吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (7): 1873-1891.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221342
• 综述 •
车用智能材料发展现状综述
- 吉林大学 汽车仿真与控制国家重点实验室,长春 130022
Review of development status of intelligent materials for vehicles
Chuan-liang SHEN( ),Xiao-yuan MA,Jing YU,Rui-zhang YE,Yu-bing YUE,Zhen-hai GAO(
),Xiao-yuan MA,Jing YU,Rui-zhang YE,Yu-bing YUE,Zhen-hai GAO( )
)
- State Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
作为新一代车用材料,智能材料为实现汽车轻量化、智能化等设计目标提供了新的研究方向和设计思路。为进一步推动车用智能材料的研究进程,本文针对压电材料、磁流变材料以及形状记忆合金3种智能材料分别展开综述,阐述了各类材料的特殊性质,系统总结了在汽车能量回收、结构振动抑制、传感器、执行器、安全防护等重要研究领域的国内外研究成果。最后,分析了目前车用智能材料商用化存在的挑战,并指出了未来研究的方向。
中图分类号:
- U465
| 1 | 郑雪芹.汽车新材料的应用及发展趋势[J].汽车纵横,2021(11):73-76. |
| Zheng Xue-qin. Application and development trend of new automotive materials[J]. Automobile Aspect,2021(11):73-76. | |
| 2 | Hornbogen E, Mertmann M. ''Intelligent''materials, composites and systems[J]. Metall, 1996, 50(12): 809-814. |
| 3 | Uchino K.Advanced Piezoelectric Materials: Science and Technology[M]. London: Woodhead Publishing, 2017. |
| 4 | Meeker T R. Publication and proposed revision of ANSI/IEEE standard 176-1987[J]. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics Ferroelectrics and Frequency Control, 1996, 43(5): 717-772. |
| 5 | Abdelkareem M A A, Xu L, Ali M K A, et al. Vibration energy harvesting in automotive suspension system: a detailed review[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 229: 672-699. |
| 6 | Mahala K M, Gadkari P, Deb A. Mathematical models for designing vehicles for ride comfort[C]∥Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Research into Design, Bangalore, India, 2009. |
| 7 | Al-Yafeai D, Darabseh T, Mourad A H I. A state-of-the-art review of car suspension-based piezoelectric energy harvesting systems[J]. Energies, 2020, 13(9): 2336. |
| 8 | Xiao H, Wang X, John S. A dimensionless analysis of a 2DOF piezoelectric vibration energy harvester[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2015, 58: 355-375. |
| 9 | Xie X D, Wang Q. Energy harvesting from a vehicle suspension system[J]. Energy, 2015, 86: 385-392. |
| 10 | Benhiba A, Bybi A, Alla R, et al. Investigation of vibrations energy harvesting from passive car suspension using quarter car model under bump excitation[J]. E3S Web of Conferences, 2022, 336: No.00053. |
| 11 | Darabseh T, Al-Yafeai D, Mourad A H I. Energy harvesting from car suspension system: mathematical approach for half car model[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Sciences, 2021, 15(1): 7695-7714. |
