吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (10): 2964-2972.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20211335
基于会话的结合全局潜在信息的图神经网络推荐模型
- 1.吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
2.吉林大学 符号计算与知识工程教育部重点实验室,长春 130012
3.东北师范大学 信息科学与技术学院,长春 130117
Global potential information combined graph neural networks for session-based recommendation
Li-yan DONG1,2( ),Wei-ye LIANG1,Yue-qun WANG1,Yong-li LI3
),Wei-ye LIANG1,Yue-qun WANG1,Yong-li LI3
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.Key Laboratory of Symbolic Computation and Knowledge Engineering of Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130012
3.School of Computer Science and Technology,Northeast Normal University,Changchun 130117,China
摘要:
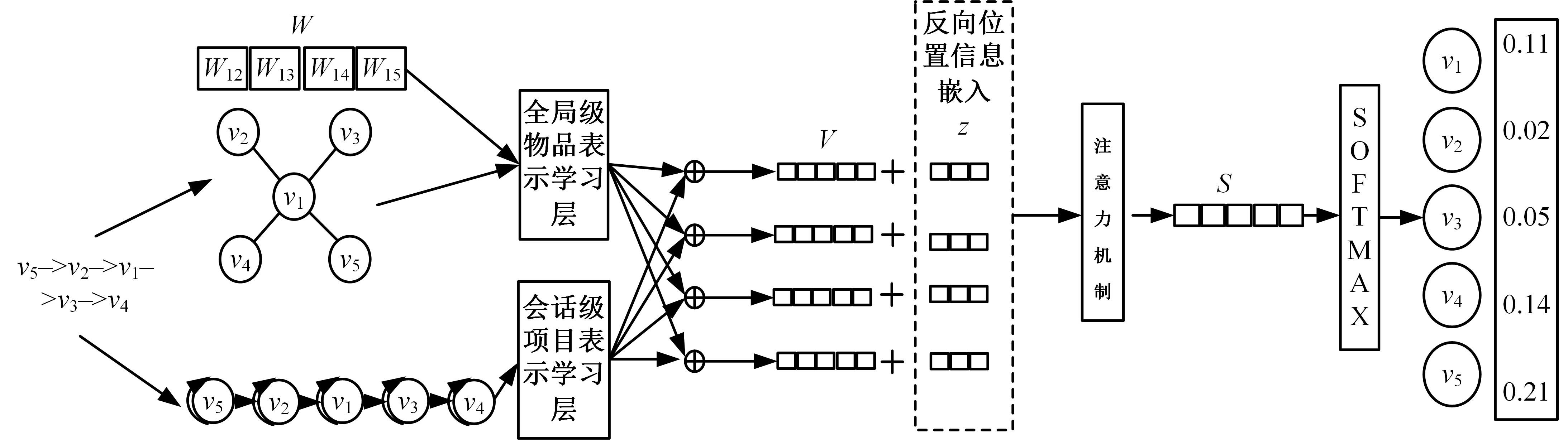
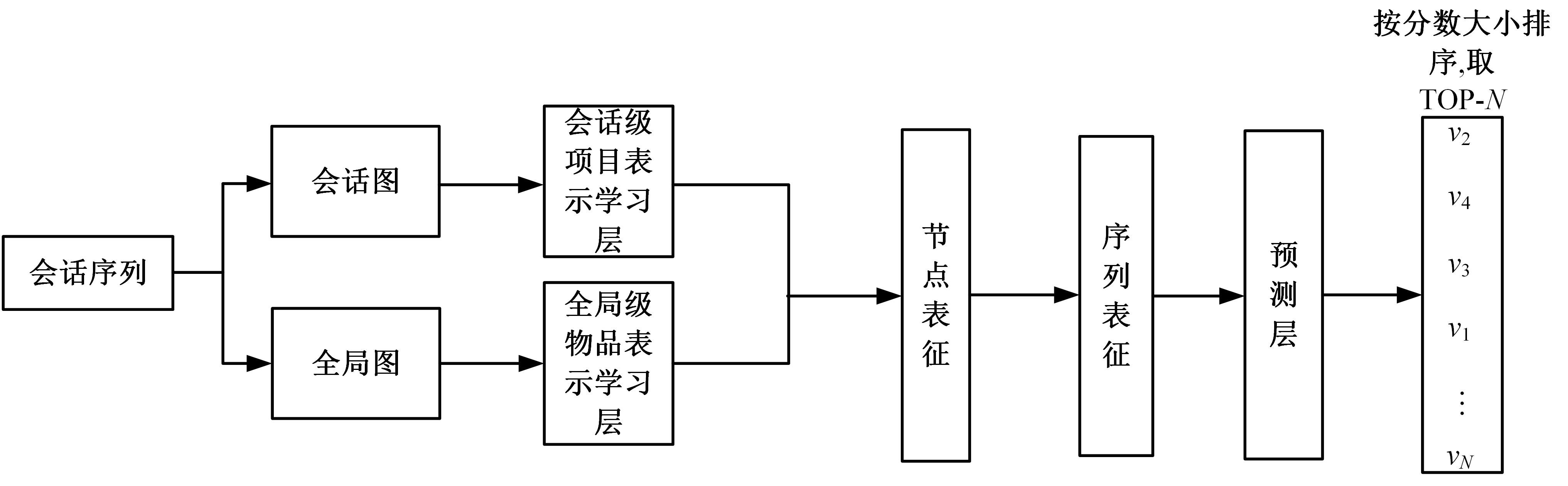
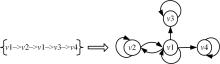
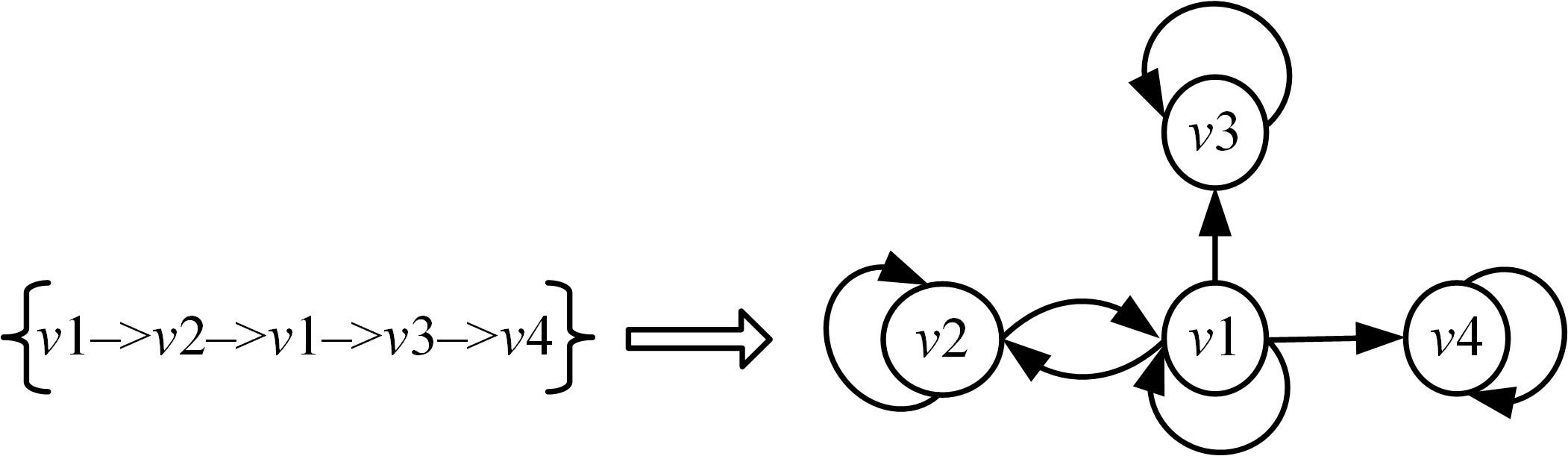
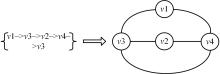
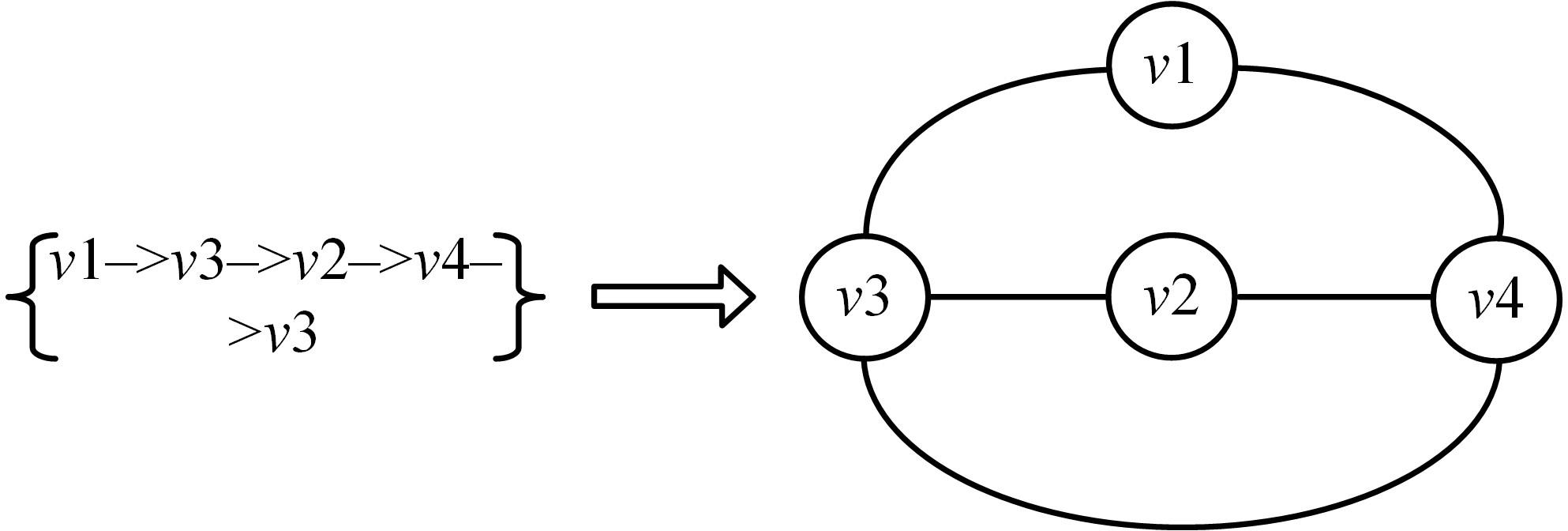
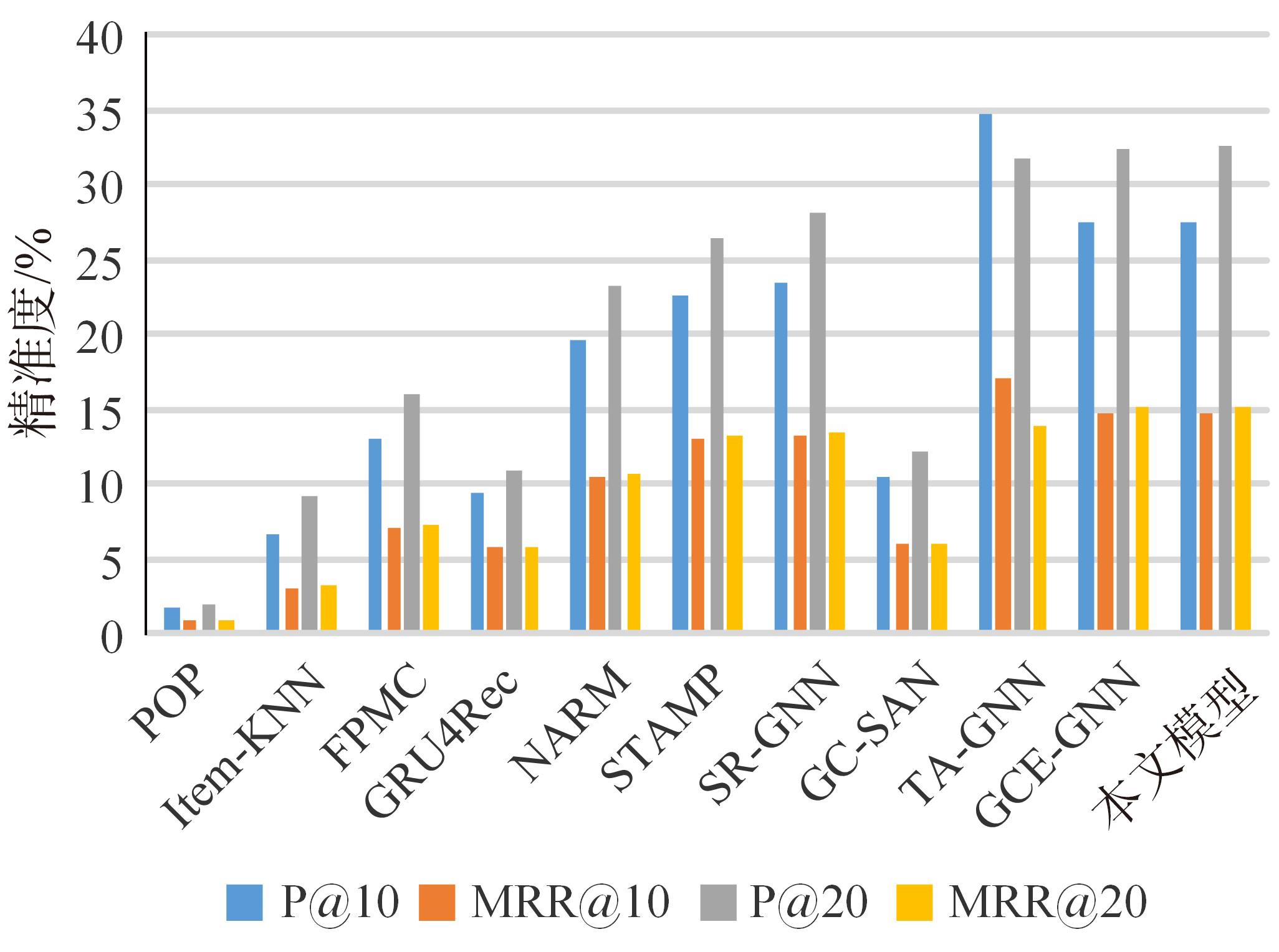
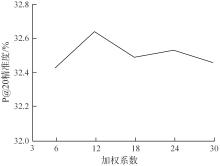
针对当前各种基于会话推荐的模型存在对物品间全局关系的获取和使用不足的问题,提出了基于会话的结合全局潜在信息的图神经网络推荐模型。该模型根据全部会话序列构建会话图与全局图,并在全局图中引入了序列中各节点间的间距信息,以及序列节点的相邻节点彼此之间的贡献度,通过模型训练获取最后的会话表征预测下一个交互行为。实验结果表明:在结合图神经网络的推荐算法中充分挖掘全局潜在信息可以有效提高推荐算法的准确率,这一改进对提高基于会话的图神经网络模型的性能有一定指导意义。
中图分类号:
- TP301.6
| 1 | Wang S, Pasi G, Hu L, et al. The era of intelligent recommendation: editorial on intelligent recommendation with advanced AI and learning[J]. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 2020, 35(5): 3-6. |
