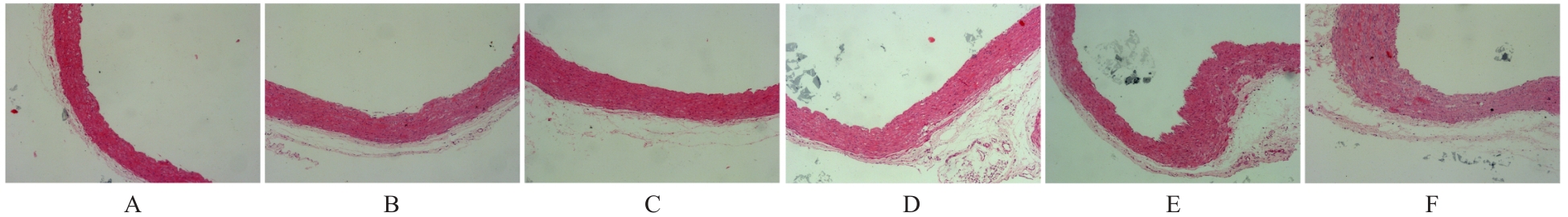
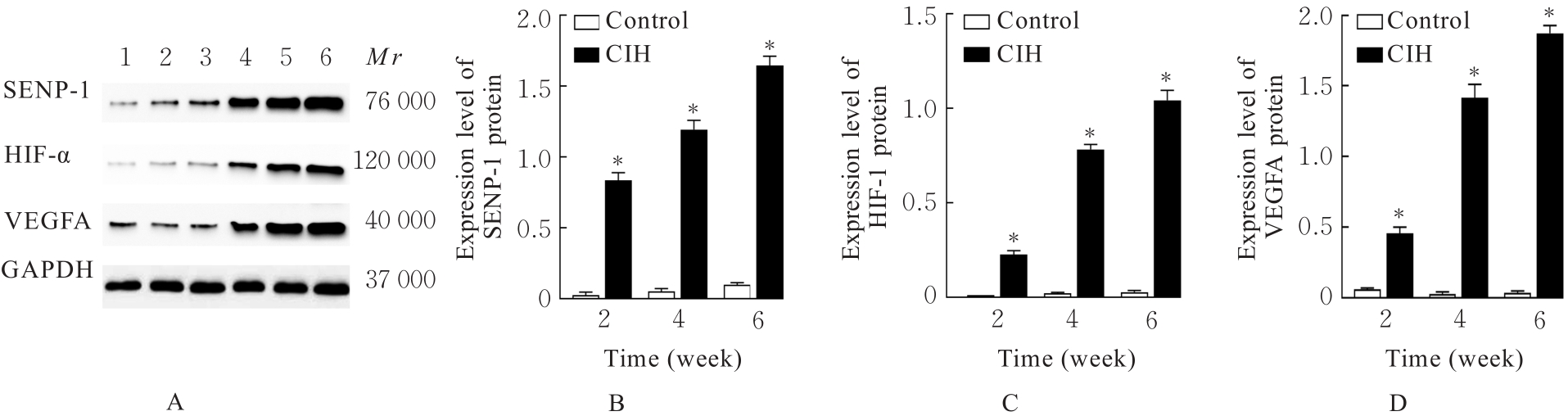
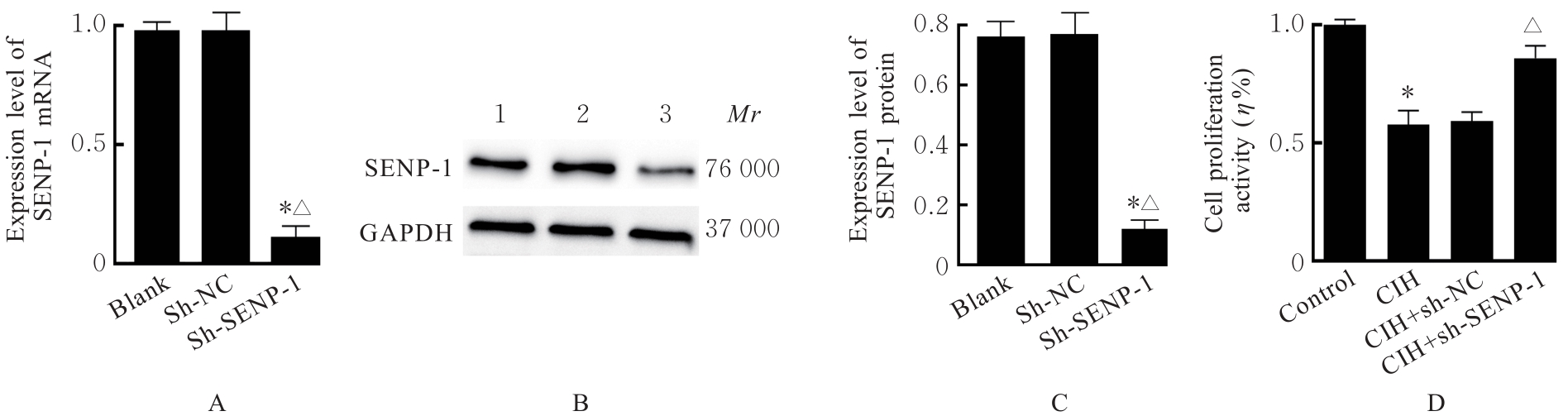
| 1 |
DAULATZAI M A. Role of sensory stimulation in amelioration of obstructive sleep apnea[J]. Sleep Disord, 2011, 2011: 596879.
