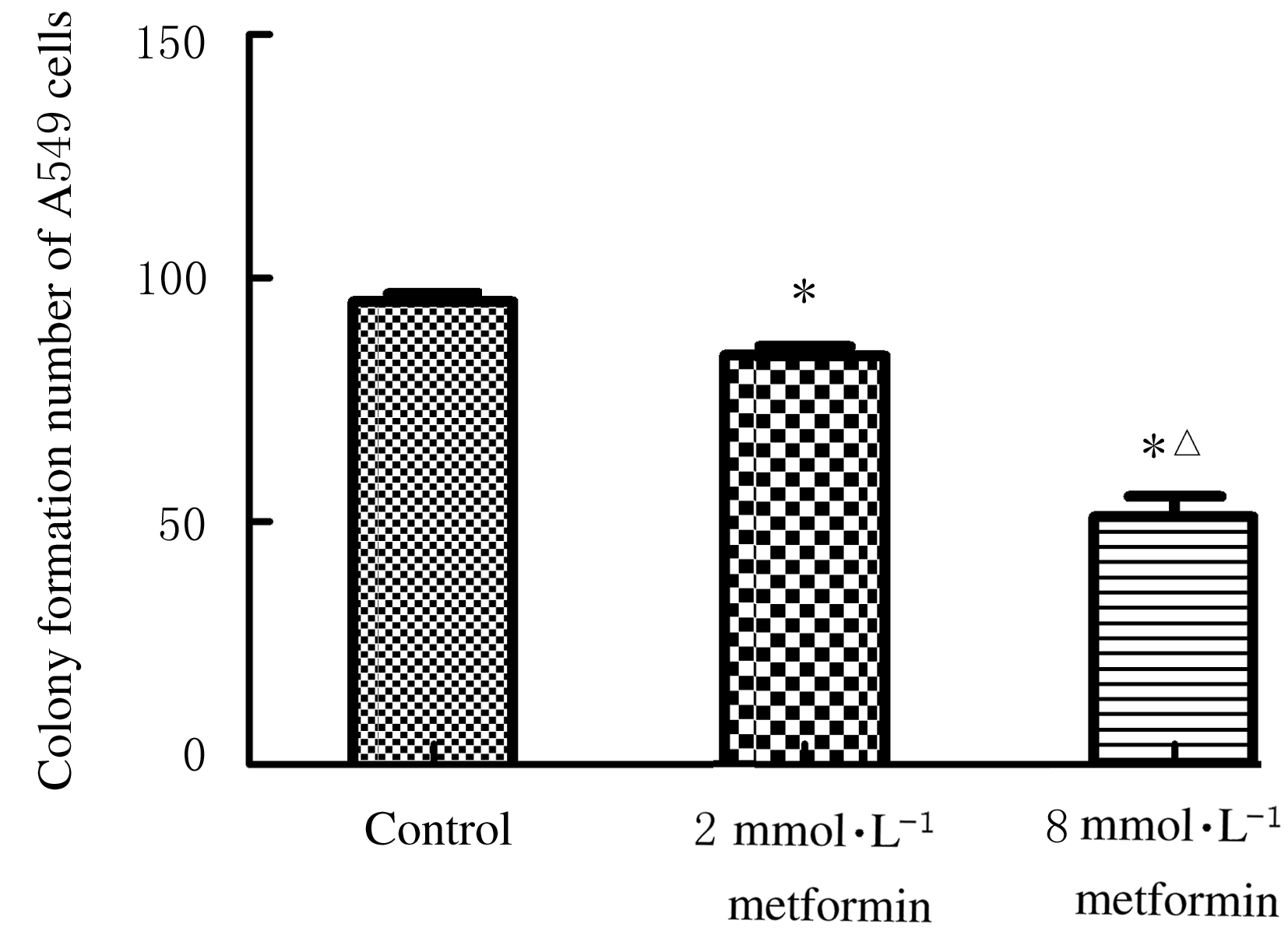
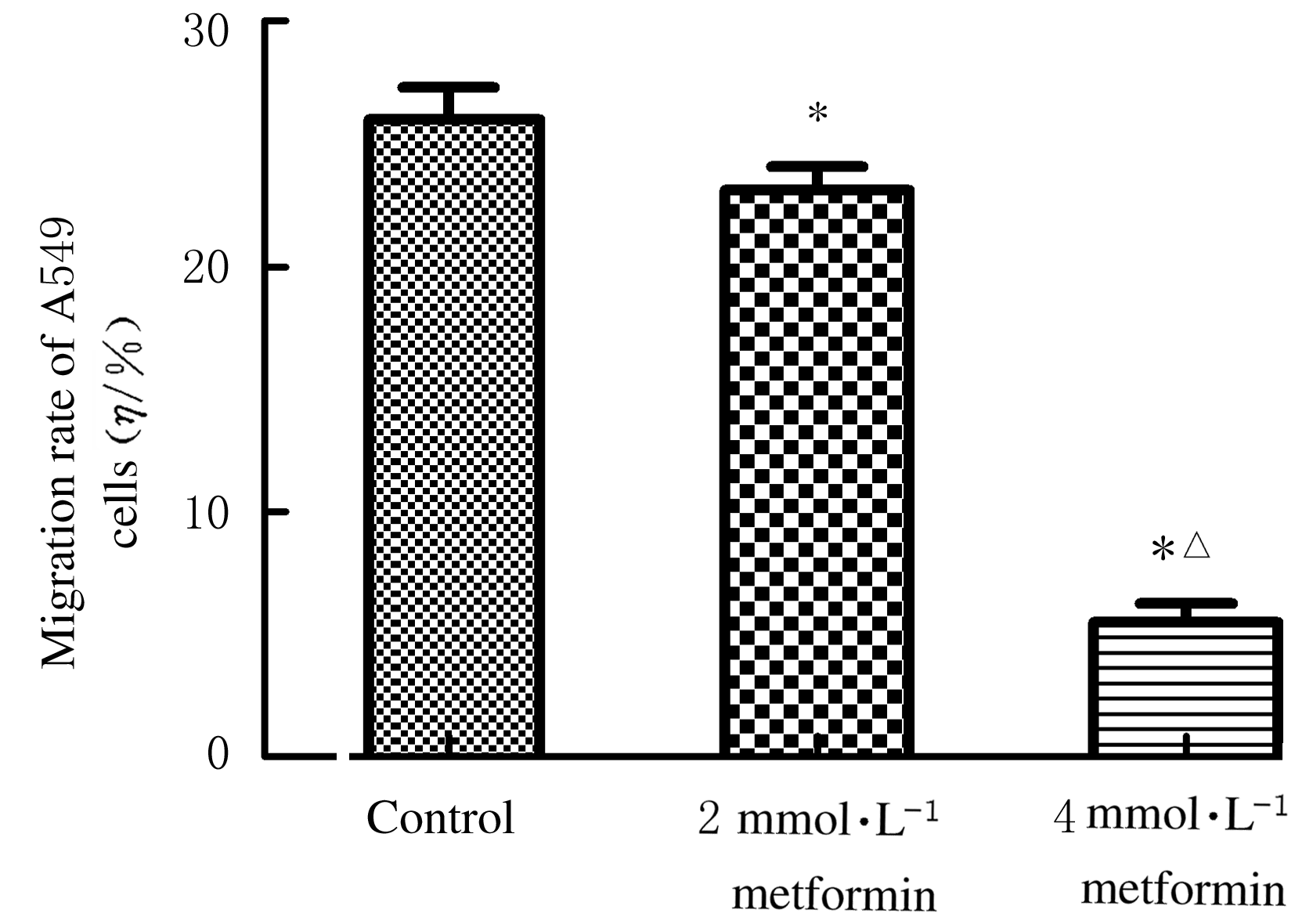
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (3): 637-643.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210313
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
