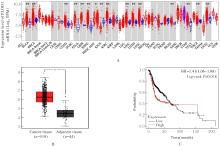
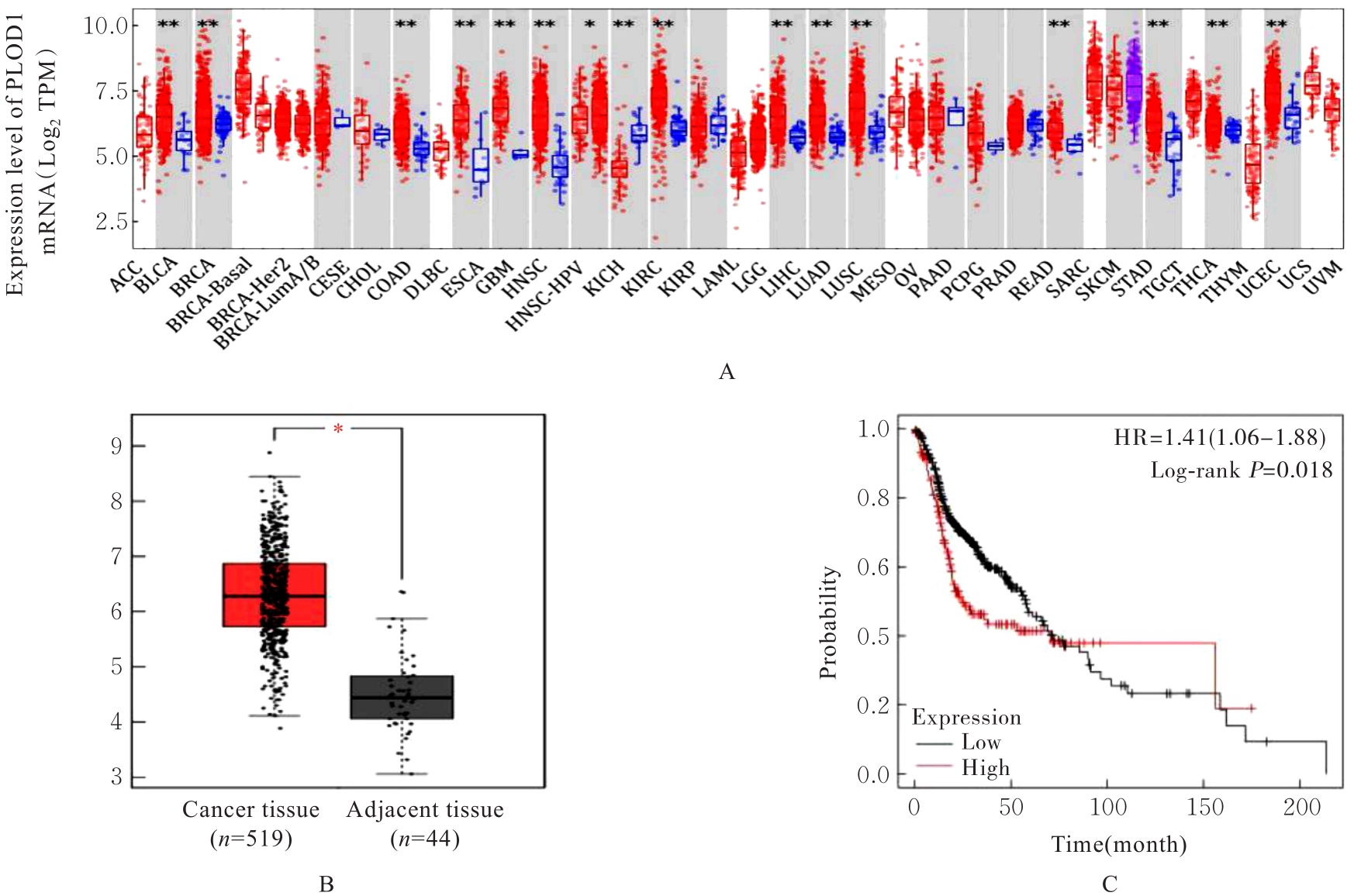
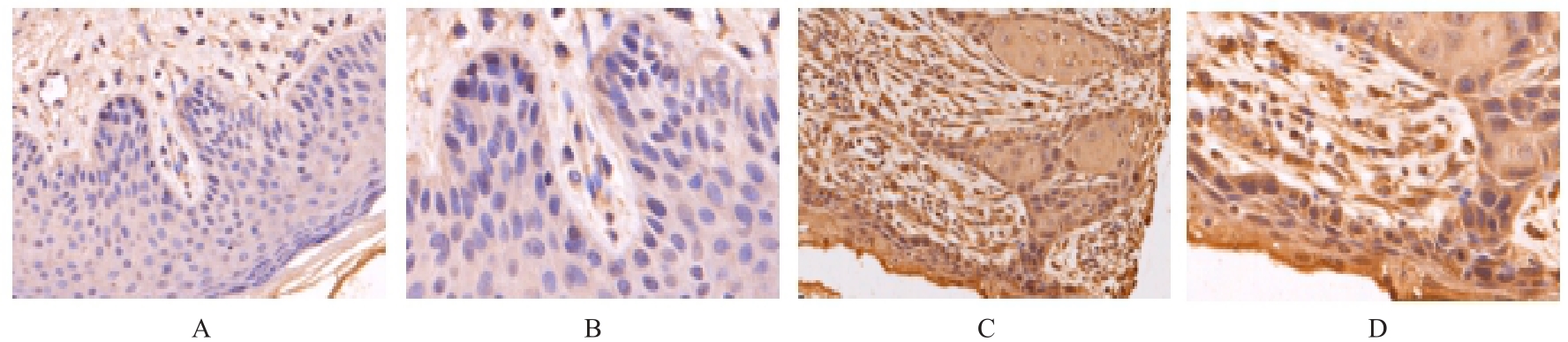
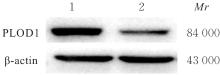
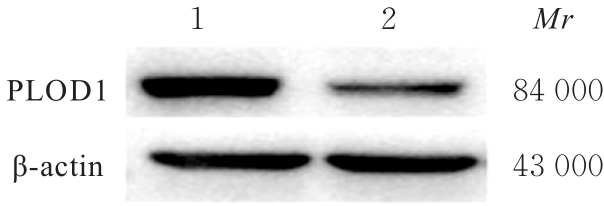
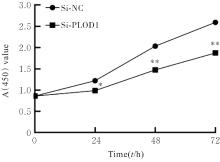
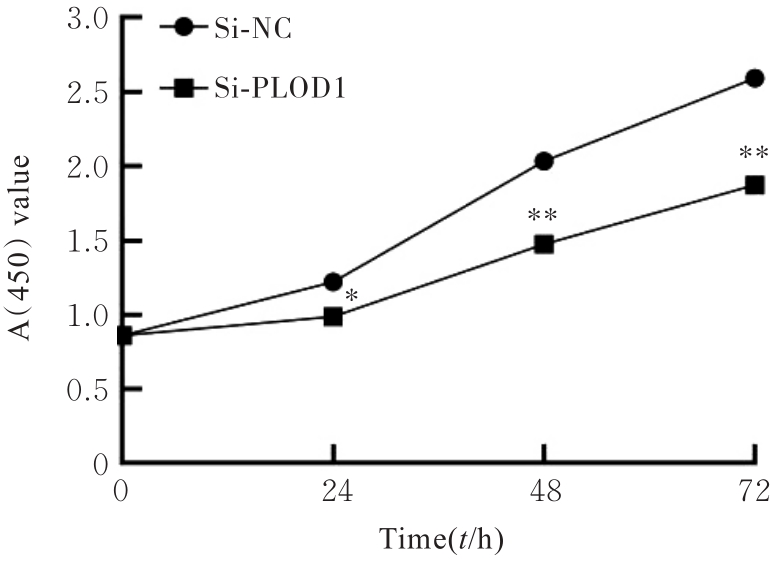
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 1035-1043.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240418
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Expressions of PLOD1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue and cells and their significances
Chaojie GUO,Jiajia ZHANG,Jie ZENG,Huiyu WANG, AIERFATI·Aimaier,Jiang XU( )
)
- Department of Stomatology,First Affiliated Hospital,Shihezi University,Shihezi 832000,China
-
Received:2023-10-11Online:2024-07-28Published:2024-08-01 -
Contact:Jiang XU E-mail:1437759520@qq.com
CLC Number:
- R739.8
Cite this article
Chaojie GUO,Jiajia ZHANG,Jie ZENG,Huiyu WANG, AIERFATI·Aimaier,Jiang XU. Expressions of PLOD1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue and cells and their significances[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1035-1043.
