吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (11): 3199-3208.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230017
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
城市群内部出行强度的距离衰减效应
- 1.北京交通大学 交通运输学院,北京 100044
2.浙江省交通运输科学研究院 运输安全研究所,杭州 310023
Distance-decay effects of travel intensity within city clusters
Li-ying WEI1( ),Huan-huan PENG1,2
),Huan-huan PENG1,2
- 1.School of Traffic and Transportation,Beijing Jiaotong University,Beijing 100044,China
2.Transportation and Safety Research Institute,Zhejiang Scientific Research Institute of Transport,Hangzhou 310023,China
摘要:
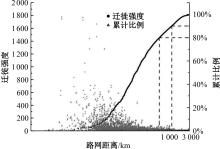
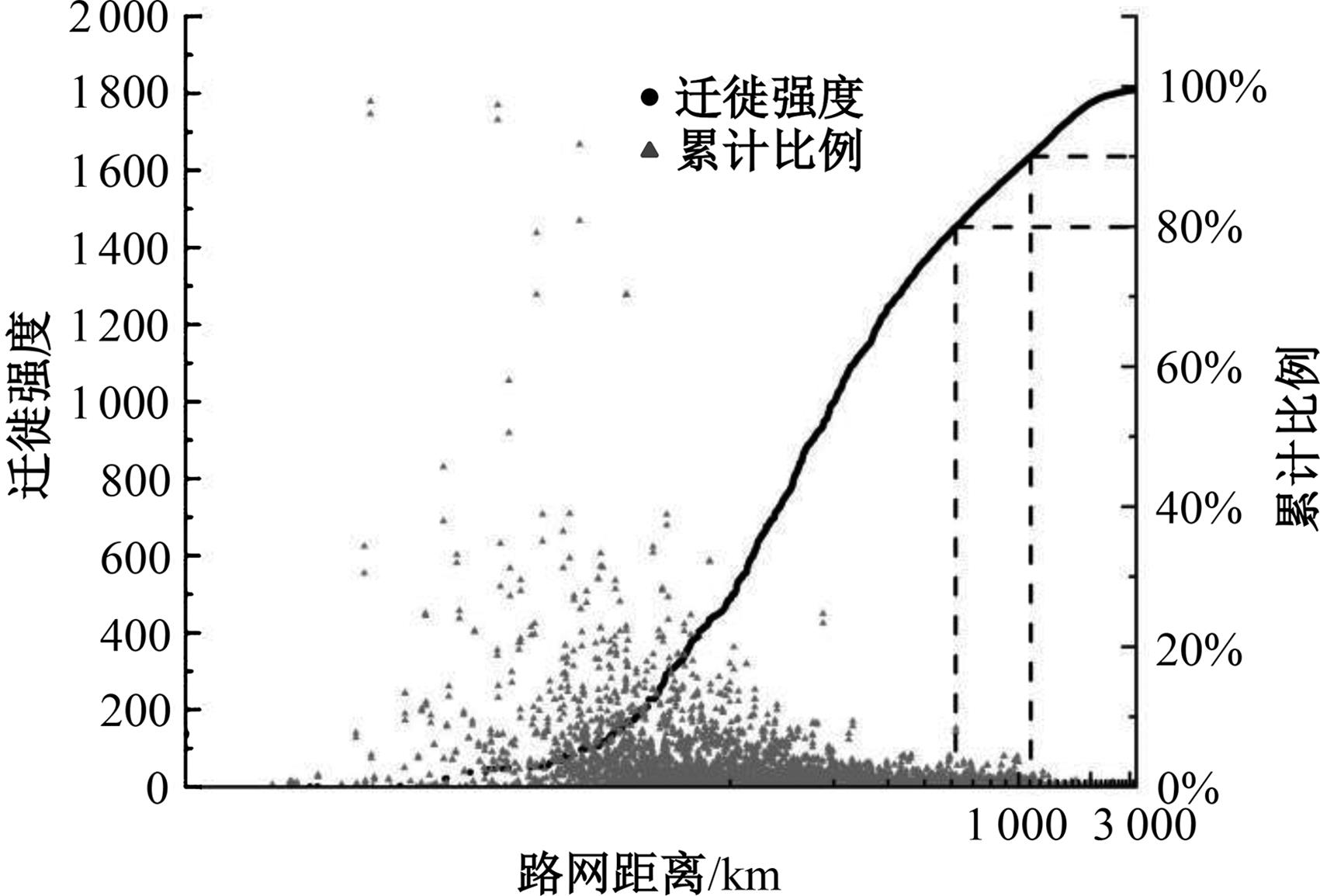
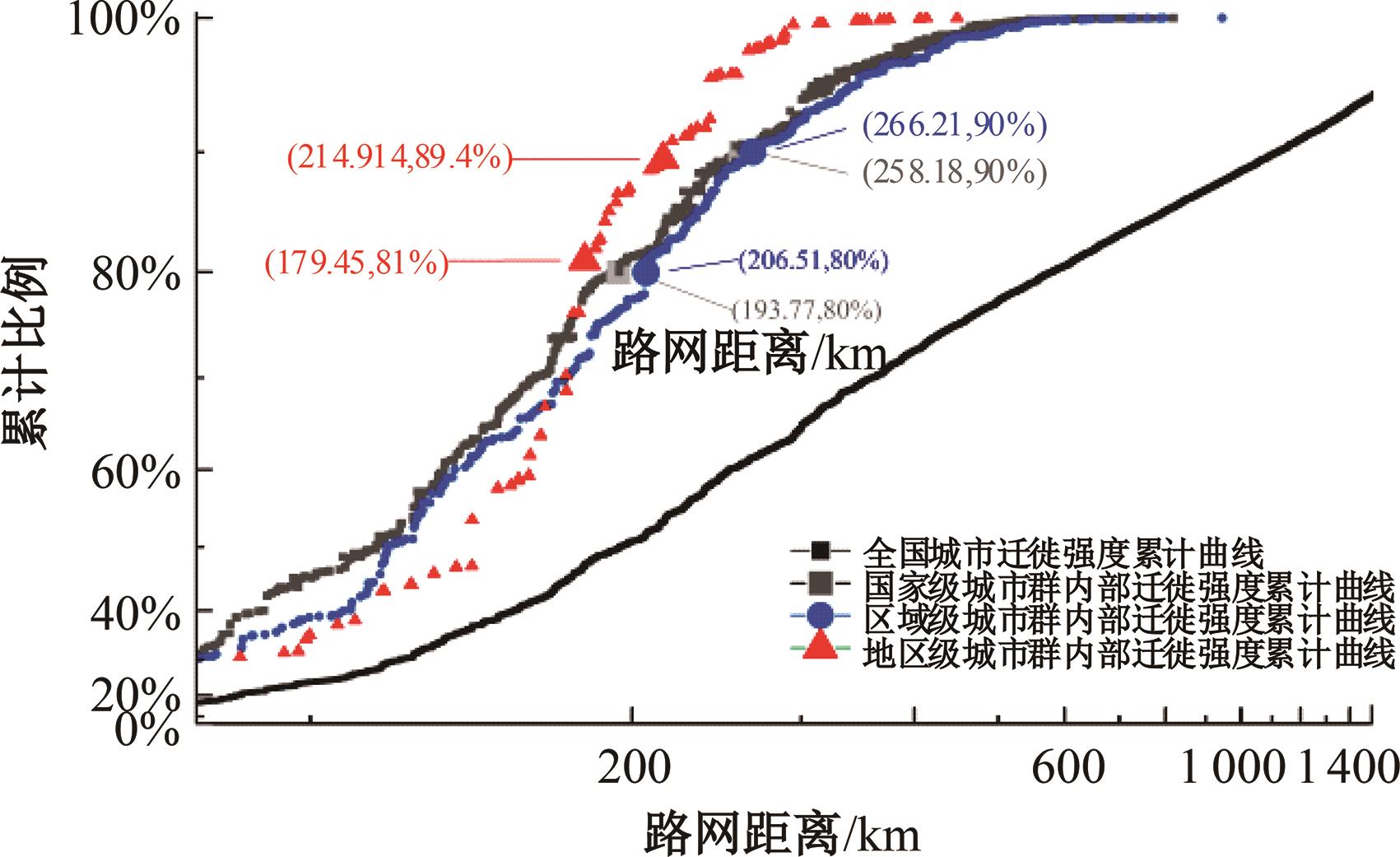
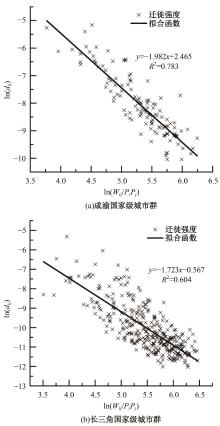
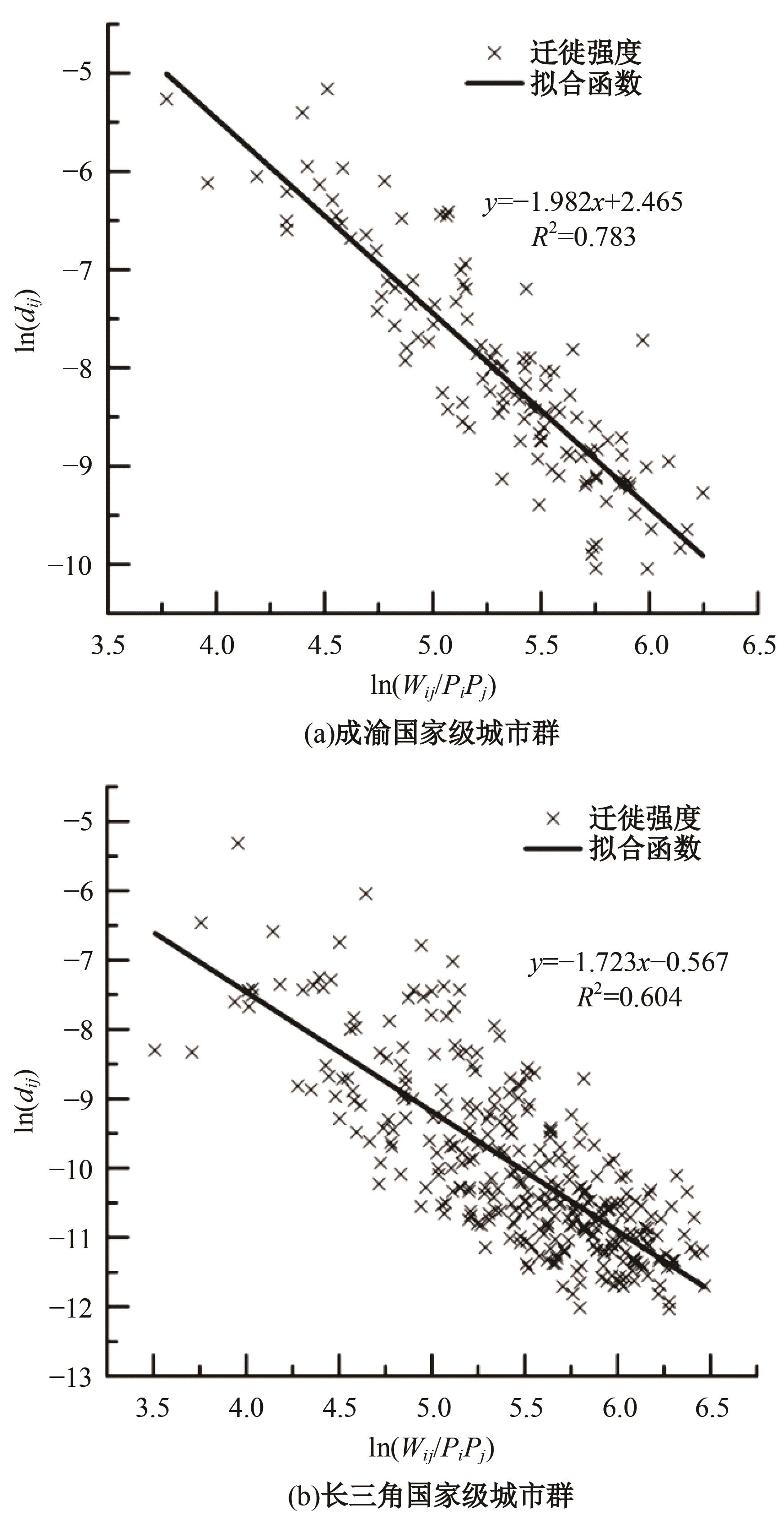
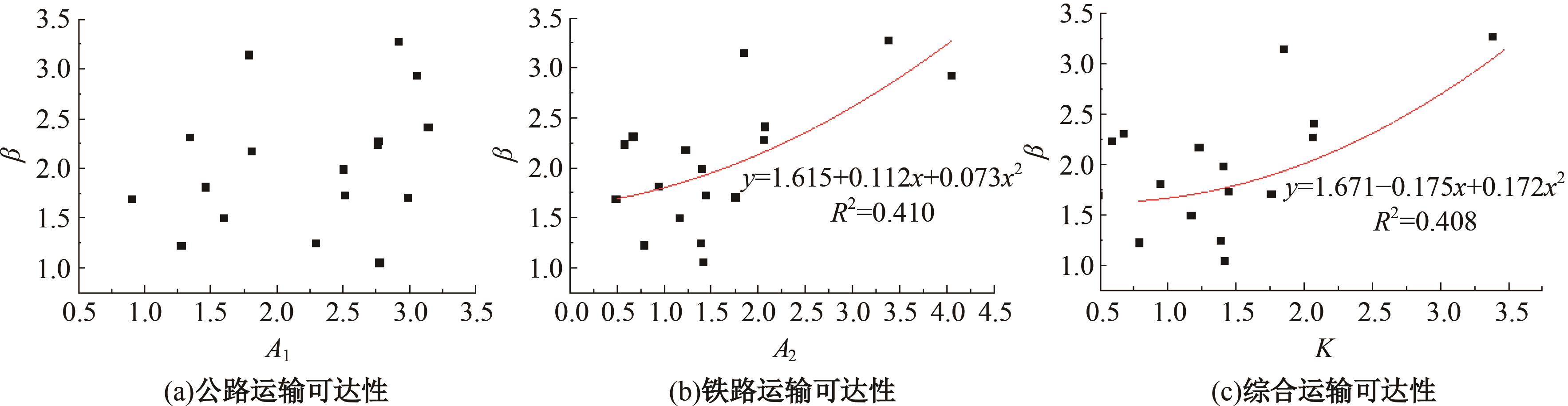
考虑城市群尺度出行特征研究存在基础数据不足、横向比较难度大等问题,本文基于网络爬虫获取全国城市之间迁徙OD流矩阵等基础数据,据此剖析迁徙强度累计比例曲线特征;提出以百度迁徙数据表征城市间出行强度,以最短路网距离作为距离参数,结合城市常住人口,构建重力模型拟合分析不同城市群内部的城市间迁徙强度随距离的变化特征。在此基础上,将基于中心城市“质量”加权的平均旅行时间定义为可达性,分别计算各城市群公路、铁路、综合交通的可达性,分析可达性与距离衰减系数的关系,发现绝大多数城市群基于路网距离的迁徙交互衰减作用较为明显,且达到城市尺度交互水平。
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | 冯慧芳,柏凤山,徐有基. 基于轨迹大数据的城市交通感知和路网关键节点识别[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2018, 18(3): 42-47. |
| Feng Hui-fang, Bai Feng-shan, Xu You-ji. Urban traffic perception and critical node identification of road network based on trajectory big data[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2018, 18(3): 42-47. | |