| 12 | Askari H, Hashemi E, Khajepour A, et al. Tire condition monitoring and intelligent tires using nanogenerators based on piezoelectric, electromagnetic, and triboelectric effects[J]. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2019, 4(1): No.1800105. |
| 13 | Behera M M. Piezoelectric energy harvesting from vehicle wheels[J]. Int J Eng Res Technol, 2015, 4(5): 1-4. |
| 14 | Hu Y, Xu C, Zhang Y, et al. A nanogenerator for energy harvesting from a rotating tire and its application as a self‐powered pressure/speed sensor[J]. Advanced Materials, 2011, 23(35): 4068-4071. |
| 15 | Maurya D, Kumar P, Khaleghian S, et al. Energy harvesting and strain sensing in smart tire for next generation autonomous vehicles[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 232: 312-322. |
| 16 | Rui X, Zeng Z, Zhang Y, et al. Design and experimental investigation of a self-tuning piezoelectric energy harvesting system for intelligent vehicle wheels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 69(2): 1440-1451. |
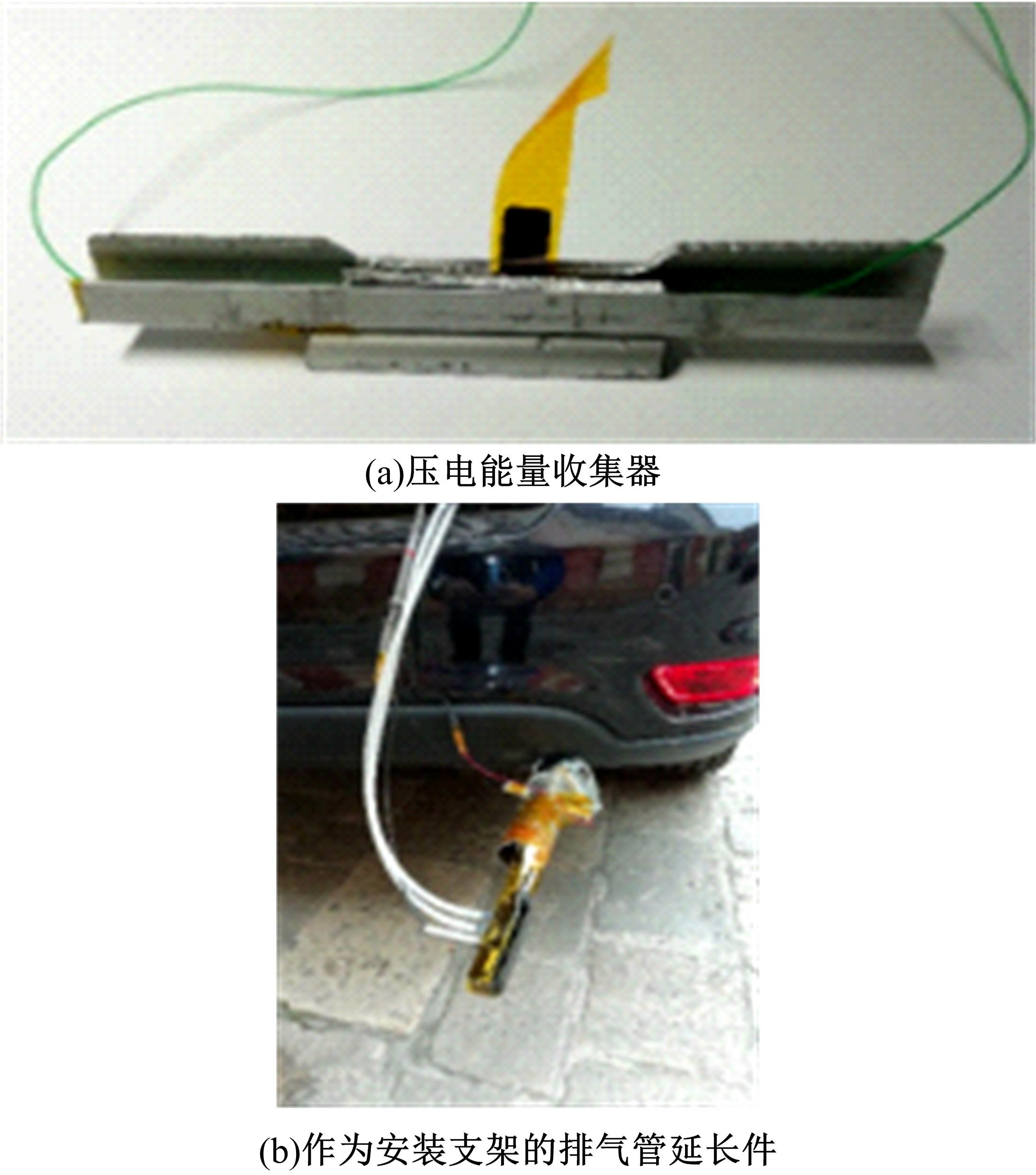
| 17 | Madaro F, Mehdipour I, Caricato A, et al. Available energy in cars' exhaust system for IoT remote exhaust gas sensor and piezoelectric harvesting[J]. Energies, 2020, 13(16):No.4169. |
| 18 | 高小林,王袁明.基于压电材料的汽车尾气涡轮发电装置设计研究[J].河南科技,2015(2):34-36. |
| Gao Xiao-lin, Wang Yuan-ming. Design and research of automobile exhaust turbine power generation device based on piezoelectric materials [J]. Henan Science and Technology,2015(2):34-36. | |
| 19 | Takigami T, Tomioka T. Investigation to suppress bending vibration of railway vehicle carbodies using piezoelectric elements[J]. Quarterly Report of RTRI, 2005, 46(4): 225-230. |
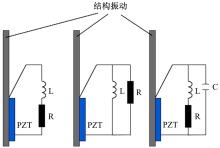
| 20 | 闫旭,郭辉,王岩松,等.周期性压电分流薄板结构振动控制方法研究[J].压电与声光,2017,39(1):126-130. |
| Yan Xu, Guo Hui, Wang Yan-song, et al. Research on vibration control method of periodic piezoelectric shunt thin plate structure[J]. Piezoelectricity & Acousto Optics, 2017,39(1):126-130. | |
| 21 | Salloum R, Töws P, Schmidt S, et al. Vibration damping of a composite control arm through embedded piezoceramic patches shunted with a negative capacitance[J]. Smarte Strukturen Und Systeme, 2016: 182-193. |
| 22 | 沈传亮,安孝文,王大学.基于压电材料的车身薄壁结构振动主动控制仿真分析[J].新型工业化,2012,2(11):50-56. |
| Shen Chuan-liang, An Xiao-wen, Wang Da-xue. Based on piezoelectric material body thin-walled structure vibration active control simulation analysis [J]. Journal of New Industrialization, 2012, 2 (11): 50-56. | |
| 23 | 安孝文. 基于压电材料的车身薄壁结构振动主动控制研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学汽车工程学院,2012. |
