吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (10): 2952-2962.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221571
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于深度频率特征注意力机制的图像去雨方法
- 1.河北工业大学 电子信息工程学院,天津 300401
2.陆军工程大学石家庄校区,石家庄 050003
3.河北工业大学 人工智能与数据科学学院,天津 300401
Image de-rain based on deep frequency feature attention mechanism
Qing YANG1,2( ),Ming YU3(
),Ming YU3( ),Gang YAN3
),Gang YAN3
- 1.College of Electronic Information Engineering,Hebei University of Technology,Tianjin 300401,China
2.Shijiazhuang Campus of Army Engineering University,Shijiazhuang 050003,China
3.School of Artificial Intelligence,Hebei University of Technology,Tianjin 300401,China
摘要:
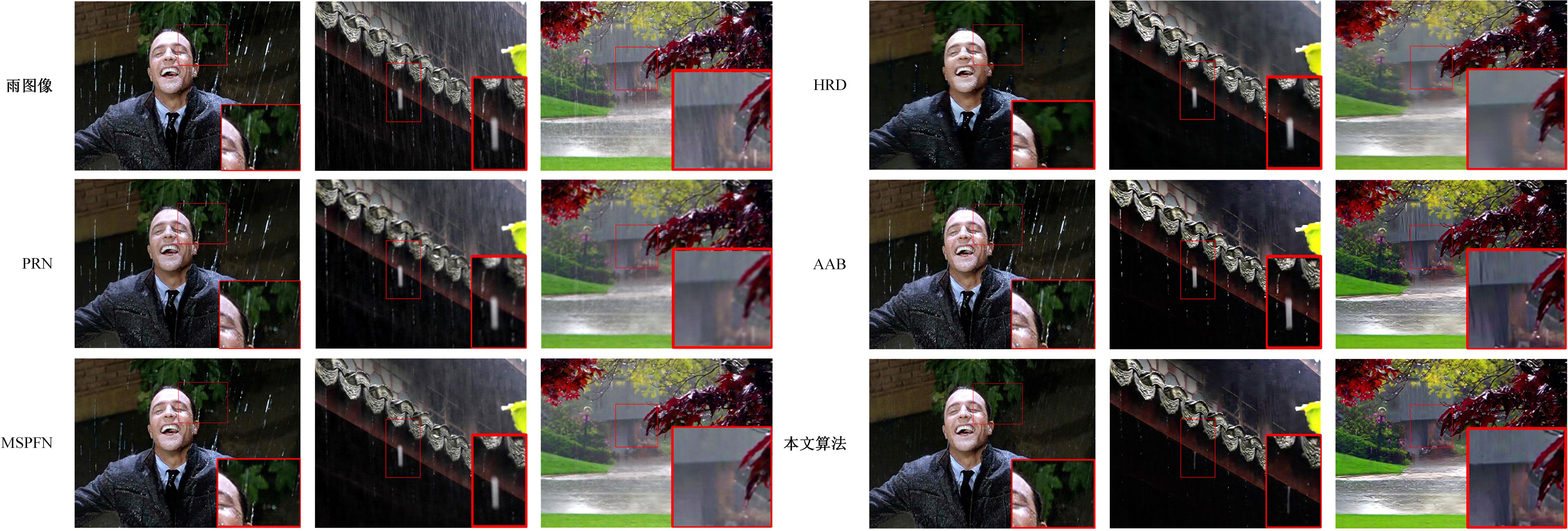
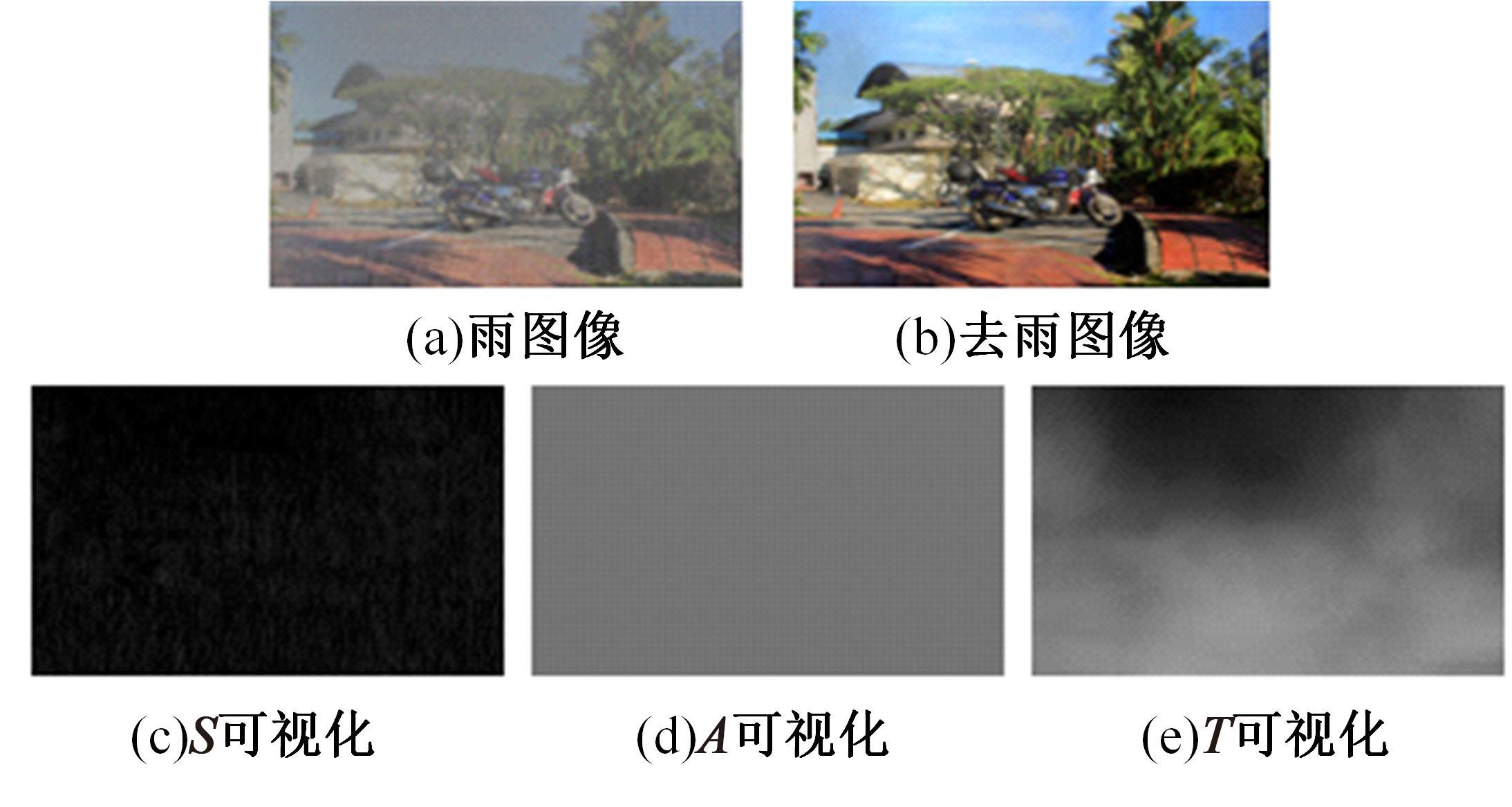
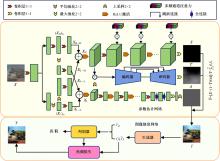
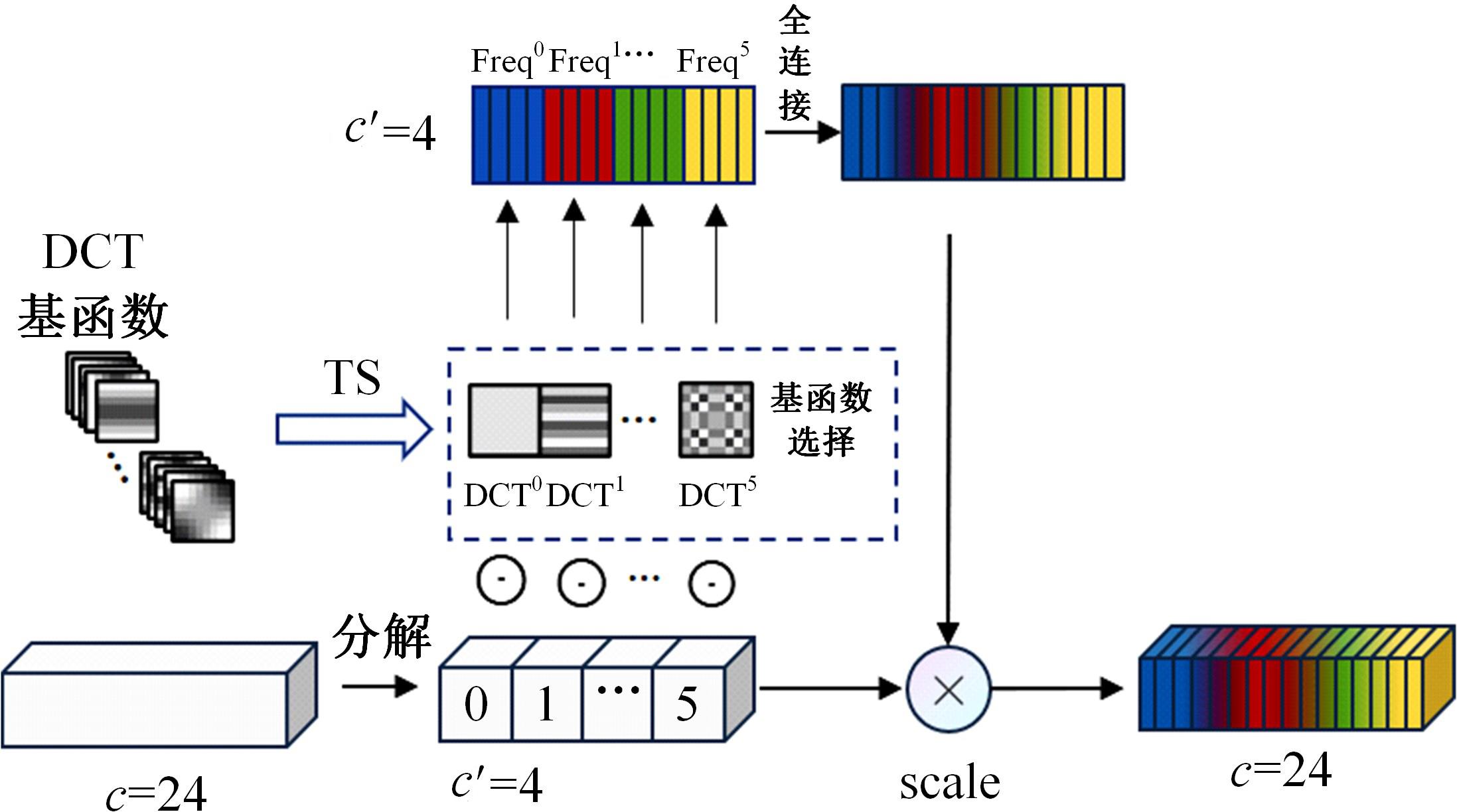
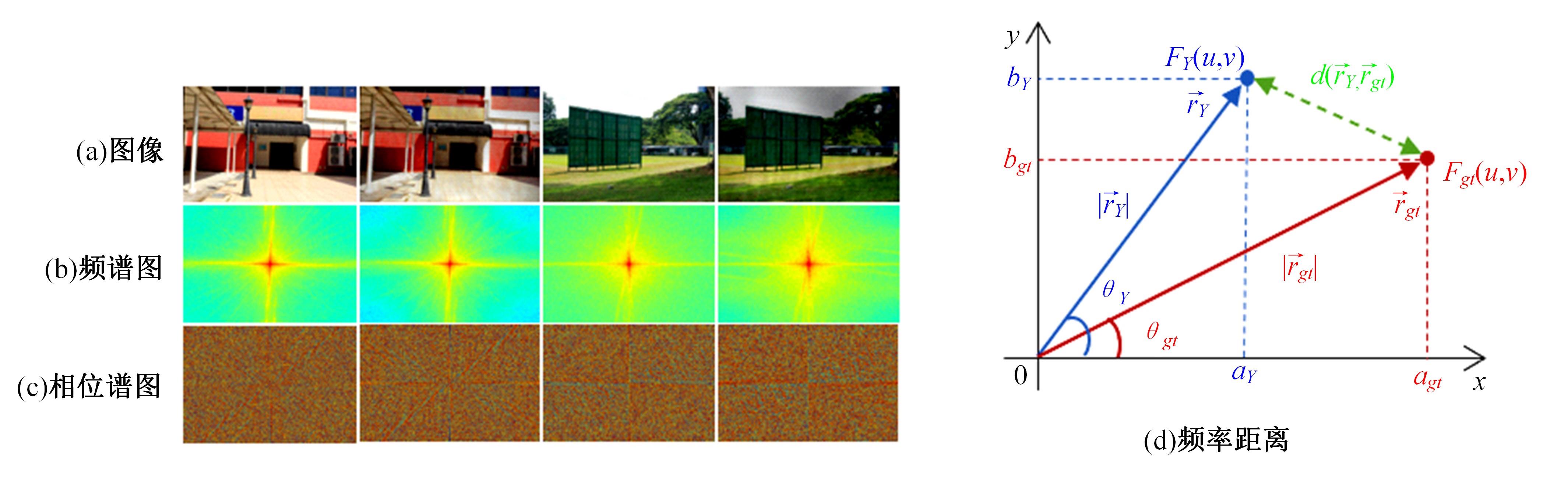
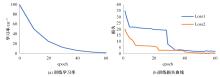
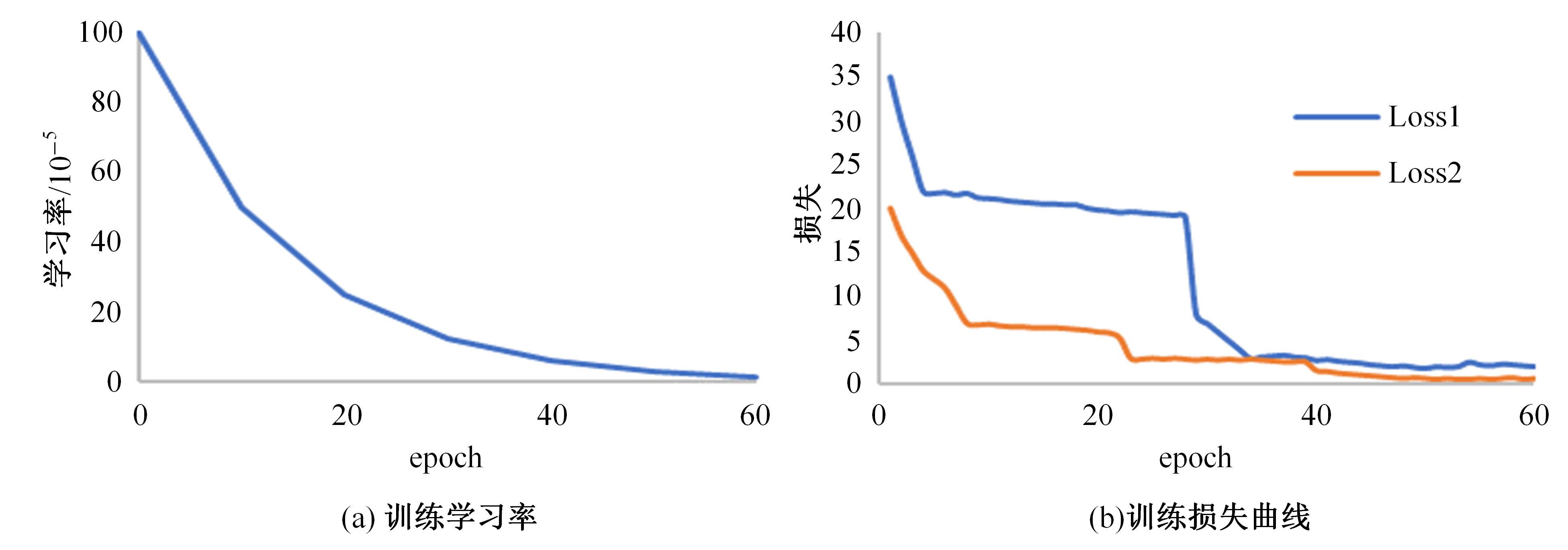
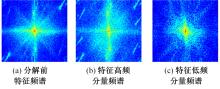
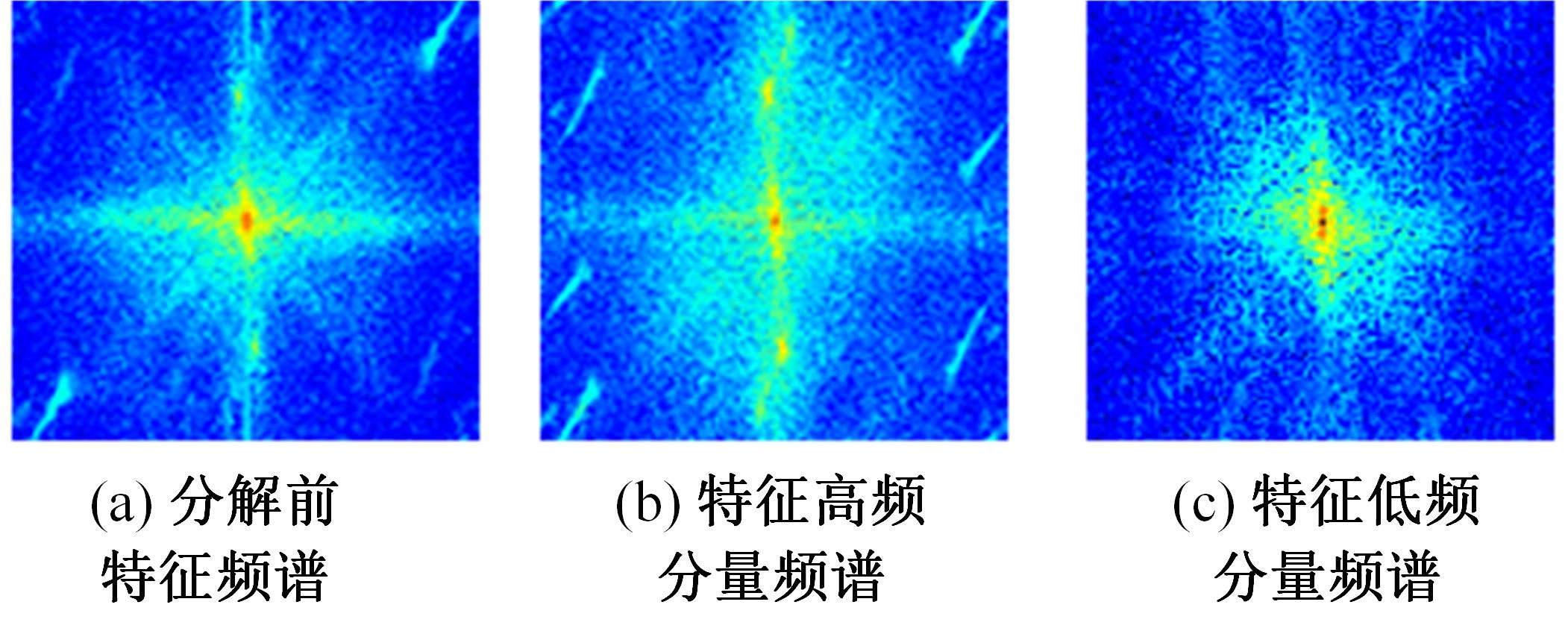
针对雨图像中由于雨线和雨幕效应导致背景信息模糊、清晰度下降的问题,本文提出一种基于深度频率特征注意力机制的图像去雨方法。首先,构建基于频率去雨模型的参数估计网络,设计基于空间尺度变换和倍频卷积的频率特征分解模块区分参数频率特征,降低低频特征空间冗余,提高运算效率。其次,在雨线检测模块中利用多频通道注意力机制映射雨线层权重信息,增强权重特征多样性,提高雨线检测性能。最后,设计基于焦频损失的去雨修复网络,进一步修复去雨模型估计图像,通过缩小频率差距提高图像修复质量,增强网络的抗干扰能力。实验结果表明,所提方法能够有效去除真实雨图像场景中的雨线,抑制雨幕效应,保留图像背景信息完整,图像清晰度较高。
