Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 1016-1025.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240416
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Barrier function of PPC/PBS composite biofilm and its osteogenetic effect on tibial bone defect models of rabbits
Ye TIAN,Xiaolu SHI,Shaobo ZHAI,Yang LIU,Zheng YANG,Yuchuan WU,Shunli CHU( )
)
- Department of Prosthodontics,Stomatology Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
-
Received:2023-09-28Online:2024-07-28Published:2024-08-01 -
Contact:Shunli CHU E-mail:chusl@jlu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
- R783.1
Cite this article
Ye TIAN,Xiaolu SHI,Shaobo ZHAI,Yang LIU,Zheng YANG,Yuchuan WU,Shunli CHU. Barrier function of PPC/PBS composite biofilm and its osteogenetic effect on tibial bone defect models of rabbits[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1016-1025.
share this article
Tab.1
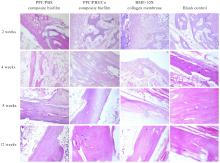
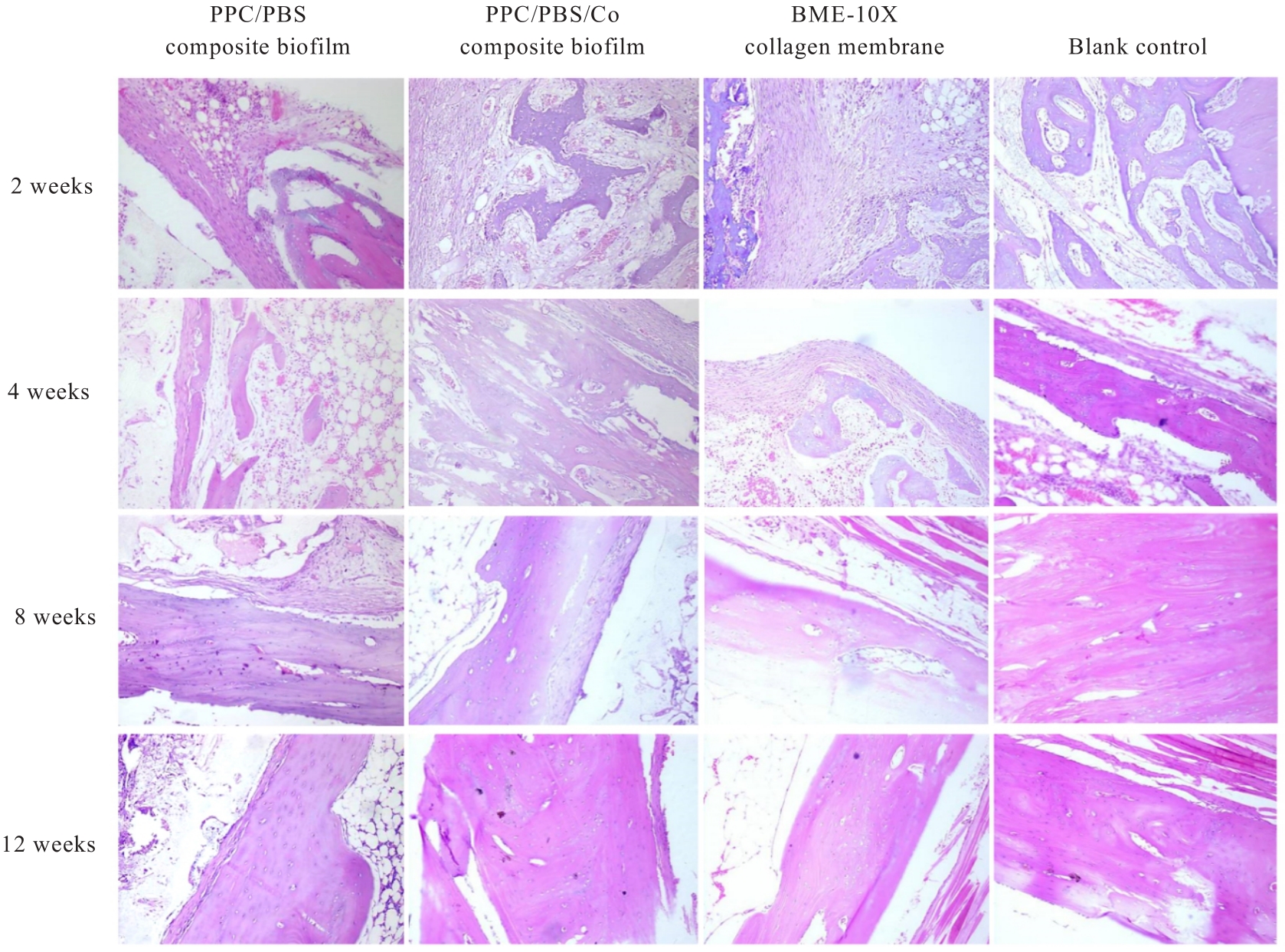
Gray values of regenerated bone in bone defect areas of rabbits in various groups at different time points"
| Group | Gray value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (week) 2 | 4 | 8 | 12 | |
| Blank control | 1 698.00±369.90 | 2 035.00±201.75 | 2 838.00±119.40 | 4 121.50±119.72 |
| PPC/PBS composite biofilm | 1 163.28±542.04 | 1 890.80±394.54 | 2 600.00±130.00# | 4 183.50±29.18# |
| BME-10X collagen membrane | 1 124.80±356.24 | 1 816.67±217.15 | 2 161.25±108.06 | 3 664.67±108.17 |
| PPC/PBS/Co composite biofilm | 1 674.00±437.97△# | 2 147.00±360.17△# | 2 776.33±138.82△# | 4 552.50±120.00*△# |
Tab.2
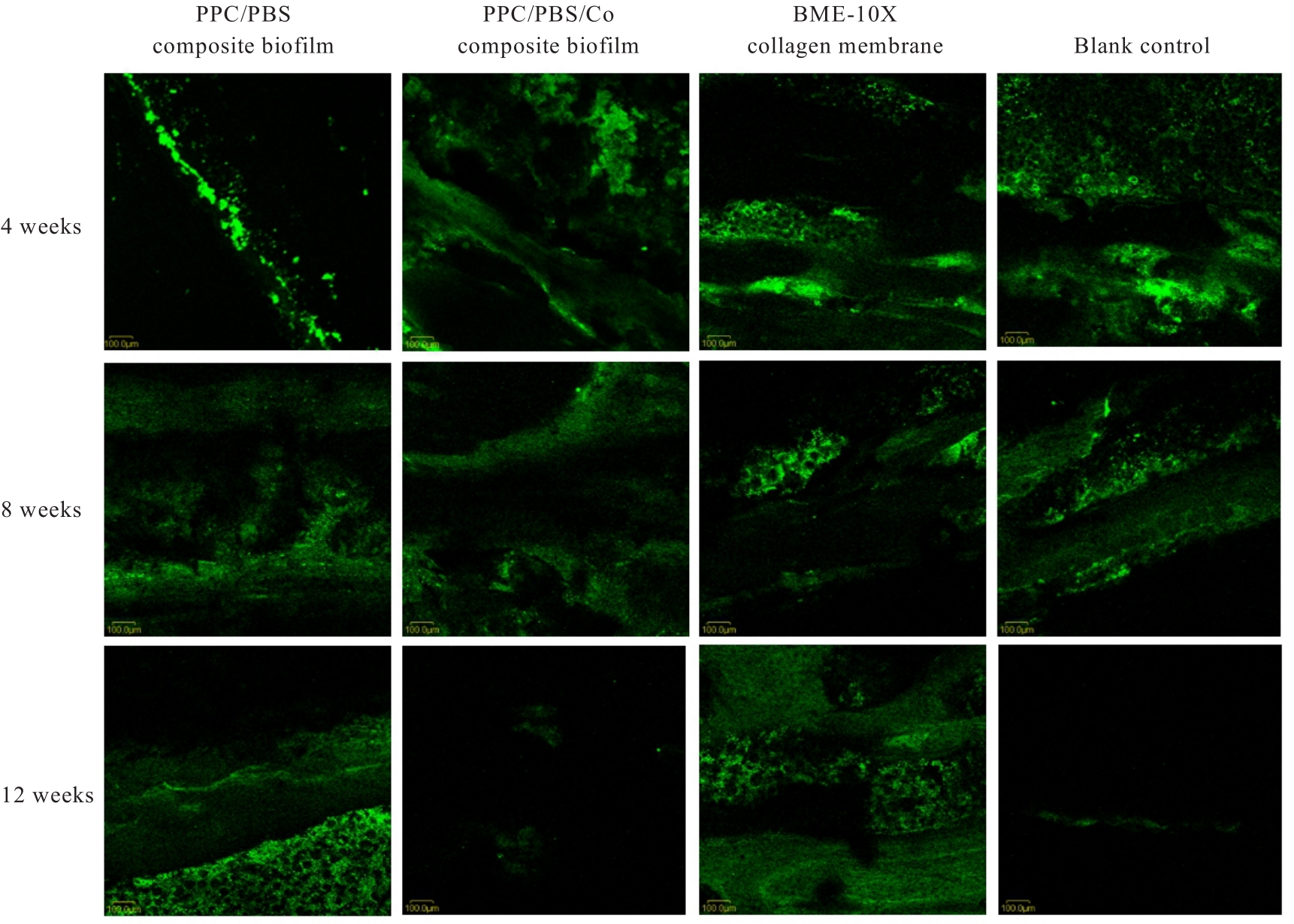
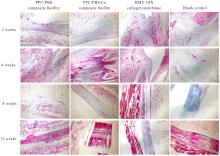
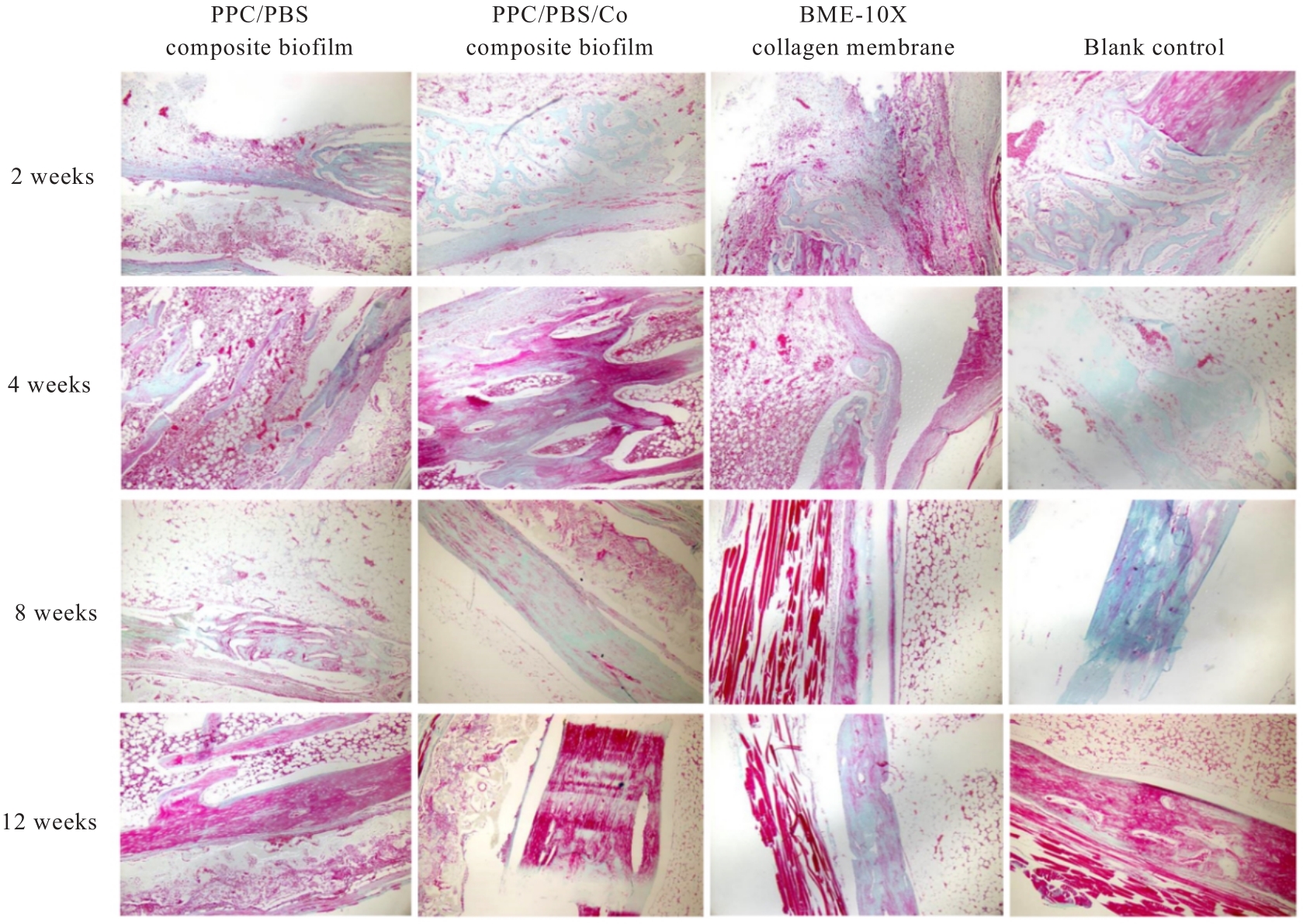