| An Xiao-wen. Active vibration control of thin-walled car body structure based on piezoelectric materials[D]. Changchun: College of Automotive Engineering, Jilin University,2012. | |
| 24 | 张勇,李鑫,王兰军.压电陶瓷在车身板件振动主动控制中的应用研究[J].科学技术与工程,2013,13(15):4264-4269. |
| Zhang Yong, Li Xin, Wang Lan-jun. Research on application of piezoceramics in active vibration control of body panels[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2013,13(15):4264-4269. | |
| 25 | Guo H, Wang Y S, Yang C, et al. Vehicle interior noise active control based on piezoelectric ceramic materials and improved fuzzy control algorithm[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2019, 150: 216-226. |
| 26 | Jung H K, Park G, Kim J K. Piezoelectric-based dither control for automobile brake squeal suppression under various braking conditions[J]. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2021, 27(19/20): 2192-2204. |
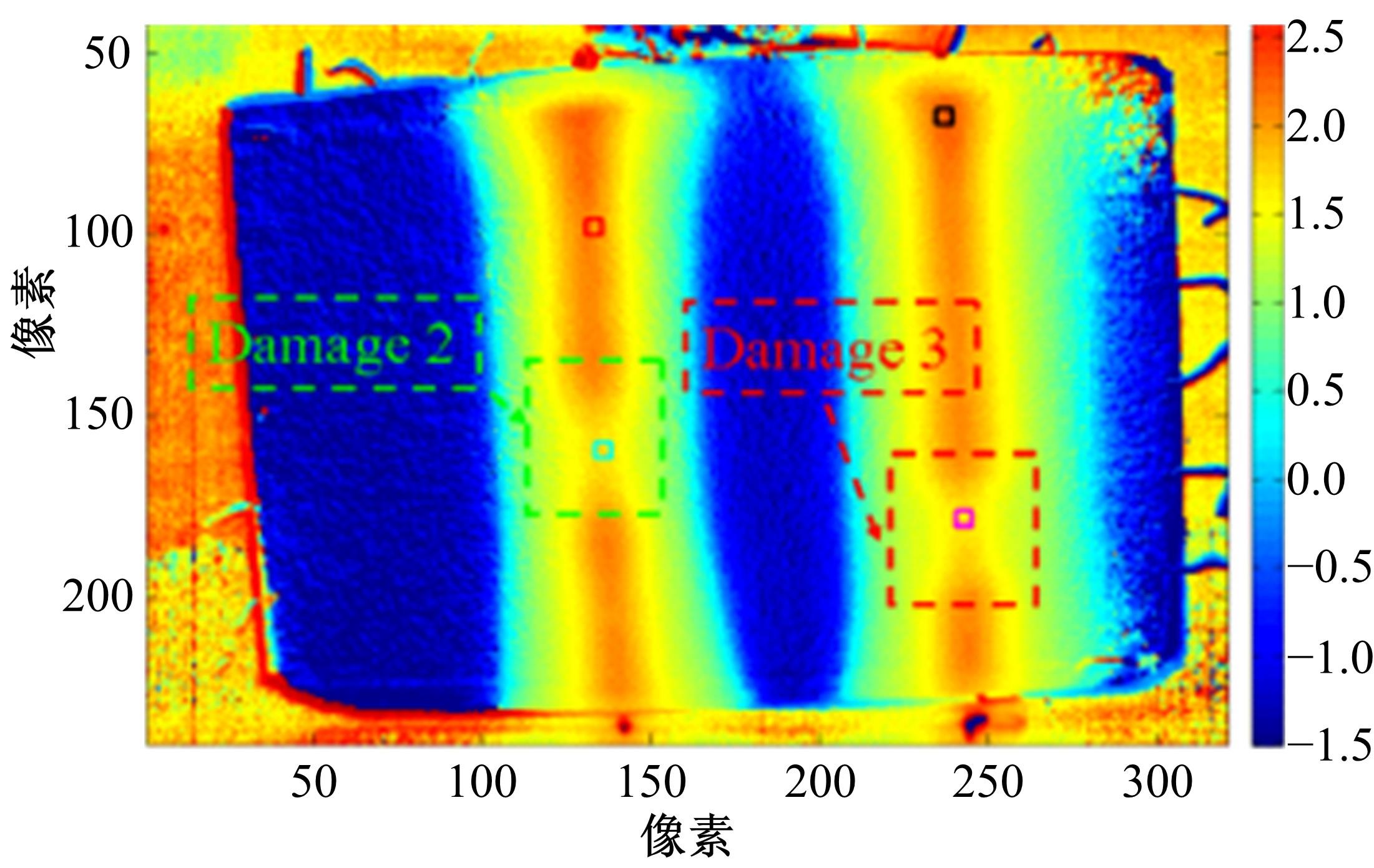
| 27 | de Medeiros R, Ribeiro M L, Tita V. Computational methodology of damage detection on composite cylinders: structural health monitoring for automotive components[J]. International Journal of Automotive Composites, 2014, 1(1): 112-128. |
| 28 | Moharana S, Sevugaperumal Arun V. Piezo impedance-based monitoring of loosening of bolts: Experimental and numerical study[J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 2022, 33(8): 1056-1071. |
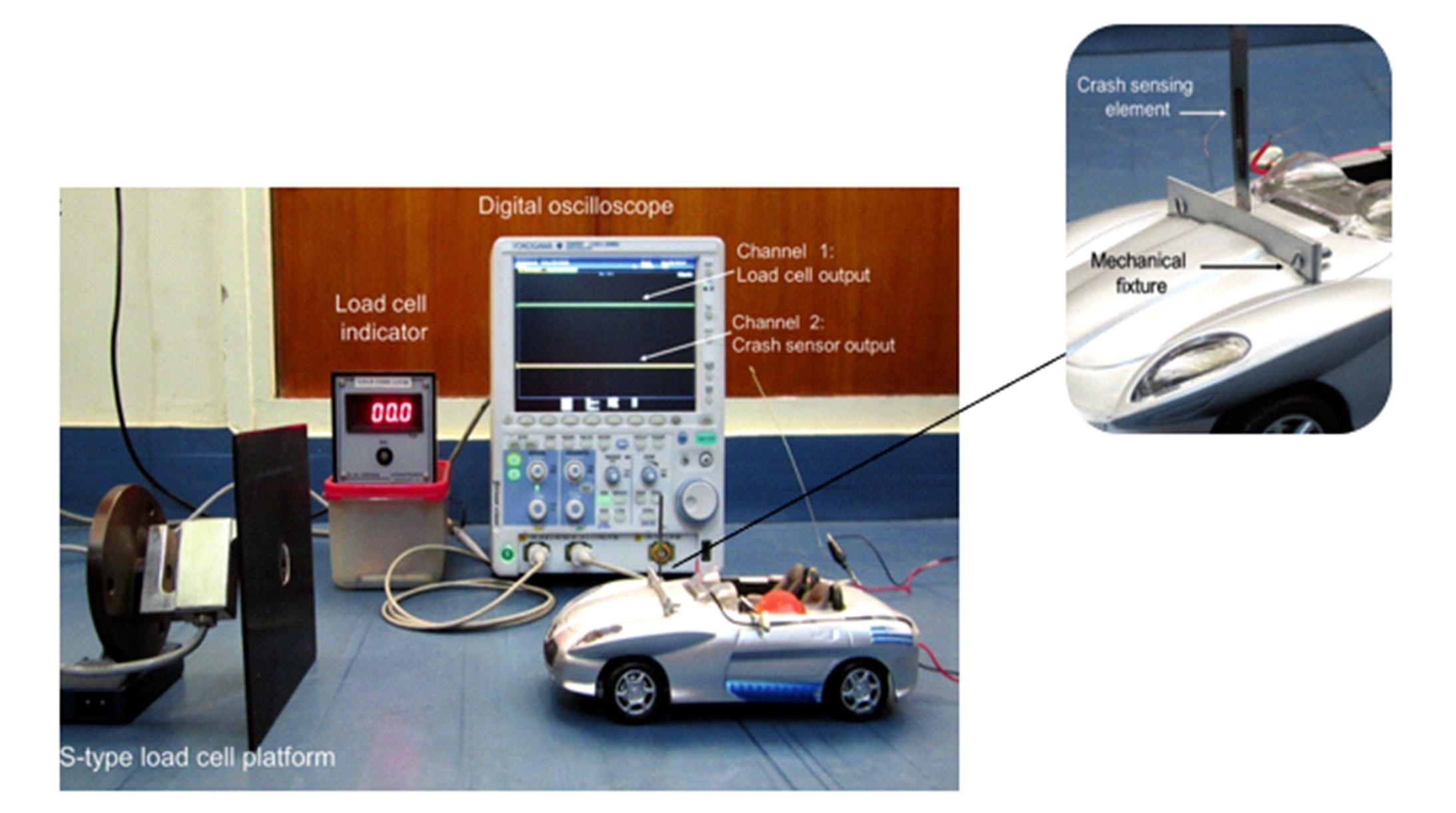
| 29 | Joshi S, Nayak M M, Rajanna K. Tailoring thin‐film piezoelectrics for crash sensing[J]. Small, 2018, 14(29): 1800608. |
| 30 | Prasanti K, Kalpana S, Savalam C S. A novel feature of increased safety during car crashes[C]∥The 2nd International Conference on Inventive Systems and Control (ICISC), Coimbatore, India, 2018: 855-859. |
| 31 | Matilainen M, Tuononen A. Tyre contact length on dry and wet road surfaces measured by three-axial accelerometer[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2015, 52: 548-558. |
| 32 | Erdogan G, Alexander L, Rajamani R. Estimation of tire-road friction coefficient using a novel wireless piezoelectric tire sensor[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2010, 11(2): 267-279. |
| 33 | Baek H J, Lee H B, Kim J S, et al. Nonintrusive biological signal monitoring in a car to evaluate a driver's stress and health state[J]. Telemedicine and e-Health, 2009, 15(2): 182-189. |
| 34 | Meteier Q, Kindt M, Angelini L, et al. Non-intrusive contact respiratory sensor for vehicles[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(3):No. 880. |
| 35 | Nagase T, Nonaka K, Koishi Y, et al. Heat-resistant, flexible piezoelectric sheet sensors based on solution-processed zinc oxide films for in-vehicle driver monitoring applications[J]. ACS Applied Electronic Materials, 2021, 3(11): 4743-4756. |
