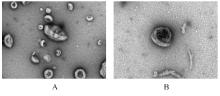
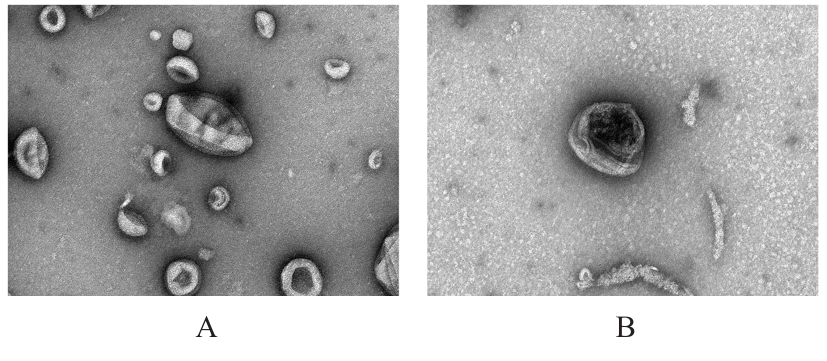
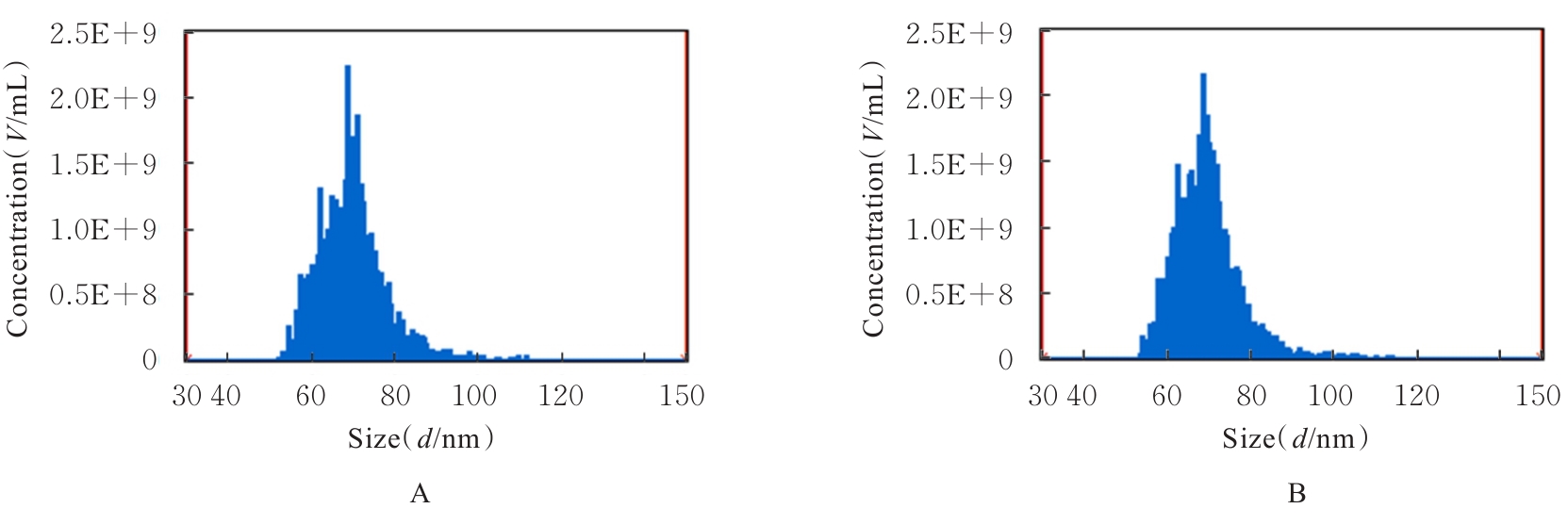
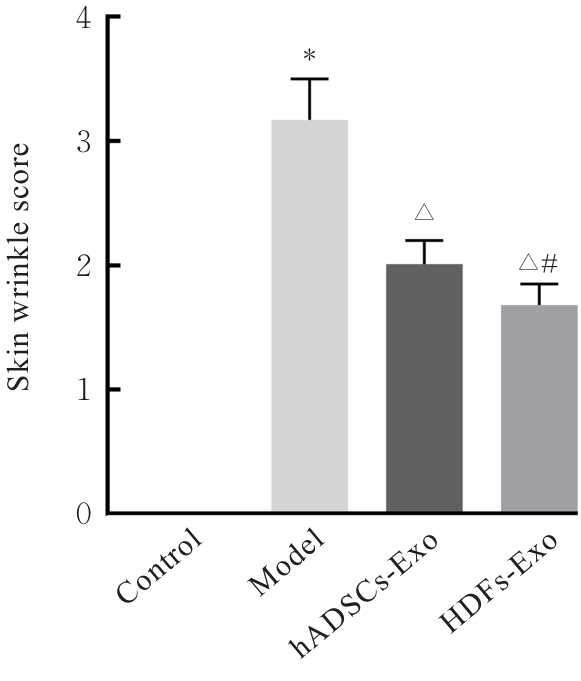
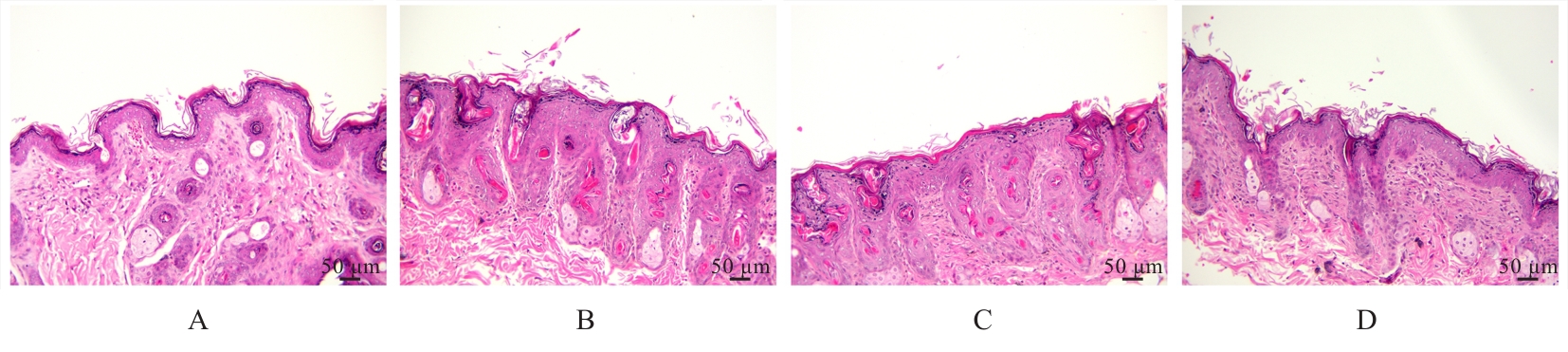
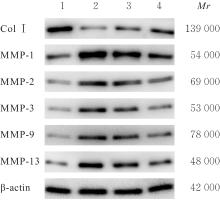
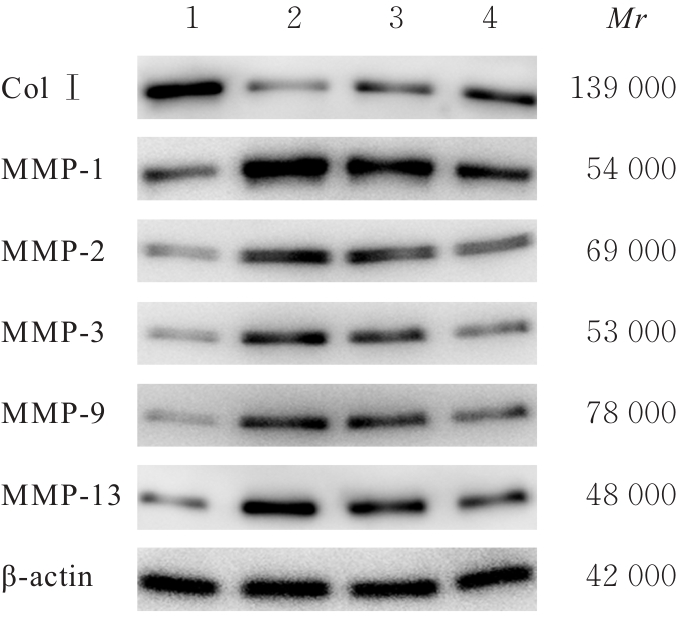
| [1] |
BERRY K, HALLOCK K, LAM C. Photoaging and topical rejuvenation[J]. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am, 2022, 30(3): 291-300.
|
| [2] |
SALMINEN A, KAARNIRANTA K, KAUPPINEN A. Photoaging: UV radiation-induced inflammation and immunosuppression accelerate the aging process in the skin[J]. Inflamm Res, 2022, 71(7/8): 817-831.
