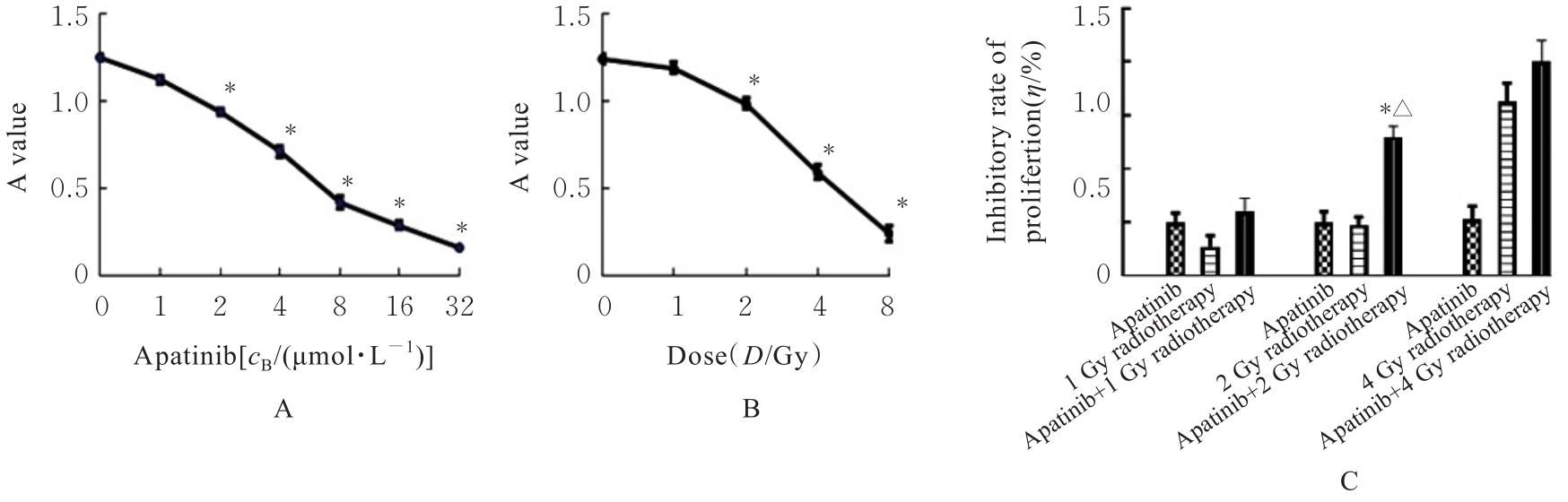
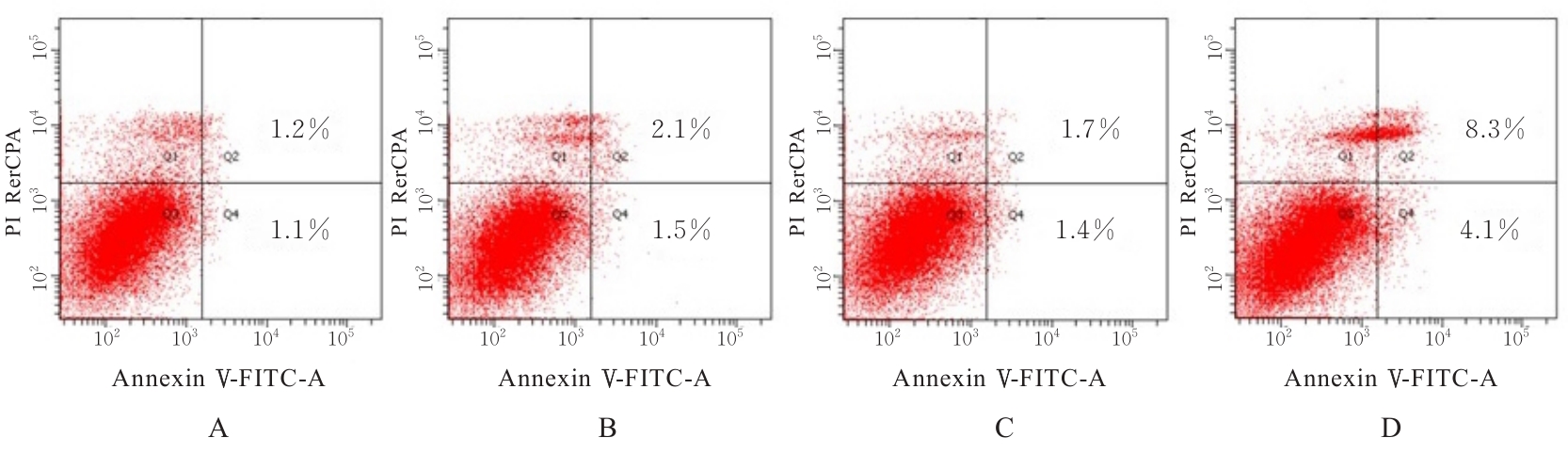
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 1009-1015.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240415
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Synergistic sensitization of apatinib mesylate and radiotherapy on hepatocarcinoma cells invitro
Yongjing YANG,Tianyang KE,Shixin LIU,Xue WANG,Dequan XU,Tingting LIU,Ling ZHAO( )
)
- Department of Radiation Oncology,Tumor Hospital,Jilin Province,Changchun 130012,China
-
Received:2023-07-15Online:2024-07-28Published:2024-08-01 -
Contact:Ling ZHAO E-mail:2267398336@qq.com
CLC Number:
- R735.7
Cite this article
Yongjing YANG,Tianyang KE,Shixin LIU,Xue WANG,Dequan XU,Tingting LIU,Ling ZHAO. Synergistic sensitization of apatinib mesylate and radiotherapy on hepatocarcinoma cells invitro[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1009-1015.
