Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 96-104.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250112
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ameliorating effect of betaine on oxygen-glucose deprivation injury in rat brain microvascular endothelial cells and its influence in PI3K/AKT pathway
Min CHEN,Huiyan ZHU,Jing TAO,Yipeng XU( )
)
- Department of Rehabilitation Medicine,People’s Hospital,Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region,Urumqi 830001,China
-
Received:2024-03-14Accepted:2024-05-20Online:2025-01-28Published:2025-03-06 -
Contact:Yipeng XU E-mail:penn119@126.com
CLC Number:
- R96
Cite this article
Min CHEN,Huiyan ZHU,Jing TAO,Yipeng XU. Ameliorating effect of betaine on oxygen-glucose deprivation injury in rat brain microvascular endothelial cells and its influence in PI3K/AKT pathway[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 96-104.
share this article
Tab.1
Survival rates of rat BMECs in various groups"
| Group | Survival rate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (t/h) | 12 | 24 | 48 | |
| Blank control | 100.00±0.00 | 100.00±0.00 | 100.00±0.00 | |
| Model | 42.26±1.72* | 46.08±2.90* | 35.68±3.31* | |
| Positive control | 96.04±4.47△ | 92.73±5.26△ | 88.71±0.96△ | |
| Betaine | ||||
| Low dose | 64.97±0.70△# | 70.97±1.50△# | 67.28±5.20△# | |
| Medium dose | 78.25±4.98△#○ | 84.88±3.25△#○ | 76.13±3.70△#○ | |
| High dose | 89.44±1.88△#○□ | 93.26±2.98△○□ | 81.97±3.00△#○□ | |
Tab.2
Activities of LDH and levels of ATP in rat BMECs in various groups"
| Group | LDH/ [λB/(U·L-1)] | ATP [mB/(μmol·g-1)] |
|---|---|---|
| Blank control | 36.21±1.13 | 3.57±0.10 |
| Model | 105.18±2.77* | 0.32±0.04* |
| Positive control | 49.43±2.38△ | 2.52±0.26△ |
| Betaine | ||
| Low dose | 81.67±2.68△# | 1.16±0.12△# |
| Medium dose | 58.99±4.90△#○ | 2.05±0.10△○ |
| High dose | 47.94±4.28△○□ | 3.27±0.15△#○□ |
Tab.3
Levels of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and IL-18 in supernatants of rat BMECs in various groups [n=3, x±s, ρB/(ng·L-1)]"
| Group | TNF-α | IL-6 | IL-1β | IL-18 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank control | 213.68±7.58 | 69.91±4.92 | 29.51±0.79 | 68.78±6.42 |
| Model | 1 068.56±6.82* | 846.25±15.75* | 103.59±6.90* | 350.93±9.56* |
| Positive control | 323.36±2.74△ | 112.20±9.02△ | 44.53±3.31△ | 95.89±2.85△ |
| Betaine | ||||
| Low dose | 526.85±2.47△# | 509.14±16.16△# | 86.91±5.25△# | 234.14±4.79△# |
| Medium dose | 427.25±5.22△#○ | 227.26±7.09△#○ | 60.44±4.09△#○ | 164.55±4.09△#○ |
| High dose | 279.35±2.27△#○□ | 110.96±3.72△○□ | 39.70±2.64△○□ | 85.63±14.69△#○□ |
Tab.4
Activities of SOD and levels of MDA in rat BMECs in various groups"
| Group | SOD [λB/(U·mg-1)] | MDA [mB/(μmol·g-1)] |
|---|---|---|
| Blank control | 131.32±4.87 | 1.00±0.08 |
| Model | 65.92±6.92* | 5.17±0.15* |
| Positive control | 111.41±5.88△ | 2.07±0.04△ |
| Betaine | ||
| Low dose | 99.03±0.64△# | 4.04±0.13△# |
| Medium dose | 115.82±2.31△○ | 3.64±0.04△#○ |
| High dose | 128.63±4.03△#○□ | 1.69±0.17△#○□ |
Tab.5
Values of TEER and HRP permeabilities of rat BMECs in various groups"
| Group | TEER(Ω·cm-2) | HRP permeability(η/%) |
|---|---|---|
| Blank control | 48.40±1.63 | 0.44±0.16 |
| Model | 14.75±3.71* | 4.98±0.06* |
