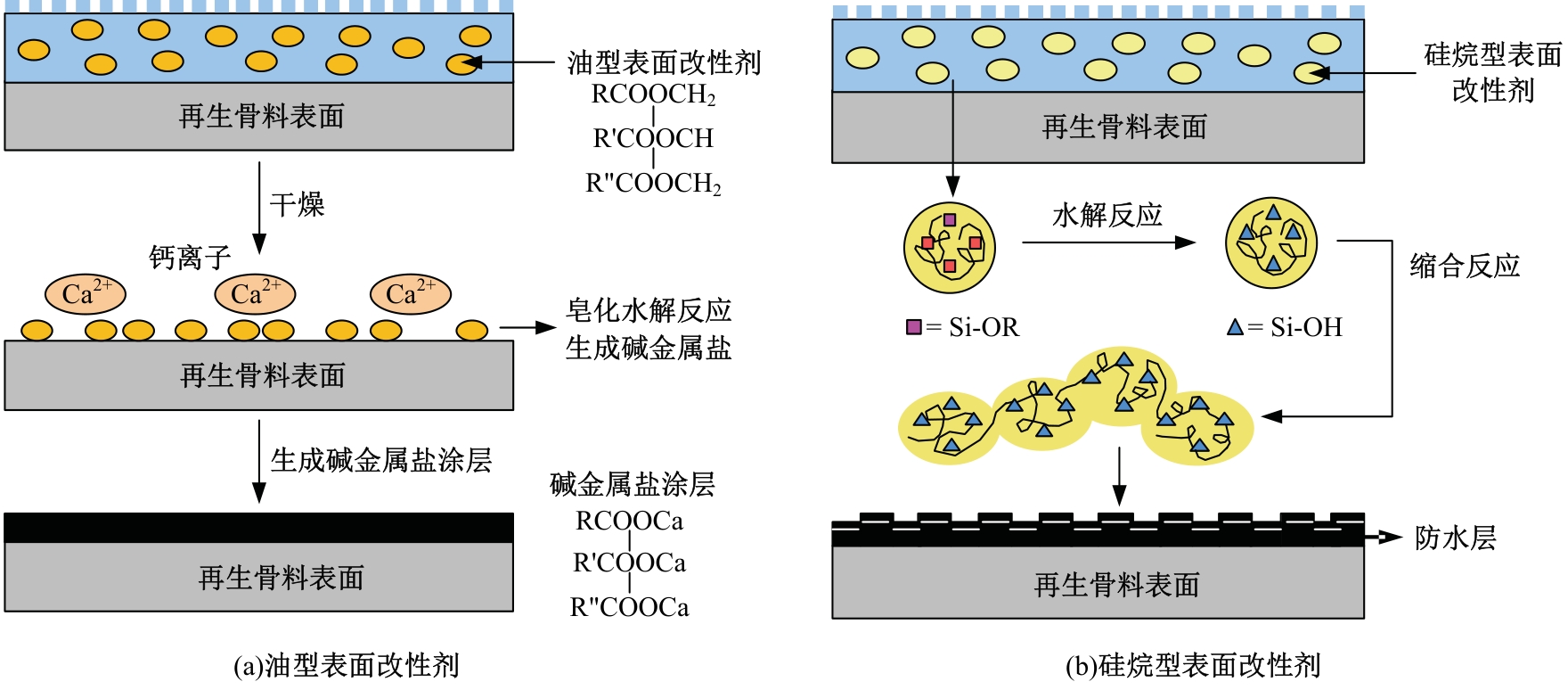
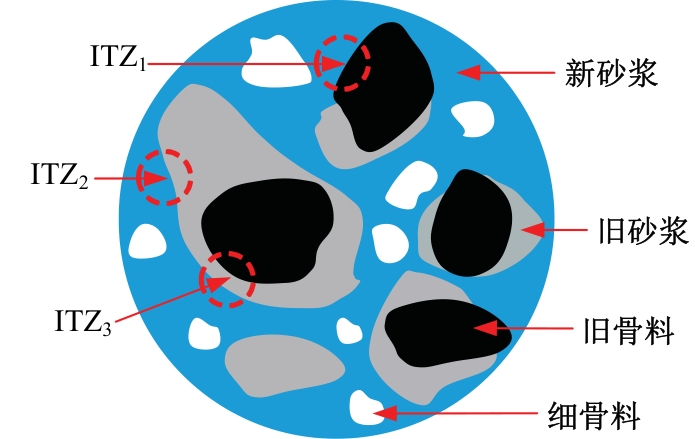
吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (3): 790-810.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20231352
再生骨料强化技术及对再生混凝土性能影响研究综述
何子明1,2( ),申爱琴2(
),申爱琴2( ),王路生2,郭寅川2,何江飞1
),王路生2,郭寅川2,何江飞1
- 1.辽宁工业大学 土木建筑工程学院,辽宁 锦州,121001
2.长安大学 公路学院,西安 710064
Review on strengthening technology of recycled concrete aggregate and its effect on performance of recycled aggregate concrete
Zi-ming HE1,2( ),Ai-qin SHEN2(
),Ai-qin SHEN2( ),Lu-sheng WANG2,Yin-chuan GUO2,Jiang-fei HE1
),Lu-sheng WANG2,Yin-chuan GUO2,Jiang-fei HE1
- 1.School of Civil and Architectural Engineering,Liaoning University of Technology,Jinzhou 121001,China
2.School of Highway,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
摘要:
为厘清国内外关于再生骨料强化技术的研究进展,系统梳理了再生骨料强化方法及提质效能,评析了不同强化方法对再生骨料混凝土性能的影响规律,总结了现有强化方法在应用过程中存在的问题并提出了建设性意见,以期为研究者设计和开发绿色高性能再生骨料混凝土提供参考和依据。
中图分类号:
- TU528
| 1 | 肖建庄, 张航华, 唐宇翔, 等. 废弃混凝土再生原理与再生混凝土基本问题[J]. 科学通报, 2023, 68(5): 510-523. |
| Xiao Jian-zhuang, Zhang Hang-hua, Tang Yu-xiang, et al. Principles for waste concrete recycling and basic problems of recycled concrete[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2023, 68(5): 510-523. | |
| 2 | 王佃超, 肖建庄, 夏冰, 等. 再生骨料碳化改性及其减碳贡献分析[J]. 同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2022, 50(11): 1610-1619. |
| Wang Dian-chao, Xiao Jian-zhuang, Xia Bing, et al. Carbonation modification of recycled aggregate and carbon dioxide sequestration analysis[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2022, 50(11): 1610-1619. | |
| 3 | Belin P, Habert G, Thiery M, et al. Cement paste content and water absorption of recycled concrete coarse aggregates[J]. Materials and Structures, 2014, 47: 1451-1465. |
| 4 | Agrela F, de Juan M S, Ayuso J, et al. Limiting properties in the characterisation of mixed recycled aggregates for use in the manufacture of concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2011, 25: 3950-3955. |
| 5 | 王雅思, 郑建岚, 游帆. 再生骨料强化方法研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2021, 35(5): 5053-5061. |
| Wang Ya-si, Zheng Jian-lan, You Fan. Review on enhancement methods of recycled aggregate[J]. Materials Reports, 2021, 35(5): 5053-5061. | |
| 6 | Sui Y, Mueller A. Development of thermo-mechanical treatment for recycling of used concrete[J]. Materials and Structures, 2012, 45: 1487-1495. |
| 7 | Dilbas H, Çakır Ö, Atis C D. Experimental investigation on properties of recycled aggregate concrete with optimized ball milling method[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 212: 716-726. |
| 8 | 肖建庄, 吴磊, 范玉辉. 微波加热再生粗骨料改性试验[J]. 混凝土, 2012(7): 55-57. |
| Xiao Jian-zhuang, Wu Lei, Fan Yu-hui. Test on modification of recycled coarse aggregate by microwave heating[J]. Concrete, 2012(7): 55-57. | |
| 9 | Purushothaman R, Amirthavalli R R, Karan L. Influence of treatment methods on the strength and performance characteristics of recycled aggregate concrete[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2015, 27: No. 04014168. |
| 10 | Tam V W Y, Tam C M, Le K N. Removal of cement mortar remains from recycled aggregate using pre-soaking approaches[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2007, 50: 82-101. |
| 11 | Wang L, Wang J, Qian X. An environmentally friendly method to improve the quality of recycled concrete aggregates[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 144: 432-441. |
| 12 | Zhao Z, Wang S, Lu L, et al. Evaluation of pre-coated recycled aggregate for concrete and mortar[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 43: 191-196. |
| 13 | Siletani A H, Asayesh S, Javid A A S, et al. Influence of coating recycled aggregate surface with different pozzolanic slurries on mechanical performance, durability, and micro-structure properties of recycled aggregate concrete[J]. Journal of Building Engineering, 2024, 83: No. 108457. |
| 14 | Zhang H, Zhao Y, Meng T, et al. Surface treatment on recycled coarse aggregates with nanomaterials[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2016, 28: No. 04015094. |
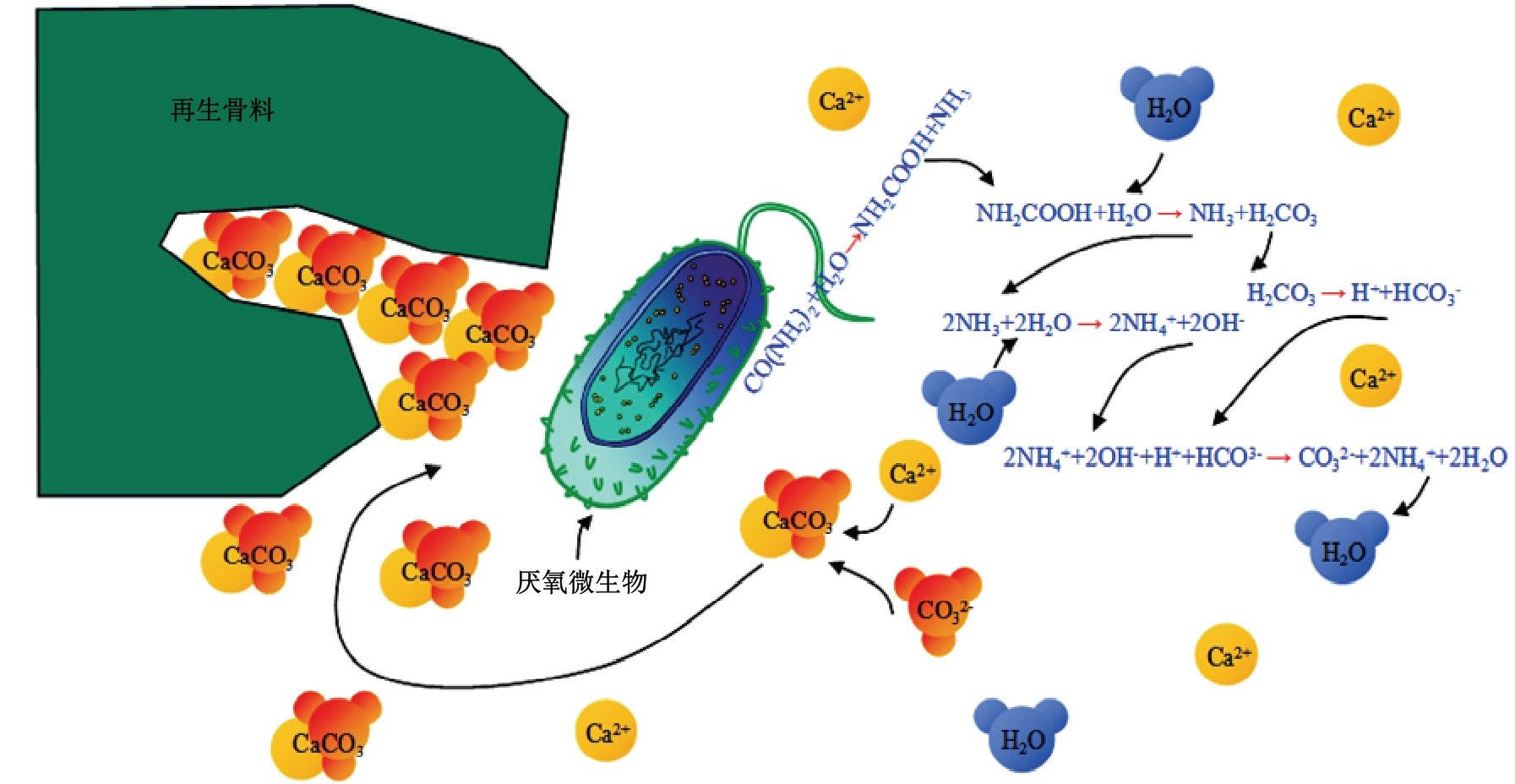
| 15 | Wang J, Vandevyvere B, Vanhessche S, et al. Microbial carbonate precipitation for the improvement of quality of recycled aggregates[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 156: 355-366. |