share this article
| 1 | CHEN W, ZHENG R, BAADE P D, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015[J]. Ca A Cancer J Clin, 2016, 66(2):115-132. |
| 2 | WANG H, ZHU X, ZHAO Y, et al. Phase 1 trial of apatinib combined with intensity-modulated radiotherapy in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. BMC Cancer, 2022, 22(1):771. |
| 3 | QIU H, KE S, CAI G, et al. An exploratory clinical trial of apatinib combined with intensity-modulated radiation therapy for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Med, 2023,12(1):213-222. |
| 4 | LIU X, LUO J, ZHANG L, et al. SIB-IMRT combined with apatinib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with poor response to transarterial chemoembolization[J]. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol, 2022,46(6):101897. |
| 5 | DVORAK H F. Tumor stroma, tumor blood vessels, and antiangiogenesis therapy[J]. Cancer J, 2015,21(4):237-243. |
| 6 | RIM C H, SEONG J. Application of radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma in current clinical practice guidelines[J]. Radiat Oncol J, 2016 Sep; 34(3):160-167. |
| 7 | JIANG S, ZHOU Y, ZOU L, et al. Low- dose Apatinib promotes vascular normalization and hypoxia reduction and sensitizes radiotherapy in lung cancer[J]. Cancer Med, 2023, 12(4): 4434-4445. |
| 8 | 冯久桓, 秦叔逵, 王 琳. 甲磺酸阿帕替尼的研究现状与进展[J]. 临床肿瘤学杂志, 2017, 22(4): 345-356. |
| 9 | 孙 菲, 孙志强, 汪建林, 等. 阿帕替尼对食管癌 Kyse150 细胞放射敏感性影响的实验研究[J].中华放射医学与防护杂志,2017, 37(11): 805-809. |
| 10 | 刘 伟,张建文. 阿帕替尼联合放疗对 HeLa 细胞周期和凋亡影响的体外研究[J].安徽医科大学学报,2018,53 (1): 55-58. |
| 11 | LIANG L J, HU C X, WEN Y X, et al. Apatinib combined with local irradiation leads to systemic tumor control via reversal of immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in lung cancer[J]. Cancer Res Treat, 2020,52(2):406-418. |
| 12 | QIN S, LI Q, GU S, et al. Apatinib as second-line or later therapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (AHELP): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021,6(7):559-568. |
| 13 | 张延藏, 王满周, 韩新巍, 等. 载药栓塞微球经肝动脉化疗栓塞术联合阿帕替尼治疗不可切除肝癌后二线追加卡瑞利珠单抗的安全性和有效性分析[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2023, 39(4): 834-842. |
| 14 | HU Y, QIN T, LI S, et al. Efficacy and safety of SBRT combined with Camrelizumab and Apatinib in HCC patients with PVTT: Study protocol of a randomized controlled trial[J]. Front Oncol, 2020,26(10):1589. |
| 15 | 姜增凯, 叶晓歌, 陈琴华. 阿帕替尼对肝癌细胞增殖和迁移能力的影响研究[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2016, 32(15):1422-1424. |
| 16 | QI X, YANG M, MA L, et al. Synergizing sunitinib and radiofrequency ablation to treat hepatocellular cancer by triggering the antitumor immune response[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2020, 8(2):e001038. |
| 17 | SONG J, GUAN Z, SONG C, et al. Apatinib suppresses the migration, invasion and angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by blocking VEGF and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2021,23(6):429. |
| 18 | 殷 亮, 王 荩, 黄凤昌, 等. 甲磺酸阿帕替尼对结肠癌 HCT-116 细胞增殖的抑制作用及其机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报,2017, 3: 367-372. |
| 19 | HSU H W, GRIDLEY D S, KIM P D, et al. Linifanib (ABT-869) enhance radiosensitivity of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells[J]. Oral Oncol, 2013, 49(6): 591-597. |
| 20 | MEIJER T W, KAANDERS J H, SPAN P N, et al. Targeting hypoxia, HIF-1, and tumor glucose metabolism to improve radiotherapy effcacy[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2012, 18(20): 5585-5594. |
| 21 | 王一, 李锦毅. 索拉非尼与阿帕替尼对人肝癌 SMMC-7721 细胞的抑制作用比较[J]. 中华灾害救援医学, 2017, 5 (12): 681-684. |
| 22 | LIN D, WU J. Hypoxia inducible factor in hepatocellular carcinoma: A therapeutic target[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2015,21(42): 12171-12178. |
| 23 | NG E W, SHIMA D T, CALIAS P, et al. Pegaptanib, a targeted anti-VEGF aptamer for ocular vascular disease[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2006, 5(2): 123-132. |
| 24 | BROWN DM, REGILLO CD. Anti-VEGF agents in the treatment of neovascular age-related macular degeneration: applying clinical trial results to the treatment of everyday patients[J]. Am J Ophthalmol, 2007, 144(4):627-37. |
| 25 | CHEN Y, CHEN X, DING X, et al. Afatinib, an EGFR inhibitor, decreases EMT and tumorigenesis of Huh-7 cells by regulating the ERK-VEGF/MMP9 signaling pathway[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2019, 20(4):3317-3325. |
