:2024-01-28Published:2024-01-31 -
Contact:Hui LI,Na LI E-mail:doctor_hui@hotmail.com;lhaln@hotmail.com
CLC Number:
- R735.3
Cite this article
Yaxin LIU,Jian LIU,Zhen LI,Zhanhong CAO,Haonan BAI,Yu AN,Xingyu FANG,Qing YANG,Hui LI,Na LI. Inhibitory effect of royal jelly acid on proliferation of human colon cancer SW620 cells and its network pharmacological analysis[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 150-160.
share this article
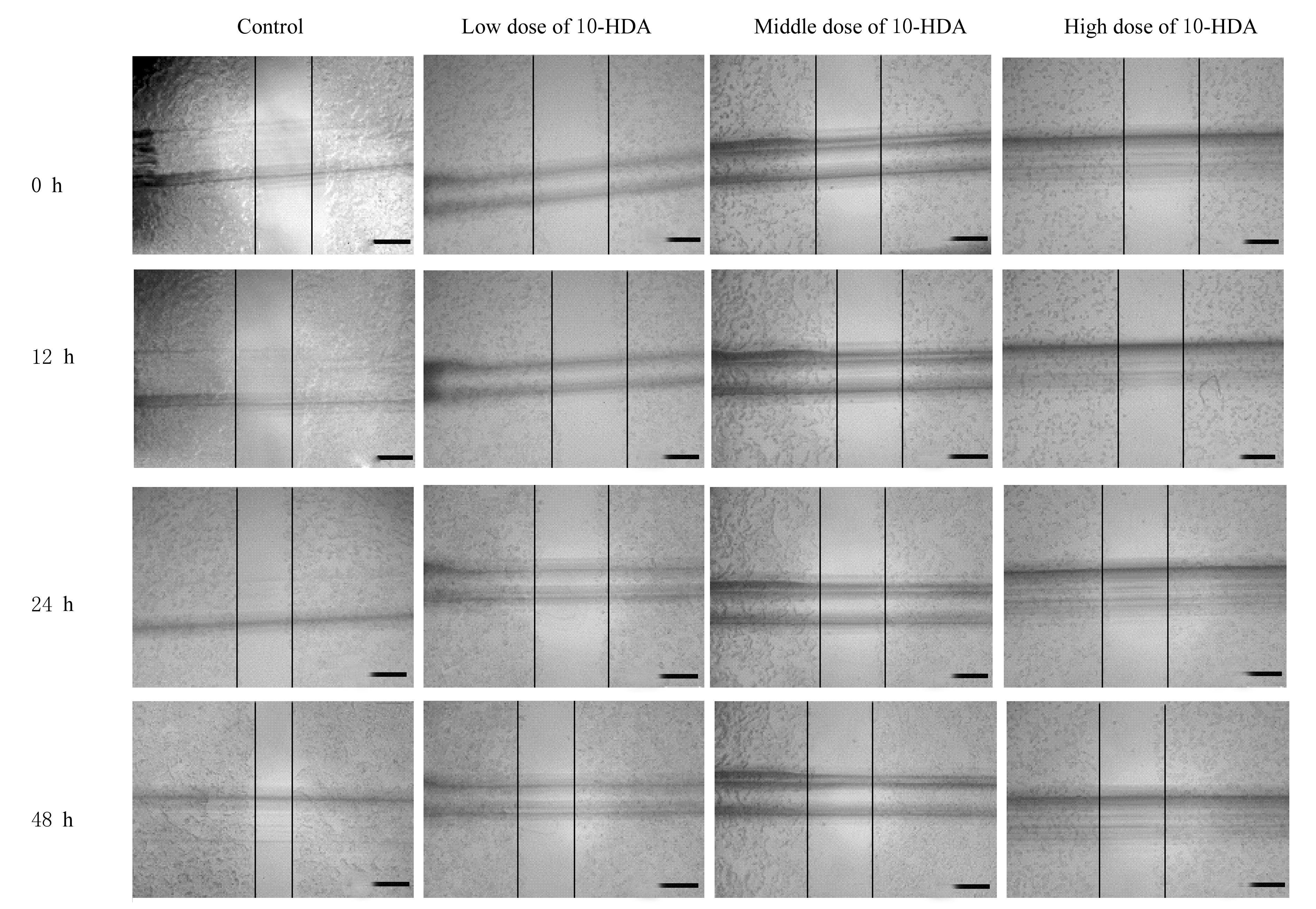
Tab. 2
Scratch healing rates of cells in various groups"
| Group | Scratch healing rate | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (t/h) 12 | 24 | 48 | |
| Control | 11.99±0.06 | 24.72±0.06 | 47.98±0.01 |
| 10-HDA | |||
| Low dose | 9.61±0.03* | 13.71±0.04* | 25.62±0.02** |
| Middle dose | 4.43±0.04* | 7.76±0.04* | 8.87±0.04** |
| High dose | 1.64±0.01* | 2.81±0.01** | 5.95±0.03** |
| *P<0.05,**P<0.01 compared with control group. | |||
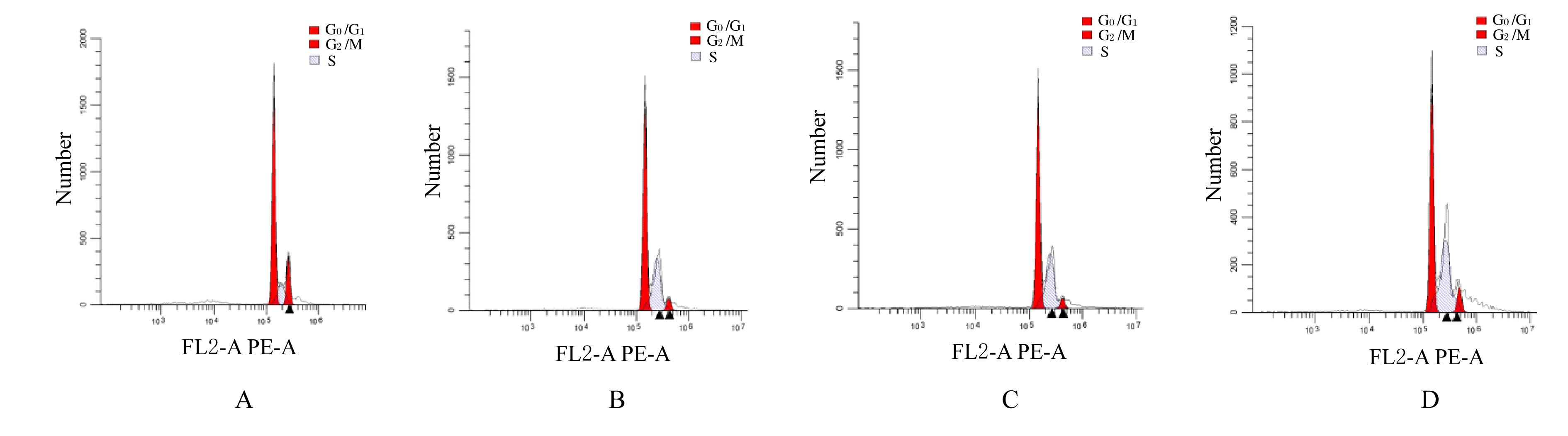
Tab. 3
Percentages of cells at different cell cycles in various groups"
| Group | Percentage of cells | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| G0/G1 | S | G2/M | |
| Control | 51.37±2.16 | 43.47±0.81 | 5.16±1.44 |
| 10-HDA | |||
| Low dose | 49.92±9.90 | 45.96±9.10 | 4.12±0.57 |
| Middle dose | 43.20±5.14 * | 53.92±1.74 * | 2.88±1.17 |
| High dose | 36.15±0.56 ** | 58.60±0.98 ** | 5.25±1.89 |
| *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared with control group. | |||
Tab. 4
Activities of T-AOC and SOD in cells in various groups"
| Group | T-AOC [mB/(mmol·g-1)] | SOD [λB/(U·mL-1)] |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.37±0.03 | 22.72±0.23 |
| 10-HDA | ||
| Low dose | 0.22±0.02 ** | 15.02±6.03* |
| Middle dose | 0.14±0.02 **△ | 14.10±3.82 **△ |
| High dose | 0.11±0.03 **△ | 10.12±3.30 **△ |
| *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared with control group; △P<0.05 compared with low dose of 10-HDA group. | ||
| 1 | SIEGEL R L, MILLER K D, JEMAL A. Cancer statistics, 2020[J]. Cancer J Clin, 2020, 70(1): 7-30. |
| 2 | ZHANG X J, LIU Z Z, CHEN S P, et al. A new discovery: total Bupleurum saponin extracts can inhibit the proliferation and induce apoptosis of colon cancer cells by regulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2022, 283: 114742. |
| 3 | 董 梁, 张 敬, 缪 柯. 川芎内酯抑制结肠癌细胞的生长和肿瘤干细胞样特性[J]. 广州中医药大学学报, 2021, 38(12): 2742-2750. |