| 16 | 徐培蓁, 陈发滨, 李泉荃, 等. 微生物矿化沉积对再生骨料界面过渡区的影响[J]. 材料导报, 2020, 34(3): 6095-6099. |
| Xu Pei-zhen, Chen Fa-bin, Li Quan-quan, et al. Effect of microbial mineralization deposition on interfacial transition zone of recycled aggregate[J]. Materials Reports, 2020, 34(3): 6095-6099. | |
| 17 | Feng C, Cui B, Wang J, et al. Changing the soaking method of microbially induced calcium carbonate precipitation technology to improve the reinforcement effect of recycled concrete aggregates[J]. Journal of Building Engineering, 2023, 68: No. 106128. |
| 18 | Zhang J, Shi C, Li Y, et al. Influence of carbonated recycled concrete aggregate on properties of cement mortar[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2015, 98: 1-7. |
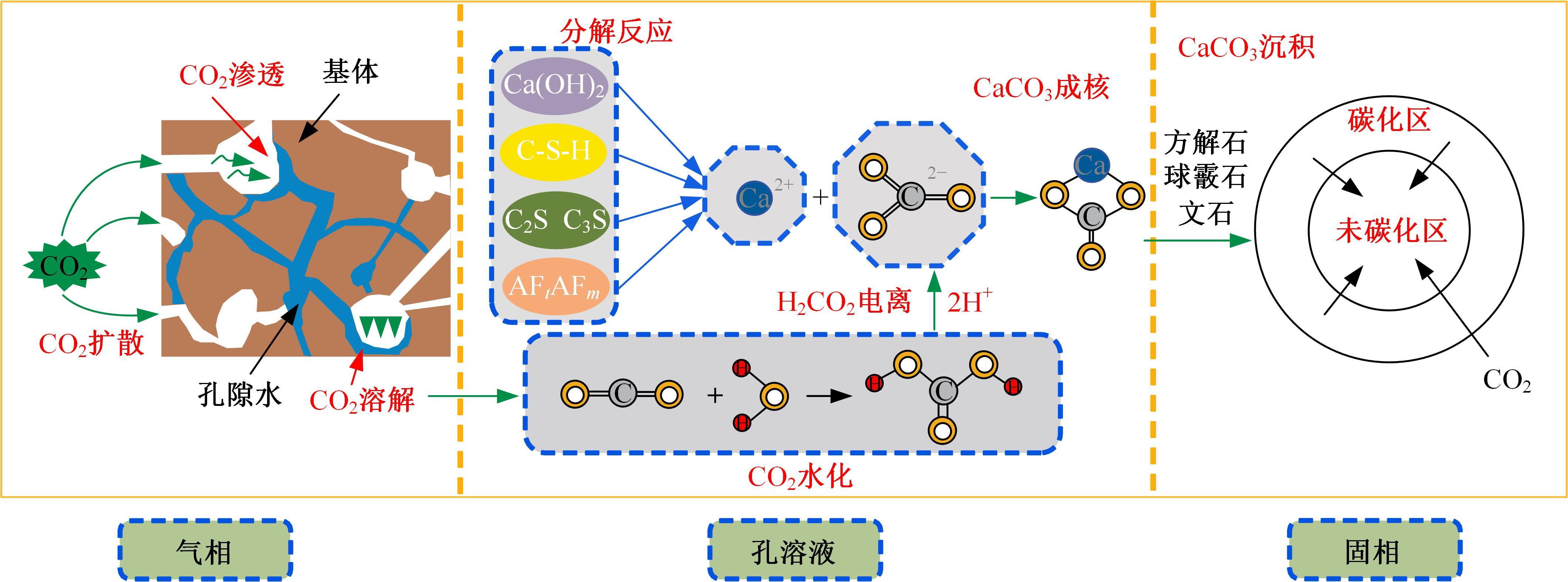
| 19 | Zhan B J, Xuan D X, Poon C S. Enhancement of recycled aggregate properties by accelerated CO2 curing coupled with limewater soaking process[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2018, 89: 230-237. |
| 20 | 赵增丰, 姚磊, 肖建庄, 等. 再生骨料CO2碳化强化技术研究进展[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2022, 50(8): 2296-2304. |
| Zhao Zeng-feng, Yao Lei, Xiao Jian-zhuang, et al. Development on accelerated carbonation technology to enhance recycled aggregates[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2022, 50(8): 2296-2304. | |
| 21 | Kou S C, Poon C S. Properties of concrete prepared with PVA-impregnated recycled concrete aggregates[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2010, 32: 649-654. |
| 22 | 鲍玖文, 李树国, 张鹏, 等. 再生粗骨料硅烷浸渍处理对混凝土介质传输性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(10): 2602-2609. |
| Bao Jiu-wen, Li Shu-guo, Zhang Peng, et al. Effect of recycled coarse aggregate after strengthening by silane impregnation on mass transport of concrete[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2020, 37(10): 2602-2609. | |
| 23 | Song X, Qiao P, Wen H. Recycled aggregate concrete enhanced with polymer aluminium sulfate[J]. Magazine of Concrete Research, 2015, 67(10): 496-502. |
| 24 | Shaban W M, Yang J, Su H, et al. Quality improvement techniques for recycled concrete aggregate: a review[J]. Journal of Advanced Concrete Technology, 2019, 17: 151-167. |
| 25 | 李秋义, 朱亚光, 高嵩. 我国高品质再生骨料制备技术及质量评定方法[J]. 青岛理工大学学报, 2009, 30(4): 1-4, 23. |
| Li Qiu-yi, Zhu Ya-guang, Gao Song. Study on the preparation technique and quality evaluation method of high quality recycled aggregate[J]. Journal of Qingdao Technological University, 2009, 30(4): 1-4, 23. | |
| 26 | Shima H, Tateyashiki H, Matsuhashi R, et al. An advanced concrete recycling technology and its applicability assessment through input-output analysis[J]. Journal of Advanced Concrete Technology, 2005, 3(1): 53-67. |
| 27 | Mulder E, de Jong T P R, Feenstra L. Closed cycle construction: an integrated process for the separation and reuse of C&D waste[J]. Waste Management, 2007, 27: 1408-1415. |
| 28 | Quattrone M, Angulo S C, John V M. Energy and CO2 from high performance recycled aggregate production[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2014, 90: 21-33. |
| 29 | Yang X, Liu Y, Liang J, et al. Straightening methods for RCA and RAC: a review[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2023, 141: No. 105145. |
| 30 | Akbarnezhad A, Ong K C G, Zhang M H, et al. Acid treatment technique for determining the mortar content of recycled concrete aggregates[J]. Journal of Testing and Evaluation, 2013, 41(3): 1-10. |
| 31 | Ismail S, Ramli M. Engineering properties of treated recycled concrete aggregate (RCA) for structural applications[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 44: 464-476. |
| 32 | Al-Bayati H K A, Das P K, Tighe S L, et al. Evaluation of various treatment methods for enhancing the physical and morphological properties of coarse recycled concrete aggregate[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 112: 284-298. |
| 33 | 王亮. 再生骨料提质的绿色化学方法研究[D]. 淮南: 安徽理工大学土木建筑学院, 2018. |
| Wang Liang. Study on green chemical methods to improve the quality of recycled concrete aggregates[D]. Huainan: School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Anhui University of Science and Technology, 2018. | |
| 34 | Shaban W, Elbaz K, Yang J, et al. Effect of pozzolan slurries on recycled aggregate concrete: mechanical and durability performance[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 276: No. 121940. |