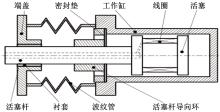
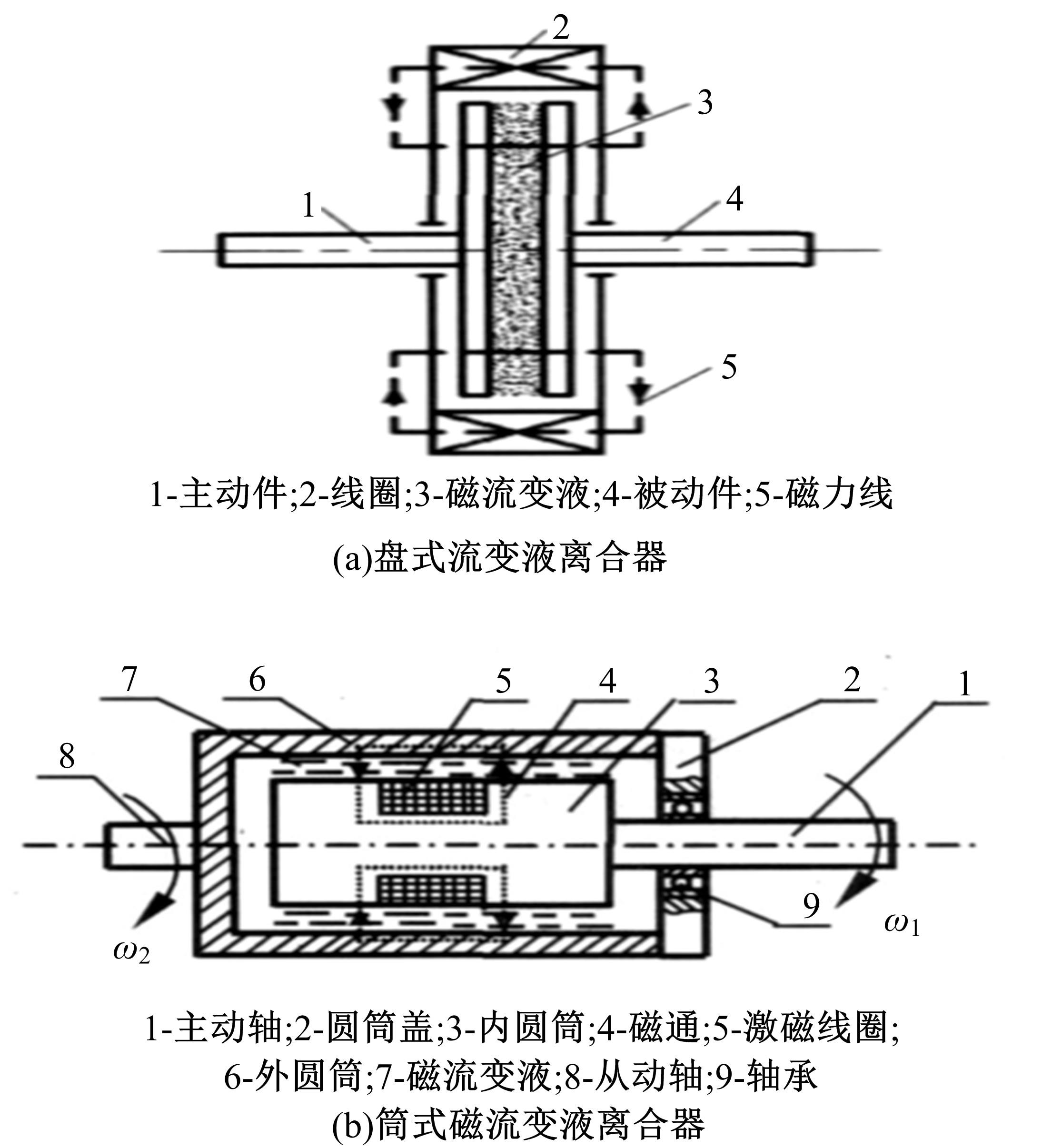
| 36 | Rabinow J. The magnetic fluid clutch[J]. Electrical Engineering, 1948, 67(12): 1167-1176. |
| 37 | 史文库,侯锁军,王雪婧,等.磁流变发动机悬置隔振性能与模糊PID控制[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(20):50-57. |
| Shi Wen-ku, Hou Suo-jun, Wang Xue-jing, et al. Vibration isolation performance and fuzzy pid control of magnetorheological engine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2012,28(20):50-57. | |
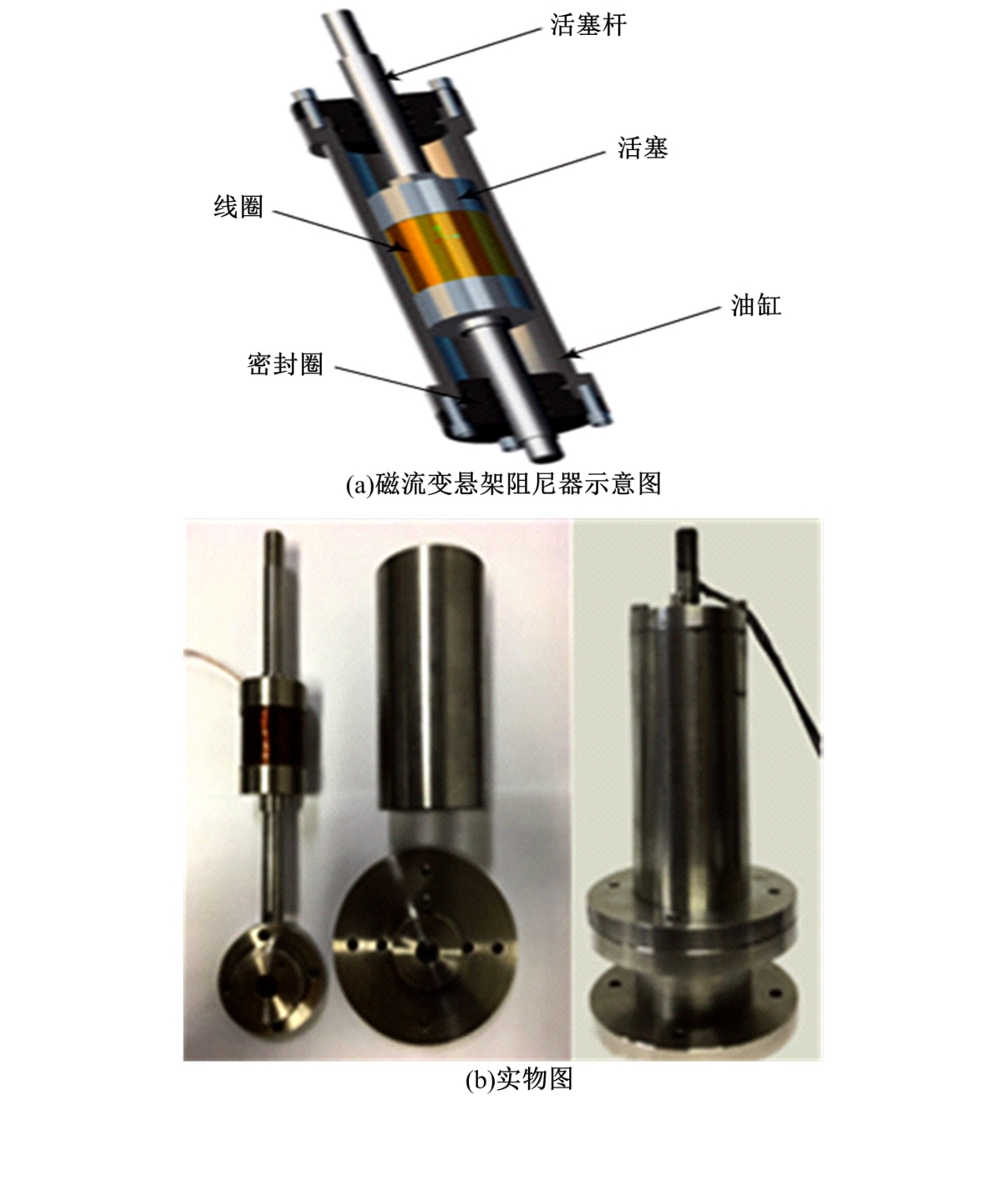
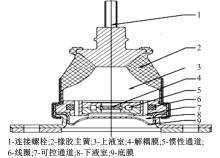
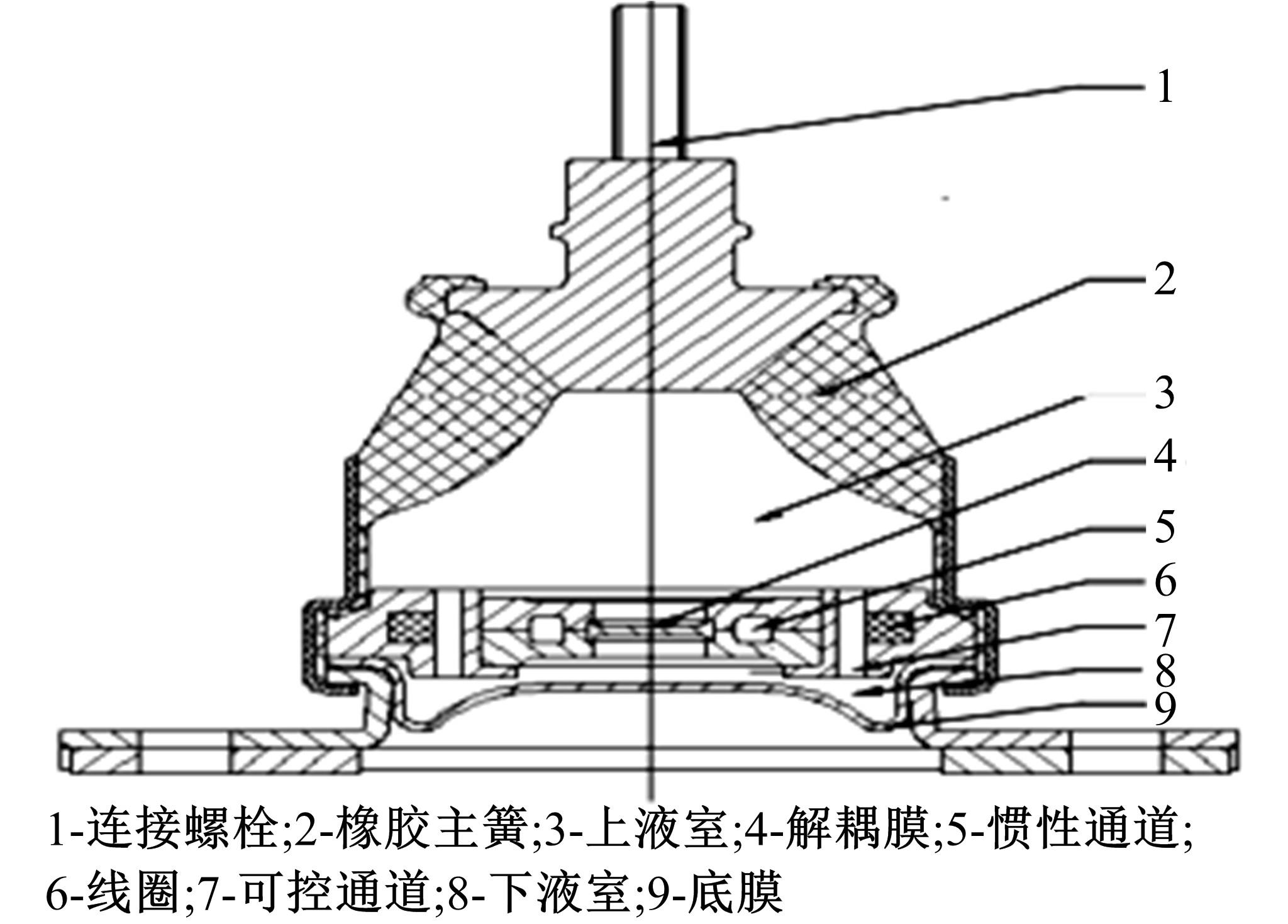
| 38 | Chen P, Bai X X, Qian L J, et al. A magneto-rheological fluid mount featuring squeeze mode: analysis and testing[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2016, 25(5): No.055002. |
| 39 | Liu Q, Bai G D, Liu Z H, et al. Magnetorheological semi-active mount system for engines: prototyping and testing[J]. Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2020, 234(13): 3081-3094. |
| 40 | Ladipo I L, Fadly J D, Faris W F. Characterization of magnetorheological elastomer (MRE) engine mounts[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2016, 3(2): 411-418. |
| 41 | Paddan G S, Griffin M J. Evaluation of whole-body vibration in vehicles[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2002, 253(1): 195-213. |
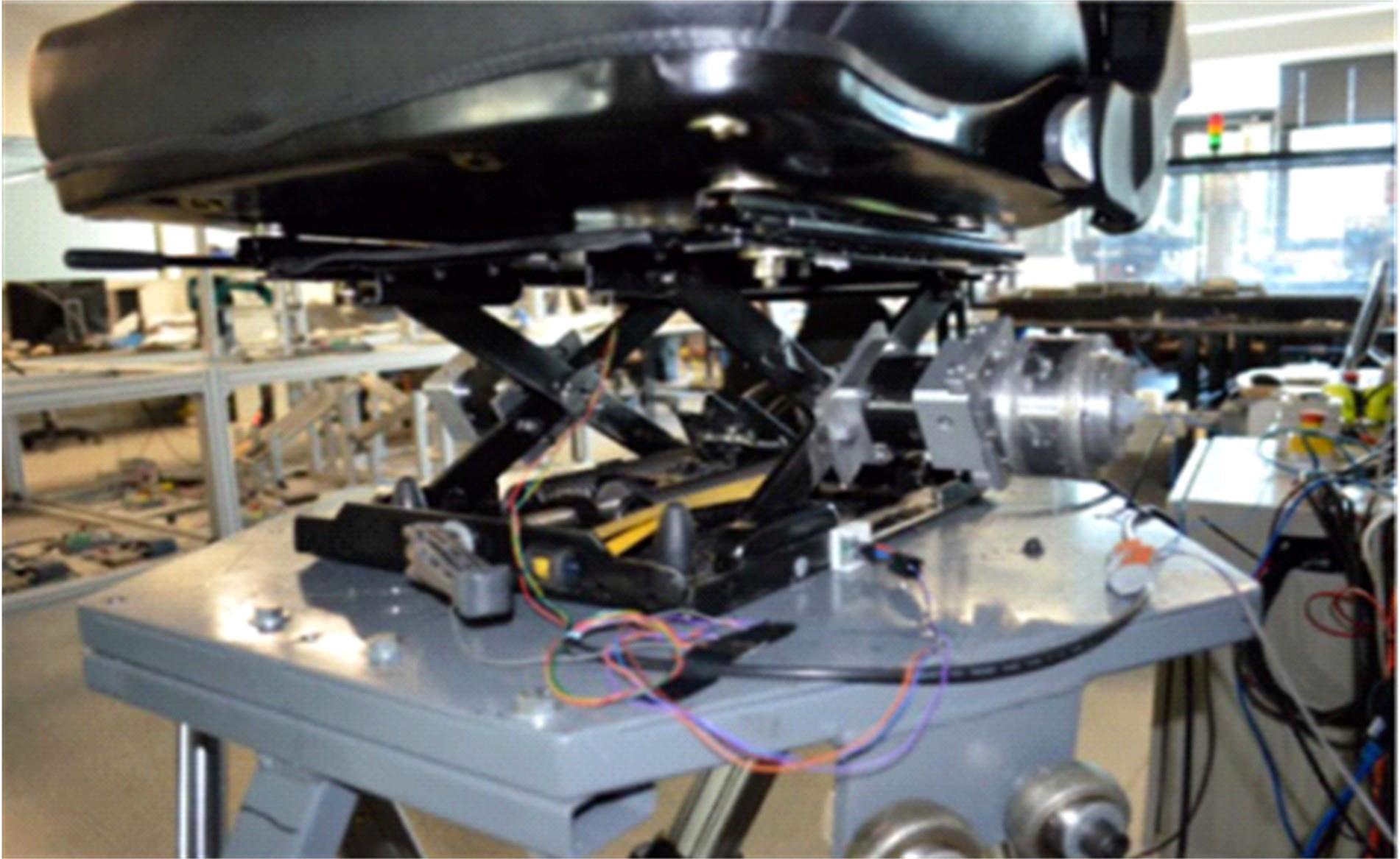
| 42 | Choi S B, Han Y M. MR seat suspension for vibration control of a commercial vehicle[J]. International Journal of Vehicle Design, 2003, 31(2): 202-215. |
| 43 | 史文库,张曙光,陈志勇,等.磁流变半主动座椅悬架建模及振动特性分析[J].西南交通大学学报,2023,58(2):253-260. |
| Shi Wen-ku, Zhang Shu-guang, Chen Zhi-yong, et al. Modeling and vibration characteristics analysis of magnetorheological semi-active seat suspension[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2023,58(2):253-260. | |
| 44 | Sun S S, Ning D H, Yang J, et al. A seat suspension with a rotary magnetorheological damper for heavy duty vehicles[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2016, 25(10): No.105032. |
| 45 | Du H, Li W, Zhang N. Semi-active variable stiffness vibration control of vehicle seat suspension using an MR elastomer isolator[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2011, 20(10):No.105003. |
| 46 | Liu C, Hemmatian M, Sedaghati R, et al. Development and control of magnetorheological elastomer-based semi-active seat suspension isolator using adaptive neural network[J]. Frontiers in Materials, 2020, 7:No.00171. |
