Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 1028-1038.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250419
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles
Analysis on influencing factors for occurrence of angina pectoris in diabetic mellitus patients and its Bayesian network risk prediction
Shuang LI,Jiayu GE,Xianzhu CONG,Aimin WANG,Yujia KONG,Fuyan SHI( ),Suzhen WANG(
),Suzhen WANG( )
)
- Department of Health Statistics,School of Public Health,Shandong Second Medical University,Weifang 261053,China
-
Received:2024-08-29Accepted:2024-10-31Online:2025-07-28Published:2025-08-25 -
Contact:Fuyan SHI,Suzhen WANG E-mail:shifuyan@sdsmu.edu.cn;wangsz@sdsmu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
- R587.1
Cite this article
Shuang LI,Jiayu GE,Xianzhu CONG,Aimin WANG,Yujia KONG,Fuyan SHI,Suzhen WANG. Analysis on influencing factors for occurrence of angina pectoris in diabetic mellitus patients and its Bayesian network risk prediction[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(4): 1028-1038.
share this article
Tab.1
Variables associated with occurrence of angina pectoris in patients with DM and their assignments"
| Variable | Assignment |
|---|---|
| Gender | Female=0, Male=1 |
| Age | |
| Nation | Others=0, White=1 |
| BMI (kg· | Normal=0, Overweight=1, Obesity=2 |
| LDL-c (mmol·L-1) | <4.14=0, |
| HDL-c (mmol·L-1) | <1.04=0, |
| TC (mmol·L-1) | <5.2=0, |
| TG (mmol·L-1) | <1.7=0, |
| HbA1c (mmol·L-1) | 20-42=0, >42=1 |
| Smoke status | Never=0, Previous=1, Current=2 |
| Drink status | Never=0, Previous=1, Current=2 |
| Maternal smoking around birth | No=0, Yes=1 |
| Breastfeeding | No=0, Yes=1 |
| Comparative body size in childhood | Average=0, Thinner=1, Plumper=2 |
| HBP | No=0, Yes=1 |
| Regular exercise | No=0, Yes=1 |
| Healthy diet | No=0, Yes=1 |
| Insomnia | Never=0, Sometimes=1, Usually=2 |
| Sleep duration | 7-8 h=0, <7 h=1, >8 h=2 |
| Angina | No=0, Yes=1 |
Tab.2
Univariate analysis on occurrence of angina pectoris in patients with DM"
