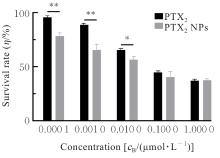
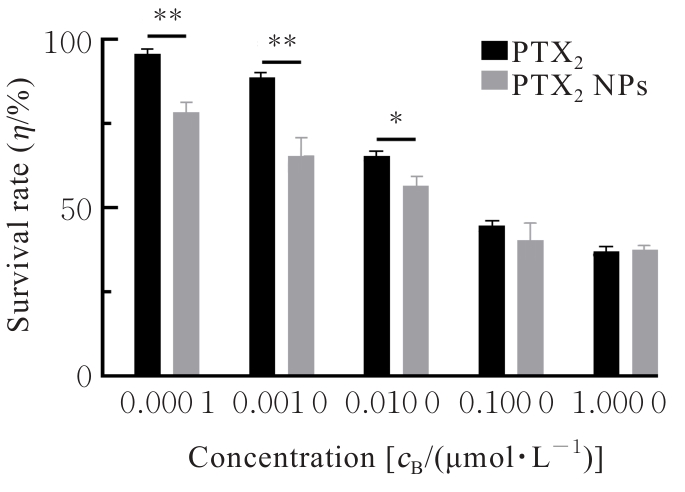
| [1] |
Panxi SUN,Xue QIN,Chongyang ZHANG,Jia LUO,Yong CHEN,Lili WEI.
Protective effect of TUG-891 on ischemic stroke induced by ischemia and hypoxia and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(4): 968-975.
|
| [2] |
Jiarui LI,Zhenlin YANG,Fan GAO,Jingjing GUO,Jinzi LI.
Effect of miR-34a-5p on hippocampal neuron apoptosis in rats with temporal lobe epilepsy and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(4): 939-947.
|
| [3] |
Fan WANG,Xin WEN,Yixuan WANG,Yuan WANG.
Effect of gap junction β2 on prognosis of patients with lung adenocarcinoma and biological behavior of lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 716-726.
|
| [4] |
Donghui LIU,Yunzhe CI,Chunyan WANG,Wenyi MA.
Effect of miR-199a-5p on expression of Caveolin-1, cell migration and apoptosis in glioma U251 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 663-671.
|
| [5] |
Cheng CHEN,Jingyao LI,Wanxiang HU,Donghui LIU,Zhihong CHEN.
Protective effect of sericin on streptozotocin-induced INS-1 cell damage by regulating PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway through Akt1 and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 590-598.
|
| [6] |
Shuyan SUN,Huakun ZHANG,Ziru ZHOU,Feng LI,Xiaobin CUI.
Expression of CRNN protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissue and influence of its overexpression in biological behavior of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma Eca9706 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 275-283.
|
| [7] |
Chongyang ZHANG,Jia LUO,Xue QIN,Panxi SUN,Lili WEI,Xiushi YU.
Protective effect of prunetin on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by regulating JNK/p38 pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 296-306.
|
| [8] |
Jing DENG,Xuan WANG,Changyu SHI,Siqi YANG,Qinling ZOU,Ming JIN.
Effect of securinine on proliferation and apoptosis of human colon cancer SW620 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 307-316.
|
| [9] |
Yue WANG,Ning MA,Jiajun LU,Chengyao WANG,Linyu CHEN,Yuchen REN,Jingwu LI,Hong SUN.
Protective effect of novel composite hydrogels on H₂O₂-induced oxidative stress injury in cardiomyocytes
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 352-359.
|
| [10] |
Jierui ZHAO,Mingxin JI,Yuhan ZHANG,Shutong CHEN,Yumiao GUO,Wei ZHANG,Peng PENG.
Effect of Juglone on apoptosis and pyroptosis of osteosarcoma cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 420-427.
|
| [11] |
Jiaxin LI,Yi WANG,Tingting WU,Shirui HAO,Xiao FU.
Protective effect of quercetin against 5-fluorouracil-induced damage in human immortalized keratinocytes and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 428-436.
|
| [12] |
Siqi LI,Guangdao CHEN,Qiyi ZENG.
Improvement effect of chrysophanol on hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis of EA. hy926 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1512-1518.
|
| [13] |
Xuan MA,Kaixiang YANG,Hai DENG,Yucheng HUANG.
Effect of parthenolide on apoptosis of chondrocyte under mechanical stretch stress by inhibiting Piezo1 expression and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1621-1631.
|
| [14] |
Jingshun ZHANG,Yinggang ZOU,Lianwen ZHENG.
Effect of over-expression SLC7A5 on apoptosis of ovarian granulosa cells in rats and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1526-1534.
|
| [15] |
Jing LOU,Lei ZHAO,Yanjie ZHU,Shuaiqiang YUAN,Fei WANG,Hangzhou ZHANG,Jiaojiao XU,Xiaoke YU,Liufa HOU.
Effect of Fuzheng Ruanjian Anticancer Formula on malignant biological behaviors of hepatocellulars carcinoma HepG2 cells by regulating Akt/MDM2/P53 signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1654-1663.
|
 )
)