| 35 | He Z, Shen A, Wu H, et al. Properties and mechanisms of brick-concrete recycled aggregate strengthened by compound modification treatment[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 315: No. 125678. |
| 36 | Shaban W M, Yang J, Su H, et al. Properties of recycled concrete aggregates strengthened by different types of pozzolan slurry[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 216: 632-647. |
| 37 | 张学兵. 再生混凝土改性及配合比设计研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学土木工程学院, 2015. |
| Zhang Xue-bing. Modification and mix proportion design of recycled concrete[D]. Changsha: College of Civil Engineering, Hunan University, 2015. | |
| 38 | Zhang H, Ji T, Liu H, et al. Modifying recycled aggregate concrete by aggregate surface treatment using sulphoaluminate cement and basalt powder[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 192: 526-537. |
| 39 | Li L, Xuan D, Chu S H, et al. Efficiency and mechanism of nano-silica pre-spraying treatment in performance enhancement of recycled aggregate concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 301: No. 124093. |
| 40 | 翁志英. 再生粗骨料强化预处理对高性能再生混凝土细观结构影响的试验研究[D]. 福州: 福州大学土木工程学院, 2013. |
| Weng Zhi-ying. Experimental study on microstructure of recycled high performance concrete affected by intensified test[D]. Fuzhou: College of Civil Engineering, Fuzhou University, 2013. | |
| 41 | 陈钿渊. 再生粗骨料强化对再生混凝土力学性能及耐久性能的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学土木工程学院, 2016. |
| Chen Dian-yuan. The influence of reinforced recycled coarse aggregate on the mechanical performance and durability of recycled concrete[D]. Harbin: School of Civil Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, 2016. | |
| 42 | Lee C H, Du J C, Shen D H. Evaluation of pre-coated recycled concrete aggregate for hot mix asphalt[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2012, 28: 66-71. |
| 43 | Tam V W Y, Wattage H, Le K N, et al. Methods to improve microstructural properties of recycled concrete aggregate: a critical review[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 270: No. 121490. |
| 44 | Grabiec A M, Klama J, Zawal D, et al. Modification of recycled concrete aggregate by calcium carbonate biodeposition[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2012, 34: 145-150. |
| 45 | 朱亚光, 戎丹萍, 徐培蓁, 等. 供氧剂浓度和浸泡位置对MICP再生骨料性能的影响[J]. 材料导报, 2021, 35(4): 4074-4078, 4087. |
| Zhu Ya-guang, Rong Dan-ping, Xu Pei-zhen, et al. Influence of oxygen supply agent concentration and soaking position on MICP recycled aggregate properties[J]. Materials Reports, 2021, 35(4): 4074-4078, 4087. | |
| 46 | Wu C R, Hong Z Q, Zhang J L, et al. Pore size distribution and ITZ performance of mortars prepared with different bio-deposition approaches for the treatment of recycled concrete aggregate[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2020, 111: No. 103631. |
| 47 | 黄燕, 胡翔, 史才军, 等. 混凝土中水泥浆体与骨料界面过渡区的形成和改进综述[J]. 材料导报, 2023, 37(1): 106-107. |
| Huang Yan, Hu Xiang, Shi Cai-jun, et al. Review on the formation and improvement of interfacial transition zone between cement paste and aggregate in concrete[J]. Materials Reports, 2023, 37(1): 106-107. | |
| 48 | Xuan D, Zhan B, Poon C S. Assessment of mechanical properties of concrete incorporating carbonated recycled concrete aggregates[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2016, 65: 67-74. |
| 49 | Pu Y, Li L, Wang Q, et al. Accelerated carbonation technology for enhanced treatment of recycled concrete aggregates: a state-of-the-art review[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 282: No. 122671. |
| 50 | Li Y, Fu T, Wang R, et al. An assessment of microcracks in the interfacial transition zone of recycled concrete aggregates cured by CO2 [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 236: No. 117543. |
| 51 | Pan G, Zhan M, Fu M, et al. Effect of CO2 curing on demolition recycled fine aggregates enhanced by calcium hydroxide pre-soaking[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 154: 810-818. |
| 52 | Galan I, Andrade C, Castellote M. Natural and accelerated CO2 binding kinetics in cement paste at different relative humidities[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2013, 49: 21-28. |