| Variable | Non-Angina (n=19 540) | Angina (n=3 172) | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 199.348 | <0.001 | ||
| Female | 7 906(40.461) | 866(27.301) | ||
| Male | 11 634(59.539) | 2 306(72.699) | ||
| Age(Year) | 307.417 | <0.001 | ||
| 8 396(42.968) | 840(26.482) | |||
| >60 | 11 144(57.032) | 2 332(73.518) | ||
| Nation | 7.720 | 0.006 | ||
| Others | 2 520(12.897) | 353(11.129) | ||
| White | 17 020(87.103) | 2 819(88.871) | ||
| BMI(kg· | 123.255 | <0.001 | ||
| Normal | 1 506(7.707) | 119(3.752) | ||
| Overweight | 4 521(23.137) | 604(19.042) | ||
| Obesity | 13 513(69.156) | 2 449(77.206) | ||
| LDL-c(mmol·L-1) | 31.424 | <0.001 | ||
| <4.14 | 18 521(94.785) | 3 080(97.100) | ||
| 1 019(5.215) | 92(2.900) | |||
| HDL-c(mmol·L-1) | 103.052 | <0.001 | ||
| <1.04 | 6 273(32.103) | 1 309(41.267) | ||
| 13 267(67.897) | 1 863(58.733) | |||
| TC(mmol·L-1) | 151.702 | <0.001 | ||
| 15 050(77.021) | 2 751(86.728) | |||
| >5.2 | 4 490(22.979) | 421(13.272) | ||
| TG(mmol·L-1) | 93.441 | <0.001 | ||
| 8 930(45.701) | 1 158(36.507) | |||
| >1.7 | 10 610(54.299) | 2 014(63.493) | ||
| HbA1c(mmol·L-1) | 39.046 | <0.001 | ||
| 20-42 | 4 060(20.778) | 507(15.984) | ||
| >42 | 15 480(79.222) | 2 665(84.016) | ||
| Smoke status | 8.692 | <0.001 | ||
| Never | 17 399(89.043) | 2 769(87.295) | ||
| Previous | 1 615(8.255) | 299(9.426) | ||
| Current | 526(2.692) | 104(3.279) | ||
| Drink status | 51.580 | 0.013 | ||
| Never | 1 689(8.642) | 291(9.174) | ||
| Previous | 1 342(6.867) | 329(10.372) | ||
| Current | 16 500(84.441) | 2 552(80.454) | ||
| Maternal smoking around birth | 10.615 | <0.001 | ||
| No | 14 465(74.028) | 2 261(71.280) | ||
| Yes | 5 075(25.972) | 911(28.720) | ||
| Breastfeeding | 1.925 | 0.165 | ||
| No | 3 248(16.622) | 496(15.637) | ||
| Yes | 16 292(83.378) | 2 676(84.363) | ||
| Comparative body size in childhood | 9.007 | 0.011 | ||
| Average | 8 944(45.773) | 1 368(43.128) | ||
| Thinner | 6 614(33.848) | 1 151(36.286) | ||
| Plumper | 3 982(20.379) | 653(20.586) | ||