Fluorescence intensities of regenerated bone tissue in bone defect areas of rabbits in various groups at different time points"
| Group | Fluorescence intensity | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (week) 4 | 8 | 12 | |
| Blank control | 25 608.67±619.50 | 22 252.00±1 263.00 | 2 531.00±127.00 |
| PPC/PBS composite biofilm | 13 720.00±1 350.65* | 28 219.00±1 411.00* | 12 078.00±604.00* |
| BME-10X collagen membrane | 14 677.67±733.50* | 33 514.00±1 676.00* | 19 940.00±997.00* |
| PPC/PBS/Co composite biofilm | 24 000.00±1 200.00△# | 21 042.00±1 052.00△# | 2 673.67±234.07△# |
Tab.3
Expression levels of BMP-2 and OPN proteins in regenerated bone tissue in bone defect areas of rabbits in various groups at different time points"
| Group | BMP-2 protein | OPN protein | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (week) 2 | 4 | 2 | 4 | |
| Blank control | 53.596±2.680 | 80.978±4.049 | 44.353±2.218 | 42.249±2.112 |
| PPC/PBS composite biofilm | 42.503±2.125 | 69.348±3.467 | 27.633±1.382 | 50.841±2.542 |
| BME-10X collagen membrane | 0.000±0.000*△ | 22.787±1.139*△ | 17.440±0.872*△ | 35.833±1.792*△ |
| PPC/PBS/Co composite biofilm | 99.288±5.215*△# | 168.271±8.414*△# | 57.961±2.898*△# | 74.972±3.749*△# |
| 1 | ALLAN B, RUAN R, LANDAO-BASSONGA E, et al. Collagen membrane for guided bone regeneration in dental and orthopedic applications[J]. Tissue Eng Part A, 2021, 27(5/6): 372-381. |
| 2 | KOFINA V, MONFAREDZADEH M, RAWAL S Y, et al. Patient-reported outcomes following guided bone regeneration: correlation with clinical parameters[J]. J Dent, 2023, 136: 104605. |
| 3 | SANZ-SÁNCHEZ I, SANZ-MARTÍN I, ORTIZ-VIGÓN A, et al. Complications in bone-grafting procedures: classification and management[J]. Periodontol 2000, 2022, 88(1): 86-102. |