| 47 | Yaakub S F, Yahaya S H, Ahmad F, et al. A comprehensive review on the related models in magneto-rheological automobile suspension system[J]. International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology, 2020, 13(7): 1700-1708. |
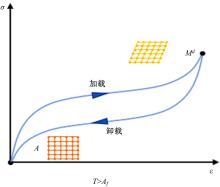
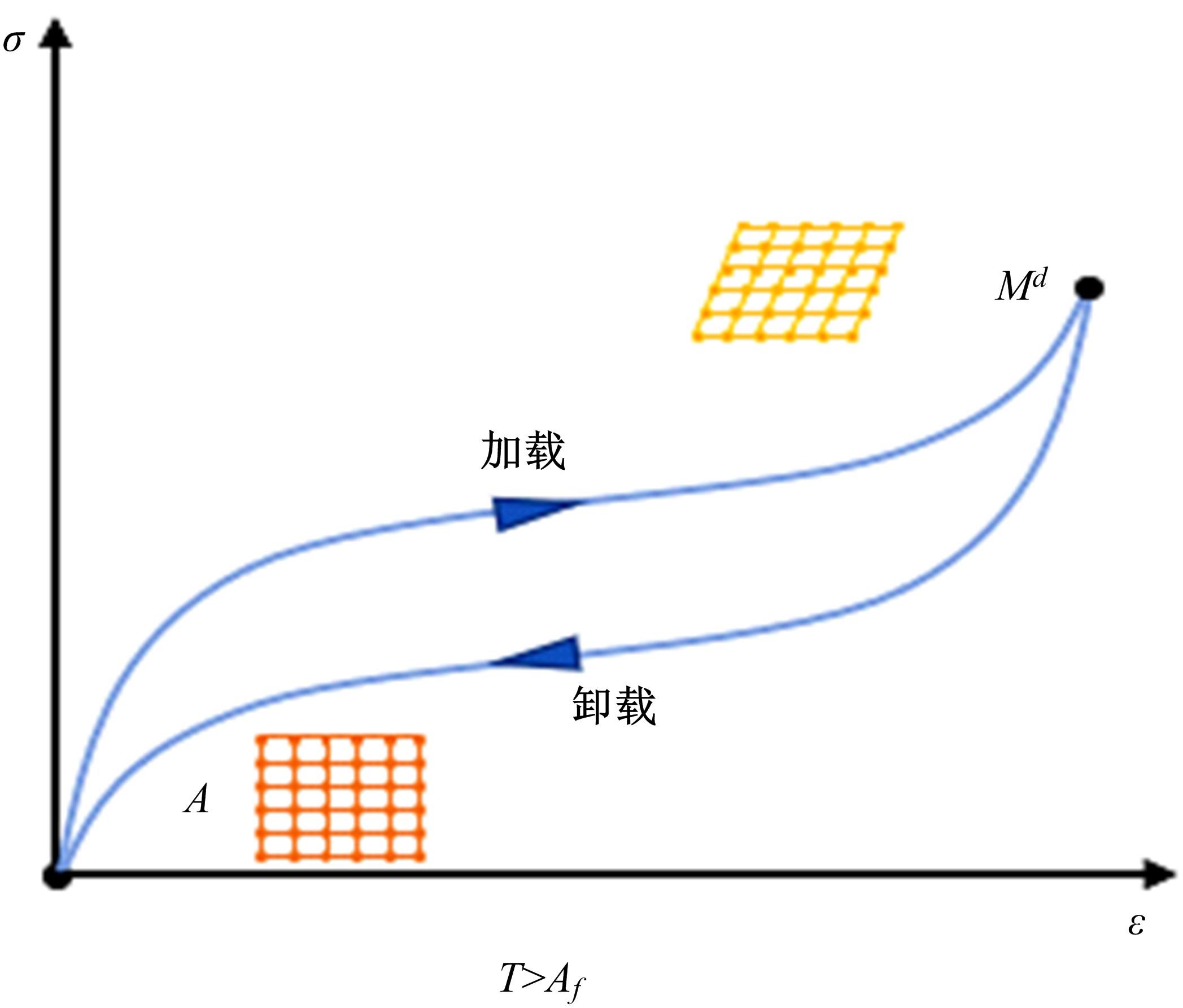
| 48 | Meng F, Zhou J. Modeling and control of a shear-valve mode MR damper for semiactive vehicle suspension[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2019(1):1-8. |
| 49 | Yao J, Shi W, Zheng J, et al. Development of a sliding mode controller for semi-active vehicle suspensions[J]. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2013, 19(8): 1152-1160. |
| 50 | Zhang X, Yang Y, Guo K, et al. Methodology on a novel magnetorheological valve controlled damper synthesis design[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2020, 29(4): No.045006. |
| 51 | 屈贤,林繁国,张金龙.基于磁流变缓冲吸能装置的汽车碰撞仿真分析[J].汽车安全与节能学报,2020,11(4):487-492. |
| Qu Xian, Lin Fan-guo, Zhang Jin-long. Simulation Analysis of vehicle collision based on magnetorheological buffer energy absorption device[J]. Journal of Automobile Safety and Energy Conservation,2020,11(4):487-492. | |
| 52 | Fekry A R, Oraby W A H, Ali M A. Vehicle body pitch control through integration of MR damping system implemented in both vehicle suspension and front-end structure[J]. Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2022: 237(5):1082-1092. |
| 53 | Bai X X, Wereley N M. Magnetorheological impact seat suspensions for ground vehicle crash mitigation[C]∥ International Society for Optics and Photonics on Active and Passive Smart Structures and Integrated Systems San Diego,USA,2014. |
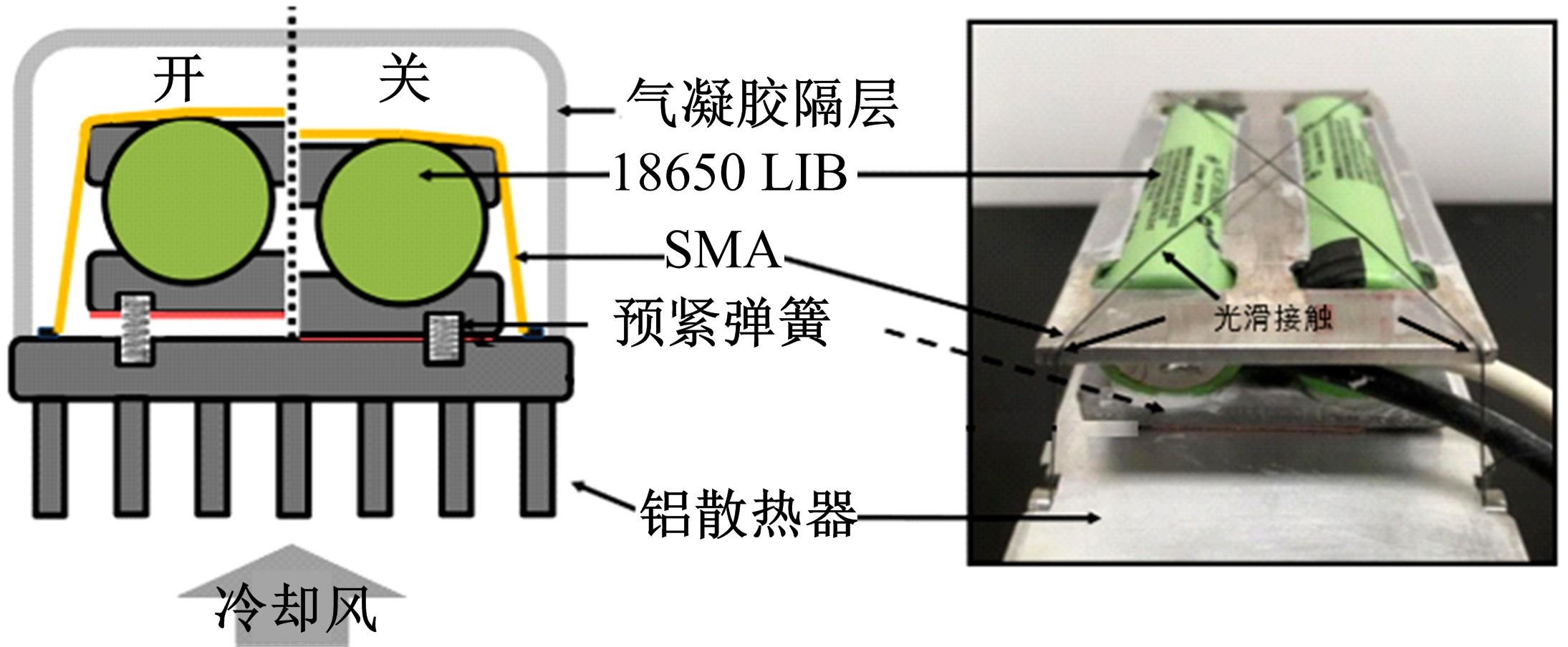
| 54 | 麻建坐,贺建民,黄金. 圆筒式磁流变离合器传动特性分析[J].重庆工学院学报:自然科学版,2009, 23(3):34-38, 42. |
| Ma Jian-zuo, He Jian-min, Huang Jin. Transmission characteristics analysis of cylinder magnetorheological clutch[J]. Journal of Chongqing Institute of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2009,23(3):34-38, 42. | |
| 55 | 张春光,苗运江,巫峰.汽车磁流变液离合器的设计[J].润滑与密封,2012,37(5):91-94. |
| Zhang Chun-guang, Miao Yun-jiang, Wu Feng. Design of vehicle magnetorheological fluid clutch[J]. Lubrication Engineering,2012,37(5):91-94. | |
| 56 | 陈德民,张宏,蔡青格,等.车用磁流变离合器设计与性能实验[J].机械强度,2016,38(1):49-53. |
| Chen De-min, Zhang Hong, Cai Qing-ge, et al. Automotive magnetorheological clutch design and performance test[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength,2016,38(1):49-53. | |
| 57 | Zhang H, Du H, Sun S, et al. A novel magneto-rheological fluid dual-clutch design for two-speed transmission of electric vehicles[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2021, 30(7):No. 075035. |
