Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 727-739.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250317
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles
Effect of KIAA1522 on proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung cancer cells and its mechanism
Yihui WANG1,Qing ZHANG1,Yingnan LI1,Liping YE1,2,3( )
)
- 1.Department of Pathophysiology,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Jinzhou Medical University,Jinzhou 121001,China
2.Institute of Biological Anthropology,Jinzhou Medical University,Jinzhou 121001,China
3.Liaoning Provincal Key Laboratory of Human Phenome Research,Jinzhou Medical University,Jinzhou 121001,China
-
Received:2024-06-12Accepted:2024-08-06Online:2025-05-28Published:2025-07-18 -
Contact:Liping YE E-mail:yeliping@jzmu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
- R734.2
Cite this article
Yihui WANG,Qing ZHANG,Yingnan LI,Liping YE. Effect of KIAA1522 on proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung cancer cells and its mechanism[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 727-739.
share this article
Tab. 1
Expressions of KIAA1522 protein in cancer tissue of NSCLC patients with different clinicopathological characteristics"
| Clinicopathological characteristic | n | KIAA1522 | P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| + | - | ||||
| Age | |||||
| ≤60 | 33 | 26 | 7 | 0.251 | 0.616 |
| >60 | 42 | 31 | 11 | ||
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 43 | 32 | 11 | 0.488 | 0.485 |
| Female | 32 | 26 | 6 | ||
| Maximum diameter of tumor(cm) | |||||
| ≤3 | 34 | 24 | 10 | 1.614 | 0.204 |
| >3 | 41 | 34 | 7 | ||
| Differentiation | |||||
| Well-moderate | 51 | 42 | 9 | 2.291 | 0.130 |
| Poor | 24 | 16 | 8 | ||
| TNM stage | |||||
| Ⅰ | 31 | 18 | 13 | 11.192 | 0.001 |
| Ⅱ+Ⅲ | 44 | 40 | 4 | ||
| Lymphnode metastasis | |||||
| Yes | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1.000 | |
| No | 73 | 56 | 17 | - | |
Tab.3
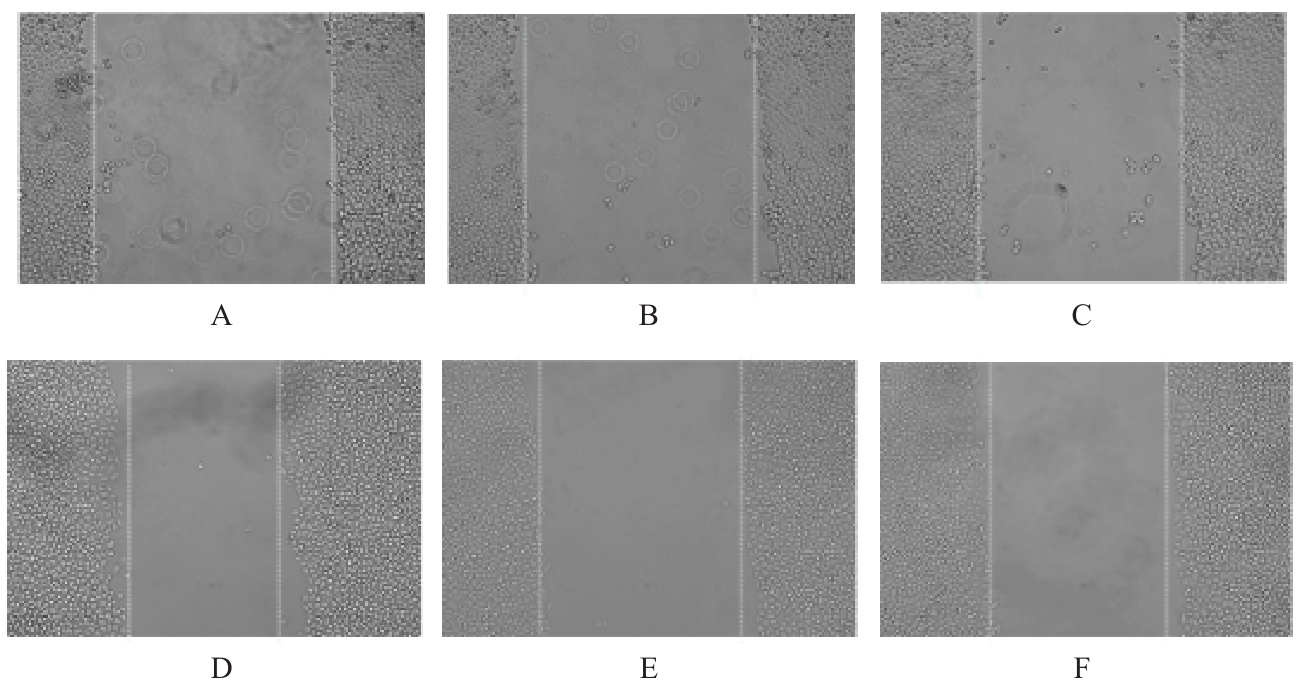
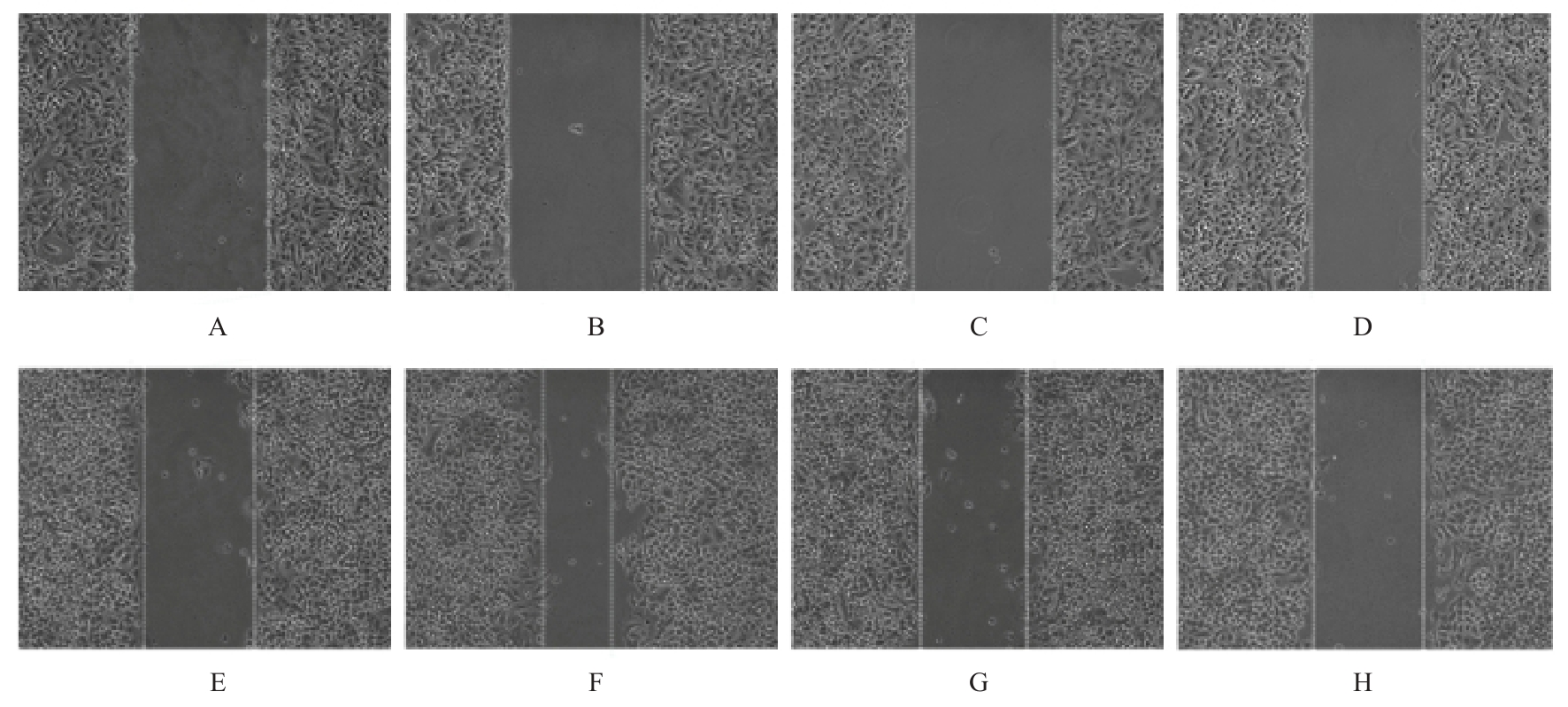
Proliferation activities of A549 cells in various groups after over-expression of KIAA1522"
