Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (4): 1028-1032.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210429
• Clinical medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
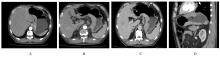
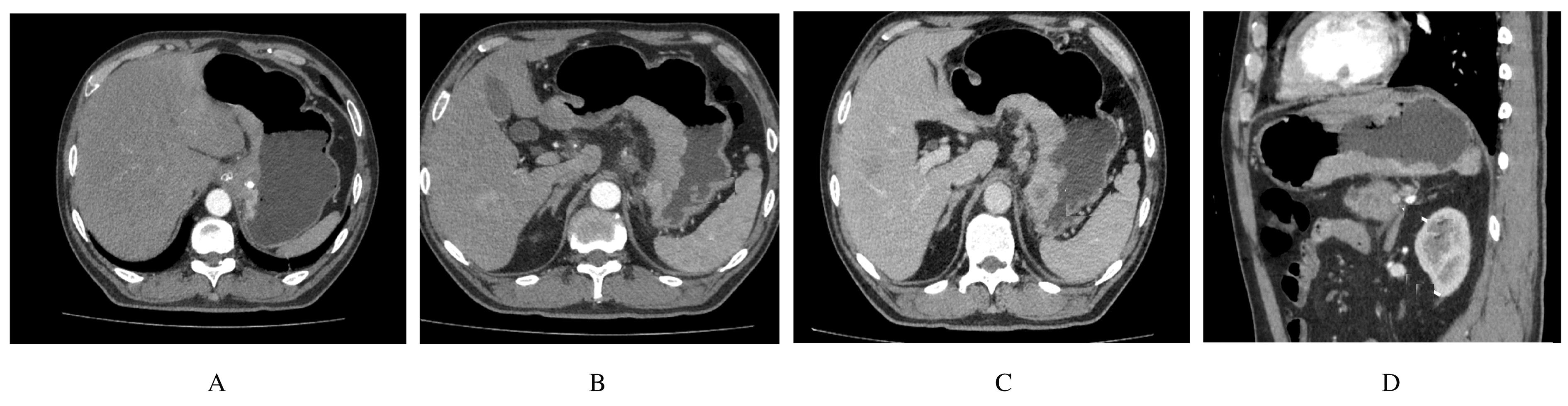
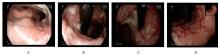
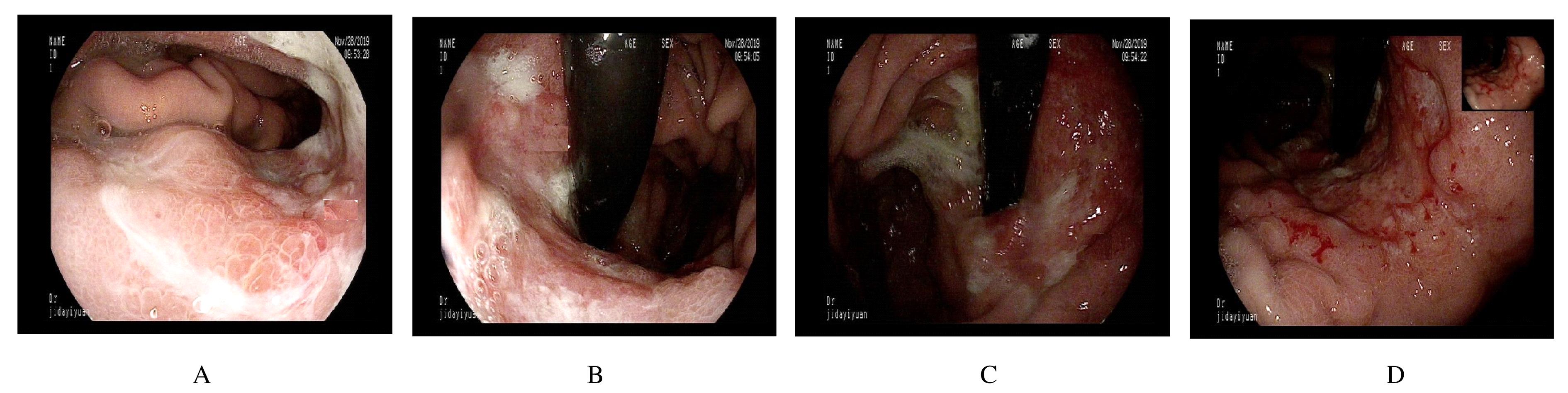