| 2 | Sri Hari Nallamala, Nallamala Sri Hari, Bajjuri Usha Rani, et al. A brief analysis of collaborative and content based filtering algorithms used in recommender systems[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2020, 981(2): No.022008. |
| 3 | Mahesh Mali, Mishra Dhirendra S, Vijayalaxmi M. Multifaceted recommender systems methods: a review[J]. Journal of Statistics and Management Systems, 2020, 23(2): 349-361. |
| 4 | Dang T K, Nguyen Q P, Nguyen V S. A study of deep learning-based approaches for session-based recommendation systems[J]. SN Computer Science, 2020, 1(4): 1-13. |
| 5 | Wang S, Cao L, Wang Y, et al. A survey on session-based recommender systems[J]. ACM Computing Surveys(CSUR), 2021, 54(7): 1-38. |
| 6 | Abdi Mohamed Hussein, Okeyo George Onyango, Mwangi Ronald Waweru. Matrix factorization techniques for context-aware collaborative filtering recommender systems: a survey[J]. Computer and Information Science, 2018, 11(2): 1-10. |
| 7 | Liu S, Wang L. A self-adaptive point-of-interest recommendation algorithm based on a multi-order Markov model[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2018, 89(4): 506-514. |
| 8 | Rendle S, Freudenthaler C, Schmidt-Thieme L. Factorizing personalized markov chains for next-basket recommendation[C]∥Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on World Wide Web, New York,USA, 2010: 811-820. |
| 9 | Hidasi B, Karatzoglou A, Baltrunas L, et al. Sessionbased recommendations with recurrent neural networks[EB/OL]. [2021-11-12]. . |