| HBP | 144.562 | <0.001 | ||
| No | 8 967(45.890) | 1 093(34.458) | ||
| Yes | 10 573(54.110) | 2 079(65.542) | ||
| Regular exercise | 12.667 | <0.001 | ||
| No | 17 230(88.178) | 2 866(90.353) | ||
| Yes | 2 310(11.822) | 306(9.647) | ||
| Healthy diet | 0.353 | 0.552 | ||
| No | 15 804(80.880) | 2 587(81.557) | ||
| Yes | 3 736(19.120) | 594(18.443) | ||
| Insomnia | 159.495 | <0.001 | ||
| Never | 4 292(21.965) | 466(14.691) | ||
| Sometimes | 8 606(44.043) | 1 296(40.858) | ||
| Usually | 6 642(33.992) | 1 410(44.451) | ||
| Sleep duration | 103.074 | <0.001 | ||
| 7-8 h | 11 864(60.716) | 1 652(52.081) | ||
| <7 h | 5 317(27.211) | 973(30.674) | ||
| >8 h | 2 359(12.073) | 547(17.245) |
Tab.3
Multifactorial Logistic regression analysis on occurrence of angina in patients with DM"
| Variable | B | SE | Wald χ2 | P | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age(referring to <60) | |||||
| 0.702 | 0.043 | 266.169 | <0.001 | 2.018(1.855-2.196) | |
| Gender(referring to female) | |||||
| Male | 0.573 | 0.047 | 151.011 | <0.001 | 1.773(1.618-1.943) |
| Nation(referring to others) | |||||
| White | -0.067 | 0.067 | 0.994 | 0.319 | 0.935(0.820-1.067) |
| BMI(referring to normal) | |||||
| Overweight | 0.276 | 0.082 | 11.391 | 0.001 | 1.318(1.123-1.547) |
| Obesity | 0.507 | 0.081 | 39.606 | <0.001 | 1.661(1.418-1.946) |
| LDL-c(referring to <1.04 mmol·L-1) | |||||
| 0.003 | 0.125 | 0.009 | 0.983 | 1.003(0.784-1.282) | |
| HDL-c(referring to <4.14 mmol·L-1) | |||||
| -0.043 | 0.044 | 0.950 | 0.330 | 0.958(0.879,1.044) | |
| TC(referring to | |||||
| >5.2 mmol·L-1 | -0.528 | 0.064 | 69.000 | <0.001 | 0.590(0.520-0.668) |
| TG(referring to | |||||
| >1.7 mmol·L-1 | 0.257 | 0.043 | 35.075 | <0.001 | 1.293(1.188-1.408) |
| HbA1c(referring to 20-42 mmol·L-1) | |||||
| >42 mmol·L-1 | 0.175 | 0.053 | 10.758 | 0.001 | 1.191(1.073-1.323) |
| Insomnia(referring to never) | |||||
| Sometimes | 0.378 | 0.059 | 41.623 | <0.001 | 1.459(1.301-1.636) |
| Usually | 0.654 | 0.060 | 119.198 | <0.001 | 1.923(1.710-2.162) |