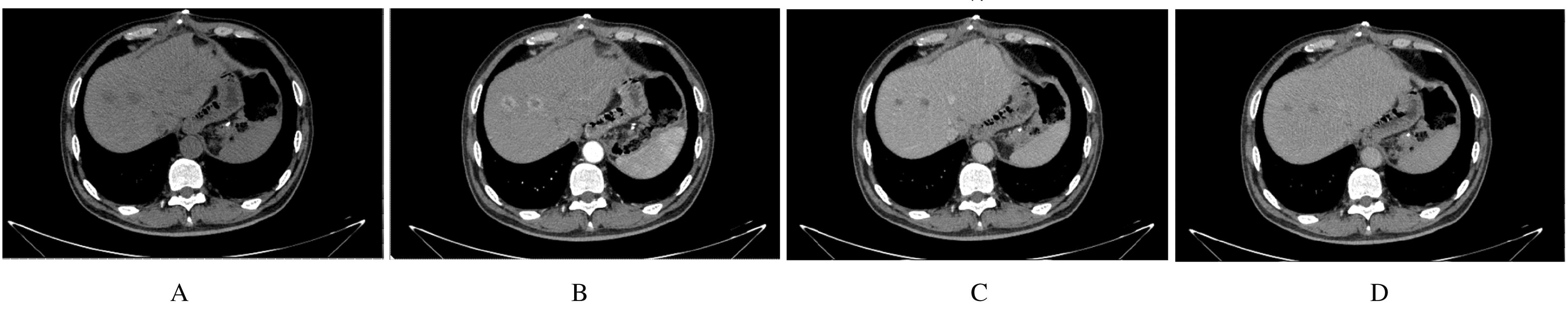
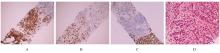
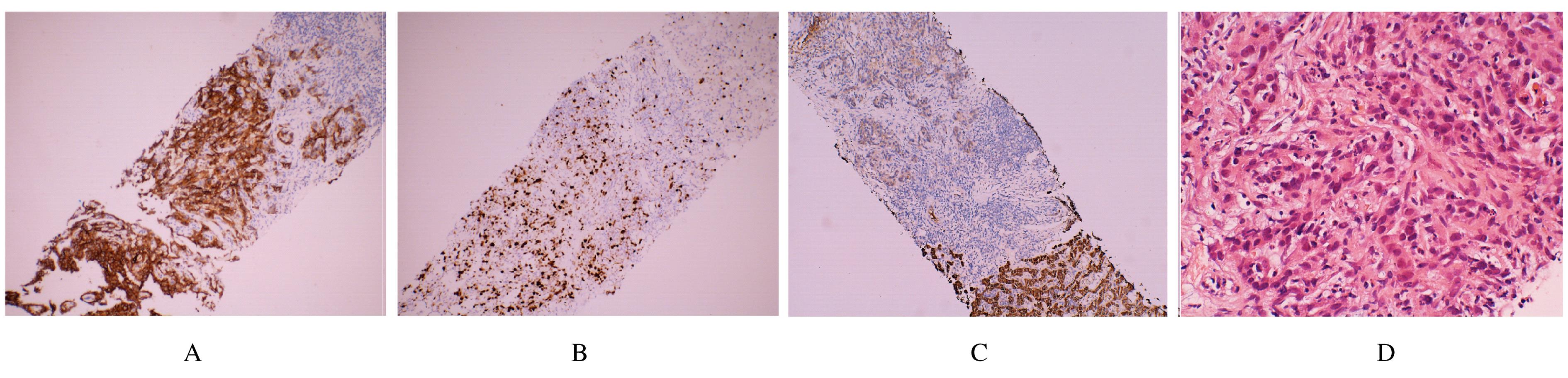
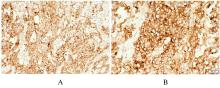
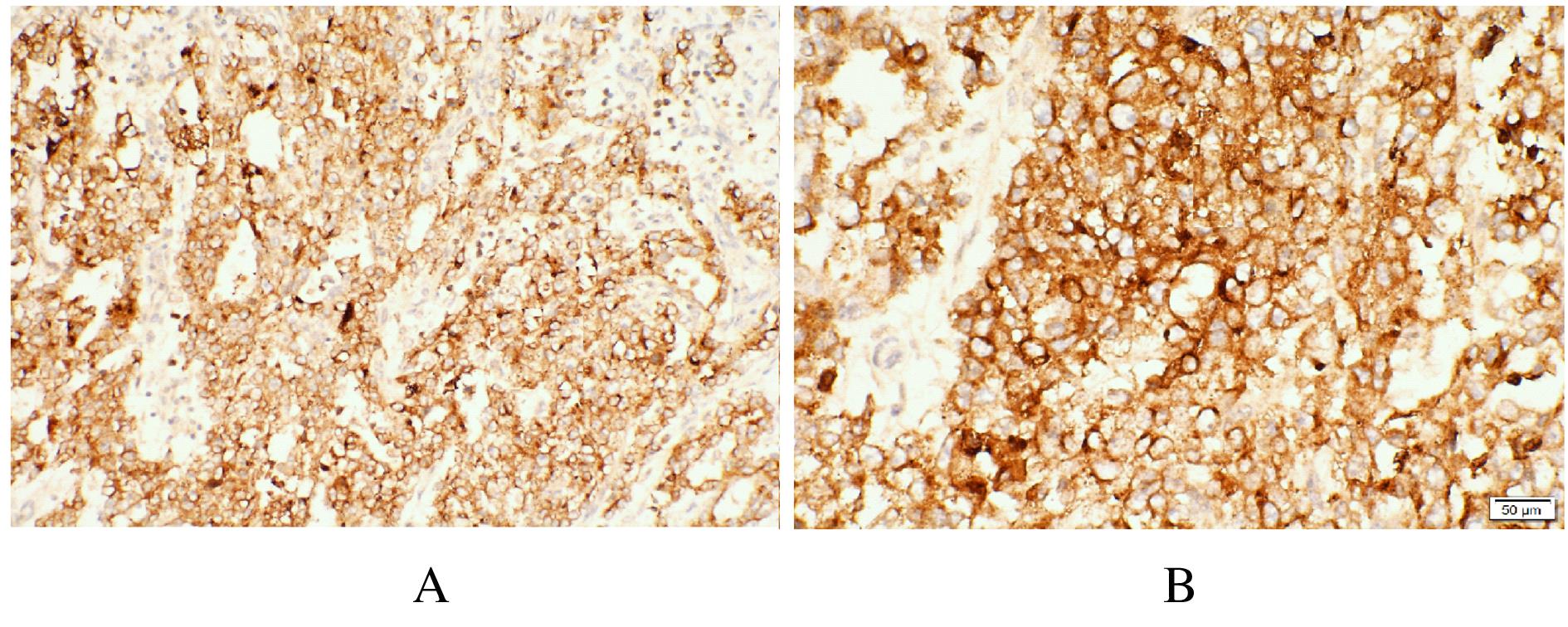
Hepatoid adenocarcinoma of stomach:A case report and literature review
Qi ZHU,Lamei LI,Yanjun CAI,Fang XU,Junqi NIU,Wanyu LI( )
)
- Department of Hepatology,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
-
Received:2020-11-09Online:2021-07-28Published:2021-07-22 -
Contact:Wanyu LI E-mail:liwanyu2006@163.com
CLC Number:
- R735.2
Cite this article
Qi ZHU,Lamei LI,Yanjun CAI,Fang XU,Junqi NIU,Wanyu LI. Hepatoid adenocarcinoma of stomach:A case report and literature review[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 1028-1032.