| 10 | Li J, Ren P, Chen Z, et al. Neural attentive session-based recommendation[C]∥Proceedings of the ACM on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, New York,USA, 2017: 1419-1428. |
| 11 | Vaswani Ashish, Shazeer Noam, Parmar Niki, et al. Attention is all you need[C]∥Proceedings of 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 5998-6008. |
| 12 | Liu Q, Zeng Y, Mokhosi R, et al. STAMP: short-term attention/memory priority model for session-based recommendation[C]∥Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, London, United Kingdom, 2018: 1831-1839. |
| 13 | Jannach D, Ludewig M. When recurrent neural networks meet the neighborhood for session-based recommendation[C]∥Proceedings of the 11th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, Como, Italy, 2017: 306-310. |
| 14 | Tuan T X, Phuong T M. 3D convolutional networks for session-based recommendation with content features[C]∥Proceedings of the 11th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, Como, Italy, 2017: 138-146. |
| 15 | Wu C, Yan M. Session-aware information embedding for e-commerce product recommendation[C]∥Proceedings of the 2017 ACM on conference on information and knowledge management, Singapore, 2017: 2379-2382. |
| 16 | Tang J, Wang K. Personalized top-n sequential recommendation via convolutional sequence embedding[C]∥Proceedings of the 11th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Berkeley, USA, 2018: 565-573. |
| 17 | Yuan F, Karatzoglou A, Arapakis I, et al. A simple convolutional generative network for next item recommendation[C]∥Proceedings of the Twelfth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Melbourne, Australia, 2019: 582-590. |