share this article
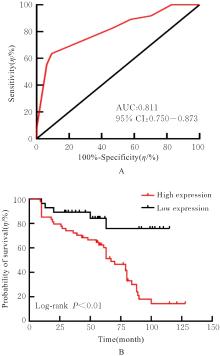
Tab. 3
Expression intensities of PLOD1 protein in cancer tissue of OSCC patients with different clinicopathological characteristics"
Clinicopathological characteristic | n | PLOD1 | χ2 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High expression | Low expression | ||||
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 54 | 34 | 20 | 0.429 | 0.512 |
| Female | 56 | 36 | 20 | ||
| Age(year) | |||||
| <65 | 34 | 22 | 12 | 0.024 | 0.876 |
| ≥65 | 76 | 48 | 28 | ||
| Differentiation | |||||
| Well | 90 | 53 | 37 | 3.756 | 0.053 |
| Moderate/Poor | 20 | 17 | 3 | ||
| T stage | |||||
| T1-T2 | 64 | 35 | 29 | 5.296 | 0.021 |
| T3-T4 | 46 | 35 | 11 | ||
| Node | |||||
| N0 | 94 | 57 | 37 | 1.699 | 0.173 |
| N1-N2 | 16 | 13 | 3 | ||
| TNM stage | |||||
| Ⅰ-Ⅱ | 63 | 33 | 30 | 8.072 | 0.004 |
| Ⅲ-Ⅳ | 47 | 37 | 10 | ||
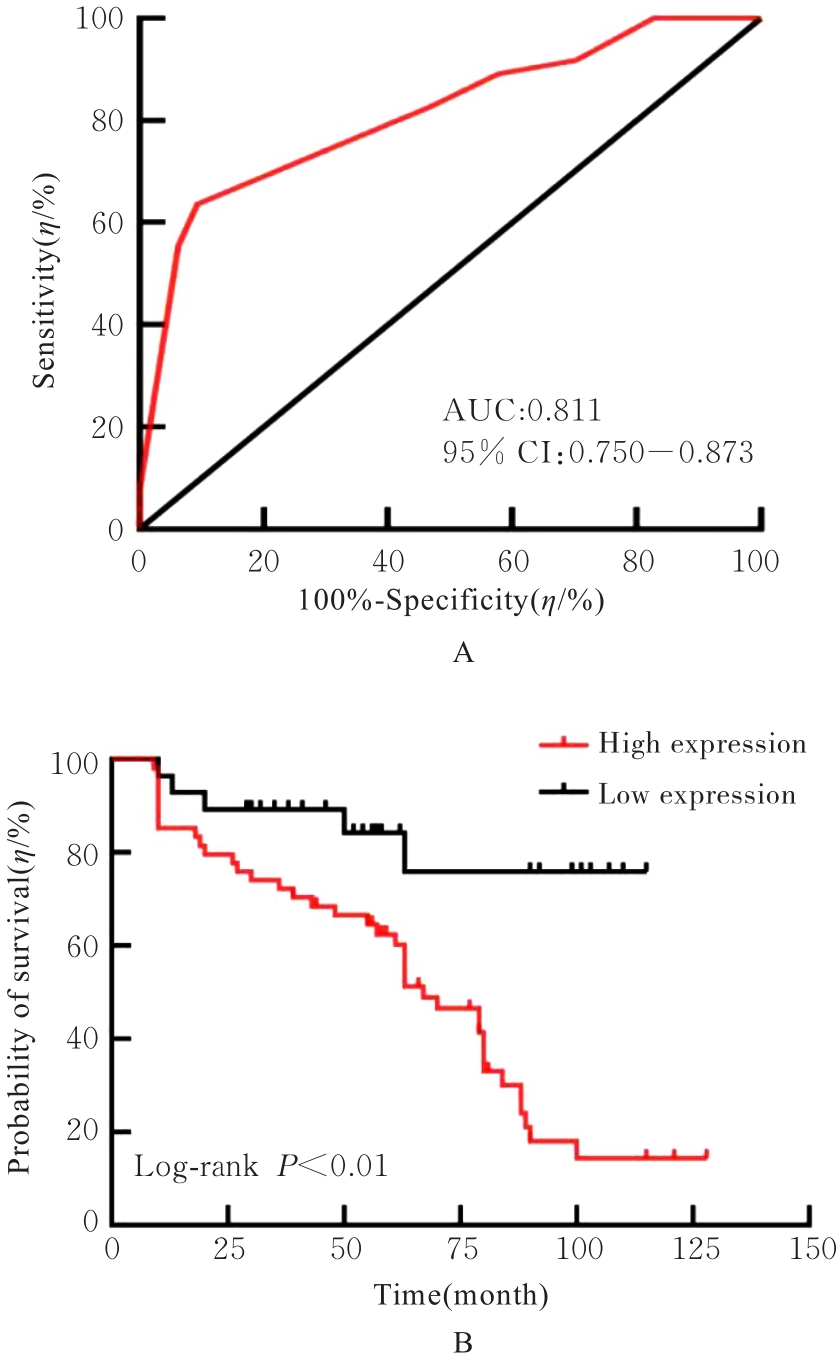
Tab. 4
Univariate and multivariate survival analysis in OSCC patients"
| Clinicopathological characteristic | HR | 95% CI | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate analysis | |||
| Gender (female vs male) | 0.615 | 0.335-1.128 | 0.116 |
| Age (≥65 years old vs <65 years old) | 0.807 | 0.435-1.500 | 0.498 |
| Differentiation (moderate/poor vs well) | 0.555 | 0.278-1.110 | 0.096 |
| Lymph node metastasis (positive vs negative) | 1.587 | 0.781-3.226 | 0.202 |
| T stage (T3-T4 vs T1-T2) | 1.890 | 1.037-3.445 | 0.038 |
| TNM stage (Ⅲ-Ⅳ vs Ⅰ-Ⅱ) | 2.184 | 1.193-3.998 | 0.011 |
| PLOD1 (high expression vs low expression) | 4.357 | 1.706-11.129 | 0.002 |
| Multivariate analysis | |||
| T stage (T3-T4 vs T1-T2) | 0.307 | 0.069-1.370 | 0.122 |
| TNM stage (Ⅲ-Ⅳ vs Ⅰ-Ⅱ) | 4.108 | 0.893-18.902 | 0.070 |
| PLOD1 (high expression vs low expression) | 3.695 | 1.340-10.189 | 0.012 |
| 1 | BUGSHAN A, FAROOQ I. Oral squamous cell carcinoma: metastasis, potentially associated malignant disorders, etiology and recent advancements in diagnosis[J]. F1000Res, 2020, 9: 229. |
| 2 | AUPÉRIN A. Epidemiology of head and neck cancers: an update[J]. Curr Opin Oncol, 2020, 32(3): 178-186. |
| 3 | SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. |
| 4 | QI Y F, XU R. Roles of PLODs in collagen synthesis and cancer progression[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2018, 6: 66. |