| 53 | Kou S C, Zhan B J, Poon C S. Use of a CO2 curing step to improve the properties of concrete prepared with recycled aggregates[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2014, 45: 22-28. |
| 54 | Gholizadeh-Vayghan A, Bellinkx A, Snellings R, et al. The effects of carbonation conditions on the physical and microstructural properties of recycled concrete coarse aggregates[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 257: No. 119486. |
| 55 | Wu K, Luo S, Zheng J, et al. Influence of carbonation treatment on the properties of multiple interface transition zones and recycled aggregate concrete[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2022, 127: No. 104402. |
| 56 | Wu L, Zhang W, Jiang H, et al. Synergistic effects of environmental relative humidity and initial water content of recycled concrete aggregate on the improvement in properties via carbonation reactions[J]. Materials, 2023, 16: No. 5251. |
| 57 | 应敬伟, 蒙秋江, 肖建庄. 再生骨料CO2强化及其对混凝土抗压强度的影响[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2017, 20(2): 277-282. |
| Ying Jing-wei, Meng Qiu-jiang, Xiao Jian-zhuang. Effect of CO2-modified recycled aggregate on compressive strength of concrete[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2017, 20(2): 277-282. | |
| 58 | 朱亚光, 徐培蓁. 硅烷与PVA对再生混凝土粗骨料改性试验研究[J]. 混凝土, 2015(3): 93-95, 101. |
| Zhu Ya-guang, Xu Pei-zhen. Experimental research on modified of recycled aggregate concrete by silane and PVA[J]. Concrete, 2015(3): 93-95, 101. | |
| 59 | Qiu J, Zhang Y, Qin Q, et al. Study on mechanical properties and microscopic mechanism of PVA-modified recycled brick aggregate concrete[J]. Sustainability, 2024, 16: No. 1292. |
| 60 | 吴素瑶. PVA改性再生骨料对再生混凝土性能的影响[D]. 淮南: 安徽理工大学土木建筑学院, 2019. |
| Wu Su-yao. Effect of PVA modified recycled aggregate on properties of recycled concrete[D]. Huainan: School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Anhui University of Science and Technology, 2019. | |
| 61 | Tsujino M, Noguchi T, Tamura M, et al. Application of conventionally recycled coarse aggregate to concrete structure by surface modification treatment[J]. Journal of Advanced Concrete Technology, 2007, 5(1): 13-25. |
| 62 | Spaeth V, Tegguer A D. Improvement of recycled concrete aggregate properties by polymer treatments[J]. International Journal of Sustainable Built Environment, 2013, 2: 143-152. |
| 63 | 段珍华, 江山山, 肖建庄, 等. 再生粗骨料含水状态对混凝土性能的影响[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2021, 24(3): 545-550. |
| Duan Zhen-hua, Jiang Shan-shan, Xiao Jian-zhuang, et al. Effect of moisture condition of recycled coarse aggregate on the properties of concrete[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2021, 24(3): 545-550. | |
| 64 | Pepe M, Filho R D T, Koenders E A B, et al. A novel mix design methodology for recycled aggregate concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 122: 362-372. |
| 65 | Ferreira L, Barra M, de Brito J. Influence of the pre-saturation of recycled coarse concrete aggregates on concrete properties[J]. Magazine of Concrete Research, 2011, 63(8): 617-627. |
| 66 | Brand A S, Roesler J R, Salas A. Initial moisture and mixing effects on higher quality recycled coarse aggregate concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2015, 79: 83-89. |
| 67 | 马昆林, 黄新宇, 胡明文, 等. 砖混再生粗骨料混凝土损伤本构关系[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2022, 25(2): 131-141. |
| Ma Kun-lin, Huang Xin-yu, Hu Ming-wen, et al. Damage constitutive model of brick-concrete recycled coarse aggregates concrete[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2022, 25(2): 131-141. | |
| 68 | Chen W, Shao Z, Wei W, et al. Properties of concrete incorporating microwave treated coarse aggregate: an experimental study[J]. Structures, 2021, 33: 693-702. |
| 69 | Güneyisi E, Gesoglu M, Algın Z, et al. Effect of surface treatment methods on the properties of self-compacting concrete with recycled aggregates[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2014, 64: 172-183. |
| 70 | 丁子奇. 再生混凝土骨料微生物矿化改性及其机理研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学建筑科学与工程学院, 2022. |
| Ding Zi-qi. Properties modification of recycled concrete aggregate based on microbial mineralization and its mechanism[D]. Yangzhou: College of Architectural Science and Engineering, Yangzhou University, 2022. | |