| 4 | 孙红霞, 刘春旭, 安学俊, 等. 北五味子多糖对人膀胱癌T24细胞增殖和凋亡的影响及其机制[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2022, 48(5): 1216-1222. |
| 5 | FAN P, SHA F F, MA C, et al. 10-hydroxydec-2-enoic acid reduces hydroxyl free radical-induced damage to vascular smooth muscle cells by rescuing protein and energy metabolism[J]. Front Nutr, 2022, 9: 873892. |
| 6 | ALBALAWI A E, ALTHOBAITI N A, ALRDAHE S S, et al. Anti-tumor effects of queen bee acid (10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid) alone and in combination with cyclophosphamide and its cellular mechanisms against Ehrlich solid tumor in mice[J]. Molecules, 2021, 26(22): 7021. |
| 7 | JOVANOVIĆ M M, ŠEKLIĆ D S, RAKOBRADOVIĆ J D, et al. Royal jelly and trans-10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid inhibit migration and invasion of colorectal carcinoma cells[J]. Food Technol Biotechnol, 2022, 60(2): 213-224. |
| 8 | YANG Y C, CHOU W M, WIDOWATI D A, et al. 10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid of royal jelly exhibits bactericide and anti-inflammatory activity in human colon cancer cells[J]. BMC Complement Altern Med, 2018, 18(1): 202. |
| 9 | 刘晓冉, 朱 娜, 李 辉, 等. 王浆酸的药理作用研究进展[J]. 特产研究, 2020, 42(4): 85-88. |
| 10 | 汪洺卉, 刘墨祎, 王鹤霖, 等. 基于锦灯笼对白血病作用机制的网络药理学和分子对接技术的生物信息学分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2023, 49(1): 74-83. |
| 11 | HAO Y, CHEN Y, HE X, et al. Polymeric nanoparticles with ROS-responsive prodrug and platinum nanozyme for enhanced chemophotodynamic therapy of colon cancer[J].Adv Sci(Weinh),2020,7(20):2001853. |
| 12 | SIEGEL R L, MILLER K D, WAGLE N S, et al. Cancer statistics, 2023[J]. Cancer J Clin, 2023, 73(1): 17-48. |
| 13 | ZHOU J C, ZHENG R S, ZHANG S W, et al. Colorectal cancer burden and trends: comparison between China and major burden countries in the world[J].Chung Kuo Yen Cheng Yen Chiu,2021,33(1): 1-10. |
| 14 | MORII Y, TSUBAKI M, TAKEDA T, et al. Perifosine enhances the potential antitumor effect of 5-fluorourasil and oxaliplatin in colon cancer cells harboring the PIK3CA mutation[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2021, 898: 173957. |
| 15 | ZHANG C H, CHEN L, BAI Q, et al. Nonmetal graphdiyne nanozyme-based ferroptosis-apoptosis strategy for colon cancer therapy[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2022, 14(24): 27720-27732. |