| 58 | Zainordin A Z, Mohamed Z, Ahmad F. The magnetorheological fluid: testing on automotive braking system[J]. International Journal of Automotive and Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 18(1):8577⁃8584. |
| 59 | 王维成, 罗一平, 王磊, 等. 基于矩形凸块的盘式磁流变制动器设计与仿真[J]. 机械传动, 2021, 45(4): 64-68, 79. |
| Wang Wei-cheng, Luo Yi-ping, Wang Lei, et al. Design and simulation of disc magnetorheological brake based on rectangular convex block[J]. Journal of Mechanical Transmission, 2021, 45(4): 64-68, 79. | |
| 60 | 黄金,周轶,王西.圆盘式与圆筒式磁流变制动器制动转矩研究[J].机械设计与制造,2020(4):71-74. |
| Huang Jin, Zhou Yi, Wang Xi. Research on braking torque of disc and cylinder magnetorheological brake[J]. Machinery Design and Manufacture, 2020(4):71-74. | |
| 61 | Acharya S, Kumar H. Investigation of magnetorheological brake with rotor of combined magnetic and non-magnetic materials[J]. SN Applied Sciences, 2019, 1(9): 1-7. |
| 62 | Ölander A. An electrochemical investigation of solid cadmium-gold alloys[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1932, 54(10): 3819-3833. |
| 63 | Buehler W J, Gilfrich J V, Wiley R C. Effect of low‐temperature phase changes on the mechanical properties of alloys near composition TiNi[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1963, 34(5): 1475-1477. |
| 64 | Kauffman G B, Mayo I. The story of nitinol: the serendipitous discovery of the memory metal and its applications[J]. The Chemical Educator, 1997, 2(2): 1-21. |
| 65 | Motors G. Chevrolet debuts lightweight "smart material" on corvette[DB/OL]. [2013-03-21]. . |
| 66 | Neugebauer R, Bucht A, Pagel K, et al. Numerical simulation of the activation behavior of thermal shape memory alloys[C]∥Industrial and Commercial Applications of Smart Structures Technologies, 2010, 7645: 137-148. |
| 67 | Czechowicz A, Lygin K, Langbein S. On the potentials of shape memory alloy valves[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2014, 23(7): 2687-2695. |
| 68 | Stöckel D. The shape memory effect: phenomenon[J]. Alloys, Applications, 2000: 1-13. |
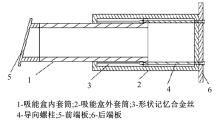
| 69 | 杜英辰. 形状记忆合金主动式发动机罩弹起装置研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学汽车工程学院,2021. |
| Du Ying-chen. Research on active hood ejection device of shape memory alloy[D]. Changchun: College of Automotive Engineering, Jilin University, 2021. | |
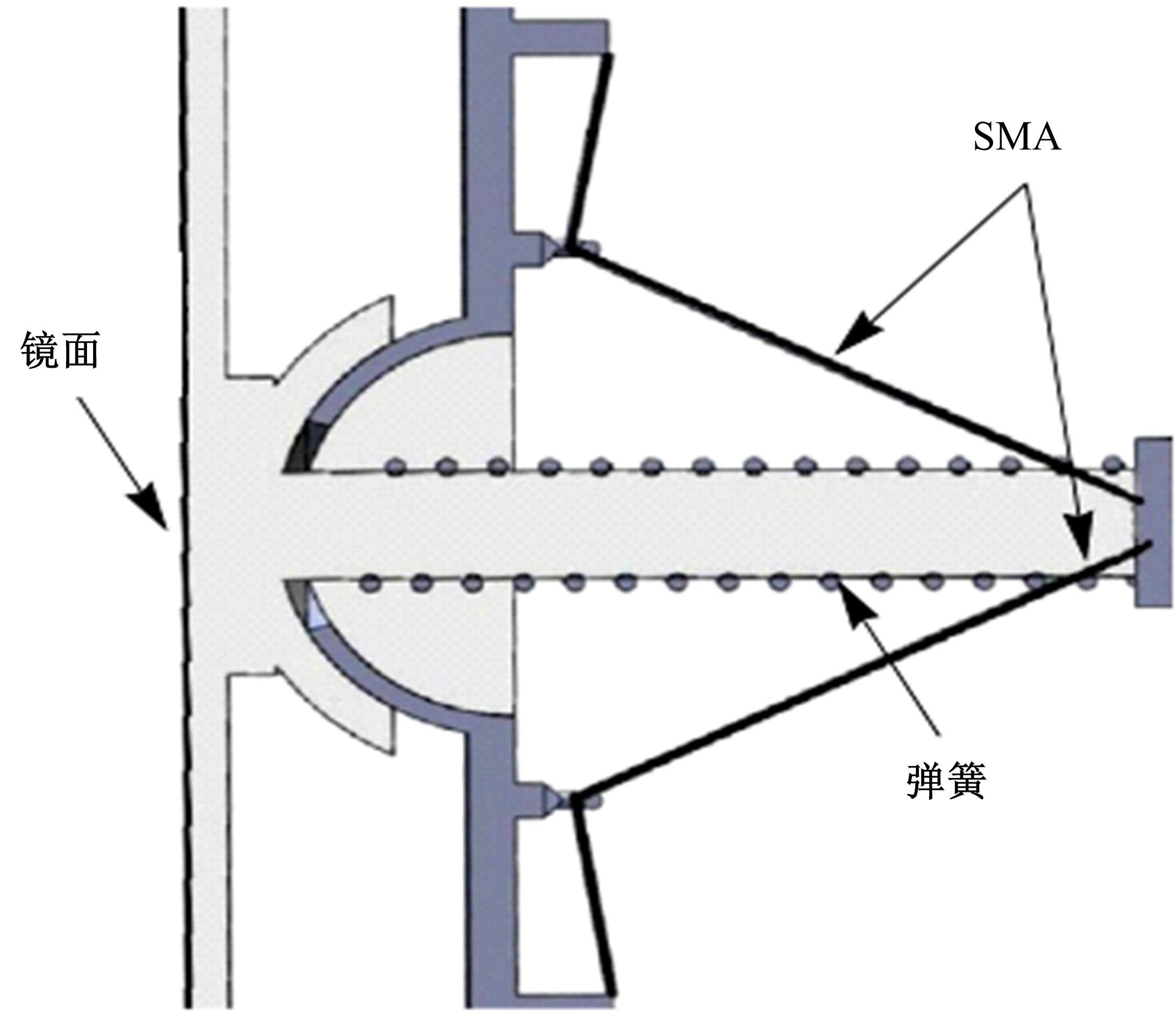
| 70 | Williams E A, Shaw G, Elahinia M. Control of an automotive shape memory alloy mirror actuator[J]. Mechatronics, 2010, 20(5): 527-534. |
