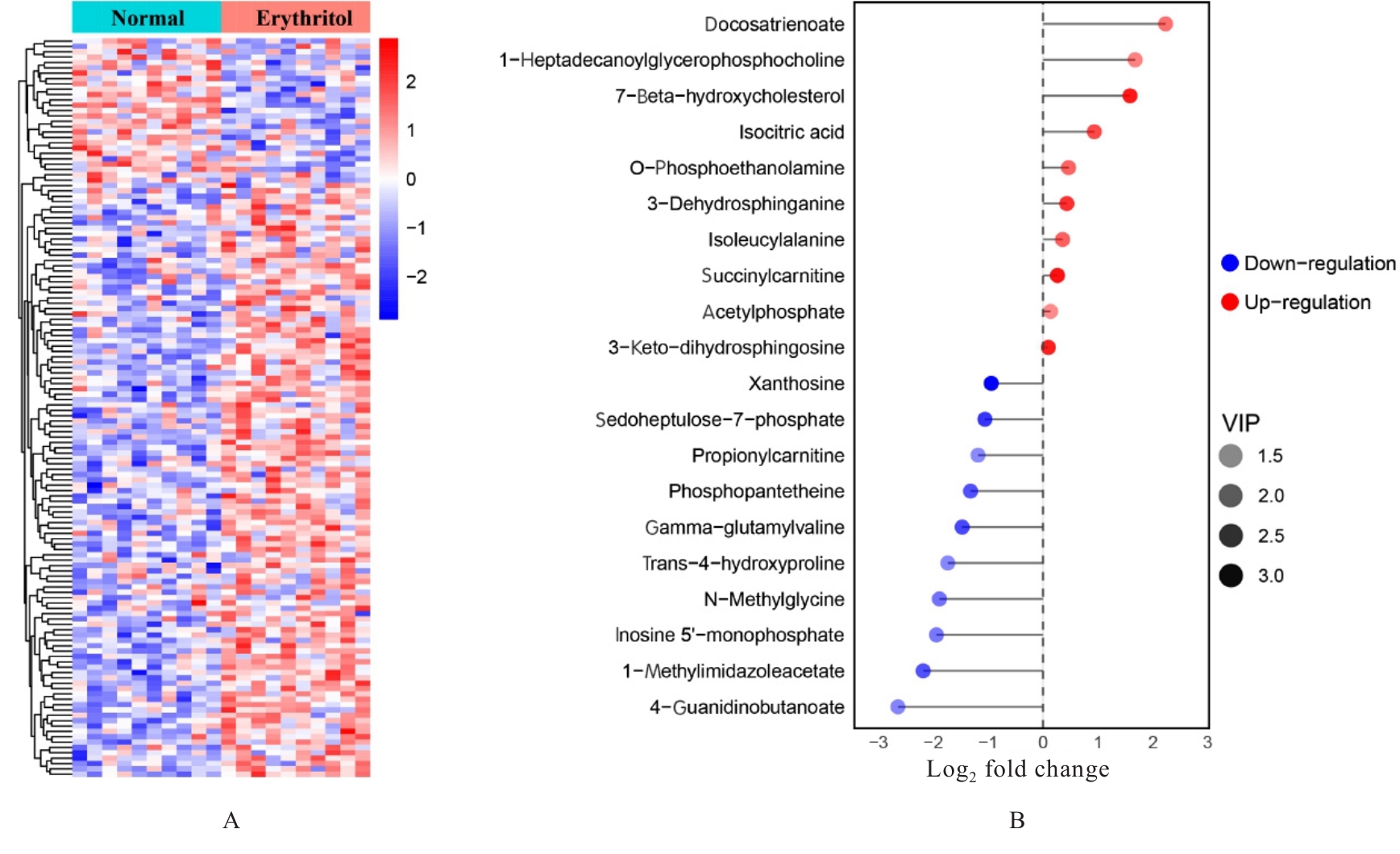
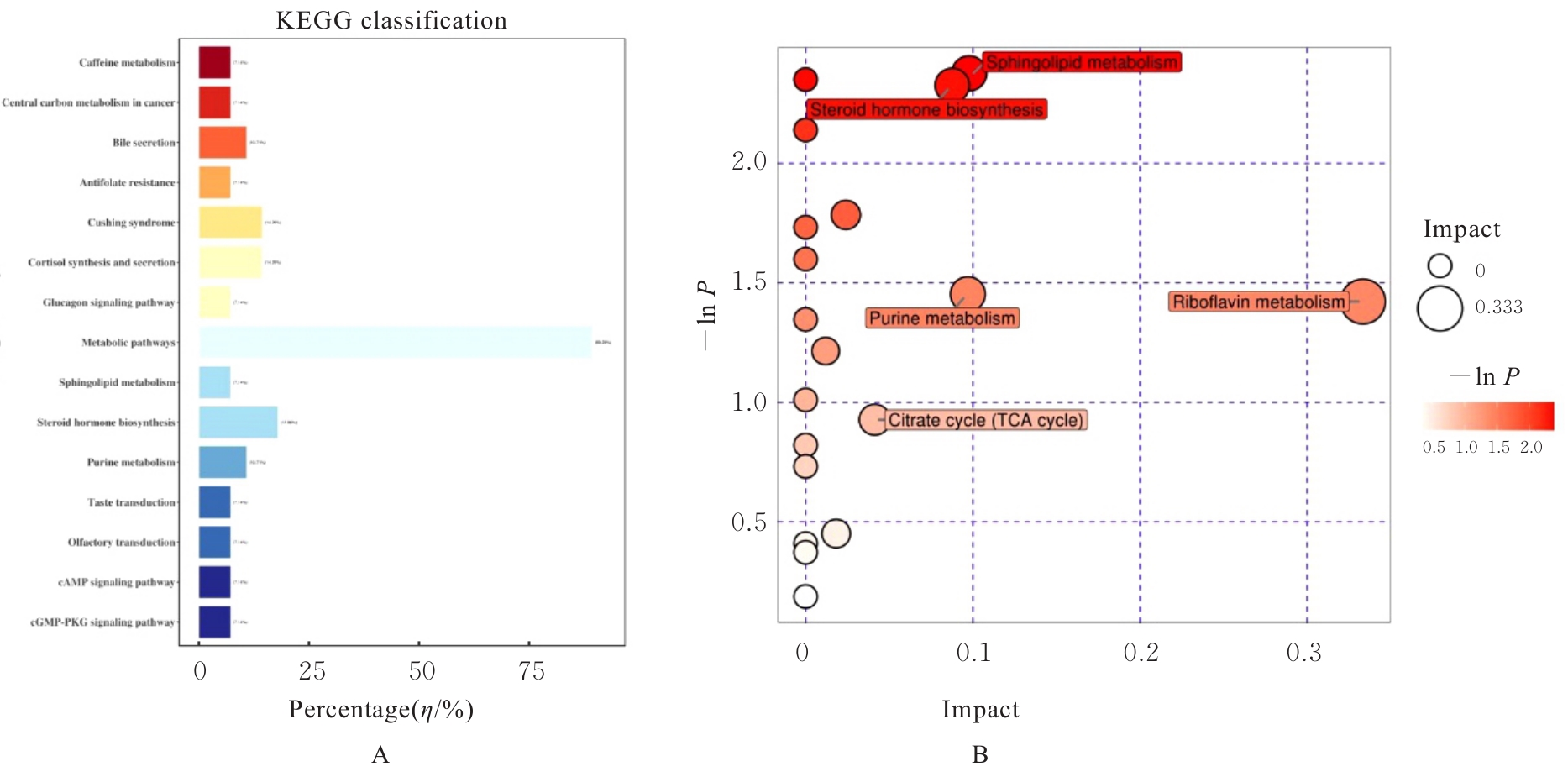
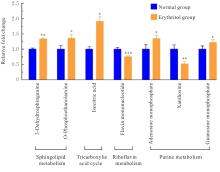
| [1] |
Yanbin ZHANG,Guangye GUO,Caihua ZHENG,Xinyan LIU.
