| [1] |
Cheng CHEN,Jingyao LI,Wanxiang HU,Donghui LIU,Zhihong CHEN.
Protective effect of sericin on streptozotocin-induced INS-1 cell damage by regulating PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway through Akt1 and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 590-598.
|
| [2] |
Yihui WANG,Qing ZHANG,Yingnan LI,Liping YE.
Effect of KIAA1522 on proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung cancer cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 727-739.
|
| [3] |
Mengyun LU,Yucheng HAN,Yihong HU,Minhui HE,Yanqun ZHANG,Xianqiong ZOU.
Effects of glycolipid transfer protein on proliferation, migration,and invasion of pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells and their mechanisms
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 284-295.
|
| [4] |
Ying YANG,Liang ZHAO,Yong YOU,Qian XU,Zhenjun YANG.
Influence of 17β-estradiol in proliferation and differentiation of hippocampal neural stem cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 317-324.
|
| [5] |
Chaohe ZHANG,Xinwei ZHANG,Xiangfeng WANG.
Protective effect of Pien-Tze-Huang on acetaminophen-induced liver injury and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 105-114.
|
| [6] |
Min CHEN,Huiyan ZHU,Jing TAO,Yipeng XU.
Ameliorating effect of betaine on oxygen-glucose deprivation injury in rat brain microvascular endothelial cells and its influence in PI3K/AKT pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 96-104.
|
| [7] |
Gao SUN,Jing HE,Qi ZHAO,Jianhong SHI,Zhiling LIAO,Yuanye TIAN,Guomin WU.
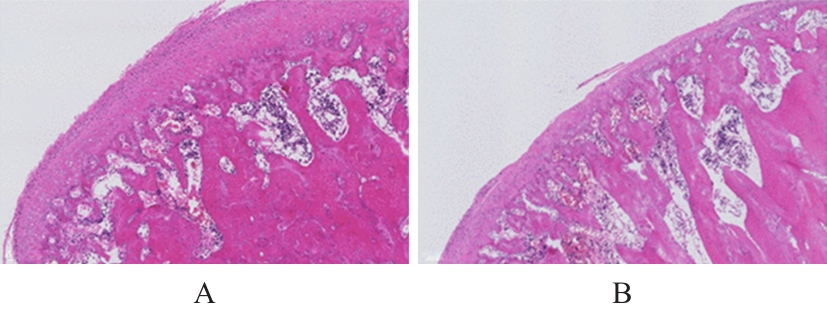
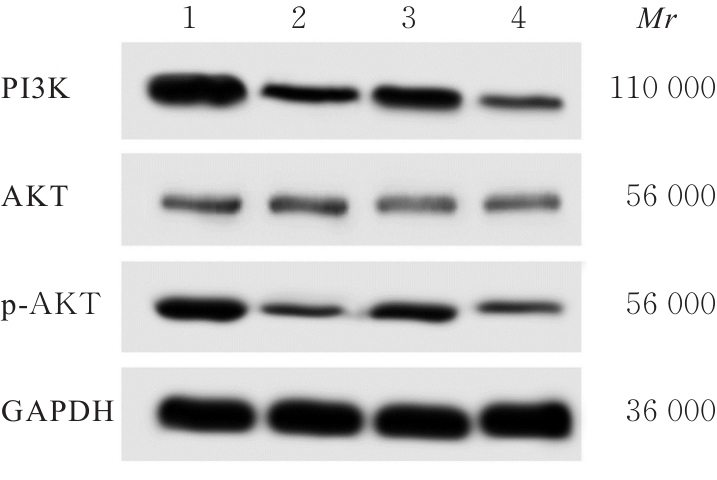
Therapeutic effect of resveratrol on osteoarthritis of temporomandibular joint and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1547-1556.
|
| [8] |
Jing LOU,Lei ZHAO,Yanjie ZHU,Shuaiqiang YUAN,Fei WANG,Hangzhou ZHANG,Jiaojiao XU,Xiaoke YU,Liufa HOU.
Effect of Fuzheng Ruanjian Anticancer Formula on malignant biological behaviors of hepatocellulars carcinoma HepG2 cells by regulating Akt/MDM2/P53 signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1654-1663.
|
| [9] |
Xueting CHI,Fangyuan CHEN,Zifeng PI,Guangfu LYU,Yuchen WANG,Yinqing LI,Xiaowei HUANG,Zhe LIN.
Improvement effect of velvet antler polypeptide on postmenopausal osteoporosis in rats and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 963-969.
|
| [10] |
Tengfei WANG, Feng CHEN, Ling QI, Ting LEI, Meihui SONG.
Inhibitory effect of D-limonene on proliferation of glioblastoma cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 647-657.
|
| [11] |
Huiling ZHANG,Di HAN,Wengxiu GUO,Haiyao PANG,Jun MENG.
Regulatory effect of SGK1 on oocyte cleavage in fertilized eggs in mice at G1 stage mediated by Cyclin B/Cdc2 pathway and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 628-637.
|
| [12] |
Yanhong WEI,Chenxue YANG,Guangmin YANG,Shuai SONG,Ming LI,Haijiao YANG,Haifeng WEI.
Inhibitory effect of downregulating HMGB2 expression on epithelial-mesenchymal transition of liver cancer LM3 cells and its AKT/mTOR signaling pathway mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 143-149.
|
| [13] |
Chunyan KANG,Xiuzhi ZHANG,Huicong ZHOU,Jie CHEN.
Effect of downregulating proline-rich protein 11 expression on drug resistance of esophageal cancer drug resistant cell EC9706/DDP and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 113-119.
|
| [14] |
Sihan LAI,Juntong LIU,Luying TAN,Jinping LIU,Pingya LI.
Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on anti-ischemic stroke mechanism of Panax quinquefolium triolsaponins
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 913-922.
|
| [15] |
Meng LIU,Xiaodong HUANG,Zheng HAN,Qingxi ZHU,Jie TAN,Xia TIAN.
Effect of cadherin-17 on proliferation and apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells and its PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway regulatory mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 1008-1017.
|
 )
)