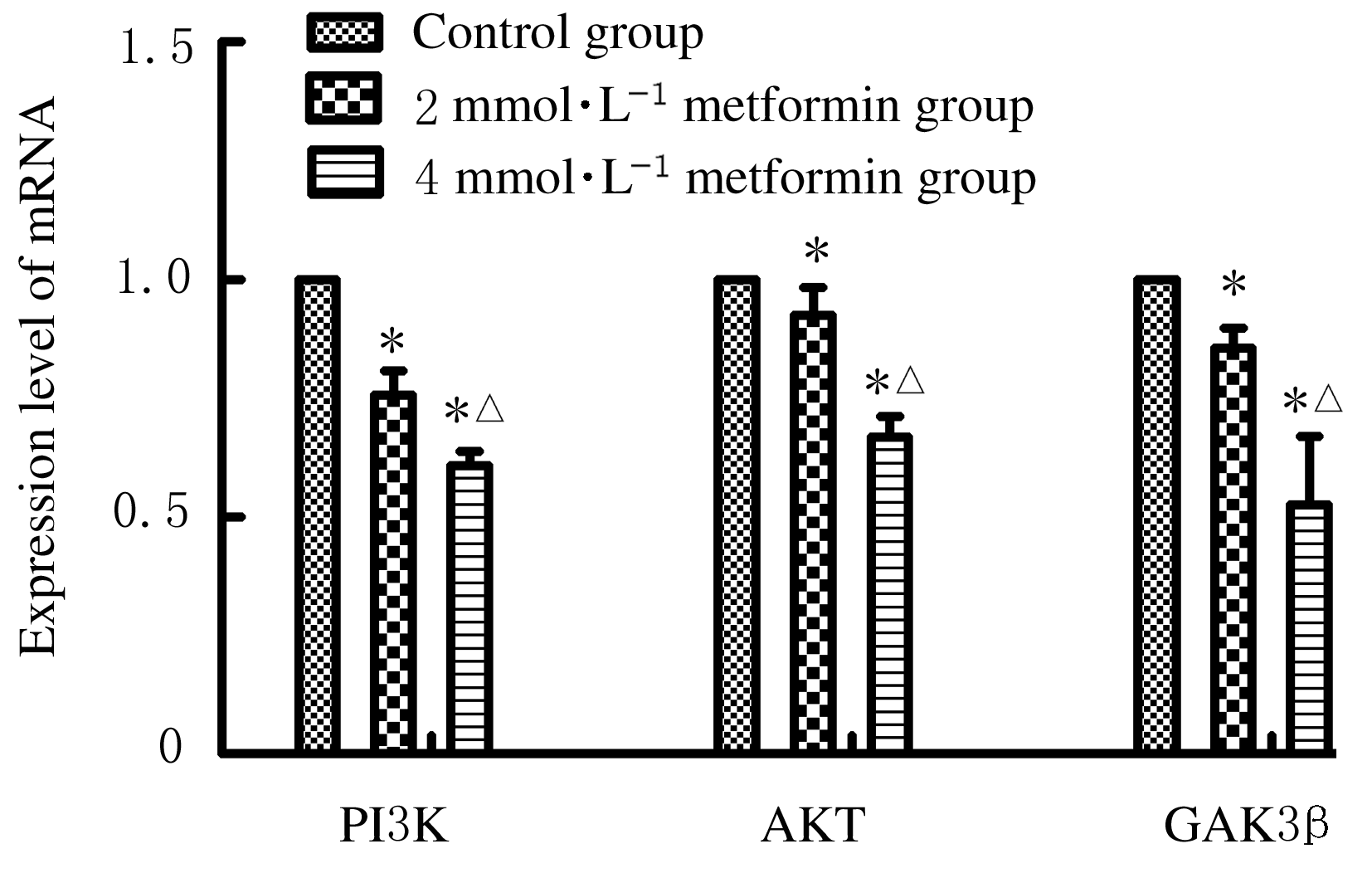
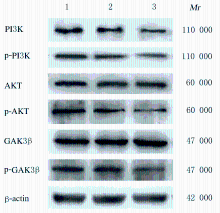
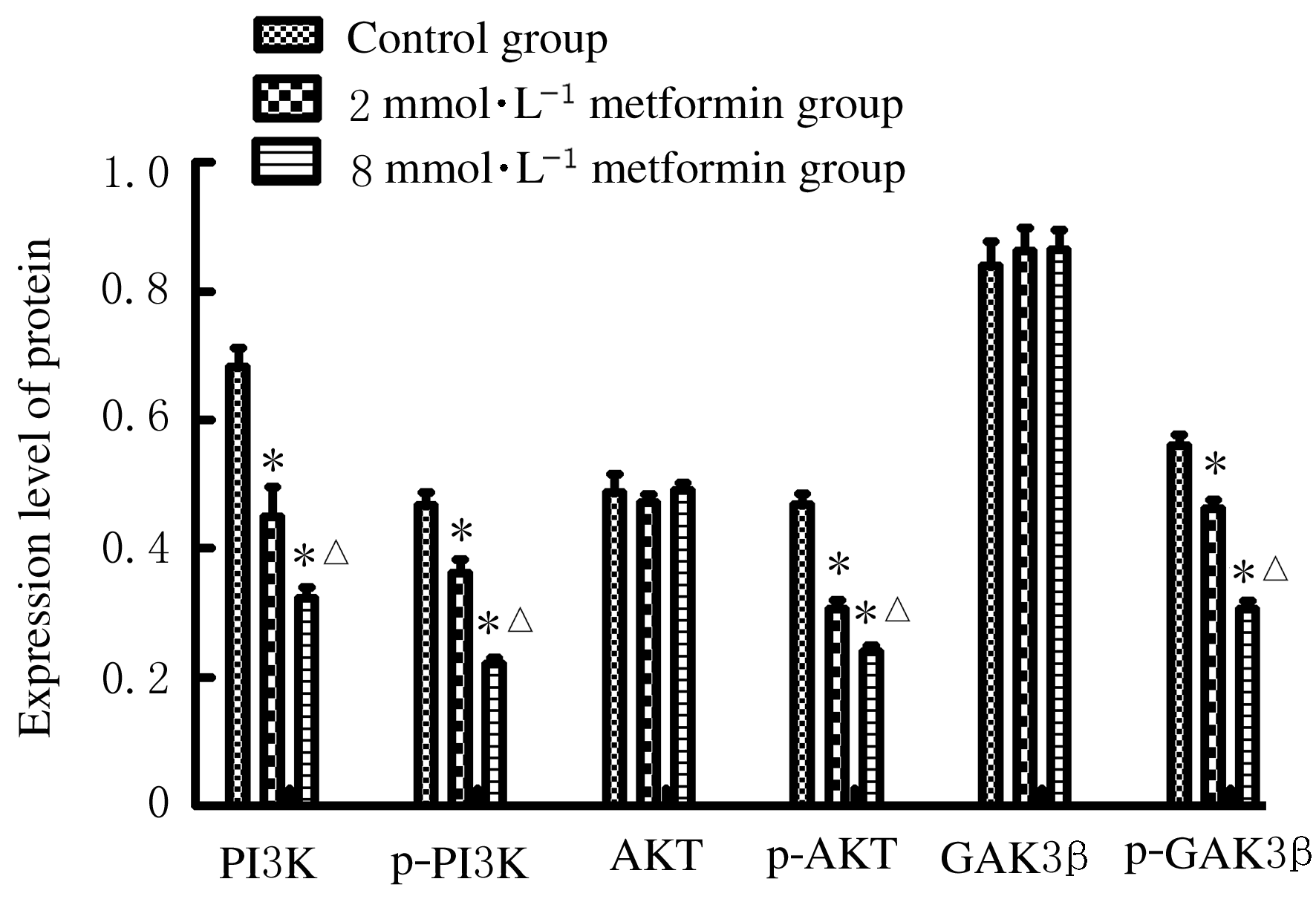
Effect of metformin on proliferation of lung cancer A549 cells through PI3K/AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway
Chunqing MU1,Lei ZHOU1,Nan ZHAO1,Hong WANG1,Zhi LI2( )
)
- 1.Institute of Translational Medicine,First Affiliated Hospital,Jinzhou Medical University,Jinzhou 121000,China
2.Institute of Translational Medicine,Jinzhou Medical University,Jinzhou 121000,China
-
Received:2020-08-19Online:2021-05-28Published:2021-05-28 -
Contact:Zhi LI E-mail:cljlizhi@163.com
CLC Number:
- R734.2
Cite this article
Chunqing MU, Lei ZHOU, Nan ZHAO, Hong WANG, Zhi LI. Effect of metformin on proliferation of lung cancer A549 cells through PI3K/AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 637-643.