中图分类号:
- TN911.73
| 1 | Garg K, Nayar S K. When does a camera see rain?[C]//Tenth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision,New York, USA, 2005: 1067-1074. |
| 2 | Chen J, Tan C H, Hou J, et al. Robust video content alignment and compensation for clear vision through the rain[J/OL]. [2020-04-26]., 2018 |
| 3 | Fu X, Huang J, Ding X, et al. Clearing the skies: a deep network architecture for single-image rain removal[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(6): 2944-2956. |
| 4 | Fu X, Huang J, Zeng D, et al. Removing rain from single images via a deep detail network[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 3855-3863. |
| 5 | Ren D, Zuo W, Hu Q, et al. Progressive image deraining networks: a better and simpler baseline[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3937-3946. |
| 6 | Jiang K, Wang Z, Yi P, et al. Multi-scale progressive fusion network for single image deraining[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 8346-8355. |
| 7 | Chen C, Li H. Robust representation learning with feedback for single image deraining[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New York, USA, 2021: 7742-7751. |
| 8 | Rai S N, Saluja R, Arora C, et al. FLUID: Few-shot self-supervised image deraining[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Hawaii,USA, 2022: 3077-3086. |
| 9 | Yang H, Zhou D, Cao J, et al. DPNet: detail-preserving image deraining via learning frequency domain knowledge[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2022: No.103740. |
| 10 | Yang W, Tan R T, Feng J, et al. Deep joint rain detection and removal from a single image[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1357-1366. |
| 11 | Li R, Cheong L F, Tan R T. Heavy rain image restoration: integrating physics model and conditional adversarial learning[C]∥Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA, 2019: 1633-1642. |
| 12 | Zamir S W, Arora A, Khan S, et al. Multi-stage progressive image restoration[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New York, USA, 2021: 14821-14831. |
| 13 | Liang J, Cao J, Sun G, et al. Swinir: image restoration using swin transformer[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, New York, USA, 2021: 1833-1844. |