| 5 | FOY M, MÉTAY C, FRANK M, et al. A severe case of PLOD1-related kyphoscoliotic Ehlers-Danlos syndrome associated with several arterial and venous complications: a case report[J]. Clin Case Rep, 2023, 11(2): e6760. |
| 6 | QI Q, HUANG W H, ZHANG H, et al. Bioinformatic analysis of PLOD family member expression and prognostic value in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Transl Cancer Res, 2021, 10(6): 2707-2724. |
| 7 | 何 平, 何成彦, 郑 岩, 等. PLOD1在结直肠癌组织中的表达及意义[J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2023, 27(3): 273-275. |
| 8 | ZHANG J, TIAN Y Z, MO S J, et al. Overexpressing PLOD family genes predict poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer[J]. Int J Gen Med, 2022, 15: 3077-3096. |
| 9 | LI T, FAN J, WANG B, et al. TIMER: a web server for comprehensive analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells[J]. Cancer Res, 2017, 77(21): e108-e110. |
| 10 | LI C W, TANG Z F, ZHANG W J, et al. GEPIA2021: integrating multiple deconvolution-based analysis into GEPIA[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2021, 49(W1): W242-W246. |
| 11 | NAGY Á, MUNKÁCSY G, GYŐRFFY B. Pancancer survival analysis of cancer hallmark genes[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 6047. |
| 12 | CHEN Y L, GUO H F, TERAJIMA M, et al. Lysyl hydroxylase 2 is secreted by tumor cells and can modify collagen in the extracellular space[J]. J Biol Chem, 2016, 291(50): 25799-25808. |
| 13 | SUN Y W, WANG S, ZHANG X W, et al. Identification and validation of PLOD2 as an adverse prognostic biomarker for oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Biomolecules, 2021, 11(12): 1842. |
| 14 | 邝新红, 卫晓慧, 孙 立, 等. 胶原翻译后修饰酶与肿瘤关系的研究进展[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2016, 43(12): 1085-1089. |
| 15 | GUO T, GU C, LI B, et al. PLODs are overexpressed in ovarian cancer and are associated with gap junctions via connexin 43[J]. Lab Invest, 2021, 101(5): 564-569. |
| 16 | CHEN R, JIANG M, HU B, et al. Comprehensive analysis of the expression, prognosis, and biological significance of PLOD family in bladder cancer[J]. Int J Gen Med, 2023, 16: 707-722. |
| 17 | 田堰鑫, 李 娜, 高 雷, 等. 肿瘤微环境与肝癌干细胞相互作用对肝细胞癌发生发展的影响[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2023, 39(3): 684-692. |
| 18 | WANG Z L, SHI Y P, YING C T, et al. Hypoxia-induced PLOD1 overexpression contributes to the malignant phenotype of glioblastoma via NF-κB signaling[J]. Oncogene, 2021, 40(8): 1458-1475. |
