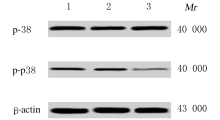
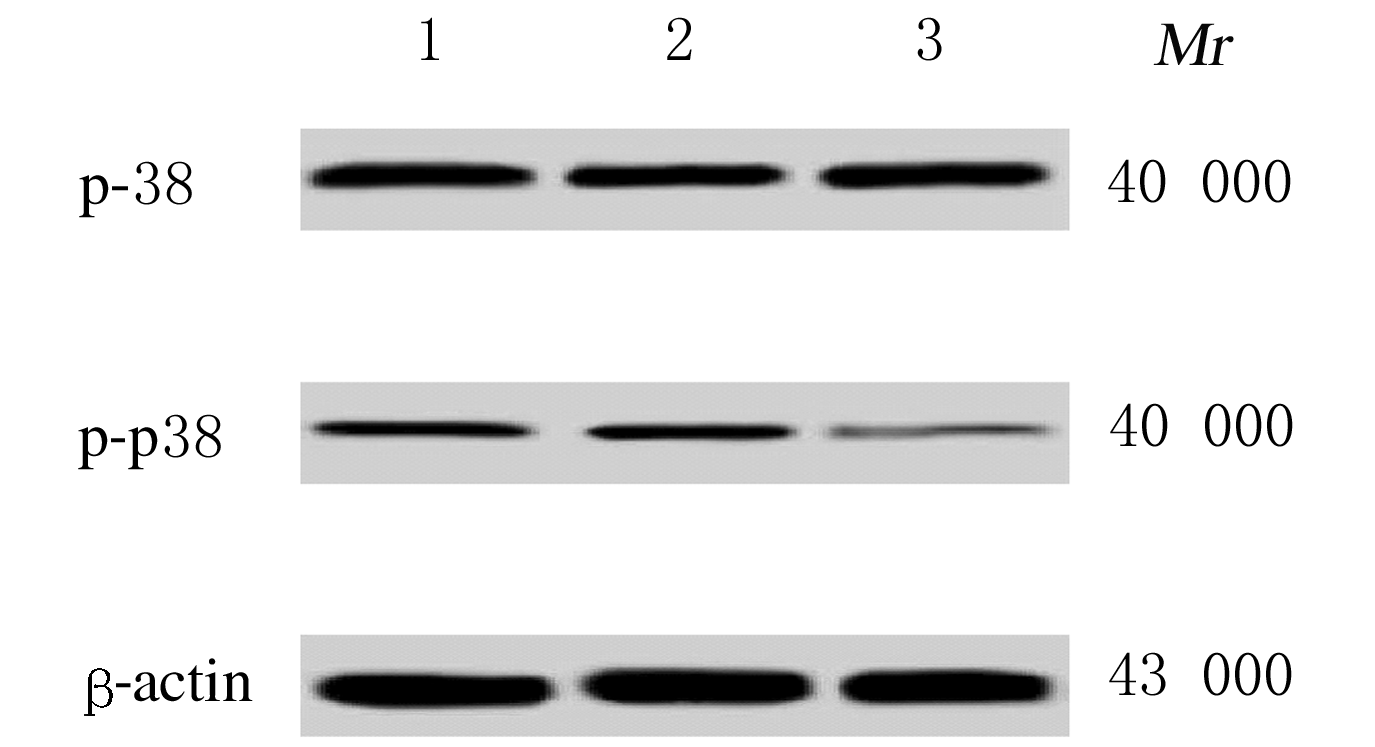
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (1): 110-117.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20210115
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Inhibitory effects of siRNA targeting silencing TAK1 gene on proliferation and migration of thyroid cancer cells and p38 MAPK signaling pathway
Chunying ZHANG,Guangwei YIN,Mingda YOU,Hong CHEN,Yaojie HU,Yanbing LI,Chunyou CHEN( )
)
- Department of Head and Neck Surgery,Tangshan Workers’ Hospital,Hebei Medical University,Tangshan 063000,China
-
Received:2020-03-15Online:2021-01-28Published:2021-01-27 -
Contact:Chunyou CHEN E-mail:yingchunzh122@sina.com
CLC Number:
- R736.1
Cite this article
Chunying ZHANG,Guangwei YIN,Mingda YOU,Hong CHEN,Yaojie HU,Yanbing LI,Chunyou CHEN. Inhibitory effects of siRNA targeting silencing TAK1 gene on proliferation and migration of thyroid cancer cells and p38 MAPK signaling pathway[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 110-117.