| 4 | XIE Y, LI S H, ZHANG T X, et al. Titanium mesh for bone augmentation in oral implantology: current application and progress[J]. Int J Oral Sci, 2020, 12(1): 37. |
| 5 | JUNG N, PARK J, PARK S H, et al. Improving bone formation by guided bone regeneration using a collagen membrane with rhBMP-2: a novel concept[J]. J Funct Biomater, 2023,14(3): 170. |
| 6 | MERAW S J, REEVE C M, LOHSE C M, et al. Treatment of peri-implant defects with combination growth factor cement[J]. J Periodontol, 2000, 71(1):8-13. |
| 7 | KU J K, UM I W, JUN M K, et al. Dentin-derived-barrier membrane in guided bone regeneration: a case report[J]. Materials, 2021, 14(9): 2166. |
| 8 | LINDNER C, ALKILDANI S, STOJANOVIC S, et al. In vivo biocompatibility analysis of a novel barrier membrane based on bovine dermis-derived collagen for guided bone regeneration (GBR)[J]. Membranes, 2022, 12(4): 378. |
| 9 | VERMA N K, KAR A K, SINGH A, et al. Control release of adenosine potentiate osteogenic differentiation within a bone integrative EGCG-g-NOCC/collagen composite scaffold toward guided bone regeneration in a critical-sized calvarial defect[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2021, 22(7): 3069-3083. |
| 10 | ARPITHA M, TEWARI S, SANGWAN, et al. Efficacy of mixture of injectable-platelet-rich fibrin and type-1 collagen particles on the closure of through-and-through periapical bone defects: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Int Endod J, 2023, 56(10): 1197-1211. |
| 11 | 闵少雄, 靳安民, 童斌辉, 等. 不同孔径的PDLLA/HA填充材料修复长骨缺损实验研究[J]. 骨与关节损伤杂志, 2003, 18(8): 542-545. |
| 12 | JUNG O, HESSE B, STOJANOVIC S, et al. Biocompatibility analyses of HF-passivated magnesium screws for guided bone regeneration (GBR)[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(22): 12567. |