|
| [3] |
CALVO M J, NAVARRO C, DURÁN P, et al. Antioxidants in photoaging: from molecular insights to clinical applications[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25(4): 2403.
|
| [4] |
唐秋月, 车启蕾, 瓦庆彪. 皮秒激光治疗面部光老化的应用进展[J]. 中国医疗美容, 2022, 12(10): 91-95.
|
| [5] |
ARYA S B, COLLIE S P, PARENT C A. The ins-and-outs of exosome biogenesis, secretion, and internalization[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2024, 34(2): 90-108.
|
| [6] |
HAJIALIASGARY NAJAFABADI A, SOHEILIFAR M H, MASOUDI-KHORAM N. Exosomes in skin photoaging: biological functions and therapeutic opportunity[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2024, 22(1): 32.
|
| [7] |
NGUYEN D D N, VU D M, VO N, et al. Skin rejuvenation and photoaging protection using adipose-derived stem cell extracellular vesicles loaded with exogenous cargos[J]. Skin Res Technol, 2024, 30(2): e13599.
|
| [8] |
PARK A Y, LEE J O, JANG Y, et al. Exosomes derived from human dermal fibroblasts protect against UVB-induced skin photoaging[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2023, 52(6): 120.
|
| [9] |
王 倩, 万品文, 曹丽楠, 等. 人参皂苷Rbl对小鼠皮肤光老化氧化应激的改善作用[J]. 广州中医药大学学报, 2021, 38(11): 2479-2484.
|
| [10] |
ZHOU C C, ZHANG B Y, YANG Y Q, et al. Stem cell-derived exosomes: emerging therapeutic opportunities for wound healing[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2023, 14(1): 107.
|
| [11] |
VYAS K S, KAUFMAN J, MUNAVALLI G S, et al. Exosomes: the latest in regenerative aesthetics[J]. Regen Med, 2023, 18(2): 181-194.
|
| [12] |
LIANG J X, LIAO X, LI S H, et al. Antiaging properties of exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in photoaged rat skin[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020: 6406395.
|
| [13] |
HU S Q, LI Z H, CORES J, et al. Needle-free injection of exosomes derived from human dermal fibroblast spheroids ameliorates skin photoaging[J]. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(10): 11273-11282.
|
| [14] |
YAN T T, HUANG L N, YAN Y L, et al. MAPK/AP-1 signaling pathway is involved in the protection mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes against ultraviolet-induced photoaging in human dermal fibroblasts[J]. Skin Pharmacol Physiol, 2023, 36(2): 98-106.
|
| [15] |
ZHANG Q, QIAO S Y, YANG C S, et al. Nuclear factor-kappa B and effector molecules in photoaging[J]. Cutan Ocul Toxicol, 2022, 41(2): 187-193.
|
| [16] |
TANG S C, HSIAO Y P, KO J L. Genistein protects against ultraviolet B-induced wrinkling and photoinflammation in in vitro and in vivo models[J]. Genes Nutr, 2022, 17(1): 4.
|
| [17] |
孙在峥, 曹惠妍, 马 伟, 等. 十精丸对光老化大鼠皮肤LCs及炎症因子水平影响的研究[J]. 中国美容医学, 2024, 33(2): 51-55.
|
| [18] |
GENG R X, KANG S G, HUANG K L, et al. α-Ionone protects against UVB-induced photoaging in epidermal keratinocytes[J]. Chin Herb Med, 2022, 15(1): 132-138.
|
| [19] |
BANG E, KIM D H, CHUNG H Y. Protease-activated receptor 2 induces ROS-mediated inflammation through Akt-mediated NF-κB and FoxO6 modulation during skin photoaging[J]. Redox Biol, 2021, 44: 102022.
|
| [20] |
CUI B N, WANG Y, JIN J H, et al. Resveratrol treats UVB-induced photoaging by anti-MMP expression, through anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antiapoptotic properties, and treats photoaging by upregulating VEGF-B expression[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2022, 2022: 6037303.
|
| [21] |
PITTAYAPRUEK P, MEEPHANSAN J, PRAPAPAN O, et al. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in photoaging and photocarcinogenesis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2016, 17(6): 868.
|
| [22] |
LOCKHART-CAIRNS M P, NEWANDEE H, THOMSON J, et al. Transglutaminase-mediated cross-linking of tropoelastin to fibrillin stabilises the elastin precursor prior to elastic fibre assembly[J]. J Mol Biol, 2020, 432(21): 5736-5751.
|