share this article
Tab.1
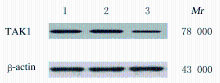
Expression levels of TAK1 mRNA and protein in normal thyroid epithelial cells and thyroid cancer cells"
| Cell | TAK1 mRNA | TAK1 protein |
|---|---|---|
| Nthyori3-1 | 1.00±0.12 | 0.12±0.04 |
| 8505C | 1.68±0.11 * | 0.48±0.06 * |
| NPA | 1.97±0.13 * | 0.82±0.08 * |
| BCPAP | 1.84±0.15 * | 0.78±0.07 * |
| KMH-2 | 2.32±0.16 * | 0.94±0.10 * |
| F | 90.663 | 144.385 |
| P | <0.01 | <0.01 |
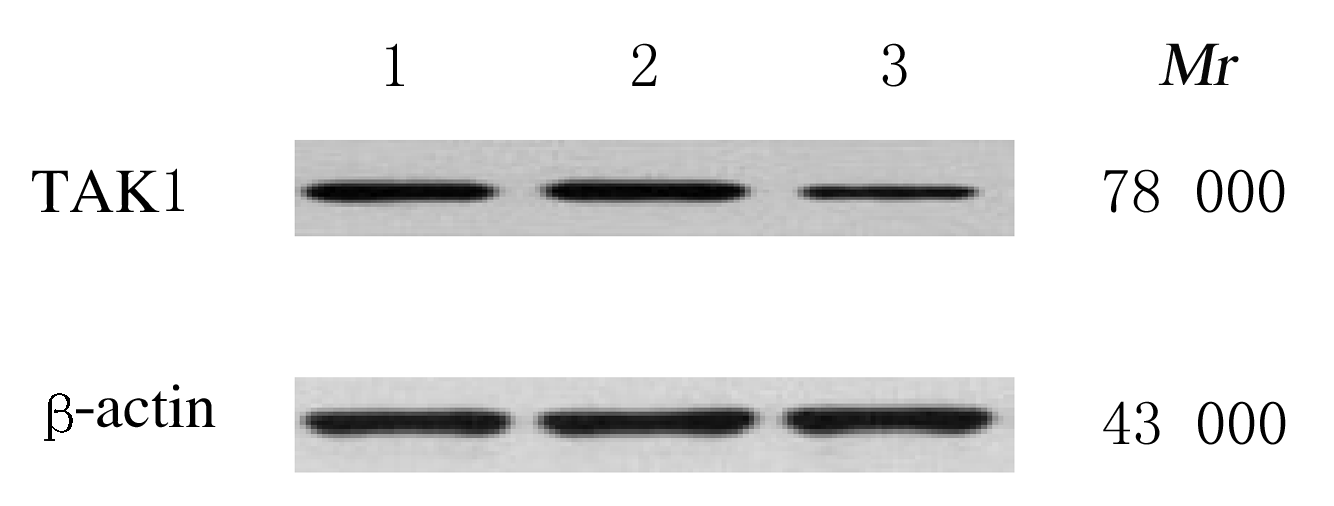
Tab.3
Proliferation activities of KMH-2 cells in various groups at different time points"
| Group | Proliferation activity | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (t/h) 24 | 48 | 72 | |
| Blank control | 0.412±0.033 | 0.784±0.041 | 1.273±0.044 |
| Negative control | 0.415±0.030 | 0.779±0.043 | 1.268±0.046 |
| siRNA-TAK1 | 0.327±0.025*△ | 0.461±0.038*△ | 0.691±0.038*△ |
| F | 20.055 | 144.586 | 427.743 |
| P | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| 1 | YANG H P, GUO Y, WANG D W, et al. Effect of TAK1 on osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by regulating BMP-2 via Wnt/β-catenin and MAPK pathway[J]. Organogenesis, 2018, 14(1):36-45. |
| 2 | HUANG F T, PENG J F, CHENG W J, et al. MiR-143 targeting TAK1 attenuates pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression via MAPK and NF-κB pathway in vitro[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2017, 62(4):944-957. |
| 3 | 廉亮亮, 齐书山, 袁洪志. miR-143-3p通过靶向TAK1抑制肺癌增殖和侵袭[J]. 生物技术通讯, 2019, 30(3):332-337. |
| 4 | 曹 赛, 程梅容, 刘素娥, 等. 食管癌组织中TAK1和TAB1的表达及与临床预后的相关性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(7):895-900. |
| 5 | LIN P F, NIU W B, PENG C, et al. The role of TAK1 expression in thyroid cancer[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2015, 8(11):14449-14456. |
| 6 | CUI D J, WU Y, WEN D H. CD34, PCNA and CK19 expressions in AFP- hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2018, 22(16):5200-5205. |
| 7 | WANG X H, HU Y D, CUI J Y, et al. Coordinated targeting of MMP-2/MMP-9 by miR-296-3p/FOXCUT exerts tumor-suppressing effects in choroidal malignant melanoma[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2018, 445(1/2):25-33. |
| 8 | CI Y Q, ZHANG Y B, LIU Y J, et al. Myricetin suppresses breast cancer metastasis through down-regulating the activity of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2/9[J]. Phytother Res, 2018, 32(7):1373-1381. |
| 9 | DALAKOURAS A, WASSENEGGER M, DADAMI E,et al. Genetically modified organism-free RNA interference: exogenous application of RNA molecules in plants[J]. Plant Physiol, 2020, 182(1):38-50. |
| 10 | GUTBROD M J, MARTIENSSEN R A. Conserved chromosomal functions of RNA interference[J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2020, 21(5):311-331. |
| 11 | BRÜGGENWIRTH I M A, MARTINS P N. RNA interference therapeutics in organ transplantation: The dawn of a new era[J]. Am J Transplant, 2020, 20(4):931-941. |
