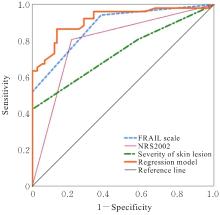
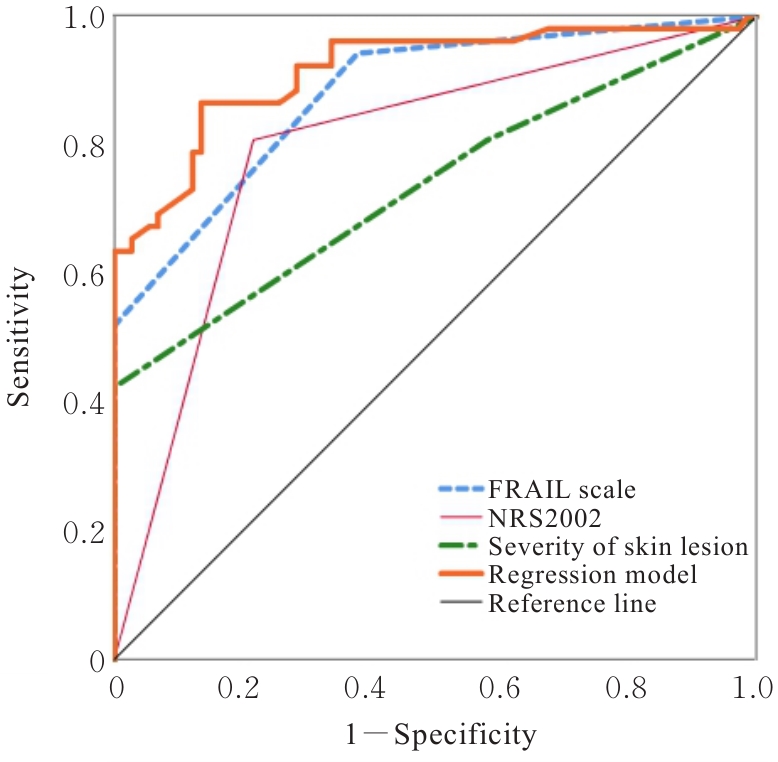
| [1] |
Jiahui FENG,Renjie LIU,Xuan CHEN.
Analysis on risk factors of development of acute hydrocephalus in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 763-769.
|
| [2] |
Xiuzhen WEI,Yaling DONG,Zhibo ZHU,Zhengjie ZHANG,Yuanjun TAN,Jie BAI,Xiayi SU,Baihong ZHANG.
Construction of prediction model for gastric cancer mismatch repair based on preoperative inflammatory indicators and clinicopathological features in gastric cancer patients
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 172-181.
|
| [3] |
Suzhen YUAN,Yan JIN,Wenwen WANG.
Analysis on clinical characteristics of patients with ovarian clear cell carcinoma and ovarian endometriosis
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1677-1682.
|
| [4] |
Jiayuan YU,Di ZHAO,Xin JIANG,Jing XU,Lili JIANG,Hongyu JIANG.
Association analysis on peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets and occurrence of carotid atherosclerosis
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1400-1405.
|
| [5] |
Honghong LI,Na YU,Minghao SHI,Ying SUN,Yao LI,Zhongjun SHEN,Xiaoyi LIU,Liyan ZHAO.
Predictive value of new thrombotic risk assessment model for venous thromboembolism in patients with malignant tumors
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1390-1399.
|
| [6] |
Xiaopeng YU,Renyi YANG,Zuomei HE,Puhua ZENG.
Establishment and validation of nomogram of cancer specific survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma with negative alpha fetoprotein based on SEER Database
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 188-197.
|
| [7] |
Peng QI,Xianying MENG,Meihua PIAO,Qiang ZHANG.
Network Meta-analysis on risk factors of recurrence of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1504-1512.
|
| [8] |
Xue DONG, Jinfeng ZANG, Caifeng XU, Hebing LIU, Zhaohua CHENG.
Construction and validation of risk prediction model of enteral nutrition feeding intolerance of patients with severe acute pancreatitis
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1586-1592.
|
| [9] |
Shaoting HUANG,You LI,Zhaochun WU,Jiawen HE,Keqi LIAO,Shengnan LI.
Construction of SOX17 over-expression lentiviral vector and stably transfected cell line
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1424-1430.
|
| [10] |
Xiunan FENG,Lu CHEN,Yu LONG,Zhenyu JIANG,Ling ZHAO.
Analysis on clinical characteristics and risk factors of patients with Sjogren’s syndrome complicated with interstitial lung disease
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1513-1518.
|
| [11] |
Tong SHEN,Yang WANG,Wei JIN,Zhihui LIN,Li YAN.
Risk factors analysis and risk model construction of cognitive frailty in elderly patients with chronic diseases
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1304-1309.
|
| [12] |
Mingfei JU,Chao LIU,Zhigang MA,Juan ZHAO,Tu WANG,Zhihao WANG.
Predictive value of residual cholesterol in occurrence of patients with acute coronary syndrome
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 765-769.
|
| [13] |
Lianyuan WANG,Yi YANG,Huiwen CONG,Haohua WANG,Qihan BAO,Chengsheng LI,Liwen ZHOU,Zichen DING,Yanli LI,Fuyan SHI,Suzhen WANG.
Bayesian quantile regression joint model analysis on risk factors of Alzheimer’s disease in people with different MMSE scores
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 395-401.
|
| [14] |
Hongyu SUN,Zihan CHEN,Baiji CUI,Xianmin FENG,Di LIU.
Becteriostatic effect of Carex meyeriana Kunth extract on infection of Staphylococcus aureus afterskin scalding in rats
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 377-384.
|
| [15] |
Feifei JIANG,Lingli SONG,Beizhen PAN,Yuefeng WANG,Haoyu LI,Liyuan SUN.
Establishment and evaluation of nucleic acid colloidal gold test strip for rapid detection of respiratory tract fungal infection
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 222-230.
|
 )
)