| 2 | 贾洪飞, 郭明雪, 罗清玉, 等. GPS数据下的城市路网关键路段识别[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(4): 1338-1343. |
| Jia Hong-fei, Guo Ming-xue, Luo Qing-yu, et al. Identifying critical links of urban road netwoks based on GPS data[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(4): 1338-1343. | |
| 3 | Ding F, Zhang Z, Zhou Y, et al. Large-scale full-coverage traffic speed estimation under extreme traffic conditions using a big data and deep learning approach: case study in China[J]. Transportation Engineering Part A Systems, 2019, 145(5): 05019001. |
| 4 | 李自圆, 孙昊, 李林波. 基于手机信令数据的长三角全域城际出行网络分析[J]. 清华大学学报: 自然科学版, 2022, 62(7): 1203-1211. |
| Li Zi-yuan, Sun Hao, Li Lin-bo. Analysis of intercity travel in the yangtze river delta based on mobile signaling data[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2022, 62(7): 1203-1211. | |
| 5 | Shang Y, Li X G, Jia B, et al. Freeway traffic state estimation method based on multisource data[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering Part A Systems, 2022, 148(4): 4022005. |
| 6 | Soriguera F, Rosas D, Robuste F. Travel time measurement in closed toll highways[J]. Transportation Research Part B Methodological, 2010, 44(10): 1242-1267. |
| 7 | Lu X J, Ma C X. The impact of inter-city traffic restriction on COVID-19 transmission from spatial econometric perspective[J]. Promet-traffic & Transportation, 2021, 33(5): 705-716. |
| 8 | 王录仓, 刘海洋, 刘清. 基于腾讯迁徙大数据的中国城市网络研究[J]. 地理学报, 2021, 76(4): 853-869. |