| Group | Proliferation activity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (t/h) | 24 | 48 | 72 | |
| OE-NC | 0.138±0.012 | 0.216±0.006 | 0.330±0.007 | |
| OE-KIAA1522 | 0.150±0.016* | 0.255±0.014* | 0.388±0.011* | |
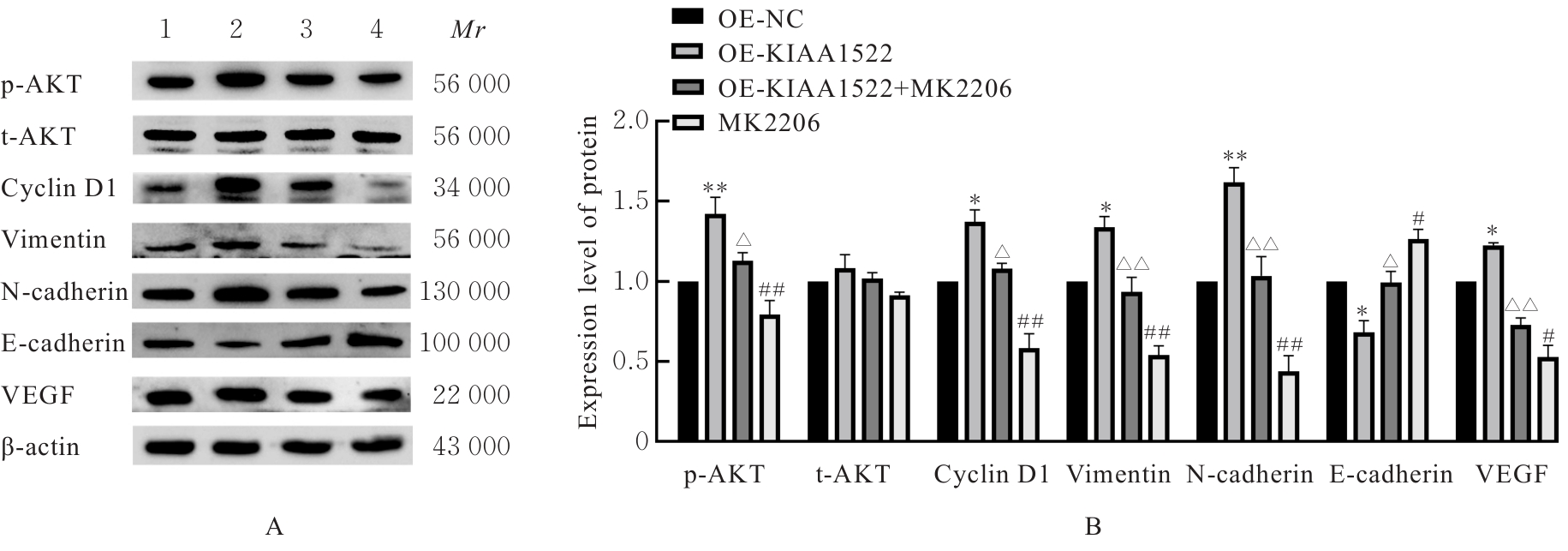
| OE-KIAA1522+MK2206 | 0.129±0.007△ | 0.191±0.013△ | 0.300±0.012△ | |
| MK2206 | 0.118±0.011# | 0.158±0.007# | 0.261±0.004# | |
| [1] | ZHANG X, ZHANG R, LIU P P, et al. ATP8B1 knockdown activated the choline metabolism pathway and induced high-level intracellular REDOX homeostasis in lung squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2022, 14(3): 835. |
| [2] | YANG D W, LIU Y, BAI C X, et al. Epidemiology of lung cancer and lung cancer screening programs in China and the United States[J]. Cancer Lett, 2020, 468: 82-87. |
| [3] | 解智慧. 一种新的介导细胞间粘附的肌动蛋白相关蛋白KIAA1522在食管癌中作用及其机制的研究[D]. 北京: 北京协和医学院, 2014. |
| [4] | XU Y Z, SUN C D, HAN B, et al. High KIAA1522 expression predicts a poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Oncol Lett, 2020, 20(1): 509-516. |
| [5] | SHI Y J, XIAO Q W, HUANG S C, et al. Poor prognostic biomarker KIAA1522 is associated with immune infiltrates in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Oncol, 2023, 2023: 3538928. |
| [6] | ÖZDEDE M, TABAN H K, AKMAN O, et al. The prognostic significance of KIAA1522 expression in non-small-cell lung cancer patients[J]. Cureus, 2023, 15(8): e44016. |
| [7] | HU B, YANG X B, YANG X, et al. LncRNA CYTOR affects the proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by regulating the miR-125b-5p/KIAA1522 axis[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2020, 13(2): 2626-2639. |
| [8] | JIANG S B, ZHANG Y G, LI Q, et al. KIAA1522 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2020, 13: 5657-5668. |
| [9] | WANG B S, JING T T, JIN W L, et al. KIAA1522 potentiates TNFα-NFκB signaling to antagonize platinum-based chemotherapy in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2020, 39(1): 170. |
| [10] | YI X, HU C H, ZHANG C, et al. KIAA1522 is a new biomarker of promoting the tumorigenesis and distant metastasis of colorectal carcinoma[J]. Cell Signal, 2022, 90: 110202. |