| Positive control | 39.59±0.89△ | 1.50±0.08△ |
| Betaine | ||
| Low dose | 26.89±3.79△# | 4.23±0.09△# |
| Medium dose | 37.84±4.13△○ | 2.96±0.13△#○ |
| High dose | 47.21±6.54△#○□ | 1.16±0.04△○□ |
Tab.6
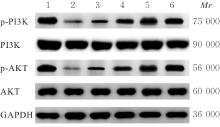
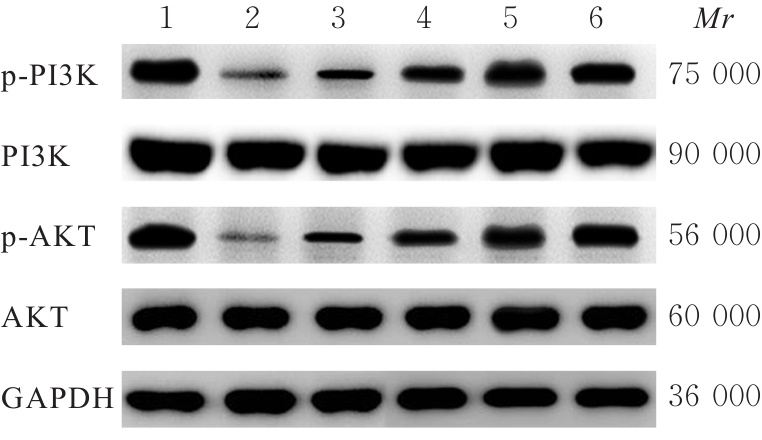
Ratios of p-PI3K/PI3K and p-AKT/AKT in rat BMECs in various groups"
| Group | p-PI3K/PI3K | p-AKT/AKT |
|---|---|---|
| Blank control | 0.87±0.09 | 0.96±0.04 |
| Model | 0.36±0.03* | 0.30±0.05* |
| Positive control | 0.75±0.04△ | 0.77±0.04△ |
| Betaine | ||
| Low dose | 0.47±0.04△# | 0.46±0.02△# |
| Medium dose | 0.67±0.04△#○ | 0.57±0.04△#○ |
| High dose | 0.90±0.05△#○□ | 0.90±0.04△#○□ |
| 1 | LIU D, XIAO H T, LIU J X, et al. Circ_0000566 contributes oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation (OGD/R)-induced human brain microvascular endothelial cell injury via regulating miR-18a-5p/ACVR2B axis[J]. Metab Brain Dis, 2023, 38(4): 1273-1284. |
| 2 | LIU W, JIA C, LUO L, et al. Novel circular RNAs expressed in brain microvascular endothelial cells after oxygen-glucose deprivation/recovery[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2019,14(12): 2104-2111. |
| 3 | SHI G, CHEN J M, ZHANG C, et al. Astragaloside Ⅳ promotes cerebral angiogenesis and neurological recovery after focal ischemic stroke in mice via activating PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9(12): e22800. |
| 4 | WANG D P, JIN K Y, ZHAO P, et al. Neuroprotective effects of VEGF-A nanofiber membrane and FAAH inhibitor URB597 against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced ischemic neuronal injury[J]. Int J Nanomedicine, 2021, 16(1): 3661-3678. |
| 5 | 李顺泽, 伍振煌, 王俊龙. 甜菜碱的生物功能、药理活性及其在动物生产中的应用研究进展[J]. 饲料研究, 2022, 45(21): 150-155. |
| 6 | 李亚杰, 张 航, 聂黎虹, 等. 甜菜碱抑制ABCB1逆转前列腺癌化疗耐药性的作用及其机制[J/OL]. 解放军医学杂志, 1-12[2025-03-01]. . |
| 7 | SARLAK M, ROUMIANI E, KHERADMAND A, et al. Evaluating the effects of betaine on testicular ischemia/reperfusion injury induced by torsion/detorsion in the rat[J]. Andrologia, 2022, 54(10): e14559. |
| 8 | 张 蕴, 韩新生, 张洪阳, 等. N-乙酰半胱氨酸通过AMPK/SIRT1途径抑制缺氧诱导的大鼠脑血管内皮细胞损伤[J]. 中国动脉硬化杂志, 2020, 28(2): 107-112. |
| 9 | 杨 华, 何强华, 张爱华, 等. 丹参酮ⅡA通过抑制TLR4/NF-κB途径减轻糖氧剥夺对大鼠脑微血管内皮细胞的炎症损伤[J]. 中国临床神经外科杂志, 2020, 25(9): 610-612. |
| 10 | 金莉莉, 于炎巧, 朱晓玉, 等. 甜菜碱及叶酸的降血脂和抗氧化作用[J]. 辽宁大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 46(2): 142-150. |
| 11 | 戴纪恒, 吴思鹏, 汪 宁, 等. 通窍活血汤含药脑脊液对OGD/R损伤大鼠BMECs的保护作用[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2020, 26(14): 42-52. |
| 12 | 徐 露, 张太君. 冰片联合灯盏花素对缺氧/复氧损伤血脑屏障通透性的影响[J]. 中国中医药信息杂志, 2016, 23(2): 76-78. |
| 13 | 张 欢, 丁纪茹, 陈 耀, 等. 消渴通痹颗粒对高糖诱导的HUVEC屏障功能的影响及保护作用[J]. 中药药理与临床, 2020, 36(3): 168-175. |
| 14 | QIAN Y, TANG B, ZHANG H, et al. Highly-expressed circ_0129657 inhibits proliferation as well as promotes apoptosis and inflammation in HBMECs after oxygen-glucose deprivation via miR-194-5p/GMFB axis[J]. Autoimmunity, 2023, 56(1): 2201405. |
| 15 | XU C, YU H L, CHEN B L, et al. Serum exosomal mir-340-5p promotes angiogenesis in brain microvascular endothelial cells during oxygen-glucose deprivation[J]. Neurochem Res, 2022, 47(4): 907-920. |
| 16 | 邱 阳, 黄力新, 贺师鹏. 甜菜碱对大鼠肝细胞膜表皮生长因子受体及其酪氨酸蛋白激酶的作用[J]. 北京医科大学学报, 1999, 31(4): 302-305. |
