Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (5): 1281-1286.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210528
• Clinical medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
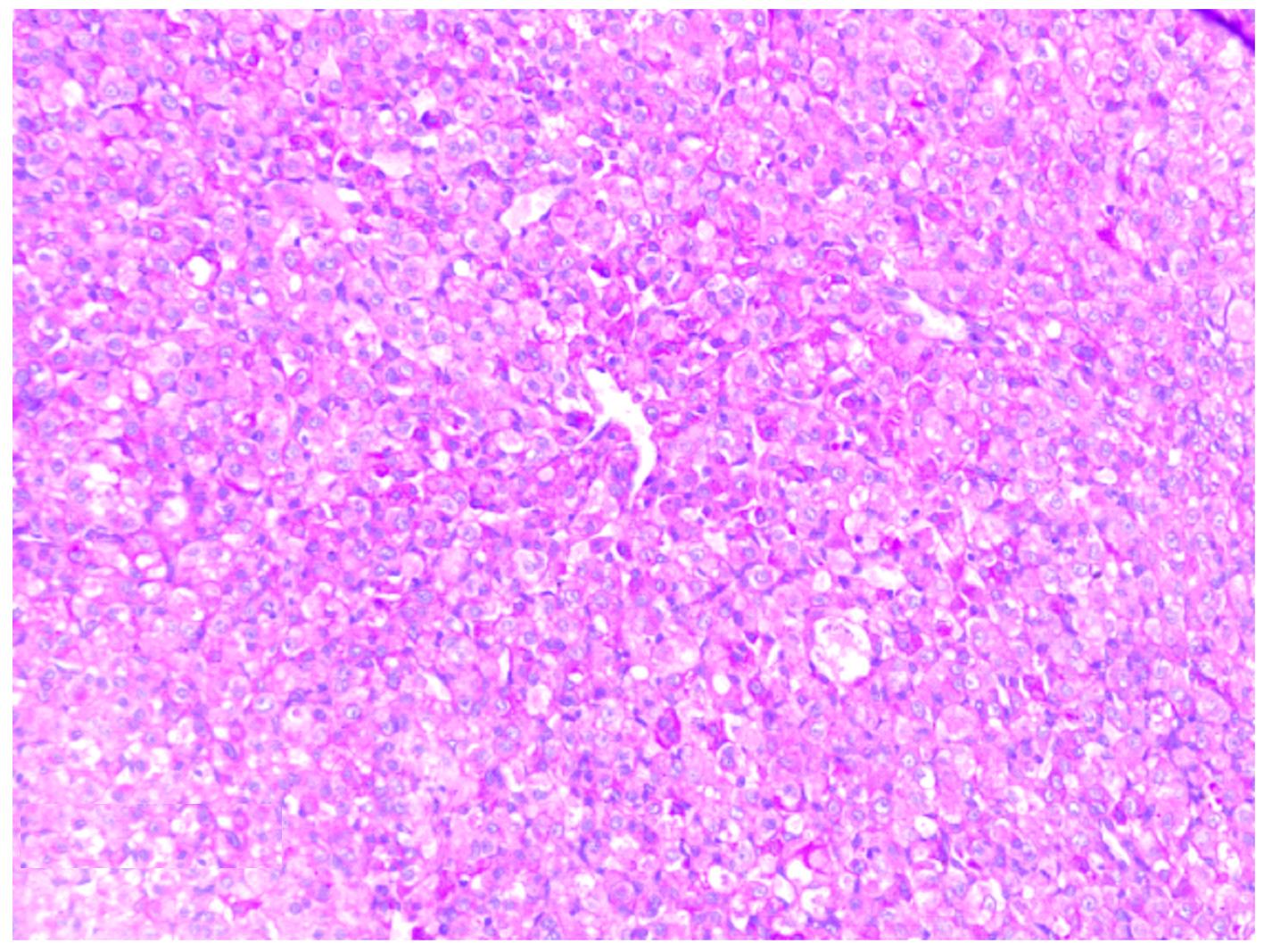
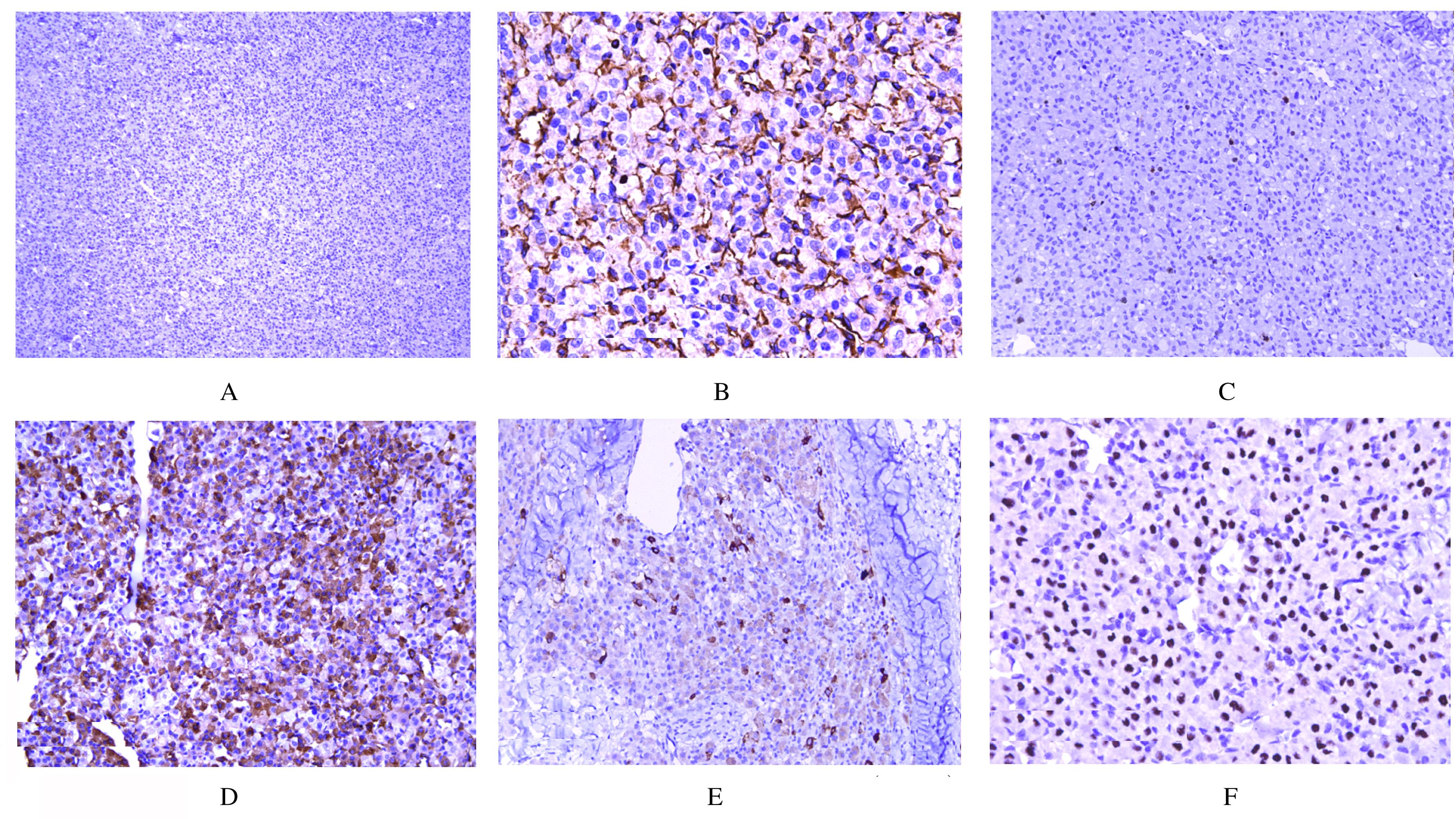
Alveolar soft part sarcoma of right buccal mucosa: A case report and literature review
Meisi REN,Yu FAN,Qingrui XUE,Tianyu WANG,Guangxiang ZANG( ),Hongchen SUN
),Hongchen SUN
- Department of Oral Pathology,Stomatology Hospital,China Medical University,Shenyang 110002,China
-
Received:2021-01-25Online:2021-09-28Published:2021-10-26 -
Contact:Guangxiang ZANG E-mail:gxzang@cmu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
- R739.8
Cite this article
Meisi REN,Yu FAN,Qingrui XUE,Tianyu WANG,Guangxiang ZANG,Hongchen SUN. Alveolar soft part sarcoma of right buccal mucosa: A case report and literature review[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1281-1286.