| HBP(referring to no) | |||||
| Yes | 0.306 | 0.042 | 54.367 | <0.001 | 1.358(1.252-1.474) |
| Comparative body size in childhood (referring to average) | |||||
| Thinner | 0.124 | 0.045 | 7.675 | 0.006 | 1.131(1.037-1.235) |
| Plumper | 0.061 | 0.054 | 1.298 | 0.255 | 1.063(0.957-1.181) |
| Maternal smoking around birth(referring to no) | |||||
| Yes | 0.141 | 0.045 | 9.917 | 0.002 | 1.152(1.055-1.257) |
| Smoke status(referring to never) | |||||
| Previous | 0.227 | 0.069 | 10.791 | 0.001 | 1.255(1.096-1.438) |
| Current | 0.264 | 0.113 | 5.441 | 0.020 | 1.302(1.043-1.626) |
| Drink status(referring to never) | |||||
| Previous | 0.084 | 0.094 | 0.797 | 0.372 | 1.088(0.905-1.308) |
| Current | -0.320 | 0.073 | 19.015 | <0.001 | 0.726(0.629-0.838) |
| Regular exercise(referring to no) | |||||
| Yes | -0.199 | 0.066 | 9.095 | 0.003 | 0.820(0.721-0.933) |
| Sleep duration(referring to <7 h) | |||||
| 7-8 h | 0.173 | 0.047 | 13.794 | <0.001 | 1.189(1.085-1.303) |
| >8 h | 0.377 | 0.056 | 45.365 | <0.001 | 1.458(1.307-1.627) |
Tab.4
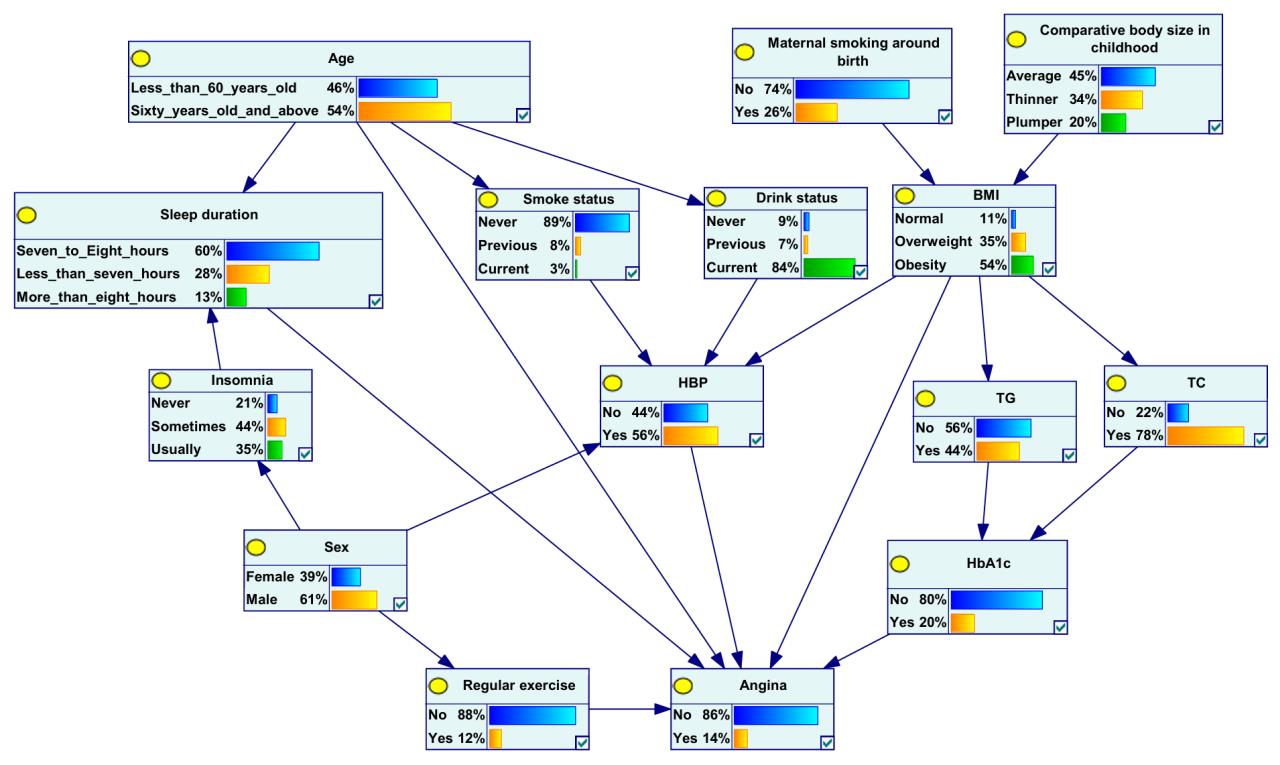
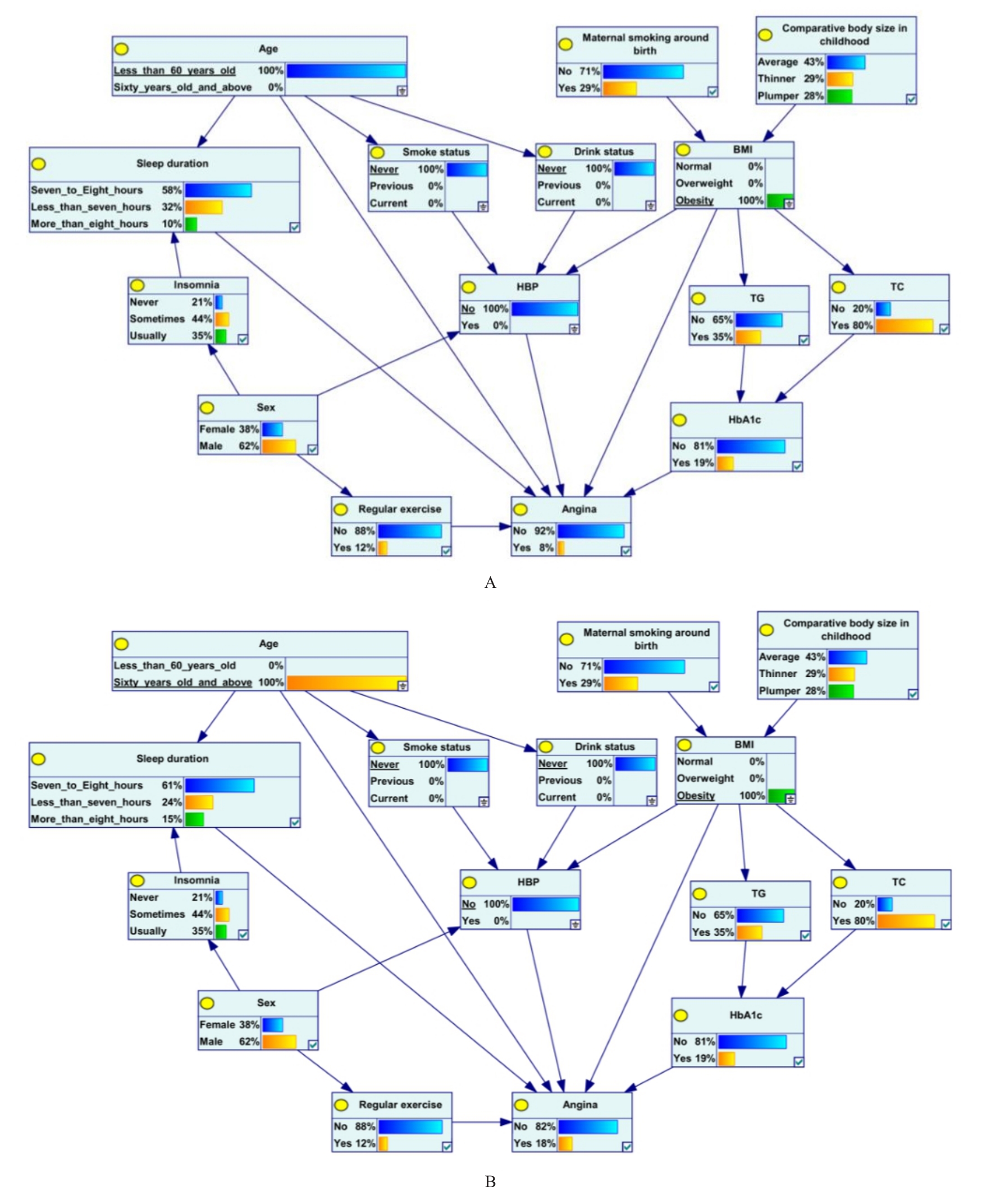
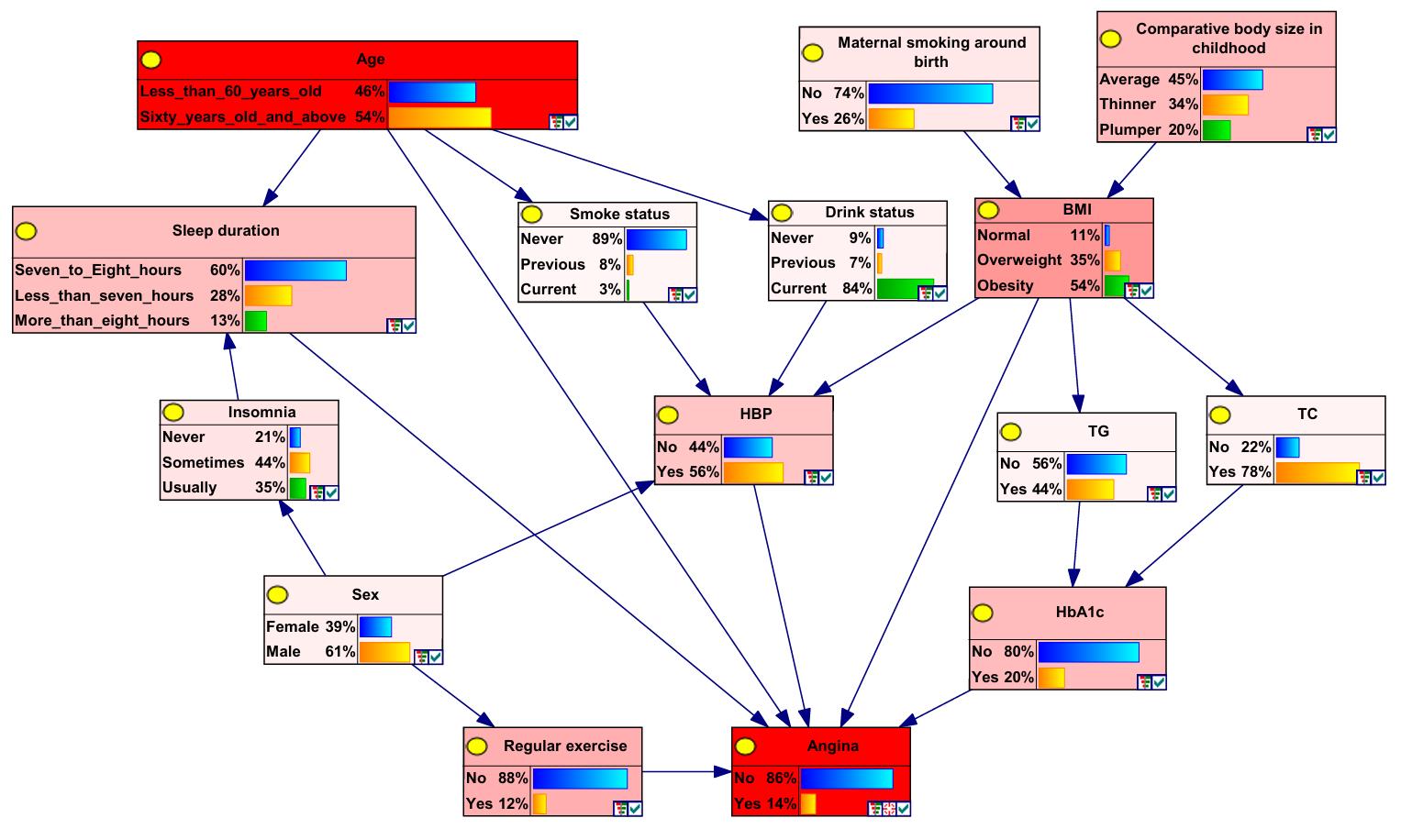
Partial conditional probabilities table of angina in patients with DM"
| BMI | HbA1c[cB/(mmol·L-1)] | HBP | Regular exercise | Sleep duration | Age (year) | Angina | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | ||||||
| Normal | 20-42 | No | No | 7-8 h | 0.976 | 0.024 | |
| Normal | 20-42 | No | No | <7 h | 0.919 | 0.081 | |
| Normal | 20-42 | No | No | >8 h | 0.998 | 0.002 | |
| Overweight | 20-42 | No | No | 7-8 h | 0.966 | 0.034 | |
| Overweight | 20-42 | No | No | <7 h | 0.871 | 0.129 | |
| Overweight | 20-42 | No | No | >8 h | 0.928 | 0.072 | |
| Obesity | 20-42 | No | No | 7-8 h | 0.952 | 0.048 | |
| Obesity | 20-42 | No | No | <7 h | 0.727 | 0.278 | |
| Obesity | 20-42 | No | No | >8 h | 0.795 | 0.205 | |
| Normal | >42 | No | No | 7-8 h | 0.984 | 0.016 | |
| Normal | >42 | No | No | <7 h | 0.869 | 0.131 | |