| Wang Lu-cang, Liu Hai-yang, Liu Qing. China's city network based on Tencent's migration big data[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2021, 76(4): 853-869. | |
| 9 | Xu X L, Wang S H, Dong J H, et al. An analysis of the domestic resumption of social production and life under the COVID-19 epidemic[J]. Plos One, 2020, 15(7): 0236387. |
| 10 | 项昀, 徐铖铖, 于维杰, 等. 基于人口迁徙大数据的城市对外交通客运方式优势出行距离研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2020, 20(1): 241-246. |
| Xiang Yun, Xu Cheng-cheng, Yu Wei-jie, et al. Dominant trip distance of urban external passenger transport mode based on big data of migration[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2020, 20(1): 241-246. | |
| 11 | 王聪, 严洁. 百度迁徙规模指数构造方法反演[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2021, 50(4): 616-626. |
| Wang Cong, Yan Jie. An inversion of the constitution of the Baidu migration scale index[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2021, 50(4): 616-626. | |
| 12 | 项昀, 王炜, 郑敦勇, 等. 区域综合网络货运交通方式的优势运距研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2016, 16(6): 33-39. |
| Xiang Yun, Wang Wei, Zheng Dun-yong, et al. Dominant transportation distance for multi transportation modes in regional integrated freight network[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2016, 16(6): 33-39. | |
| 13 | 方创琳. 中国城市群地图集[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020. |
| 14 | 陈卓, 金凤君, 杨宇, 等. 高速公路流的距离衰减模式与空间分异特征——基于福建省高速公路收费站数据的实证研究[J]. 地理科学进展, 2018, 37(8): 1086-1095. |