| 12 | YANG L D, JOSEPH S, SUN T L, et al. TAK1 regulates endothelial cell necroptosis and tumor metastasis[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2019, 26(10):1987-1997. |
| 13 | YUNG M M, TANG H W, CAI P C, et al. GRO-α and IL-8 enhance ovarian cancer metastatic potential via the CXCR2-mediated TAK1/NFκB signaling cascade[J]. Theranostics, 2018,8(5):1270-1285. |
| 14 | CHEN J M, ZHANG N, WEN J M, et al. Silencing TAK1 alters gene expression signatures in bladder cancer cells[J]. Oncol Lett, 2017, 13(5):2975-2981. |
| 15 | JIAO H L, YE Y P, YANG R W, et al. Downregulation of SAFB Sustains the NF-κB pathway by targeting TAK1 during the progression of colorectal cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2017,23(22):7108-7118. |
| 16 | TOTZKE J, GURBANI D, RAPHEMOT R, et al. Takinib, a selective TAK1 inhibitor, broadens the therapeutic efficacy of TNF-α inhibition for cancer and autoimmune disease[J]. Cell Chem Biol, 2017, 24(8):1029-1039.e7. |
| 17 | GUAN S, LU J X, ZHAO Y L, et al. TAK1 inhibitor 5Z-7-oxozeaenol sensitizes cervical cancer to doxorubicin-induced apoptosis[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(20):33666-33675. |
| 18 | BAN Z F, HE J N, TANG Z Z, et al. LRG-1 enhances the migration of thyroid carcinoma cells through promotion of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by activating MAPK/p38 signaling[J]. Oncol Rep, 2019, 41(6):3270-3280. |
| 19 | HAN S E, PARK C H, NAM-GOONG I S, et al. Anticancer effects of baicalein in FRO thyroid cancer cells through the up-regulation of ERK/p38 MAPK and Akt pathway[J]. In Vivo, 2019, 33(2):375-382. |
| 20 | WU L P, CAO Z Y, JI L, et al. Loss of TRADD attenuates pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy through regulating TAK1/P38 MAPK signalling in mice[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2017, 483(2):810-815. |
| 21 | FAN Y W, LI M Y, MA K, et al. Dual-target MDM2/MDMX inhibitor increases the sensitization of doxorubicin and inhibits migration and invasion abilities of triple-negative breast cancer cells through activation of TAB1/TAK1/p38 MAPK pathway[J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2019, 20(5):617-632. |
| 22 | 苏书娟. 牡荆葡基黄酮调节TAK1/AMPK通路增强人肝癌细胞的放射敏感性[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2018, 34(8):1158-1162. |
| [1] | Runhong MU,Xinzhu LIU,Rui LIN,Yupeng LI,Luyao WANG,Chunyu WANG,Xiao GUO. Effect of PRDX6 over-expression of proliferation, invasion and migration of liver cancer cells and its molecular mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 559-565. |
| [2] | Cuilan LIU,Jianjun LI,He JIANG,Jing LIU,Dan WANG,Chen LI,Di ZHAO. Effect of urolithin B on biological behaviors of human glioblastome U118 MG cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 566-574. |
| [3] | Xining LI,Wei WENG,Zheyuan SHEN,Xiaojie DOU,Yu ZHAO,Jikang MIN. Effect of mTOR phosphorylation level on proliferation,autophagy,and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 575-586. |