| Normal | >42 | No | No | >8 h | 0.999 | 0.001 | |
| Overweight | >42 | No | No | 7-8 h | 0.941 | 0.059 | |
| Overweight | >42 | No | No | <7 h | 0.825 | 0.175 | |
| Overweight | >42 | No | No | >8 h | 0.952 | 0.048 | |
| Obesity | >42 | No | No | 7-8 h | 0.932 | 0.068 | |
| Obesity | >42 | No | No | <7 h | 0.785 | 0.215 | |
| Obesity | >42 | No | No | >8 h | 0.872 | 0.128 | |
| [1] | Society of Diabetes, Shanghai Medical Association;Society of Endocrinology, Shanghai Medical Association. 成人糖尿病患者血压管理专家共识[J]. 上海医学, 2021, 44(1): 8-18. |
| [2] | COLES B, ZACCARDI F, HVID C, et al. Cardiovascular events and mortality in people with type 2 diabetes and multimorbidity: a real-world study of patients followed for up to 19 years[J]. Diabetes Obes Metab, 2021, 23(1): 218-227. |
| [3] | 陈 松, 杨 姣. 心绞痛介入治疗联合药物治疗的长期疗效观察[J]. 中国现代药物应用, 2024, 18(5): 78-81. |
| [4] | 刘婧南, 丁慧茹, 韩东旭, 等. 2型糖尿病患者血清A20水平下降的相关因素分析[J]. 同济大学学报(医学版), 2025, 46(03): 418-425. |
| [5] | 刘虹宏, 张冬花, 杨永红, 等. 糖尿病对未发生过心肌梗死的老年冠心病患者存活心肌的影响[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2023, 25(10): 1042-1045. |
| [6] | 卢亚男, 刘丽俊, 高 宇, 等. 糖化白蛋白、糖化白蛋白/糖化血红蛋白与2型糖尿病合并冠心病相关性的研究[J]. 中国糖尿病杂志, 2023, 31(9): 678-682. |
| [7] | GOLDBERG R B, ORCHARD T J, CRANDALL J P, et al. Effects of long-term metformin and lifestyle interventions on cardiovascular events in the diabetes prevention program and its outcome study[J]. Circulation, 2022, 145(22): 1632-1641. |
| [8] | 王旭春, 宋伟梅, 潘金花, 等. MMPC-Tabu混合算法的贝叶斯网络模型在高脂血症相关因素研究中的应用[J]. 中国卫生统计, 2022, 39(3): 345-350, 355. |
| [9] | BIEDERMANN A, TARONI F. Bayesian networks and probabilistic reasoning about scientific evidence when there is a lack of data[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2006, 157(2/3): 163-167. |
| [10] | CLIFTON L, LIU X N, COLLISTER J A, et al. Assessing the importance of primary care diagnoses in the UK Biobank[J]. Eur J Epidemiol, 2024, 39(2): 219-229. |
| [11] | LUGNER M, RAWSHANI A, HELLERYD E, et al. Identifying top ten predictors of type 2 diabetes through machine learning analysis of UK Biobank data[J]. Sci Rep, 2024, 14(1): 2102. |
