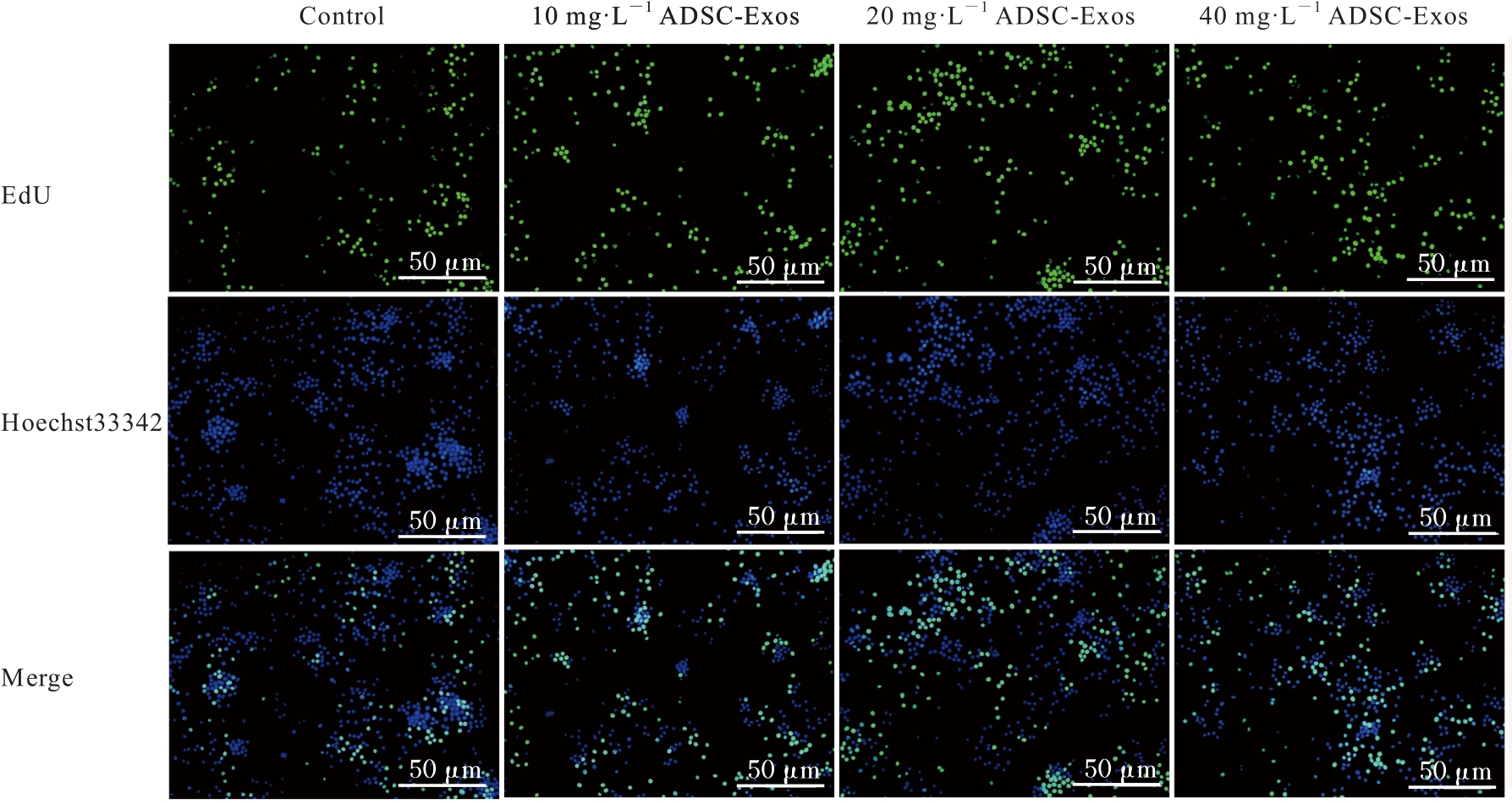
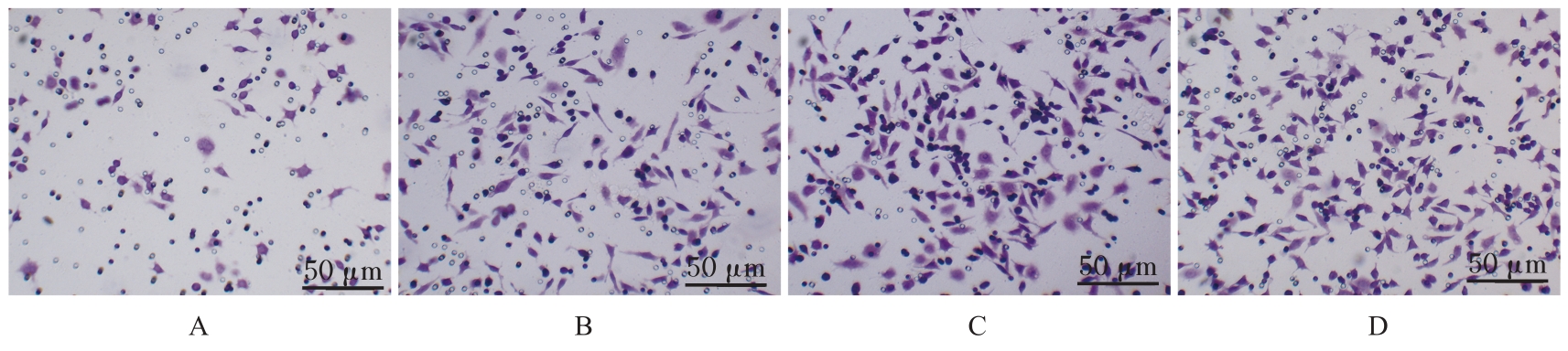
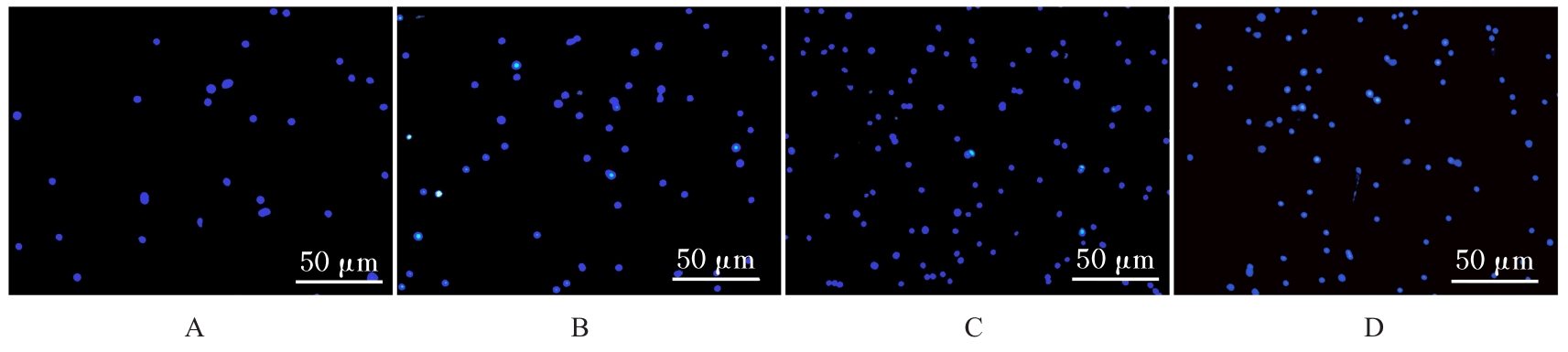
| 1 |
BELLEI B, MIGLIANO E, PICARDO M. Research update of adipose tissue-based therapies in regenerative dermatology[J]. Stem Cell Rev Rep, 2022, 18(6): 1956-1973.
|
| 2 |
ZHAO H B, CHEN W, CHEN J L, et al. ADSCs promote tenocyte proliferation by reducing the methylation level of lncRNA Morf4l1 in tendon injury[J]. Front Chem, 2022, 10: 908312.
|
| 3 |
LIU C Y, YIN G, SUN Y D, et al. Effect of exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells on the apoptosis of Schwann cells in peripheral nerve injury[J]. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2020, 26(2): 189-196.
|
| 4 |
ZHU H F, WU X Y, LIU R, et al. ECM-inspired hydrogels with ADSCs encapsulation for rheumatoid arthritis treatment[J]. Adv Sci, 2023, 10(9): e2206253.
|
| 5 |
RAU C S, KUO P J, WU S C, et al. Enhanced nerve regeneration by exosomes secreted by adipose-derived stem cells with or without FK506 stimulation[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(16): 8545.