| [11] | XIE Z H, YU J, SHANG L, et al. KIAA1522 overexpression promotes tumorigenicity and metastasis of esophageal cancer cells through potentiating the ERK activity[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2017, 10: 3743-3754. |
| [12] | HUA H, ZHANG H Y, CHEN J Z, et al. Targeting Akt in cancer for precision therapy[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2021, 14(1): 128. |
| [13] | ZHAO L M, LI J, LIU Y P, et al. Flotillin1 promotes EMT of human small cell lung cancer via TGF-β signaling pathway[J]. Cancer Biol Med, 2018, 15(4): 400-414. |
| [14] | KONG D G, ZHOU H B, NEELAKANTAN D, et al. VEGF-C mediates tumor growth and metastasis through promoting EMT-epithelial breast cancer cell crosstalk[J]. Oncogene, 2021, 40(5): 964-979. |
| [15] | FAN Y G, JIANG Y, GONG L, et al. Epidemiological and demographic drivers of lung cancer mortality from 1990 to 2019: results from the global burden of disease study 2019[J]. Front Public Health, 2023, 11: 1054200. |
| [16] | GUO B Q, YU L, SUN Y H, et al. Long non-coding RNA USP2-AS1 accelerates cell proliferation and migration in ovarian cancer by sponging miR-520d-3p and up-regulating KIAA1522[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2020, 12: 10541-10550. |
| [17] | LIN J, LIAO S S, LIU Z W, et al. LncRNA FGD5-AS1 accelerates cell proliferation in pancreatic cancer by regulating miR-520a-3p/KIAA1522 axis[J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2021, 22(3): 257-266. |
| [18] | NOWAK E, BEDNAREK I. Aspects of the epigenetic regulation of EMT related to cancer metastasis[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(12): 3435. |
| [19] | HUANG Y H, HONG W Q, WEI X W. The molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies of EMT in tumor progression and metastasis[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2022, 15(1): 129. |
| [20] | 张 瑞, 陈进宏. 结直肠癌肝转移的非根治性切除手术治疗策略[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40(7): 1295-1300. |
| [21] | RAVAGGI A, GAMBINO A, FERRARI F, et al. VEGF-D serum level as a potential predictor of lymph node metastasis and prognosis in vulvar squamous cell carcinoma patients[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 818613. |