| 71 | Ameduri S, Brindisi A, Ciminello M, et al. Car Soundproof improvement through an SMA adaptive system[J]. Actuators, 2018, 7(4):No. 88. |
| 72 | Ruth D J S, Dhanalakshmi K, Choi S B. A sensaptic adas device using shape memory alloy wires: Design and control[J]. Materials, 2021, 14(13): No.3494. |
| 73 | Imran H Y, Majid D L A A, Ethaib S, et al. Utilization of shape memory alloy (SMA) for temperature detection and warning in an automobile engine[C]∥IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2021, 1058(1): No.012039. |
| 74 | Suman A, Fortini A, Merlin M. A shape memory alloy-based morphing axial fan blade: functional characterization and perspectives[J]. Energy Procedia, 2015, 82: 273-279. |
| 75 | Hao M, Li J, Park S, et al. Efficient thermal management of Li-ion batteries with a passive interfacial thermal regulator based on a shape memory alloy[J]. Nature Energy, 2018, 3(10): 899-906. |
| 76 | Bodaghi M, Shakeri M, Aghdam M M. Passive vibration control of plate structures using shape memory alloy ribbons[J]. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2017, 23(1): 69-88. |
| 77 | Huang Y, Zhang Z, Li C, et al. Sound radiation of orthogonal antisymmetric composite laminates embedded with pre-strained SMA wires in thermal environment[J]. Materials, 2020, 13(17):No.3657. |
| 78 | Shen C, Su W, Sun G, et al. Preliminary study of vibration characteristics of intelligent beam with the influence of SMA's restoring force[J]. MATEC Web of Conferences, 2018, 238: No.05007. |
| 79 | Sellitto A, Riccio A. Overview and future advanced engineering applications for morphing surfaces by shape memory alloy materials[J]. Materials, 2019, 12(5): No.708. |
| 80 | Daynes S, Weaver P M. Review of shape-morphing automobile structures: concepts and outlook[J]. Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2013, 227(11): 1603-1622. |
| 81 | Chillara V S C, Dapino M J. Review of morphing laminated composites[J]. Applied Mechanics Reviews, 2020, 72(1):No. 010801. |
| 82 | Chillara V S C, Headings L M, Tsuruta R, et al. Shape memory alloy-actuated prestressed composites with application to morphing automotive fender skirts[J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 2019, 30(3): 479-494. |
| 83 | Han M W, Rodrigue H, Cho S, et al. Woven type smart soft composite for soft morphing car spoiler[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2016, 86: 285-298. |
| 84 | Hein A, Holder D, Maier J, et al. Potential analysis of smart materials and methodical approach developing adaptive designs using shape memory alloys[C]∥ Proceedings of Nord Design, Linköping, Sweden, 2018. |