share this article
| 1 | CHRISTOPHERSON W M, FOOTE F W, STEWART F W.Alveolar soft-part sarcomas;structurally characteristic tumors of uncertain histogenesis[J]. Cancer, 1952, 5(1): 100-111. |
| 2 | CHEN J Y, CHEN X, WANG Y H, et al. Imaging findings and histologic appearances of alveolar soft part sarcoma in the prostate: a case report and review of the literature[J].Clin Genitourin Cancer,2015,13(4):e315-e319. |
| 3 | QIU L L, LI Y M, ALI S I, et al. Alveolar soft part sarcoma occurring in the penis of a 3-year-old boy: a rare case report[J]. Medicine, 2017, 96(45): e8383. |
| 4 | MULLINS B T, HACKMAN T. Adult alveolar soft part sarcoma of the head and neck: a report of two cases and literature review[J]. Case Rep Oncol Med, 2014, 2014: 597291. |
| 5 | PORTERA C A, HO V, PATEL S R, et al. Alveolar soft part sarcoma: clinical course and patterns of metastasis in 70 patients treated at a single institution[J]. Cancer, 2001, 91(3): 585-591. |
| 6 | KAYTON M L, MEYERS P, WEXLER L H, et al. Clinical presentation, treatment, and outcome of alveolar soft part sarcoma in children, adolescents, and young adults[J]. J Pediatr Surg, 2006, 41(1): 187-193. |
| 7 | FANBURG-SMITH J C, MIETTINEN M, FOLPE A L,et al. Lingual alveolar soft part sarcoma; 14 cases: novel clinical and morphological observations[J]. Histopathology, 2004, 45(5): 526-537. |
| 8 | WANG H W, DAI W, QIN X J, et al. A new clinical manifestation for cheek alveolar soft-part sarcoma: a case report and review of the literature[J]. J Oral Surg Maxillofac, 2014, 72(4): 817-822. |
| 9 | ALEGRÍA-LANDA V, LORA V, COTA C, et al. Alveolar soft-part sarcoma of the tongue[J]. Am J Dermatopathol, 2019, 41(3): 218-220. |
| 10 | SHELKE P, SARODE G S, SARODE S C, et al. Alveolar soft-part sarcoma of the oral cavity: a review of literature[J]. Rare Tumors, 2018, 10: 2036361318810907. |
| 11 | WAKELY P E, MCDERMOTT J E, ALI S Z. Cytopathology of alveolar soft part sarcoma: a report of 10 cases[J]. Cancer Cytopathol,2009,117(6): 500-507. |
| 12 | WANG B, WANG H, WEI J, et al. Alveolar soft part sarcoma of the right calf: a case report[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2020, 99(5): e18952. |
| 13 | FLORES R J, HARRISON D J, FEDERMAN N C, et al. Alveolar soft part sarcoma in children and young adults: a report of 69 cases[J]. Pediatr Blood Cancer, 2018, 65(5): e26953. |
| 14 | HEI Y, KANG L, YANG X J, et al. Orbital alveolar soft part sarcoma: a report of 8 cases and review of the literature[J]. Oncol Lett, 2018, 15(1): 304-314. |
| 15 | ALROMAIH S, ALQARYAN S, ALABOOD S,et al. Alveolar soft-part sarcoma in olfactory cleft: a case report and clinicopathological review[J]. Ear Nose Throat J, 2020: 0145561320955134. |
| 16 | MARTÍNEZ R, NIKLANDER S, DEICHLER J,et al. Alveolar soft-part sarcoma of the masseter and mandibular ramus: Report of a case and review of the literature[J]. J Dent Sci, 2018, 13(1): 75-79. |
| 17 | WANG Y, CUI J, YAN X, et al. Alveolar soft part sarcoma with multiple brain and lung metastases in pregnancy: a case report and literature review[J].Medicine(Baltimore), 2017, 96(46): e8790. |
| 18 | MARKER P, JENSEN M L, SIEMSSEN S J. Alveolar soft-part sarcoma of the oral cavity: report of a case and review of the literature[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 1995, 53(10): 1203-1208. |
| 19 | LAZAR A J, DAS P, TUVIN D, et al. Angiogenesis-promoting gene patterns in alveolar soft part sarcoma[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2007, 13(24): 7314-7321. |
| 20 | DAIGELER A, KUHNEN C, HAUSER J, et al. Alveolar soft part sarcoma: clinicopathological findings in a series of 11 cases[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2008, 6:71. |
| 21 | LIEBERMAN P H, BRENNAN M F, KIMMEL M, et al. Alveolar soft-part sarcoma. A clinico-pathologic study of half a century[J]. Cancer, 1989, 63(1):1-13. |