| [22] | LI C, WANG H F, FANG H, et al. FOXP3 facilitates the invasion and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer cells through regulating VEGF, EMT and the Notch1/Hes1 pathway[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2021, 22(3): 958. |
| [23] | MAHARATI A, MOGHBELI M. PI3K/AKT signaling pathway as a critical regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal tumor cells[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2023, 21(1): 201. |
| [24] | ZHENG Y H, JI H X, YI W L, et al. PRMT5 facilitates angiogenesis and EMT via HIF-1α/VEGFR/Akt signaling axis in lung cancer[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2023, 15(13): 6163-6178. |
| [25] | HAN P, WANG Q L, ZHANG X. Expression of TRAP1 in gastric cancer tissue and its correlation with malignant biology[J]. Asian Pac J Trop Med, 2016, 9(1): 67-71. |
| [1] | Cheng CHEN,Jingyao LI,Wanxiang HU,Donghui LIU,Zhihong CHEN. Protective effect of sericin on streptozotocin-induced INS-1 cell damage by regulating PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway through Akt1 and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 590-598. |
| [2] | Fan WANG,Xin WEN,Yixuan WANG,Yuan WANG. Effect of gap junction β2 on prognosis of patients with lung adenocarcinoma and biological behavior of lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 716-726. |
| [3] | Shuyan SUN,Huakun ZHANG,Ziru ZHOU,Feng LI,Xiaobin CUI. Expression of CRNN protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissue and influence of its overexpression in biological behavior of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma Eca9706 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 275-283. |
| [4] | Mengyun LU,Yucheng HAN,Yihong HU,Minhui HE,Yanqun ZHANG,Xianqiong ZOU. Effects of glycolipid transfer protein on proliferation, migration,and invasion of pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 284-295. |
| [5] | Jing DENG,Xuan WANG,Changyu SHI,Siqi YANG,Qinling ZOU,Ming JIN. Effect of securinine on proliferation and apoptosis of human colon cancer SW620 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 307-316. |