| 71 | Tam V W Y, Butera A, Le K N. Carbon-conditioned recycled aggregate in concrete production[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2016, 133: 672-680. |
| 72 | Li L, Xuan D, Sojobi A O, et al. Development of nano-silica treatment methods to enhance recycled aggregate concrete[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2021, 118: No. 103963. |
| 73 | 秦拥军, 陈楠, 蔺鹏杰, 等. 掺锂渣再生混凝土三点弯曲梁双K断裂特性[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(6): 2121-2127. |
| Qin Yong-jun, Chen Nan, Lin Peng-jie, et al. Double K fracture characteristics of recycled concrete three⁃point bending beam mixed with lithium slag[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(6): 2121-2127. | |
| 74 | 张鸿儒. 基于界面参数的再生骨料混凝土性能劣化机理及工程应用[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学建筑工程学院, 2016. |
| Zhang Hong-ru. Deterioration mechanism of recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) based on interface parameters and the application of RAC[D]. Hangzhou: College of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Zhejiang University, 2016. | |
| 75 | Akbarnezhad A, Ong K C G, Zhang M H, et al. Microwave-assisted beneficiation of recycled concrete aggregates[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2011, 25: 3469-3479. |
| 76 | Saravanakumar P, Abhiram K, Manoj B. Properties of treated recycled aggregates and its influence on concrete strength characteristics[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 111: 611-617. |
| 77 | 徐洪坡. 水玻璃强化再生粗骨料混凝土力学性能的试验研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛理工大学土木工程学院, 2018. |
| Xu Hong-po. Experimental study on mechanical properties of recycled coarse aggregate concrete strengthened with sodium silicate[D]. Qingdao: School of Civil Engineering, Qingdao University of Technology, 2018. | |
| 78 | Yang J, Shaban W M, Elbaz K, et al. Properties of concrete containing strengthened crushed brick aggregate by pozzolan slurry[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 247: No. 118612. |
| 79 | 孙道胜, 李泽英, 刘开伟, 等. 再生粗骨料的形态及缺陷对再生混凝土干燥收缩和力学性能的影响[J]. 材料导报, 2021, 35(11): 11027-11033, 11056. |
| Sun Dao-sheng, Li Ze-ying, Liu Kai-wei, et al. Influence of shapes and defects in recycled aggregate on drying shrinkage and mechanical properties of recycled aggregate concrete[J]. Materials Reports, 2021, 35(11): 11027-11033, 11056. | |
| 80 | 崔正龙, 张含. 再生粗骨料释水特性对混凝土干燥收缩性能影响[J]. 工程科学与技术, 2020, 52(6): 139-144. |
| Cui Zheng-long, Zhang Han. Effect of recycled coarse aggregate suction and drainage on drying shrinkage of concrete[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2020, 52(6): 139-144. | |
| 81 | 肖建庄, 许向东, 范玉辉. 再生混凝土收缩徐变试验及徐变神经网络预测[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2013, 16(5): 752-757. |
| Xiao Jian-zhuang, Xu Xiang-dong, Fan Yu-hui. Shrinkage and creep of recycled aggregate concrete and their prediction by ANN method[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2013, 16(5): 752-757. | |
| 82 | Silva S, Evangelista L, de Brito J. Durability and shrinkage performance of concrete made with coarse multi-recycled concrete aggregates[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 272: No. 121645. |
| 83 | Wang Q, Geng Y, Wang Y, et al. Drying shrinkage model for recycled aggregate concrete accounting for the influence of parent concrete[J]. Engineering Structures, 2020, 202: No. 109888. |
| 84 | Mao Y, Liu J, Shi C. Autogenous shrinkage and drying shrinkage of recycled aggregate concrete: a review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 295: No. 126435. |
| 85 | Pedro D, de Brito J, Evangelista L. Structural concrete with simultaneous incorporation of fine and coarse recycled concrete aggregates: mechanical, durability and long-term properties[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 154: 294-309. |
| 86 | 陈欣. 基于水化特性的再生骨料混凝土收缩性能研究[D]. 福州: 福州大学土木工程学院, 2017. |
| Chen Xin. Shrinkage property of recycled concrete based on hydration characteristics[D]. Fuzhou: College of Civil Engineering, Fuzhou University, 2017. | |
| 87 | Chinzorigt G, Lim M K, Yu M, et al. Strength, shrinkage and creep and durability aspects of concrete including CO2 treated recycled fine aggregate[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2020, 136: No. 106062. |
| 88 | Ismail S, Ramli M. Mechanical strength and drying shrinkage properties of concrete containing treated coarse recycled concrete aggregates[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2014, 68: 726-739. |