| 16 | WANG J Y, CHANG H K, SU M, et al. The potential mechanisms of cinobufotalin treating colon adenocarcinoma by network pharmacology[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 934729. |
| 17 | ZHANG Y, CHEN H G, ZHAO C, et al. Research progress on anti-hepatocellular carcinoma mechanism of active ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2020, 45(14): 3395-3406. |
| 18 | TSAI P J, LAI Y H, MANNE R K, et al. Akt: a key transducer in cancer[J]. J Biomed Sci, 2022, 29(1): 76. |
| 19 | LI X, ZHAO L, CHEN C, et al. Can EGFR be a therapeutic target in breast cancer?[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2022, 1877(5): 188789. |
| 20 | 方 翌, 郭旭鸿, 魏丽慧, 等. 八宝丹阻滞人结肠癌细胞周期抑制结肠癌细胞生长[J]. 福建中医药, 2023, 54(1): 25-28. |
| 21 | MA L, LI X, ZHAO X P, et al. Oxaliplatin promotes siMAD2L2‑induced apoptosis in colon cancer cells[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2021, 24(3): 629. |
| 22 | CAI R, ZHOU Y P, LI Y H, et al. Baicalin blocks colon cancer cell cycle and inhibits cell proliferation through miR-139-3p upregulation by targeting CDK16[J]. Am J Chin Med, 2023, 51(1): 189-203. |
| 23 | 胡乃华. 石斛多糖通过改善肠道屏障功能、调节肠道微生物群、减少氧化应激和炎症反应改善右旋糖酐-硫酸钠诱导的小鼠结肠炎[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2022, 34(1): 41. |
| 24 | 王继凤, 刘晓冉, 隋 欣, 等. 基于cAMP/PKA/CREB信号通路独参汤对衰老模型大鼠认知功能障碍的影响[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2021,47(4):865-873. |
| 25 | SUN H N, XIE D P, REN C X,et al. Ethyl β-carboline-3-carboxylate increases cervical cancer cell apoptosis through ROS-p38 MAPK signaling pathway[J]. In Vivo, 2022, 36(3): 1178-1187. |
| 26 | 刘俊秀, 周 佳, 律广富, 等. 参红补血颗粒对气滞血瘀型血管内皮功能障碍小鼠血管内皮的保护作用及其机制[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2022, 48(6): 1437-1447. |
| 27 | LIU T F, HAN Y W, ZHOU T, et al. Mechanisms of ROS-induced mitochondria-dependent apoptosis underlying liquid storage of goat spermatozoa[J]. Aging, 2019, 11(18): 7880-7898. |
| 28 | TAO S C, LI J Y, WANG H, et al. Anti-colon cancer effects of Dendrobium officinale kimura & migo revealed by network pharmacology integrated with molecular docking and metabolomics studies[J]. Front Med, 2022, 9: 879986. |
| 29 | 陈小忠, 王 培, 谢明祥, 等. 下调SLP-2基因表达抑制脑胶质瘤细胞增殖及诱导凋亡的机制研究[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2018, 34(1): 55-59. |