share this article
Tab. 1
Proliferation rates of A549 cells in various groups at different time points (n=3,x±s, η/%)"
| Group | Proliferation rate of A549 cells | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (t/d) 24 | 48 | 72 | ||
| Control | 100.00±0.00 | 100.00±0.00 | 100.00±0.00 | |
| Metformin (mmol·L-1) | ||||
| 1 | 96.95±1.88* | 91.09±0.41* | 91.54±4.25* | |
| 2 | 91.80±1.23* | 87.87±3.46* | 81.91±1.00* | |
| 4 | 87.01±8.19* | 84.13±1.06* | 76.24±0.22* | |
| 8 | 84.46±1.61* | 74.79±0.41* | 60.32±2.98* | |
| 16 | 81.90±6.79* | 67.20±2.00* | 52.99±2.13* | |
| 32 | 79.60±1.37* | 57.04±3.77* | 22.68±0.30* | |
|
| [1] | Runhong MU, Xinzhu LIU, Rui LIN, Yupeng LI, Luyao WANG, Chunyu WANG, Xiao GUO. Effect of PRDX6 over-expression of proliferation, invasion and migration of liver cancer cells and its molecular mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 559-565. |
| [2] | Cuilan LIU, Jianjun LI, He JIANG, Jing LIU, Dan WANG, Chen LI, Di ZHAO. Effect of urolithin B on biological behaviors of human glioblastome U118 MG cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 566-574. |
| [3] | Xining LI, Wei WENG, Zheyuan SHEN, Xiaojie DOU, Yu ZHAO, Jikang MIN. Effect of mTOR phosphorylation level on proliferation,autophagy,and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 575-586. |
| [4] | Jia FENG, Haichan XU, Jian WEN, Zehua WU, Yi CHEN. Effect of betulinic acid on proliferation and apoptosis of myeloma cells by regulating JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 615-622. |
| [5] | Lei XIE, Xiaoli LIU, Jing GE, Yawei LI. Effects of baicalin combined with metformin on endocrine, inflammatory factors and insulin resistance in rats with polycystic ovary syndrome and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 623-629. |
| [6] | Bo MA, Jiangang LI, Jun WANG, Junli HOU, Liang LI. Promotion effect of miR-106b on invasion and migration of colon cancer cells through targeting TGF-β/Smad pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 630-636. |
| [7] | Xiaohui LI, Ziwei QU, Xin LU, Qingbin MENG, Huatao CHEN, Jun REN, Chengpei TAN. Regulatory effect of exosomes carrying miR-196b-5p derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on biological characteristics of colon cancer cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 660-668. |
| [8] | Ying YANG, Wei ZHAO, Dan LYU. Effect of C19ORF12 on proliferation and chemo-sensitivity of gastric cancer MKN45 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 687-693. |
| [9] | Zhangqi LOU,Qifan YU,Xuezhi SHEN,Hongqing CHEN,Yufeng LUO,Qianye CHEN,Guofen ZHENG,Yuemin DING,Xiong ZHANG. Effect of DEHP exposure in pregnant mice on neurobehavior of offsprings and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 323-329. |
| [10] | Haoxuan TANG,Nanfeng MENG,Meiling DU,Wei WANG,Tao HE. Inhibitory effect of new VEGF monoclonal antibody combined with all-trans retinoic acid on proliferation of breast cancer MCF-7 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 344-351. |
| [11] | Nuan WANG,Lijuan YANG,Juanjuan DAI,Aili WANG,Yan WU,Chengxia LIU. Promotion effects of MARCH1 on migration and invasion of human gastric cancer cells through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 352-359. |
| [12] | Jing WANG,Jing LIU,Xujing WEI,Yafei DU,Guiying FANG,Lin LI. Effects of oridonin on proliferation, migration, invasion and expression of lncRNA CCAT1 of endometrial carcinoma HEC-1B cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 384-389. |
| [13] | Qi ZHAO,Changhai HE,Zhi WANG,Xuefeng WANG,Xiaofei LIU. Inhibitory effect of ALKBH3 knockdown on growth, migration and tumor angiogenesis of bladder cancer cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 397-406. |
| [14] | Chunying ZHANG,Guangwei YIN,Mingda YOU,Hong CHEN,Yaojie HU,Yanbing LI,Chunyou CHEN. Inhibitory effects of siRNA targeting silencing TAK1 gene on proliferation and migration of thyroid cancer cells and p38 MAPK signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 110-117. |
| [15] | . Inhibitory effect of curcumin on tumor growth in colorectal cancer mice and its mechanism of PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathwayPEI Yongbin, WANG Guiqi, LI Wei, JIANG Xia, JIANG Haibo, ZHAO Zengren (Department of General Surgery,First Hospital,Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050031,China) [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 145-151. |