| 13 | KIM K, SU Y C, KUCINE A J, et al. Guided bone regeneration using barrier membrane in dental applications[J]. ACS Biomater Sci Eng, 2023, 9(10): 5457-5478. |
| 14 | NIU H Y, MA Y F, WU G Y, et al. Multicellularity-interweaved bone regeneration of BMP-2-loaded scaffold with orchestrated kinetics of resorption and osteogenesis[J]. Biomaterials, 2019, 216: 119216. |
| 15 | ULLAH I, HUSSAIN Z, ULLAH S, et al. An osteogenic, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory nanocomposite hydrogel platform to accelerate bone reconstruction[J]. J Mater Chem B, 2023, 11(25):5830-5845. |
| [1] | Xiaolu SHI,Ye TIAN,Shaobo ZHAI,Yang LIU,Shunli CHU. Preparation of PPC/PBS-based guided bone regeneration membrane and evaluation of its physiochemical properties and biological characteristics [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1473-1483. |
| [2] | Degeng XIA,Qingyu ZHANG,Junjun JIAO,Tingrui XU,Tianyi ZHANG,Yang ZHONG,Zhulan ZHAO,Ning MA,Li ZHANG. Multidisciplinary aesthetic restoration of anterior dental area of patient with failed treatment experience: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 1058-1064. |
| [3] | Zhulan ZHAO,Qingyu ZHANG,Degeng XIA,Yang ZHONG,Tianyi ZHANG,Yu HUANG,Li ZHANG,Ning MA. Clinical repair effect of combined orthodontic treatment with implant prosthesis in severe invasive periodontitis:A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1292-1297. |
| [4] | HUANG Yu, ZHAO Zhulan, ZHONG Yang, XU Lishuo, LIU Chenguang, MA Ning, ZHANG Li. Soft tissue augmentation and bone regeneration combined with immediate implantation of patient with severe chronic periodontitis:A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 1082-1086. |