| [6] | Ying YANG,Liang ZHAO,Yong YOU,Qian XU,Zhenjun YANG. Influence of 17β-estradiol in proliferation and differentiation of hippocampal neural stem cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 317-324. |
| [7] | Yan WANG,Zouyu ZHAO,Panpan YU,Ping YANG. Expression of I kappa B kinase-interacting protein in cervical cancer tissue and its effect on proliferation, migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 341-351. |
| [8] | Yaqi ZHANG,Jing MI,Jingrong YANG,Xinming LI,Li LI. Effect of up-regulation of miR-31 expression on osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells through Wnt-β/catenin signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 412-419. |
| [9] | Chaohe ZHANG,Xinwei ZHANG,Xiangfeng WANG. Protective effect of Pien-Tze-Huang on acetaminophen-induced liver injury and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 105-114. |
| [10] | Pengli WU,Fengyu LI,Bo LIU,Yang LYU. Effect of silencing DDX39A gene on proliferation, migration and invasion of esophageal cancer TE-1 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 115-123. |
| [11] | Mengmeng ZHAO,Yalu WANG,Yuxiang XU,Kaige YANG,Yuwen CAO,Wenhu ZHOU,Jing FEI,Wen WANG,Chenghua LUO,Jianming HU. Effects of hydrogen sulfide synthase CBS and CSE on malignant biological behaviour of breast cancer cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 34-43. |
| [12] | Lu YANG,Jiacai FU,Fengjin LI,Ling QI. Inhibitory effect of schisandrin on migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 44-50. |
| [13] | Fang ZHAO,Zhenling LI,Lihua PIAO,Longzhe HAN,Yinji CUI,Chunji QUAN,Xuemei JIN. Effect of Yes-associated proteins on biological behaviors of human cervical cancer SiHa cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 68-75. |
| [14] | Min CHEN,Huiyan ZHU,Jing TAO,Yipeng XU. Ameliorating effect of betaine on oxygen-glucose deprivation injury in rat brain microvascular endothelial cells and its influence in PI3K/AKT pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 96-104. |
| [15] | Gao SUN,Jing HE,Qi ZHAO,Jianhong SHI,Zhiling LIAO,Yuanye TIAN,Guomin WU. Therapeutic effect of resveratrol on osteoarthritis of temporomandibular joint and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1547-1556. |
|
||