share this article
| 1 | ALPERT E, PINN V W, ISSELBACHER K J. Alpha-fetoprotein in a patient with gastric carcinoma metastatic to the liver[J]. N Engl J Med, 1971, 285(19): 1058-1059. |
| 2 | ISHIKURA H, KIRIMOTO K, SHAMOTO M, et al. Hepatoid adenocarcinomas of the stomach. An analysis of seven cases[J]. Cancer, 1986, 58(1): 119-126. |
| 3 | METZGEROTH G, STRÖBEL P, BAUMBUSCH T, et al. Hepatoid adenocarcinoma-review of the literature illustrated by a rare case originating in the peritoneal cavity[J]. Onkologie, 2010, 33(5): 263-269. |
| 4 | SU J S, CHEN Y T, WANG R C,et al.Clinicopathological characteristics in the differential diagnosis of hepatoid adenocarcinoma: a literature review[J].World J Gastroenterol, 2013, 19(3): 321-327. |
| 5 | SØREIDE J A, GREVE O J, GUDLAUGSSON E, et al. Hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the stomach: proper identification and treatment remain a challenge[J]. Scand J Gastroenterol, 2016, 51(6): 646-653. |
| 6 | ZHOU K, WANG A Q, AO S, et al. The prognosis of hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the stomach: a propensity score-based analysis[J].BMC Cancer, 2020,20(1):671. |
| 7 | ZENG X Y, YIN Y P, XIAO H, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the stomach: evaluation of a pooled case series[J]. Curr Med Sci, 2018, 38(6): 1054-1061. |
| 8 | 孙 凡, 周少飞, 孙凯丽. 胃肝样腺癌14例临床病理分析并文献复习[J]. 肿瘤学杂志, 2019, 25(8): 763-766. |
| 9 | 郑晓丹, 刘 洋, 张淑红, 等. 胃肝样腺癌3例的临床病理分析并文献复习[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2017, 16(20): 2066-2069. |
| 10 | QU B G, BI W M, QU B T, et al. PRISMA-compliant article: clinical characteristics and factors influencing prognosis of patients with hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the stomach in China[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2016, 95(15): e3399. |
| 11 | SØREIDE J A. Therapeutic approaches to gastric hepatoid adenocarcinoma: current perspectives[J]. Ther Clin Risk Manag, 2019, 15: 1469-1477. |
| 12 | 任为正, 苏茂生, 杜晓霞, 等. 胃肝样腺癌:一种易误诊为原发性肝癌的特殊类型的胃腺癌 [J]. 中华肝胆外科杂志, 2016, 22(7): 500-502. |
| 13 | 于丽丽, 何向蕾, 吴建宇, 等. GPC3、HSP70、SALL4和AFP联合表达对胃肝样腺癌诊断的意义[J]. 浙江医学, 2020, 42(8): 780-782, 786, 884. |
| 14 | 李汝东, 侯家晨, 崔晓晗, 等. 胃肝样腺癌诊疗现状及进展[J]. 实用肿瘤学杂志, 2017, 31(1): 53-56. |
| 15 | CHEN E B, WEI Y C, LIU H N, et al. Hepatoid adenocarcinoma of stomach: emphasis on the clinical relationship with alpha-fetoprotein-positive gastric cancer [J]. Biomed Res Int, 2019, 2019: 6710428. |
| 16 | 王雅坤, 张小田. 产甲胎蛋白胃癌和胃肝样腺癌[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2017, 39(11): 801-807. |
| 17 | 茅 翔, 罗 奋, 陈宗祐, 等. 提高对胃肝样腺癌和产甲胎蛋白胃癌的认识[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2015,37(6): 401-403. |
| 18 | 俞程彬, 马贵亮, 毛伟征. 胃肝样腺癌的诊治现状[J]. 中国普外基础与临床杂志, 2020, 27(4): 515-520. |
| 19 | 张楠楠, 邓靖宇. 临床非常见型胃癌的研究进展[J]. 中华胃肠外科杂志, 2018, 21(2): 228-234, 235. |
| 20 | 关露露, 赵青芳, 陈小兵. 胃肝样腺癌研究进展[J]. 肿瘤基础与临床, 2017, 30(2): 173-175. |
| [1] | Ping HU,Nan JIANG,Yinghua LI,Hongguang ZHAO. Analysis on characteristics of 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging of patient with primary small cell osteosarcoma of coccyx:A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 216-221. |