| 18 | Xu Keyulu, Hu Wei-hua, Jure Leskovec, et al. How powerful are graph neural networks?[EB/OL]. [2021-11-12]. . |
| 19 | Wu S, Tang Y, Zhu Y, et al. Session-based recommendation with graph neural networks[C]∥Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Palo Alto, USA, 2019: 346-353. |
| 20 | Xu C, Zhao P, Liu Y, et al. Graph contextualized self-attention network for session-based recommendation[C]∥Proceedings of the 28th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, USA, 2019: 3940-3946. |
| 21 | Yu F, Zhu Y, Liu Q, et al. TAGNN: Target attentive graph neural networks for session-based recommendation[C]∥Proceedings of the 43rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Xi'an, China, 2020: 1921-1924. |
| 22 | Qiu R, Li J, Huang Z, et al. Rethinking the item order in session-based recommendation with graph neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Atlanta,USA, 2019: 579-588. |
| 23 | Wang Z, Wei W, Cong G, et al. Global context enhanced graph neural networks for session-based recommendation[C]∥Proceedings of the 43rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Xi'an, China, 2020: 169-178. |
| 24 | Sarwar B, Karypis G, Konstan J, et al. Item-based collaborative filtering recommendation algorithms[C]∥Proceedings of the 2001 International Conference on World Wide Web, Hong Kong, China, 2001:285-295. |
| 25 | Wu Z, Pan S, Chen F, et al. A comprehensive survey on graph neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(1): 4-24. |