| [12] | DI GIUSEPPE D, BOTTAI M, ASKLING J, et al. Physical activity and risk of rheumatoid arthritis in women: a population-based prospective study[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2015, 17(1): 40. |
| [13] | 张 杰. 健康生活方式的代谢特征与类风湿关节炎发病风险关联性研究: 基于英国生物银行队列[D]. 合肥: 安徽医科大学, 2023. |
| [14] | PEDERSEN B K, FISCHER C P. Beneficial health effects of exercise: the role of IL-6 as a myokine[J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2007, 28(4): 152-156. |
| [15] | NIELSEN S, PEDERSEN B K. Skeletal muscle as an immunogenic organ[J]. Curr Opin Pharmacol, 2008, 8(3): 346-351. |
| [16] | 吕志刚, 李 叶, 王洪喜, 等. 贝叶斯网络的结构学习综述[J]. 西安工业大学学报, 2021, 41(1): 1-17. |
| [17] | ZHANG Z, ZHANG J, WEI Z, et al. Application of tabu search-based Bayesian networks in exploring related factors of liver cirrhosis complicated with hepatic encephalopathy and disease identification[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 6251. |
| [18] | 邵文娟, 贾 潇, 蔡可书, 等. 基于贝叶斯网络的膝骨关节炎患病风险定量预测研究[J]. 北京体育大学学报, 2024, 47(3): 124-132. |
| [19] | WANG Y H, LIU H Z, HU X D, et al. Association between hemoglobin glycation index and 5-year major adverse cardiovascular events: the REACTION cohort study[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2023, 136(20): 2468-2475. |
| [20] | XU S, QIN Z, YUAN R X, et al. The hemoglobin glycation index predicts the risk of adverse cardiovascular events in coronary heart disease patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2022, 9: 992252. |
| [21] | PAKHARE M, ANJANKAR A. Critical correlation between obesity and cardiovascular diseases and recent advancements in obesity[J]. Cureus, 2024, 16(1): e51681. |
| [22] | ZHANG Z Q, DING J W, WANG X N, et al. Abnormal circadian rhythms are associated with plaque instability in acute coronary syndrome patients[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2019, 12(10): 3761-3771. |
| [23] | 赵丹红, 李婷艳, 蔡海琴. 活血宁心安神方联合穴位贴敷治疗冠心病稳定型心绞痛合并失眠临床研究[J]. 新中医, 2023, 55(12): 155-159. |