|
| 2 |
LUI M M S, LAM D C L, IP M S M. Significance of endothelial dysfunction in sleep-related breathing disorder[J]. Respirology, 2013, 18(1): 39-46.
|
| 3 |
YAN Y R, ZHANG L, LIN Y N, et al. Chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced mitochondrial dysfunction mediates endothelial injury via the TXNIP/NLRP3/IL-1β signaling pathway[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2021, 165: 401-410.
|
| 4 |
DING H B, HUANG J F, WU D W, et al. Silencing of the long non-coding RNA MEG3 suppresses the apoptosis of aortic endothelial cells in mice with chronic intermittent hypoxia via downregulation of HIF-1α by competitively binding to microRNA-135a[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2020, 12(5): 1903-1916.
|
| 5 |
ZHOU F, DAI A G, JIANG Y L, et al. SENP-1 enhances hypoxia-induced proliferation of rat pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells by regulating hypoxia-inducible factor-1α[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2016, 13(4): 3482-3490.
|
| 6 |
ZHOU J, SUN C. SENP1/HIF-1α axis works in angiogenesis of human dental pulp stem cells[J]. J Biochem Mol Toxicol, 2020, 34(3): e22436.
|
| 7 |
温 雯, 姚巧玲, 陈玉岚, 等. 瞬时受体电位通道C与阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征大鼠心脏和肾脏损害的关系[J]. 浙江大学学报(医学版), 2020, 49(4): 439-446.
|
| 8 |
ZHAO F, MENG Y, WANG Y, et al. Protective effect of Astragaloside Ⅳ on chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial dysfunction through the calpain-1/SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 920977.
|
| 9 |
REDLINE S, AZARBARZIN A, PEKER Y. Obstructive sleep apnoea heterogeneity and cardiovascular disease[J]. Nat Rev Cardiol, 2023, 20(8): 560-573.
|
| 10 |
雷培良, 李 兵. CPAP治疗对OSAHS患者心血管系统并发症的影响[J]. 激光杂志, 2010, 31(1): 91, 93.
|
| 11 |
王海娟, 张晓雪, 韩玉洁, 等. 邢氏夏枯草汤对慢性间歇性低氧高血压大鼠血管内皮损伤的保护作用及其机制[J]. 中药药理与临床, 2022, 38(3): 43-48.
|
| 12 |
STANEK A, BROŻYNA-TKACZYK K, MYŚLIŃSKI W. Oxidative stress markers among obstructive sleep apnea patients[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2021, 2021: 9681595.
|
| 13 |
MELIANTE P G, ZOCCALI F, CASCONE F, et al. Molecular pathology, oxidative stress, and biomarkers in obstructive sleep apnea[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(6): 5478.
|
| 14 |
MANIACI A, IANNELLA G, COCUZZA S, et al. Oxidative stress and inflammation biomarker expression in obstructive sleep apnea patients[J]. J Clin Med, 2021, 10(2): 277.
|
| 15 |
YANG C L, ZHOU Y Q, LIU H J, et al. The role of inflammation in cognitive impairment of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome[J]. Brain Sci, 2022, 12(10): 1303.
|
| 16 |
黄家容, 张凤蕊, 平 芬. miRNA在阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征中的作用研究进展[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2023, 48(6): 735-741.
|
| 17 |
ARNAUD C, BOCHATON T, PÉPIN J L, et al. Obstructive sleep apnoea and cardiovascular consequences: Pathophysiological mechanisms[J]. Arch Cardiovasc Dis, 2020, 113(5): 350-358.
|
| 18 |
SEMENZA G L. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1: mechanisms and consequences[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2000, 59(1): 47-53.
|
| 19 |
MARTINEZ C A, JIRAMONGKOL Y, BAL N, et al. Intermittent hypoxia enhances the expression of hypoxia inducible factor HIF1A through histone demethylation [J]. J Biol Chem, 2022, 298(11): 102536.
|
| 20 |
CHENG J K, KANG X L, ZHANG S, et al. SUMO-specific protease 1 is essential for stabilization of HIF1alpha during hypoxia[J]. Cell, 2007, 131(3): 584-595.
|
| 21 |
HSU H L, LIAO P L, CHENG Y W, et al. Chloramphenicol induces autophagy and inhibits the hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha pathway in non-small cell lung cancer cells[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(1): 157.
|
| 22 |
XU Y, ZUO Y, ZHANG H Z, et al. Induction of SENP1 in endothelial cells contributes to hypoxia-driven VEGF expression and angiogenesis[J]. J Biol Chem, 2010, 285(47): 36682-36688.
|
 )
)