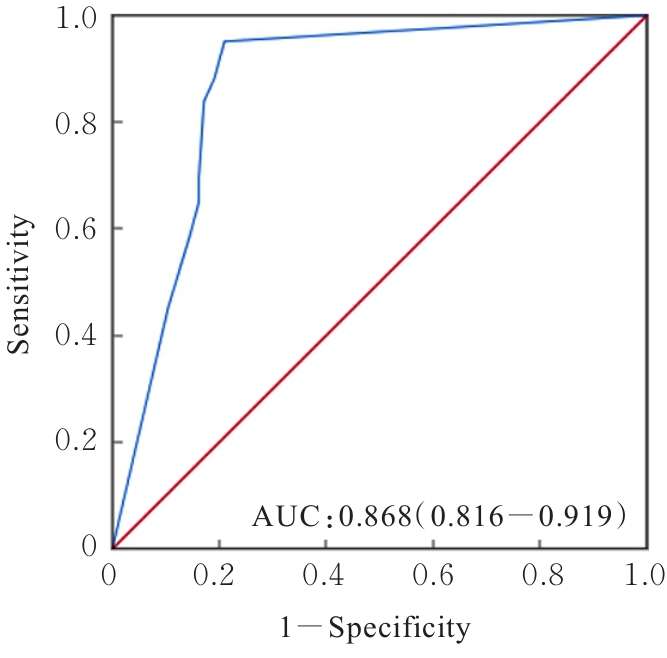
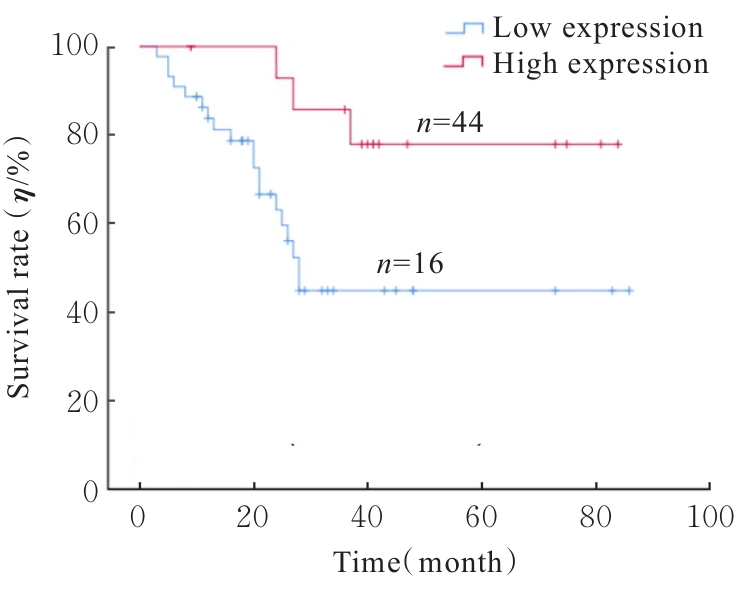
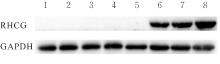
| [1] |
Xialing HUANG,Dandan ZHANG,Xuemei ZHANG.
Analysis on relationship between methylation of MSX1 gene and clinical pathological features and prognosis of patients with cervical cancer
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 749-756.
|
| [2] |
Shuyan SUN,Huakun ZHANG,Ziru ZHOU,Feng LI,Xiaobin CUI.
Expression of CRNN protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissue and influence of its overexpression in biological behavior of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma Eca9706 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 275-283.
|
| [3] |
Xiaoyan WANG,Xuelian LI,Bin LIANG,Wenfei TIAN,Hailin MA,Zhijing MO.
Analysis on relationship between CALU and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients and its mechanism based on transcriptome and single cell sequencing data
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 447-459.
|
| [4] |
Haiying GENG,Yan YU,Chunmei DAI,Youfeng WEN,Ning LI.
Expression of TRIM24 protein in human clear cell renal cell carcinoma tissue and its clinical significance
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 486-492.
|
| [5] |
Xi YANG,Qin YUAN,Lan YANG,Wenjie ZHANG.
Bioinformatics analysis on PDE1B expression and prognosis of gastric cancer and tumor microenvironment
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1664-1676.
|
| [6] |
Shimeng LI,Xin QI,Sitong LIN,Xiangwen SAN,Ling JIN,Sitong ZHANG.
Reactive plasmacytosis caused by methimazole in patients with Graves’ disease: One case report and literature review
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1414-1419.
|
| [7] |
Jiaxin YI,Yangyu ZHANG,Yingli FU,Yuchen PAN,Yongjie HAN,Jing JIANG,Yanhua WU.
Effect of MEIS1 expression on survival in patients after radical gastrectomy and its value in prognostic evaluation
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1358-1364.
|
| [8] |
Chaojie GUO,Jiajia ZHANG,Jie ZENG,Huiyu WANG, AIERFATI·Aimaier,Jiang XU.
Expressions of PLOD1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue and cells and their significances
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1035-1043.
|
| [9] |
Yilin REN,Yichen ZANG,Lele XUE,Kaige YANG,Sufang CHEN,Weinan WANG,Chenghua LUO,Weihua LIANG,Lianghai WANG,Feng LI,Jianming HU.
Bioinformatics analysis based on effect of M2 macrophage-derived Siglec15 on malignant biological behaviour of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells and its experimental validation
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 881-890.
|
| [10] |
Yuanguo WANG,Peng ZHANG.
Bioinformatics analysis based on relationship between SSP1 and TGFB1 and occurrence, prognosis, and immune invasion of esophageal adenocarcinoma
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1076-1086.
|
| [11] |
Yueying SONG,Chao GAO,Wenjun CHEN,Aiyu SHAO,Yichun QIAO,Zhuolin LI.
Screening of miRNAs related to prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer and its gene network based on TCGA Database
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 392-399.
|
| [12] |
Yulu QUAN,Pingping ZHANG,Yan LUO,Jing HUO,Xiaoping YU,Yanmei SUN,Yali LI.
Aortic stenosis of fetus caused by chimeric Y-chromosome isobaric double-adherent granules:A case report and literature review
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 260-264.
|
| [13] |
Guangcai WAN,Ting LI,Weixiu SUN,Xiuyan YU.
Modification and effect evaluation of pretreatment methods for rapid detection specimens of SARS-CoV-2
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1649-1654.
|
| [14] |
Zhirui CHUAN,Hongying YANG,Zhiyao LI,Dong CHEN,Huijing NI,Xiaokai LU,Haitao CHEN,Xiaomao LUO.
Effect of shear wave elastography on differential diagnosis of benign and malignant breast non-mass lesions
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1625-1634.
|
| [15] |
Zhongjun SHEN,Shishun XIE,Hexin XIAO,Liyan ZHAO.
Change of hemoglobin level in reticulocytes in patients with anemia and its diagnostic value
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1554-1560.
|
 ),Xiaobin CUI1,2(
),Xiaobin CUI1,2( )
)