| 89 | Wang J, Zhang J, Cao D, et al. Comparison of recycled aggregate treatment methods on the performance for recycled concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 234: No. 117366. |
| 90 | Tam V W Y, Butera A, Le K N. An investigation of the shrinkage, concrete shrinkage reversibility and permeability of CO2-treated concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 365: No. 130120. |
| 91 | Fathifazl G, Razaqpur A G, Isgor O B, et al. Creep and drying shrinkage characteristics of concrete produced with coarse recycled concrete aggregate[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2011, 33: 1026-1037. |
| 92 | Kou S C, Poon C S, Agrela F. Comparisons of natural and recycled aggregate concretes prepared with the addition of different mineral admixtures[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2011, 33: 788-795. |
| 93 | Kisku N, Rajhans P, Panda S K, et al. Microstructural investigation of recycled aggregate concrete produced by adopting equal mortar volume method along with two stage mixing approach[J]. Structures, 2020, 24: 742-753. |
| 94 | 李秋义, 韩帅, 莫建, 等. 物理化学强化对再生混凝土抗氯离子渗透性能的影响[J]. 材料科学与工程学报, 2016, 34(3): 432-436, 459. |
| Li Qiu-yi, Han Shuai, Mo Jian, et al. Influence of physical and chemical enhancement of recycled coarse aggregate on coefficient of chloride migration of recycled concrete[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Engineering, 2016, 34(3): 432-436, 459. | |
| 95 | Kim Y, Hanif A, Kazmi S M S, et al. Properties enhancement of recycled aggregate concrete through pretreatment of coarse aggregates: comparative assessment of assorted techniques[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 191: 339-349. |
| 96 | Shi C, Wu Z, Cao Z, et al. Performance of mortar prepared with recycled concrete aggregate enhanced by CO2 and pozzolan slurry[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2018, 86: 130-138. |
| 97 | Zhu Y G, Kou S C, Poon C S, et al. Influence of silane-based water repellent on the durability properties of recycled aggregate concrete[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2013, 35: 32-38. |
| 98 | 岳公冰. 再生混凝土多重界面结构与性能损伤机理研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛理工大学土木工程学院, 2018. |
| Yue Gong-bing. Study on the recycled concrete multi-interface structure and the damage mechanism of performance[D]. Qingdao: School of Civil Engineering, Qingdao University of Technology, 2018. | |
| 99 | 祁兵. 多因素耦合作用下再生混凝土抗侵蚀性能与机理研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学材料科学与工程学院, 2017. |
| Qi Bing. Erosion resistance and mechanism of recycled aggregate concrete under multi coupling factors[D]. Nanjing: School of Materials Science and Engineering, Southeast University, 2017. | |
| 100 | Bulatovic V, Melešev M, Radeka M, et al. Evaluation of sulfate resistance of concrete with recycled and natural aggregates[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 152: 614-631. |
| 101 | 易超. 建筑垃圾资源化制备再生骨料混凝土的研究[D]. 广州: 暨南大学力学与建筑工程学院, 2014. |
| Yi Chao. The study on the resource recovery of construction waste for recycled aggregate concrete[D]. Guangzhou: School of Mechanics and Construction Engineering, Jinan University, 2014. | |
| 102 | 安新正. 腐蚀环境下再生混凝土结构耐久性试验研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学力学与土木工程学院, 2012. |
| An Xin-zheng. Experimental study on durability of recycled concrete structure exposed in corroded environment[D]. Beijing: School of Mechanics and Civil Engineering, China University of Mining and Technology, 2012. | |
| 103 | 程海丽, 张迪. 水玻璃强化再生骨料混凝土的抗冻性和抗侵蚀性探析[J]. 新型建筑材料, 2008(8): 5-7. |
| Cheng Hai-li, Zhang Di. Discussions on frost resistance and resistance to sulfate attack of water glass reinforced reclaimed aggregate concrete[J]. New Building Materials, 2008(8:) 5-7. | |
| 104 | Kazmi S M S, Munir M J, Wu Y F, et al. Effect of different aggregate treatment techniques on the freeze-thaw and sulfate resistance of recycled aggregate concrete[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2020, 178: No. 103126. |
| 105 | 王家滨. 喷射混凝土耐久性能劣化规律及机理研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学土木工程学院, 2016. |
| Wang Jia-bin. Study of deterioration law and mechanism of shotcrete durability performance[D]. Xi'an: School of Civil Engineering, Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, 2016. | |