| 30 | LIU A H, ZUO Z F, LIU L L, et al. Down-regulation of NTSR3 inhibits cell growth and metastasis, as well as the PI3K-AKT and MAPK signaling pathways in colorectal cancer[J]. Biochimie Biol Cell, 2020, 98(5): 548-555. |
| 31 | ZHANG C H, LIU H, ZHAO W L, et al. G3BP1 promotes human breast cancer cell proliferation through coordinating with GSK-3β and stabilizing β-catenin[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2021, 42(11): 1900-1912. |
| 32 | LI K, ZHANG J W, TIAN Y H, et al. The Wnt/β-catenin/VASP positive feedback loop drives cell proliferation and migration in breast cancer[J]. Oncogene, 2020, 39(11): 2258-2274. |
| 33 | SONG Q, HAN Z, WU X, et al. β-Arrestin1 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis through GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9: 650067. |
| 34 | ERES N, BELLMUNT J. Regulatory proteins of the cell cycle: alterations in the cycline D1 pathway as a paradigm. Findings in breast cancer[J]. Med Clin, 1998, 111(15): 592-596. |
| [1] | Huijuan SONG,Zhenhua XU,Dongning HE. Effect of apolipoprotein C1 expression on proliferation and apoptosis of human liver cancer HepG2 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 128-135. |
| [2] | Xiaoni WANG,Tao GUO,Qiyun LUO,Lifeng GUAN. Effect of usnic acid on biological behaviors of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts and JNK/MAPK signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1445-1451. |
| [3] | Aihua REN,Xinda JU,Aofei LIU,Yongchao LIU,Yanfeng LIU. Effect of ganoderic acid A on proliferation and apoptosis of human non-small cell lung cancer PC-9 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1466-1472. |
| [4] | Xiaoying ZHANG,Yuanhada HE,Jingyuan WANG,Ruijun SU,Qi WANG,Rongke LU,Bo ZHENG,Jian ZHENG. Relationship between expression levels of cyclooxygenase-2 and β-catenin in endometrium tissue of adenomyosis patients and dysmenorrhea [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1539-1546. |
| [5] | Lu FU, Yanjue YE, Jiangying LI, Ziyi TANG, Li YIN. Expressions of Sirtuins protein in testis tissue and GC-2 cells in male reproductive system damage model mice induced by bisphenol A and their significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1107-1116. |
| [6] | Xing LIU,Jiali LIU,Liangui NIE,Maojun LIU,Junxiong ZHAO,Liuyang WANG,Jun YANG. Improvement effect of SO2 on myocardial fibrosis after acute myocardial ischemic injury in rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1125-1133. |