| Chen Zhuo, Jin Feng-jun, Yang Yu, et al. Distance-decay pattern and spatial differentiation of expressway flow: an empirical study using data of expressway toll station in Fujian Province[J]. Progress in Geography, 2018, 37(8): 1086-1095. | |
| 15 | 刘瑜, 龚俐, 童庆禧. 空间交互作用中的距离影响及定量分析[J]. 北京大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014, 50(3): 526-534. |
| Liu Yu, Gong Li, Tong Qing-xi. Quantifying the distance effect in spatial interactions[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2014, 50(3): 526-534. | |
| 16 | Hansen W G. How accessibility shapes land use[J]. Journal of the American Institute of Planners, 1959, 25(2): 73-76. |
| 17 | 徐明非, 欧晓培, 王元庆. 城市群公路可达性与衔接提升研究[J]. 中国公路学报, 2020, 33(11): 245-254. |
| Xu Ming-fei, Xiao-pei Ou, Wang Yuan-qing. Study on highway accessibility of urban agglomerations and its connection improvement[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2020, 33(11): 245-254. | |
| 18 | 戢晓峰, 郝京京, 陈方. 综合运输可达性与物流经济的空间分异及耦合[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2015, 15(5): 24-31. |
| Ji Xiao-feng, Hao Jing-jing, Chen Fang. Spatial differentiation and coupling between integrated transport accessibility and logistics economy[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2015, 15(5): 24-31. |
| [1] | 高天洋,胡大伟,姜瑞森,吴雪,刘慧甜. 基于模块化车辆的区域灵活接驳公交线路优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 537-545. |
| [2] | 马书红,张俊杰,陈西芳,廖国美. 利用出租车时序数据识别城市功能区[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 603-613. |