|
| 6 |
SHAPOURI-MOGHADDAM A, MOHAMMADIAN S, VAZINI H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2018, 233(9): 6425-6440.
|
| 7 |
GAO W J, LIU J X, LIU M N, et al. Macrophage 3D migration: a potential therapeutic target for inflammation and deleterious progression in diseases[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2021, 167: 105563.
|
| 8 |
LEY K, MILLER Y I, HEDRICK C C. Monocyte and macrophage dynamics during atherogenesis[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2011, 31(7): 1506-1516.
|
| 9 |
ZOU Y, ZHANG J Q, XU J W, et al. SIRT6 inhibition delays peripheral nerve recovery by suppressing migration, phagocytosis and M2-polarization of macrophages[J]. Cell Biosci, 2021, 11(1): 210.
|
| 10 |
ZHANG L, JIAO G J, REN S W, et al. Exosomes from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells enhance fracture healing through the promotion of osteogenesis and angiogenesis in a rat model of nonunion[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2020, 11(1): 38.
|
| 11 |
WANG Y, SU J, FU D H, et al. The role of YB1 in renal cell carcinoma cell adhesion[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2018, 15(12): 1304-1311.
|
| 12 |
李大伟, 张析哲, 周 琪. 雪旺细胞对周围神经损伤修复作用的研究进展[J]. 临床医药文献电子杂志, 2019, 6(5): 197-198.
|
| 13 |
LI Y M, LI D Y, YOU L, et al. dCas9-based PDGFR-β activation ADSCs accelerate wound healing in diabetic mice through angiogenesis and ECM remodeling[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(6): 5949.
|
| 14 |
ZAREI F, ABBASZADEH A. Application of cell therapy for anti-aging facial skin[J]. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther, 2019, 14(3): 244-248.
|
| 15 |
张雅群, 付 丽, 任译延, 等. 大鼠脂肪间充质干细胞的分离、培养及其向少突胶质前体细胞的诱导分化[J]. 解剖学报, 2022, 53(5): 557-562.
|
| 16 |
CHEN J, REN S, DUSCHER D, et al. Exosomes from human adipose-derived stem cells promote sciatic nerve regeneration via optimizing Schwann cell function[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(12): 23097-23110.
|
| 17 |
YIN G, YU B, LIU C Y, et al. Exosomes produced by adipose-derived stem cells inhibit schwann cells autophagy and promote the regeneration of the myelin sheath[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2021, 132: 105921.
|
| 18 |
汪文涛, 米旭光, 周 阳, 等. 骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体诱导自噬对MPP+抑制SH-SY5Y细胞存活的影响及其机制[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2022, 48(3): 606-614.
|
| 19 |
袁 博, 谢利德, 付秀美. 许旺细胞源性外泌体促进损伤周围神经的修复与再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 935-940.
|
| 20 |
FENG N H, JIA Y J, HUANG X X. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells alleviate neural injury caused by microglia activation via suppressing NF-κB and MAPK pathway[J]. J Neuroimmunol, 2019, 334: 576996.
|
| 21 |
SENGUPTA S, PARENT C A, BEAR J E. The principles of directed cell migration[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2021, 22(8): 529-547.
|
| 22 |
ZHANG H, WANG Y F, ZHAO Y H, et al. PTX3 mediates the infiltration, migration, and inflammation-resolving-polarization of macrophages in glioblastoma[J]. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2022, 28(11): 1748-1766.
|
| 23 |
XU J W, FU L Y, DENG J Y, et al. MiR-301a deficiency attenuates the macrophage migration and phagocytosis through YY1/CXCR4 pathway[J]. Cells, 2022, 11(24): 3952.
|
| 24 |
CANFRÁN-DUQUE A, ROTLLAN N, ZHANG X B, et al. Macrophage-derived 25-hydroxycholesterol promotes vascular inflammation, atherogenesis, and lesion remodeling[J]. Circulation, 2023, 147(5): 388-408.
|
| 25 |
汪 鹏, 仇建南, 王忠夏, 等. 肝癌微环境中肿瘤相关巨噬细胞的研究进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2023, 39(5): 1212-1218.
|
| 26 |
STAHNKE S, DÖRING H, KUSCH C, et al. Loss of Hem1 disrupts macrophage function and impacts migration, phagocytosis, and integrin-mediated adhesion[J]. Curr Biol, 2021, 31(10): 2051-2064.
|
 ),Lide XIE1(
),Lide XIE1( )
)