| [1] | 范大娟,黄志球,曹彦. 面向SaaS隐私保护的自适应访问控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(10): 2897-2908. |
| [2] | 袁满,江运龙,胡超. 关联数据链接有效性评估的新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1792-1797. |
| [3] | 吕帅,刘京. 基于深度强化学习的随机局部搜索启发式方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1420-1426. |
| [4] | 钱榕,张茹,张克君,金鑫,葛诗靓,江晟. 融合全局和局部特征的胶囊图神经网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1048-1054. |
| [5] | 魏晓辉,孙冰怡,崔佳旭. 基于图神经网络的兴趣活动推荐算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 278-284. |
| [6] | 袁满,胡超,仇婷婷. 基于Linked data的数据完整性评估新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1826-1831. |
| [7] | 刘磊,瓮杰,郭德贵. 面向编译器测试的部分求值静态输入确定方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 262-267. |
| [8] | 马健, 樊建平, 刘峰, 李红辉. 面向对象软件系统演化模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 545-550. |
| [9] | 罗养霞, 郭晔. 基于数据依赖特征的软件识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1894-1902. |
| [10] | 应欢, 王东辉, 武成岗, 王喆, 唐博文, 李建军. 适用于商用系统环境的低开销确定性重放技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(1): 208-217. |
| [11] | 李勇, 黄志球, 王勇, 房丙午. 基于多源数据的跨项目软件缺陷预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 2034-2041. |
| [12] | 王念滨, 祝官文, 周连科, 王红卫. 支持高效路径查询的数据空间索引方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(3): 911-916. |
| [13] | 陈鹏飞, 田地, 杨光. 基于MVC架构的LIBS软件设计与实现[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 242-245. |
| [14] | 康辉, 王家琦, 梅芳. 基于Pi演算的并行编程语言[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 235-241. |
| [15] | 特日跟, 江晟, 李雄飞, 李军. 基于整数数据的文档压缩编码方案[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 228-234. |
|
||