| 19 | YAMADA Y, KATO M, ARAI T, et al. Aberrantly expressed PLOD1 promotes cancer aggressiveness in bladder cancer: a potential prognostic marker and therapeutic target[J]. Mol Oncol, 2019, 13(9): 1898-1912. |
| 20 | XU F S, GUAN Y B, XUE L, et al. The effect of a novel glycolysis-related gene signature on progression, prognosis and immune microenvironment of renal cell carcinoma[J]. BMC Cancer, 2020, 20(1): 1207. |
| 21 | NOOROLYAI S, SHAJARI N, BAGHBANI E, et al. The relation between PI3K/AKT signalling pathway and cancer[J]. Gene, 2019, 698: 120-128. |
| 22 | AOKI M, FUJISHITA T. Oncogenic roles of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR axis[J]. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol, 2017, 407: 153-189. |
| 23 | 符良斌, 廖天安, 王 鸿, 等. TGF-β1对人舌鳞状细胞癌上皮-间质转化的诱导作用及其对PI3K/AKT信号通路的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2015, 41(4): 790-793. |
| 24 | ZHANG Y X, WU Y J, SU X B. PLOD1 promotes cell growth and aerobic glycolysis by regulating the SOX9/PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in gastric cancer[J]. Front Biosci, 2021, 26(8): 322-334. |
| [1] | Hua CHEN,Na SHA,Ning LIU,Yang LI,Haijun HU. Effect of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on biological behavior of human liposarcoma SW872 cells through YAP [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1000-1008. |
| [2] | Yongjing YANG,Tianyang KE,Shixin LIU,Xue WANG,Dequan XU,Tingting LIU,Ling ZHAO. Synergistic sensitization of apatinib mesylate and radiotherapy on hepatocarcinoma cells invitro [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1009-1015. |
| [3] | Yuanguo WANG,Peng ZHANG. Bioinformatics analysis based on relationship between SSP1 and TGFB1 and occurrence, prognosis, and immune invasion of esophageal adenocarcinoma [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1076-1086. |
| [4] | Yilin REN,Yichen ZANG,Lele XUE,Kaige YANG,Sufang CHEN,Weinan WANG,Chenghua LUO,Weihua LIANG,Lianghai WANG,Feng LI,Jianming HU. Bioinformatics analysis based on effect of M2 macrophage-derived Siglec15 on malignant biological behaviour of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells and its experimental validation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 881-890. |
| [5] | Guoxing YU,Xin ZHANG,Hengwei DU,Bingjie CUI,Na GAO,Cuilan LIU,Jing DU. Effect of urolithin C on proliferation, apoptosis and autophagy of human acute myeloid leukemia HL-60 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 908-916. |