| 22 | TANABE K, NAKAMURA S, HYUGA T, et al. Pediatric primary alveolar soft part sarcoma of the bladder[J]. Case Rep Urol, 2018, 2018: 1-4. |
| 23 | WHALEY R D, THOMPSON L D R. Primary thyroid gland alveolar soft part sarcoma[J]. Head Neck Pathol, 2020, 14(3): 701-706. |
| 24 | JABER O I, KIRBY P A. Alveolar soft part sarcoma[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med,2015, 139(11): 1459-1462. |
| [1] | Junjie HOU,Xuguang MI,Xiaonan LI,Xiaonan LI,Ying YANG,Xianzhuo JIANG,Ying ZHOU,Zhiqiang NI,Ningyi JIN,Yanqiu FANG. Treatment of advanced rectal cancer with rectovaginal fistula through bevacizumab combined with FOLFIRI regimen: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 790-795. |
| [2] | Qian LI,Jingyi YUAN,Jiaqi ZHOU,Min ZHAO,Ke WANG. Pulmonary imaging changes as first manifestation of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 796-800. |
| [3] | Qian LI,Jiaqi ZHOU,Jingyi YUAN,Min ZHAO,Xin DI,Ke WANG. Spindle cell carcinoma of lung: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1557-1561. |
| [4] | Aiping WEN,Le LUO,Zhiwei MENG,Jingji JIN,Honggui ZHOU,Jihong ZHU. Expression of Tip60 protein in endometrial adenocarcinoma tissue and its clinical significance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1244-1249. |
| [5] | Qi ZHU,Lamei LI,Yanjun CAI,Fang XU,Junqi NIU,Wanyu LI. Hepatoid adenocarcinoma of stomach:A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 1028-1032. |
| [6] | BAN Shuofeng, ZHANG Shichen, SUN Yidan, WANG Jing, HAN Bing. Expressions of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D and epithelial cell adhesion molecule in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue and their significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(03): 589-593. |
| [7] | LIU Xiuhua, WANG Man, DONG Xinjie, LIU Jingnan, HAN Wei, GUAN Yinghui. Expression of filamin A in cancer tissue of cervical cancer patients and its clinical significance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(06): 1238-1242. |
| [8] | WANG Chuang, YU Shuli, LI Tao, LYU Rongrong, QI Jiemin. Expressions of heparanase and integrin α5β1 proteins in hydatidform mole tissue and their clinnical significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(06): 1361-1366. |
| [9] | LIU Jiaying, TIAN Chang, CONG Shan, ZHAO Min, WANG Ke. Pulmonary sarcoidosis diagnosed by PET/CT as pulmonary lymphangitic carcinomatosis: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(06): 1445-1448. |
| [10] | YANG Baoxia, LI Ping, WANG Cong, ZHANG Peng, ZHENG Baihong, XU Zhong. Acute necrotizing encephalopathy of children with good prognosis: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(06): 1449-1453. |
| [11] | LI Hua, CAO Yansha, ZHAO Jinping, REN Fu, LI Ning. Expression of SIRT6 protein in colon cancer tissue detected by tissue microarray technique and its clinical significance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(04): 893-898. |
| [12] | TIAN Yanhua, SU Kai, WANG Sanchun, TONG Weifang, ZHANG Xu, WEI Mingxue, FENG Qingjie. Sarcomatoid carcinoma of throat: A report of 5 cases and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(03): 697-700. |
| [13] | CAO Yingkun, LIU Liping, MA Xiaoshan, YE Guowei, JIANG Yining, BAI Shiqi, LI Yunqian. Left temporal low-grade myofibroblastic sarcoma of infant: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(03): 705-708. |
| [14] | TIAN Chang, LIU Jiaying, CONG Shan, ZHAO Min, WANG Ke. Acute gout attack with persistent medium and high fever as first manifestation: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(03): 714-717. |
| [15] | LIU Jiaying, TIAN Chang, CONG Shan, ZHAO Min, WANG Ke. Sjogren's syndrome with pulmonary bullae in both lungs as lung imaging performance: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(02): 414-417. |