| 17 | 谢竹青, 马连龙, 王 辉, 等. 甜菜碱对大鼠肝脏缺血-再灌注损伤的作用[J]. 中国新药与临床杂志, 2020, 39(1): 48-52. |
| 18 | 向家培, 华晓芳, 王 勇, 等. 甜菜碱对大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤炎症及心肌细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 安徽医学, 2018, 39(11): 1297-1300. |
| 19 | LU L, LU T T, SHEN J L, et al. Alisol A 24-acetate protects against brain microvascular endothelial cells injury through inhibiting miR-92a-3p/tight junctions axis[J]. Aging, 2021, 13(11): 15353-15365. |
| 20 | WU Z Y, LIANG Y D, YU S Z. Downregulation of microRNA-103a reduces microvascular endothelial cell injury in a rat model of cerebral ischemia by targeting AXIN2[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2020, 235(5): 4720-4733. |
| 21 | 夏霜莉, 杨 媛, 廖 陈, 等. 3,4-二羟基苯甲醛作用星形胶质细胞减轻脑微血管内皮细胞和神经元氧糖剥夺/再灌注损伤[J]. 上海中医药大学学报, 2021, 35(4): 67-72, 100. |
| 22 | FAN Y L, DING S H, SUN Y M, et al. MiR-377 regulates inflammation and angiogenesis in rats after cerebral ischemic injury[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2018, 119(1): 327-337. |
| 23 | HE Z R, ZHAO Y Y, ZHU Y X, et al. Interfering TUG1 attenuates cerebrovascular endothelial apoptosis and inflammatory injury after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion via TUG1/miR-410/FOXO3 ceRNA axis[J]. Neurotox Res, 2022, 40(1): 1-13. |
| 24 | RESCHKE M, SALVADOR E, SCHLEGEL N, et al. Isosteviol sodium (STVNA) reduces pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6 and GM-CSF in an in vitro murine stroke model of the blood-brain barrier (BBB)[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2022, 14(9): 1753. |
| 25 | 王 慧, 兰小兵, 郑 萍, 等. 獐牙菜苦苷对PC12细胞氧糖剥夺再灌注损伤的保护作用及机制[J]. 中国药理学与毒理学杂志, 2022, 36(2): 90-97. |
| 26 | 高 伟, 李慧颖, 李 丹. 普拉克索下调TXNIP表达对氧糖剥夺/再灌注心肌细胞p38/JNK通路的作用研究[J]. 河北医药, 2023, 45(7): 965-970. |
| 27 | 张 创, 余孝君, 唐 波, 等. 胱天蛋白酶11介导的Hippo信号通路在脑缺血再灌注小鼠血脑屏障破坏中的作用和机制[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2023, 39(2): 250-258. |
| 28 | 陈 丽, 折 霞, 谷超超, 等. 脂肪酸结合蛋白7对脑缺血再灌注大鼠血脑屏障通透性的影响[J]. 中风与神经疾病杂志, 2020, 37(11): 1004-1010. |
| 29 | 窦晋芳, 常佩芬, 胡超群, 等. 清开灵注射液对Aβ42刺激下小鼠体外血脑屏障转运Aβ的影响及机制研究[J]. 现代中医临床, 2021, 28(3): 28-33. |
| 30 | 孙瑞, 于德水. 抑制miR-429促进ZO-1、Occludin和Claudin-5蛋白表达改善血脊髓屏障通透性的体外实验研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2020, 34(9): 1163-1169. |
| 31 | HUA Y P, ZHAI Y, WANG G Y, et al. Tong-Qiao-Huo-Xue decoction activates PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway to reduce BMECs autophagy after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2022, 298: 115585. |
| 32 | LI Y Z, GUO S Q, LIU W C, et al. Silencing of SNHG12 enhanced the effectiveness of MSCs in alleviating ischemia/reperfusion injuries via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Front Neurosci, 2019, 13: 645. |
| 33 | 王圣鑫, 闫向丽, 郑昊圳, 等. 毛蕊异黄酮苷和芍药苷联用对氧糖剥夺再灌注HT22细胞PI3K/AKT信号通路的影响[J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2020, 31(2): 138-142. |
| [1] | Chaohe ZHANG,Xinwei ZHANG,Xiangfeng WANG. Protective effect of Pien-Tze-Huang on acetaminophen-induced liver injury and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 105-114. |
| [2] | Gao SUN,Jing HE,Qi ZHAO,Jianhong SHI,Zhiling LIAO,Yuanye TIAN,Guomin WU. Therapeutic effect of resveratrol on osteoarthritis of temporomandibular joint and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1547-1556. |