| [4] | Bo MA,Jiangang LI,Jun WANG,Junli HOU,Liang LI. Promotion effect of miR-106b on invasion and migration of colon cancer cells through targeting TGF-β/Smad pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 630-636. |
| [5] | Xiaohui LI,Ziwei QU,Xin LU,Qingbin MENG,Huatao CHEN,Jun REN,Chengpei TAN. Regulatory effect of exosomes carrying miR-196b-5p derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on biological characteristics of colon cancer cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 660-668. |
| [6] | Yaoyu FENG,Chenglei ZHANG,Lijuan HOU,Yifu WANG,Xiuling WU,Yunhai MA. Effect of miR-222-3p knockdown targeting PTEN on 131I radiotherapy resistance of thyroid cancer and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 677-686. |
| [7] | Ying YANG,Wei ZHAO,Dan LYU. Effect of C19ORF12 on proliferation and chemo-sensitivity of gastric cancer MKN45 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 687-693. |
| [8] | Nuan WANG,Lijuan YANG,Juanjuan DAI,Aili WANG,Yan WU,Chengxia LIU. Promotion effects of MARCH1 on migration and invasion of human gastric cancer cells through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 352-359. |
| [9] | Jing WANG,Jing LIU,Xujing WEI,Yafei DU,Guiying FANG,Lin LI. Effects of oridonin on proliferation, migration, invasion and expression of lncRNA CCAT1 of endometrial carcinoma HEC-1B cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 384-389. |
| [10] | Qi ZHAO,Changhai HE,Zhi WANG,Xuefeng WANG,Xiaofei LIU. Inhibitory effect of ALKBH3 knockdown on growth, migration and tumor angiogenesis of bladder cancer cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 397-406. |
| [11] | . Inhibitory effect of curcumin on tumor growth in colorectal cancer mice and its mechanism of PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathwayPEI Yongbin, WANG Guiqi, LI Wei, JIANG Xia, JIANG Haibo, ZHAO Zengren (Department of General Surgery,First Hospital,Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050031,China) [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 145-151. |
| [12] | Lu LIU,Tianfu ZHANG,Xiaofeng WANG,Chenfei KONG. Regulatory effects of syndecan-1 on migration, invasion and cell cycle of tongue squamous cell carcinoma CAL27 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 59-65. |
| [13] | GE Jing, XIE Lei, LI Lin, WEI Xujing, CHEN Ran, WANG Na. Expression of integrin-linked kinase in endometrial carcinoma tissue and its effects on migration and invasion abilities of cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 1011-1015. |
| [14] | WEI Xujing, LI Lin, ZHANG Hongzhen, WANG Jing, XU Jing. Effects of LncRNA CCAT1 on proliferation,invasion and migration of endometrial cancer cells through TGF-β1/smad signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 1016-1022. |
| [15] | ZHOU Ning, WU Rui, MA Zhenkai, CHEN Weiwei, LI Xuelin, GONG Kaikai, YANG Lijuan, DAI Juanjuan, WU Yan. Effects of down-regulation of ADAR1 expression on proliferation, migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human lung cancer cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 669-674. |