| [2] | Aiping WEN,Le LUO,Zhiwei MENG,Jingji JIN,Honggui ZHOU,Jihong ZHU. Expression of Tip60 protein in endometrial adenocarcinoma tissue and its clinical significance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1244-1249. |
| [3] | Meisi REN,Yu FAN,Qingrui XUE,Tianyu WANG,Guangxiang ZANG,Hongchen SUN. Alveolar soft part sarcoma of right buccal mucosa: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1281-1286. |
| [4] | LI Ying, QIU Tianyuan, BAO Xingfu, HU Min. Evaluation on expansion efficiency of microimplant-assisted rapid palatal expansion in treatment of maxillary transverse deficiency in adolescents with CBCT [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 1050-1055. |
| [5] | ZHANG Li, QUAN Tao, LIU Dayong, JIA Zhi. Effects of different root canal filing materals on root flexure resistance after random load fatigue test detected by Micro-CT [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 822-827. |
| [6] | ZHOU Dongkui, LU Mingqian, FENG Xuesong, LIU Yufei, SONG Hao, XU Liang. Follicular dendritic cell sarcoma of small intestine and ileocecal region: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 858-862. |
| [7] | GUO Fei, ZHU Lin, XU Hong, XIE Zongyu, ZHANG Li, DENG Xuefei. Analysis on correlation between image features of chest MSCT and prognosis in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 867-874. |
| [8] | BAN Shuofeng, ZHANG Shichen, SUN Yidan, WANG Jing, HAN Bing. Expressions of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D and epithelial cell adhesion molecule in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue and their significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(03): 589-593. |
| [9] | LIU Xiuhua, WANG Man, DONG Xinjie, LIU Jingnan, HAN Wei, GUAN Yinghui. Expression of filamin A in cancer tissue of cervical cancer patients and its clinical significance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(06): 1238-1242. |
| [10] | WANG Chuang, YU Shuli, LI Tao, LYU Rongrong, QI Jiemin. Expressions of heparanase and integrin α5β1 proteins in hydatidform mole tissue and their clinnical significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(06): 1361-1366. |
| [11] | LI Hua, CAO Yansha, ZHAO Jinping, REN Fu, LI Ning. Expression of SIRT6 protein in colon cancer tissue detected by tissue microarray technique and its clinical significance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(04): 893-898. |
| [12] | TIAN Yanhua, SU Kai, WANG Sanchun, TONG Weifang, ZHANG Xu, WEI Mingxue, FENG Qingjie. Sarcomatoid carcinoma of throat: A report of 5 cases and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(03): 697-700. |
| [13] | JING Wenhua, LI Hongyu, GUAN Yinghui. Comparison of values between Wells score and YEARS algorithm in dignosis of pulmonary embolism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(01): 88-93. |
| [14] | MU Tianchi, LIU Chao, FU Shuai, LI Qiyang, WANG Xinmeng, XIAO Jianying. Expression of activator of basal transcription 1 in gastric cancer tissue and its clinical significance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(01): 94-99. |
| [15] | FENG Qing, WEN Ming. CT manifestations of hepatic lesions without obvious enhancement in arterial phase and their significancs in differential diagnosis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(01): 163-169. |