| [7] | Yong GUO,Shengyan WANG,Jingjing YI,Sen CUI. Effect of salidroside on apoptosis of CD71+ nucleated red blood cells in bone marrow in high altitude polycythemia model rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1174-1181. |
| [8] | Yuanying SONG,Jing KAN,Kun PENG,Yue LI. Effect of honeysuckle extract on proliferation and apoptosis of airway smooth muscle cells in asthmatic model mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 1001-1007. |
| [9] | Meng LIU,Xiaodong HUANG,Zheng HAN,Qingxi ZHU,Jie TAN,Xia TIAN. Effect of cadherin-17 on proliferation and apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells and its PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway regulatory mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 1008-1017. |
| [10] | Li JIN,Xiaohong ZHANG,Chaoyang HU,Fengzhi LI,Yongliang CUI,Yang LI,Qianqian LIU,Yanjun QIAO. Effects of quercetin on growth and lung metastasis of transplanted tumor and cell invasion, and cell migration in human lung cancer A549 cells transplanted tumor model mice and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 1018-1026. |
| [11] | Xuying WANG,Mingzhen JING,Jin YU,Rong FU,Ru YANG. Effects of miR-181a-5p and BACH2 expressions on apoptosis and invasion of leukemic CCRF-CEM cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 840-849. |
| [12] | Guan LIU,Guizhou TAO,Hongxin WANG. Effect of baicalin on myocardial hypertrophy and apoptosis induced by abdominal aorta ligation in rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 850-857. |
| [13] | Yuanyuan LIANG,Song ZHAO,Jing HU,Ni AN,Yanlu WEI,Rongjian SU. Effect of motesanib combined with EZH2 inhibitor GSK126 on proliferation and apoptosis of liver cancer Huh7 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 896-904. |
| [14] | Xueru HUANG,Xuhao DING,Suxian CHEN,Qi TAN,Yueming WU,Xiaomin NIU,Yadi WANG,Qing TONG. Effect of PMS2 on biological behaviors of colon cancer SW480 cells through ERK/ERCC1 pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 931-940. |
| [15] | Hongli CUI,Siqi FAN,Wenfei GUAN,E MENG,Jiatong LIU,Xuetong SUN,Chunxu CAO,Lixin LIU,Yali QI,Fang FANG,Zhicheng WANG. Inhibitory effect of irradiation enhanced by gallic acid-lecithin complex-induced oxidative stress on proliferation of A549 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 941-946. |
|
||