| 14 | Chen W T, Huang Z K, Tsai C C, et al. Learning multiple adverse weather removal via two-stage knowledge learning and multi-contrastive regularization: toward a unified model[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 17653-17662. |
| 15 | Tancik M, Srinivasan P, Mildenhall B, et al. Fourier features let networks learn high frequency functions in low dimensional domains[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2020, 33: 7537-7547. |
| 16 | Chen Y, Fan H, Xu B, et al. Drop an octave: reducing spatial redundancy in convolutional neural networks with octave convolution[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 2019: 3435-3444. |
| 17 | Li X, Wu J, Lin Z, et al. Recurrent squeeze-and-excitation context aggregation net for single image deraining[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 254-269. |
| 18 | Qin Z, Zhang P, Wu F, et al. Fcanet: frequency channel attention networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, New York, USA, 2021: 783-792. |
| 19 | Isola P, Zhu J Y, Zhou T, et al. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1125-1134. |
| 20 | Jiang L, Dai B, Wu W, et al. Focal frequency loss for image reconstruction and synthesis[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, New York, USA, 2021: 13919-13929. |
| 21 | Li S, Ren W, Wang F, et al. A comprehensive benchmark analysis of single image deraining: current challenges and future perspectives[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2021, 129(4): 1301-1322. |
| 22 | Saad M A, Bovik A C, Charrier C. Blind image quality assessment: a natural scene statistics approach in the DCT domain[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(8): 3339-3352. |
| 23 | Liu L, Liu B, Huang H, et al. No-reference image quality assessment based on spatial and spectral entropies[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2014, 29(8): 856-863. |
| [1] | 葛动元,向文江,李健,刘恩辰,姚锡凡. 基于机器视觉的电动汽车充电自动定位方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3465-3471. |
| [2] | 曾春艳,严康,王志锋,王正辉. 多尺度生成对抗网络下图像压缩感知重建算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(10): 2923-2931. |
| [3] | 侯春萍,赵春月,王致芃,田海瑞. 基于有效异常样本构造的视频异常检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1823-1829. |
| [4] | 李厚杰,王法胜,贺建军,周瑜,李威,窦宇轩. 基于伪样本正则化Faster R⁃CNN的交通标志检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1251-1260. |