| [3] | 李昱燃,汪飞,朱才华,韩飞,李岩. 污染天气居民通勤模式选择影响因素的链式效用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 577-590. |
| [4] | 徐慧智,蒋时森,王秀青,陈爽. 基于深度学习的车载图像车辆目标检测和测距[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 185-197. |
| [5] | 郑长江,陶童统,陈志超. 基于流量可调重分配的级联失效模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2441-2450. |
| [6] | 温晓岳,钱国敏,孔桦桦,缪月洁,王殿海. TrafficPro:一种针对城市信控路网的路段速度预测框架[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2214-2222. |
| [7] | 闫云娟,查伟雄,石俊刚,严丽平. 基于随机充电需求的充电桩优化双层模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2238-2244. |
| [8] | 曲大义,刘浩敏,杨子奕,戴守晨. 基于车路协同的交通瓶颈路段车流动态分配机制及模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2187-2196. |
| [9] | 陈桂珍,程慧婷,朱才华,李昱燃,李岩. 考虑驾驶员生理信息的城市交叉口风险评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1277-1284. |
| [10] | 赵晓华,刘畅,亓航,欧居尚,姚莹,郭淼,杨海益. 高速公路交通事故影响因素及异质性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 987-995. |
| [11] | 杨秀建,贾晓寒,张生斌. 考虑汽车队列动态特性的混合交通流特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 947-958. |
| [12] | 吴文静,熊康贝,贾洪飞,罗清玉. 城市群轨道交通直通线路优化设置方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 711-718. |
| [13] | 范博松,邵春福. 城市轨道交通突发事件风险等级判别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 427-435. |
| [14] | 郑长江,胡欢,杜牧青. 考虑枢纽失效的多式联运快递网络结构设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2304-2311. |
| [15] | 王殿海,胡佑薇,蔡正义,曾佳棋,姚文彬. 基于BPR函数的城市道路间断流动态路阻模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 1951-1961. |
|
||