| [5] | CHEN Chen, HAN Qing, CHEN Bingpeng, WANG Chenyu, ZHANG Kesong, YANG Kerong, WANG Jincheng. Application of individualized semi-shoulder prosthesis for proximal humerus reconstruction under assistance of 3D printing technology [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(03): 614-620. |
| [6] | JIAO Peng, CHEN Fei, JIN Quan, CHEN Nannan, ZHANG Li, MA Ning. Comprehensive treatment of anterior esthetic zone in patient with loosening and falling of teeth induced by severe periodontitis: A case reeport and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(02): 421-424. |
| [7] | CHEN Fei, SHI Jinxian, JIAO Peng, JIN Quan, XU Lishuo, ZHANG Li, MA Ning. Periodontal surgical treatment in patient with residual root and crown of anterior teeth induced by unfitting prosthesis: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(01): 170-174. |
| [8] | CHE Hongze, CHE Yanhai, LU Qing, CHEN Nannan, CHEN Fei, JIN Quan, MA Ning. Repair effect of nHA-Mg porous composite materials modified by PLGA on jaw bone defect of rabbits [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(02): 276-280. |
| [9] | ZHU Yang, LI Daowei, FANG Tengjiaozi, SHI Ce, WANG Dandan, SUN Hongchen. Promotive effect of PLGA nanofiber scaffold adsorped Epo gene mediated by adenovirus on bone defect repair [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(04): 711-715. |
| [10] | LIU Rui,LI Ming-he,JI Xin,HAN Cheng-min. Evaluation on biocompatibility of carbon-fiber-reinforced polyether-ether-ketone after implantation in rabbit models with single bone cortex defect of mandibula [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2014, 40(03): 569-573. |
| [11] | GAO Xin,HE Zhong-qin,WANG Cheng-kun,ZHANG Zhi-min,WANG Zhi-gang,ZHONG Cheng,OUYANG Jie. Physicochemical characteristics of calcinated bone ceramics used for bone defects repair [J]. J4, 2009, 35(1): 138-141. |
|