| [5] | 刘富, 权美静, 王柯, 刘云, 康冰, 韩志武, 侯涛. 仿蝎子振源定位机理的位置指纹室内定位方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2076-2082. |
| [6] | 丁宁, 常玉春, 赵健博, 王超, 杨小天. 基于USB 3.0的高速CMOS图像传感器数据采集系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1298-1304. |
| [7] | 刘东亮, 王秋爽. 基于NGSIM数据的车辆瞬时速度获取方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 330-335. |
| [8] | 武伟, 王世刚, 赵岩, 韦健, 钟诚. 蜂窝式立体元图像阵列的生成[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 290-294. |
| [9] | 王方石, 王坚, 李兵, 王博. 基于深度属性学习的交通标志检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 319-329. |
| [10] | 武伟, 王世刚, 王宏志, 赵岩, 钟诚, 韦健. 基于Maya的立体元图像阵列的生成[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1314-1320. |
| [11] | 王品, 何璇, 吕洋, 李勇明, 邱明国, 刘书君. 基于多特征支持向量机和弹性区域生长的膝软骨自动分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(5): 1688-1696. |
| [12] | 卢彦飞, 张涛, 郑健, 李铭, 章程. 基于局部标准差与显著图的模糊图像质量评价方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1337-1343. |
| [13] | 郑欣, 彭真明, 邢艳. 基于活跃度的图像分割算法性能评价新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 311-317. |
| [14] | 李一兵, 杨鹏, 叶方, 刘丹丹. 基于交互势函数和均场参数估计的分层MRF模型的纹理图像分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(6): 2075-2079. |
| [15] | 赵旦峰, 王博, 杨大伟. 基于随机置乱的内容感知图像缩放算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(4): 1324-1328. |
|
||