| [1] | Qi WANG,Lingyu JIANG,Xiangrong LIU. Research progress in application of weight-adjusted waist circumference index in risk prediction and evaluation of obesity-related diseases [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 848-854. |
| [2] | Aimin WANG,Fenglin WANG,Yiming HUANG,Yaqi XU,Wenjing ZHANG,Xianzhu CONG,Weiqiang SU,Suzhen WANG,Mengyao GAO,Shuang LI,Yujia KONG,Fuyan SHI,Enxue TAO. CatBoost algorithm and Bayesian network model analysis based on risk prediction of cardiovascular and cerebro vascular diseases [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1044-1054. |
| [3] | Xue FANG,Yu KANG,Xiaoxi SHA,Zhifen HAN,Yan ZHANG. Detection of gastrocnemius muscle hardness of diabetic patients under different functional states by ultrasonic shear wave elastography and its clinical significance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 451-456. |
| [4] | Jiaxin WANG,Zhenqi WANG,Xuan ZHANG. Expressions of CDKAL1 gene and its splice isomers in peripheral blood lymphocytes of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and their clinical significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1290-1295. |
| [5] | Jing GUAN,Shen HA,Hao YUAN,Ying CHEN,Pengju LIU,Zhi LIU,Shuang JIANG. Protective effect of Modified Xiao-Xian-Xiong Decoction on liver injury in rats with type 2 diabete mellitus and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 608-616. |
| [6] | Xiaowei HUANG,Siqi ZHANG,Yixin ZHANG,Bo LIU,Xin WANG,Fenglan JI,Runze YANG,Huibo XU,Tao DING. Relationship between syndrome manifestations and differentially expressed genes in rat model of type 2 diabetes mellitus with Qi and Yin deficiency explored through transcriptomics [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 625-633. |
| [7] | Junxiong ZHAO,Qian WU,Liangui NIE,Shengquan LIU,Zhentao JIANG,Jian CHEN,Ting XIAO,Jun YANG. Ameliorative effect of SO2 on myocardial fibrosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 8-14. |