| 106 | Li Y, Wang R, Li S, et al. Resistance of recycled aggregate concrete containing low-and high-volume fly ash against the combined action of freeze-thaw cycles and sulfate attack[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 166: 23-34. |
| 107 | Kazmi S M S, Munir M J, Wu Y F, et al. Effect of recycled aggregate treatment techniques on the durability of concrete: a comparative evaluation[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 264: No. 120284. |
| 108 | Liu Z, Chin C S, Xia J. Novel method for enhancing freeze-thaw resistance of recycled coarse aggregate concrete via two-stage introduction of denitrifying bacteria[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 346: No. 131159. |
| 109 | 鲍玖文, 于子浩, 张鹏, 等. 再生粗骨料混凝土及其构件抗冻性能研究进展[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2022, 43(4): 142-157. |
| Bao Jiu-wen, Yu Zi-hao, Zhang Peng, et al. Review on frost resistance property of recycled coarse aggregate concrete and its structural components[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2022, 43(4): 142-157. | |
| 110 | 陈德玉, 刘来宝, 严云, 等. 不同因素对再生骨料混凝土抗冻性的影响[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2011, 33(5): 54-58. |
| Chen De-yu, Liu Lai-bao, Yan Yun, et al. Effect of different factors on frost resistance of recycled aggregate concrete[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2011, 33(5): 54-58. | |
| 111 | Xiao J, Li H, Yang Z. Fatigue behavior of recycled aggregate concrete under compression and bending cyclic loadings[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 38: 681-688. |
| 112 | Tan Y, Zhou C, Zhou J. Influence of the steel fiber content on the flexural fatigue behavior of recycled aggregate concrete[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2020, 2020: No. 8839271. |
| 113 | Saini B S, Singh S P. Flexural fatigue strength prediction of self compacting concrete made with recycled concrete aggregates and blended cements[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 264: No. 120233. |
| 114 | Zhou J, Fu T, Zhong C, et al. Flexural fatigue behaviors of silicon carbide recycled concrete in corrosive environments[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2021, 2021: No. 7459777. |
| 115 | 徐明, 王韬, 陈忠范. 高温后再生混凝土单轴受压应力-应变关系试验研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2015, 36(2): 158-164. |
| Xu Ming, Wang Tao, Chen Zhong-fan. Experimental research on uniaxial compressive stress-strain relationship of recycled concrete after high temperature[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2015, 36(2): 158-164. | |
| 116 | Wang W, Wu J, Wang Z, et al. Chloride diffusion coefficient of recycled aggregate concrete under compressive loading[J]. Materials and Structures, 2016, 49: 4729-4736. |
| 117 | 鲍玖文, 王云伟, 牟新宇, 等. 持压荷载与干湿循环作用下再生混凝土氯盐侵蚀行为[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(2): 1015-1024. |
| Bao Jiu-wen, Wang Yun-wei, Mou Xin-yu, et al. Chloride ingress behavior of recycled aggregate concrete subjected to sustained compressive loading and drying-wetting cycles[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(2): 1015-1024. | |
| 118 | Qi B, Gao J, Chen F, et al. Chloride penetration into recycled aggregate concrete subjected to wetting-drying cycles and flexural loading[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 174: 130-137. |
| 119 | 王建刚. 复杂环境条件下再生混凝土耐久性衰变规律及改善机理[D]. 北京: 北京工业大学城市交通学院, 2020. |
| Wang Jian-gang. Decay law and improvement mechanism of durability of recycled concrete under complex environmental conditions[D]. Beijing: College of Metropolitan Transportation, Beijing University of Technology, 2020. | |
| 120 | 水中和, 潘智生, 朱文琪, 等. 再生集料混凝土的微观结构特征[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2003, 25(12): 99-102. |
| Shui Zhong-he, Pan Zhi-sheng, Zhu Wen-qi, et al. Microscopic structural features of the recycled aggregate concrete[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2003, 25(12): 99-102. | |
| 121 | 黄庆华, 周承宗, 顾祥林, 等. 混凝土界面过渡区水分传输特性试验研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2019, 40(1): 174-180. |
| Huang Qing-hua, Zhou Cheng-zong, Gu Xiang-lin, et al. Microscopic structural features of the recycled aggregate concrete[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2019, 40(1): 174-180. | |