| 26 | ZHANG H H, ZHANG Y, CHENG Y N, et al. Metformin incombination with curcumin inhibits the growth, metastasis, and angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo [J]. Mol Carcinog, 2018, 57(1):44-56. |
| 27 | LIAO J, JIN H, LI S, et al. Apatinib potentiates irradiation effect via suppressing PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019,38(1):454. |
| 28 | 朱丽珍, 许晓磊, 阿卜杜萨拉木·艾尼, 等. 肝细胞癌免疫治疗研究进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2023, 39(5):1197-1203. |
| [1] | Hua CHEN,Na SHA,Ning LIU,Yang LI,Haijun HU. Effect of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on biological behavior of human liposarcoma SW872 cells through YAP [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1000-1008. |
| [2] | Chaojie GUO,Jiajia ZHANG,Jie ZENG,Huiyu WANG, AIERFATI·Aimaier,Jiang XU. Expressions of PLOD1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue and cells and their significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1035-1043. |
| [3] | Jinlian LI,Lanzhen HUANG,Xishi HUANG,Kangzhi LI,Jiali JIANG,Miaomiao ZHANG,Qunying WU. Bioinformatics analysis on key genes related to prognosis, diagnosis, and immune cell infiltration of hepatocellular carcinoma and their potential therapeutic drugs [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1062-1075. |
| [4] | Yilin REN,Yichen ZANG,Lele XUE,Kaige YANG,Sufang CHEN,Weinan WANG,Chenghua LUO,Weihua LIANG,Lianghai WANG,Feng LI,Jianming HU. Bioinformatics analysis based on effect of M2 macrophage-derived Siglec15 on malignant biological behaviour of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells and its experimental validation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 881-890. |
| [5] | Guoxing YU,Xin ZHANG,Hengwei DU,Bingjie CUI,Na GAO,Cuilan LIU,Jing DU. Effect of urolithin C on proliferation, apoptosis and autophagy of human acute myeloid leukemia HL-60 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 908-916. |
| [6] | Chao LIANG,Juanjuan DAI,Ning ZHOU,Dandan WANG,Jie ZHAO,Di AN,Yan WU. Effect of oridonin on cell proliferation, migration, and apoptosis of human nasopharynx carcinoma HONE-1 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 917-924. |
| [7] | Shan CAO,Yijia ZHANG,Yang BAI,Fang CHEN,Sha XIE,Qianqian HAN. Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro experimental verification based on anti-atherosclerosis mechanism of Xiaoban Tongmai Formula [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 925-938. |
| [8] | Tengfei WANG, Feng CHEN, Ling QI, Ting LEI, Meihui SONG. Inhibitory effect of D-limonene on proliferation of glioblastoma cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 647-657. |
| [9] | Jiacai FU,Lingsha QING,Lu YANG,Meihui SONG,Xianying ZHANG,Xiaocui LIU,Fengjin LI,Ling QI. Inhibitory effect of Schisandrin B on proliferation of pancreatic cancer Pan02 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 638-646. |
| [10] | Yuan WANG,Zhijuan WANG,Mingshu ZHANG,Yihui WANG,Qing ZHANG,Liping YE. Effects of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 on invasion and migration of lung cancer A549 and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 666-675. |
| [11] | Lin CHEN,Limin YAN,Huaijie XING,Min CHEN,Xiaoyan LI,Chaosheng ZENG. Improvement effect of Xuebijing on brain tissue injury and Th17/Treg immune imbalance in cerebrospinal fluid in NMDA receptor encephalitis model mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 697-707. |
| [12] | Bo YUAN,Jiayi XIE,Siyu JIANG,Yajun MENG,Qinghua ZHU,Xiaofei LI,Xiumei FU,Lide XIE. Effect of adipose-derived stem cell-derived exosomes on migration ability of macrophages in vitro [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 718-727. |
| [13] | Li ZHANG,Binfeng XIA,Huihui HUANG,Ru WANG,Min KONG,Xia YIN. Research progress in pathophysiological mechanism and clinical diagnosis and treatment of hypertension associated with vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor inhibitors [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 854-863. |
| [14] | Shuang CHEN,Hong LI. Effect of silencing FOXK1 gene on proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer HGC-27 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 371-378. |
| [15] | Linru WANG,Jing ZHANG,Dongchan ZHAO,Jinjun WANG,Wenxian HU. Effect of silencing FOXO1 gene on autophagy and apoptosis of human aortic vascular smooth muscle cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 431-441. |
|