| 85 | 李立军, 孙凌玉, 黄彬城, 等. 智能材料与汽车结构健康监测[J]. 汽车技术, 2018(5): 46-52. |
| Li Li-jun, Sun Ling-yu, Huang Bin-cheng, et al. Intelligent materials and vehicle structure health monitoring [J]. Automobile Technology, 2018(5): 46-52. | |
| 86 | Wu W, Liu Q, Zong Z, et al. Experimental investigation into transverse crashworthiness of CFRP adhesively bonded joints in vehicle structure[J]. Composite Structures, 2013, 106: 581-589. |
| 87 | Xia Y, Wierzbicki T, Sahraei E, et al. Damage of cells and battery packs due to ground impact[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 267: 78-97. |
| 88 | Pinto F, Ciampa F, Meo M, et al. Multifunctional SMArt composite material for in situ NDT/SHM and de-icing[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2012, 21(10):No.105010. |
| 89 | Pinto F, Maroun F Y, Meo M. Material enabled thermography[J]. NDT & E International, 2014, 67: 1-9. |
| 90 | Rizzo F, Pinto F, Meo M. Development of multifunctional hybrid metal/carbon composite structures[J]. Composite Structures, 2019, 222:No.110907. |
| 91 | Kim E H, Lee I, Roh J H, et al. Effects of shape memory alloys on low velocity impact characteristics of composite plate[J]. Composite Structures, 2011, 93(11): 2903-2909. |
| 92 | 马晓宇. 基于形状记忆合金的复合材料车身板件的耐冲击性研究[D].长春:吉林大学汽车工程学院,2018. |
| Ma Xiao-yu. Research on impact resistance of composite body panels based on shape memory alloy[D]. Changchun: College of Automotive Engineering, Jilin University,2018. | |
| 93 | Saeedi A, Shokrieh M M. A novel self-healing composite made of thermally reversible polymer and shape memory alloy reinforcement[J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 2019, 30(10): 1585-1593. |
| 94 | 吴志鹏. 形状记忆合金汽车吸能装置特性研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学汽车工程学院,2017. |
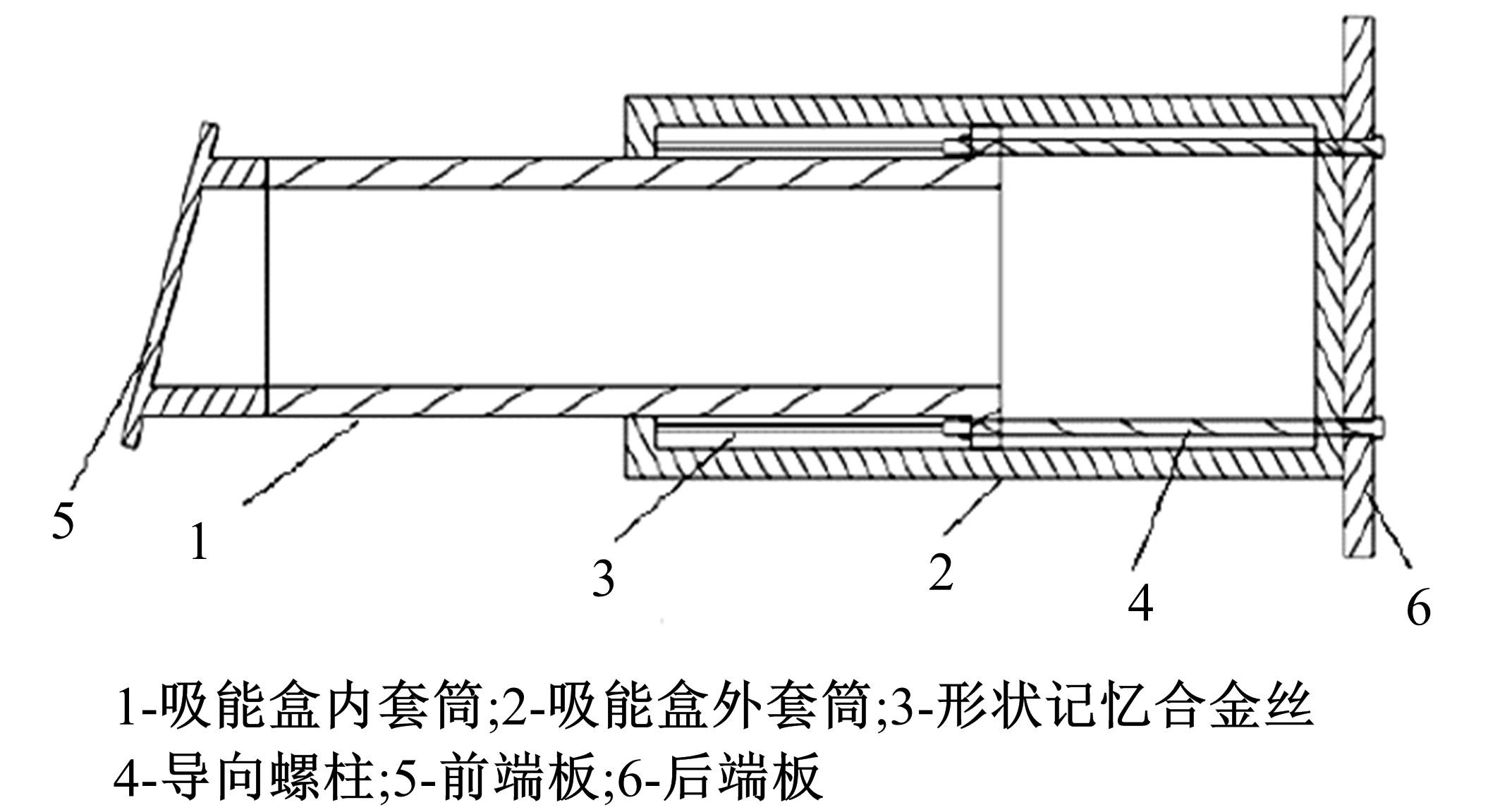
| Wu Zhi-peng. Research on Characteristics of Shape Memory Alloy Automotive Energy Absorption Device [D]. Changchun: College of Automotive Engineering, Jilin University,2017. |
| [1] | 杨帆,张旭东,赵蒙,折波,邓俊楷. 基于有限元计算的形状记忆合金⁃金属玻璃复合材料变形行为[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 172-180. |
| [2] | 周淼磊, 高巍, 高琳琳, 刘富. 磁控形状记忆合金执行器迟滞非线性模型 [J]. , 2012, (03): 714-718. |
| [3] | 刘旺中, 陈照波, 黄山云, 焦映厚. 形状记忆合金迟滞模型 [J]. , 2012, (03): 719-725. |
| [4] | 曹宗杰,王铭伟,全吉成,胡进海 . 缺陷压电结构电弹性问题断裂分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2006, 36(增刊2): 157-160. |
| [5] | 周勇, 王鑫伟, 孙亚飞, 谈梅兰. 压电复合材料层合板弯曲变形及脱粘损伤的有限元分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2004, (2): 180-184. |
| [6] | 韩立军, 赵熹华. TiNi形状记忆合金精密脉冲电阻对焊接头的形状恢复率[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2001, (1): 14-18. |
|
||