| [3] | Jing LOU,Lei ZHAO,Yanjie ZHU,Shuaiqiang YUAN,Fei WANG,Hangzhou ZHANG,Jiaojiao XU,Xiaoke YU,Liufa HOU. Effect of Fuzheng Ruanjian Anticancer Formula on malignant biological behaviors of hepatocellulars carcinoma HepG2 cells by regulating Akt/MDM2/P53 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1654-1663. |
| [4] | Xueting CHI,Fangyuan CHEN,Zifeng PI,Guangfu LYU,Yuchen WANG,Yinqing LI,Xiaowei HUANG,Zhe LIN. Improvement effect of velvet antler polypeptide on postmenopausal osteoporosis in rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 963-969. |
| [5] | Tengfei WANG, Feng CHEN, Ling QI, Ting LEI, Meihui SONG. Inhibitory effect of D-limonene on proliferation of glioblastoma cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 647-657. |
| [6] | Kaihua YU,Kun WEI,Jie ZHANG,Xuemei YI,Gang WANG,Lei PANG. Heart failure patient with acute left lower limb arterial embolism complicated with myonephropathic metabolic syndrome: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 529-535. |
| [7] | Chunyan KANG,Xiuzhi ZHANG,Huicong ZHOU,Jie CHEN. Effect of downregulating proline-rich protein 11 expression on drug resistance of esophageal cancer drug resistant cell EC9706/DDP and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 113-119. |
| [8] | Yanhong WEI,Chenxue YANG,Guangmin YANG,Shuai SONG,Ming LI,Haijiao YANG,Haifeng WEI. Inhibitory effect of downregulating HMGB2 expression on epithelial-mesenchymal transition of liver cancer LM3 cells and its AKT/mTOR signaling pathway mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 143-149. |
| [9] | Xian ZHU,Xinxu CHEN,Yibin CHEN,Changxuan LI,Jie LIU,Tan WANG. Improvement effect of sodium cromoglycate on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1182-1191. |
| [10] | Meng LIU,Xiaodong HUANG,Zheng HAN,Qingxi ZHU,Jie TAN,Xia TIAN. Effect of cadherin-17 on proliferation and apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells and its PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway regulatory mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 1008-1017. |
| [11] | Sihan LAI,Juntong LIU,Luying TAN,Jinping LIU,Pingya LI. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on anti-ischemic stroke mechanism of Panax quinquefolium triolsaponins [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 913-922. |
| [12] | Yifei SUN,Dinuo LI,Yubin WANG. Inhibitory effect of curcumin on proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer MGC-803 cells by down-regulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway protein expression [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 332-340. |
| [13] | Jun ZHU,Nan ZHOU,Deming LI. Improvement effect of propofol postconditioning on focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 46-54. |
| [14] | Heran YANG,Xingjiang LI,Jiahang HU,Yanwei LI. Effect of Ghrelin on neural differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1490-1497. |
| [15] | Hongxia SUN,Chunxu LIU,Xuejun AN,Guanghua CUI,Jingyu WANG,Shuangxi TONG,Xiaoqiu YANG. Effect of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharide on proliferation and apoptosis of human bladder cancer T24 cells and its mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1216-1222. |
|
||