| 122 | 陈惠苏, 孙伟, Piet Stroeven. 水泥基复合材料集料与浆体界面研究综述(二): 界面微观结构的形成、劣化机理及其影响因素[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2004, 32(1): 70-79. |
| Chen Hui-su, Sun Wei, Piet Strpven. Interfacial transition zone between aggregate and paste in cementitious composites (Ⅱ): Mechanism of formation and degradation of interfacial transition zone microstructure, and its influence factors[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2004, 32(1): 70-79. | |
| 123 | Zeng W, Zhao Y, Zheng H, et al. Improvement in corrosion resistance of recycled aggregate concrete by nano silica suspension modification on recycled aggregates[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2020, 106: No. 103476. |
| 124 | 李恒, 郭庆军, 王家滨, 等. 再生混凝土界面结构及耐久性综述[J]. 材料导报, 2020, 34(7): 13050-13057. |
| Li Heng, Guo Qing-jun, Wang Jia-bin, et al. Meso-/Micro-structure of interfacial transition zone and durability of recycled aggregate concrete: a review[J]. Materials Reports, 2020, 34(7): 13050-13057. | |
| 125 | 水中和, 万惠文. 老混凝土中骨料-水泥界面过渡区(ITZ)(Ⅰ):元素与化合物在ITZ的富集现象[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2002, 24(4): 21-23, 74. |
| Shui Zhong-he, Wan Hui-wen. Aggregate cement interfacial transition zone (ITZ) in old concrete(Ⅰ):concentrations of elements and compounds to the ITZ[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2002, 24(4): 21-23, 74. | |
| 126 | 水中和, 万惠文. 老混凝土中骨料-水泥界面过渡区(ITZ)(Ⅱ):元素在界面区的分布特征[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2002, 24(5): 22-25. |
| Shui Zhong-he, Wan Hui-wen. Distributions of chemical elements in aggregate cement interfacial transition zone in old concrete(Ⅱ)[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2002, 24(5): 22-25. | |
| 127 | 万惠文, 徐金龙, 水中和, 等. 再生混凝土ITZ结构与性质的研究[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2004, 26(11): 29-32. |
| Wan Hui-wen, Xu Jin-long, Shui Zhong-he, et al. Study on the structure and properties of interfacial transition zone(ITZ) of the regenerated concrete[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2004, 26(11): 29-32. | |
| 128 | Poon C S, Shui Z H, Lam L. Effect of microstructure of ITZ on compressive strength of concrete prepared with recycled aggregates[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2004, 18: 461-468. |
| 129 | Xiao J, Li W, Sun Z, et al. Properties of interfacial transition zones in recycled aggregate concrete tested by nanoindentation[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2013, 37: 276-292. |
| 130 | Zhang H, Ji T, Liu H. Performance evolution of the interfacial transition zone (ITZ) in recycled aggregate concrete under external sulfate attacks and dry-wet cycling[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 229: No. 116938. |
| 131 | Zhang H, Ji T, Liu H. Improving the sulfate resistance of recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) by using surface-treated aggregate with sulfoaluminate cement (SAC)[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 297: No. 123535. |
| 132 | Yue G, Ma Z, Liu M, et al. Damage behavior of the multiple ITZs in recycled aggregate concrete subjected to aggressive ion environment[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 245: No. 118419. |
| 133 | Liu Z, Chin C S, Xia J. Improving recycled coarse aggregate (RCA) and recycled coarse aggregate concrete (RCAC) by biological denitrification phenomenon[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 301: No. 124338. |
| [1] | 袁杰,王军博,陈歆,黄馨,张傲翔,崔安琪. 人工智能在超高性能混凝土中的应用研究进展[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(3): 771-789. |
| [2] | 冯琼,田浩正,乔宏霞,念腾飞,韩文文. 自然暴露与盐雾加速环境下钢筋混凝土劣化规律及等效关系[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 494-505. |
| [3] | 李岩,张久鹏,陈子璇,黄果敬,王培. 基于PCA-PSO-SVM的沥青路面使用性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1729-1735. |
| [4] | 张家旭,郭崇,王晨,赵健,王欣志. 基于半实物仿真平台的自动泊车系统性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1552-1560. |
| [5] | 许金凯, 王煜天, 张世忠. 驱动冗余重型并联机构的动力学性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1138-1143. |
| [6] | 郑欣, 彭真明, 邢艳. 基于活跃度的图像分割算法性能评价新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 311-317. |
| [7] | 孙超杰, 马彦, 周秀文, 陈虹. 基于LQG基准的怠速控制系统PID控制器性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(增刊1): 183-188. |
| [8] | 陈立军,杨善让,王升龙,米利俊. 复合制冷循环电站空冷系统的热力学分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(增刊2): 283-0286. |
|
||