| [6] | Shan CAO,Yijia ZHANG,Yang BAI,Fang CHEN,Sha XIE,Qianqian HAN. Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro experimental verification based on anti-atherosclerosis mechanism of Xiaoban Tongmai Formula [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 925-938. |
| [7] | Yuan WANG,Zhijuan WANG,Mingshu ZHANG,Yihui WANG,Qing ZHANG,Liping YE. Effects of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 on invasion and migration of lung cancer A549 and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 666-675. |
| [8] | Yiyan YU,Zhimin ZHANG,Jiawen CHEN,Xin LIU,Yan LI,Hongyan ZHAO. Research progress in relationship between macrophage polarization and oral diseases [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 864-871. |
| [9] | Shuang CHEN,Hong LI. Effect of silencing FOXK1 gene on proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer HGC-27 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 371-378. |
| [10] | Yueying SONG,Chao GAO,Wenjun CHEN,Aiyu SHAO,Yichun QIAO,Zhuolin LI. Screening of miRNAs related to prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer and its gene network based on TCGA Database [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 392-399. |
| [11] | Huijuan SONG,Zhenhua XU,Dongning HE. Effect of apolipoprotein C1 expression on proliferation and apoptosis of human liver cancer HepG2 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 128-135. |
| [12] | Yanhong WEI,Chenxue YANG,Guangmin YANG,Shuai SONG,Ming LI,Haijiao YANG,Haifeng WEI. Inhibitory effect of downregulating HMGB2 expression on epithelial-mesenchymal transition of liver cancer LM3 cells and its AKT/mTOR signaling pathway mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 143-149. |
| [13] | Jie ZENG,Xueyan YU,Ting LUO,Jiang XU. Effect of PD-L1 on proliferation, migration, and invasion of human oral squamous carcinoma cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 18-24. |
| [14] | Jia ZHOU,Zhidong QIU,Zhe LIN,Guangfu LYU,Jiaming XU,He LIN,Kexin WANG,Yuchen WANG,Xiaowei HUANG. Effect of chelerythrine on migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human ovarian cancer SKOV3 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 25-32. |
| [15] | Yuxue SUN,Ziqiang LIU,Hao WU,Liming ZHAO,Tao GAO,Haiyan HUANG,Chaoyue LI. Inhibitory effect of berberine on migration and invasion of human glioma T98G cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 50-57. |
|