Research progress in association between Helicobacter pylori and metabolic syndrome and its effect on occurrence and development of metabolic syndrome
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1757-1762.
|
| [2] |
Hongyan LI,Qiqi WANG,Wenzhou XU,Bin ZHAO.
Efficacy evaluation of endoscopic-assisted subgingival scaling combined with erythritol subgingival sandblasting in treatment of peri-implantitis
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 465-472.
|
| [3] |
ZHANG Yezhuo, YANG Yuefeng, YANG Yetong, ZHANG Ying, LIU Yajuan.
Effects of poria cocos compound extract on blood glucose and lipid levels in rats with type 2 diabetes mellitus
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 937-941.
|
| [4] |
DU Xingxu, QIAO Zijing, YANG Shuo, XU Zhiying, YANG Bo, LI He, CHEN Jianguang, WANG Chunmei.
Effect of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharide on serum inflammatory factors in T2DM rats and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(01): 50-55.
|
| [5] |
JIN Aihong, ZHOU Xiaping, YU Zhiying.
Expressions of Versican and ADAMTS-1 in polycysticovary syndrome patients and their clincal significances
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(02): 400-404.
|
| [6] |
SUN Zhumei, LIANG Weishi, KANG Jiali, MENG Xubing, WANG Jianxing, HAN Shuying.
Dynamic pathological characteristics of kidney in db/db mice with type 2 diabetes mellitus
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(03): 499-503.
|
| [7] |
HUO Lianguang, YAN Qingtao, YAN Jingyue, LI Na, SU Han, ZHANG Meijia, MAO Shumei, GAO Zhiqin, QU Meihua.
Improvement effect of duodenal-jejunal bypass on inflammatory status of biliopancreatic limb of ZDF rats and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(06): 1155-1160.
|
| [8] |
MA Dan,XIE Xiao-na,ZOU Jing-tao,LIU Yu-jia,SUN Zhong-hua,GAO Ying.
Protective effect of Injection of Milkvetch Root on kidney of diabetic rats and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2014, 40(02): 271-275.
|
| [9] |
CHANG Yu-Dong, ZHANG Zheng-Yao, DING Yun-Lu, CHEN Qing-Wu, DIAO An-Hong.
Inhibitory effect of ginkgo biloba extract on alpha-glucosidase and its hypoglycemic mechanism
[J]. J4, 2011, 37(3): 427-432.
|
| [10] |
YU Shu-Shu, ZHAO Li-Hua.
Influence of blood glucose concentration on |levels of IL-6 and PDGF in patients with acute myocardial infarction treated by primary percutaneous coronary intervention
[J]. J4, 2010, 36(6): 1114-1117.
|
| [11] |
LI Na, QU Xiao-Bo, HU Li-Na, LIN Zhe.
Hyperglycemic effects of mangiferin hydrastis granulein in GK rats with diabetes mellitus
[J]. J4, 2010, 36(3): 483-486.
|
| [12] |
WANG Gui-zhi,QIAO Jun-hua,LIANG Ping,LIU Chun-yan.
Correlation analysis between bone density measured by quantitative CT and blood sugar level of aged patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus
[J]. J4, 2008, 34(6): 1067-1070.
|
| [13] |
ZHANG Ming, QU Ji-bing, LI Hong, CHEN Han, CHEN Li, YANG Shi-jie.
Effect of maternal ethanol heavy consumption during gestation on blood glucose in newborn rats and its mechanism
[J]. J4, 2007, 33(5): 794-797.
|
| [14] |
BU Feng-quan, LIU Zhong-ying, SHI Yan, ZHANG Jing, MIAO Chun-sheng, LI Cai.
Time-effect relationship of hypoglycemic effect of fenugreek seed extracts on experimental diabetic rats
[J]. J4, 2007, 33(1): 88-90.
|
| [15] |
GAN Zhen-wei, ZHANG Ya-jie, LIU Hua-feng, LI Chen-xu, ZHANG Jing-ling, XIE Lin.
Effects of zinc and chromium on declining blood glucose level and improving antioxidant activity in diabetic mice
[J]. J4, 2006, 32(3): 410-412.
|
 )
)