| [8] | Xiaojuan ZHU,Haitao DAI,Yan LI,Lingxin CUI,Ya WANG,Jiang XU,Nan WU. Improvement effect of grape seed proanthocyanidin extract on periodontal inflammation in diabetic periodontitis rats and its influence on expression levels of TLR4 and NF-κB in periodontal tissue [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 31-38. |
| [9] | Jiaqing YAN,Ying ZHU,Min HU. Effect of initial periodontal therapy in patient with type 1 diabetes mellitus complicated with periodontitis: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1586-1592. |
| [10] | Shasha LIU,Yun ZHAO,Guoqiang SUN,Feifei CHEN. Expressions of Apelin and APJ in placental tissue of gestational diabetes mellitus patients and its effect on insulin resistance and behavior of trophoblast cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1314-1323. |
| [11] | Xin SHEN,Yang LIU,Hongyu CHEN,Jie ZHANG,Qingli CHENG,Guang YANG. Regulatory effect of high glucose on polarization of RAW264.7 macrophages via miR-125b in mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 847-857. |
| [12] | Weigang WANG,Xiaohong LI,Bing LIU,Tao DING,Kang WEI,Jianming TIAN. Effect of genistein chromium complex on glucose and lipid metabolism in obese rats induced by sodium glutamate [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 892-897. |
| [13] | Minmin DAI,Ying CHANG,Na XU,Yan WANG,Meng XU,Wenyue XU,Jiawang MA,Wensen LIU,Zhengai CHEN. Improvement effect of Rubus root polysaccharide on pancreatic mitochondrial function in type 2 diabetic mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 938-945. |
| [14] | Yongxin ZHAI,Huaifeng TA,Yi ZHANG,Qijia SUN,Ming ZHANG,Shuqiang FENG,Ranwei LI. Effect of preoperative glycemic level on infection-related complications of diabetic patients after flexible ureteroscopic lithotripsy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 766-772. |
| [15] | Peipei ZHANG,Donghui GAO,Yue TIAN,Hongyan LI. Effect of guided biofilm therapy for periodontitis in diabetic patient: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 493-499. |
|
||