吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2018, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (6): 1703-1711.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20170520
沥青面层不同深度车辙等效温度预估模型
- 同济大学 道路与交通工程教育部重点实验室,上海 201804
Prediction model on rutting equivalent temperature for asphalt pavement at different depth
LI Yi( ),LIU Li-ping,SUN Li-jun(
),LIU Li-ping,SUN Li-jun( )
)
- The Key Laboratory of Road and Traffic Engineering, Ministry of Education, Tongji University,Shanghai 201804,China
摘要:
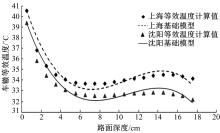
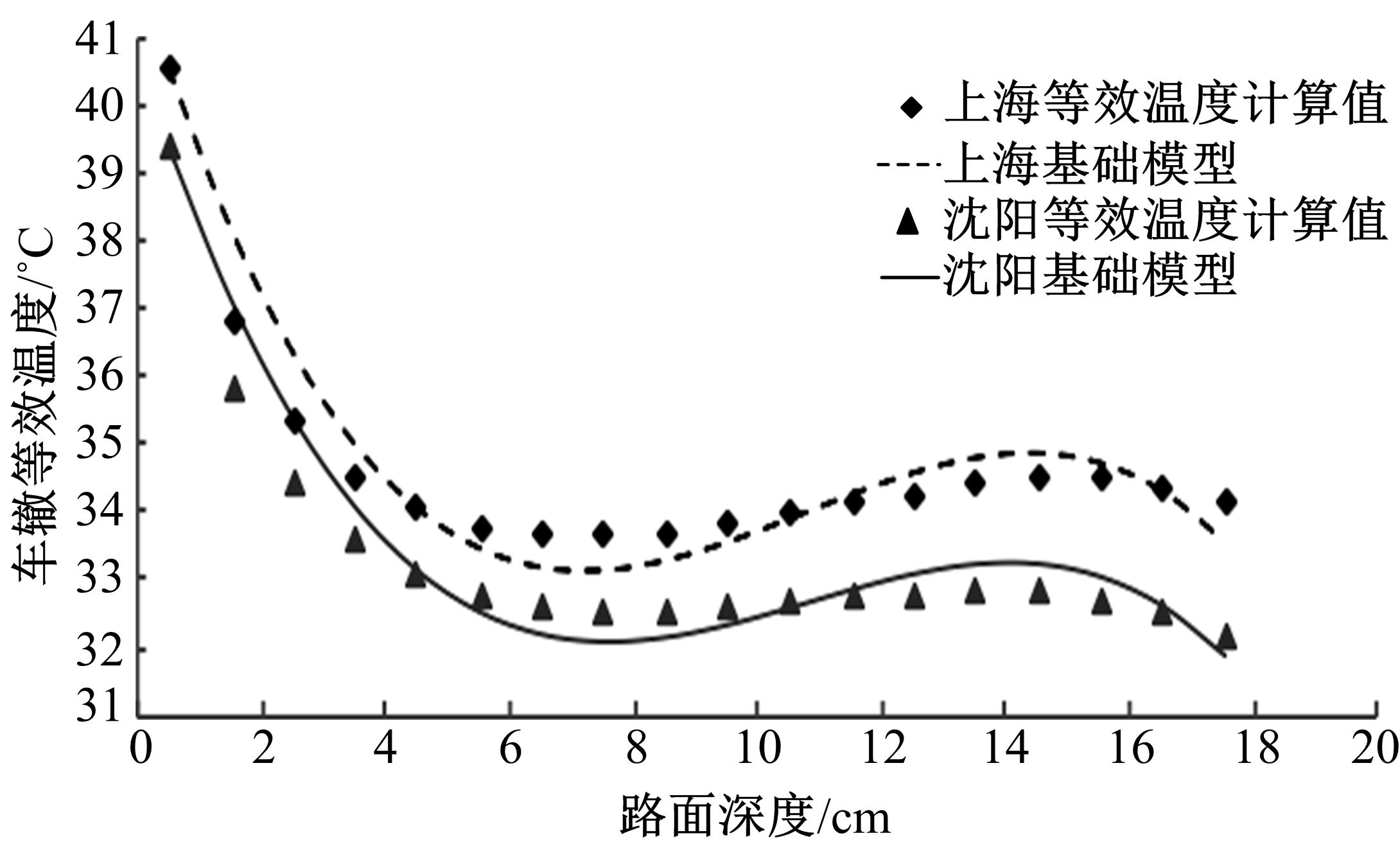
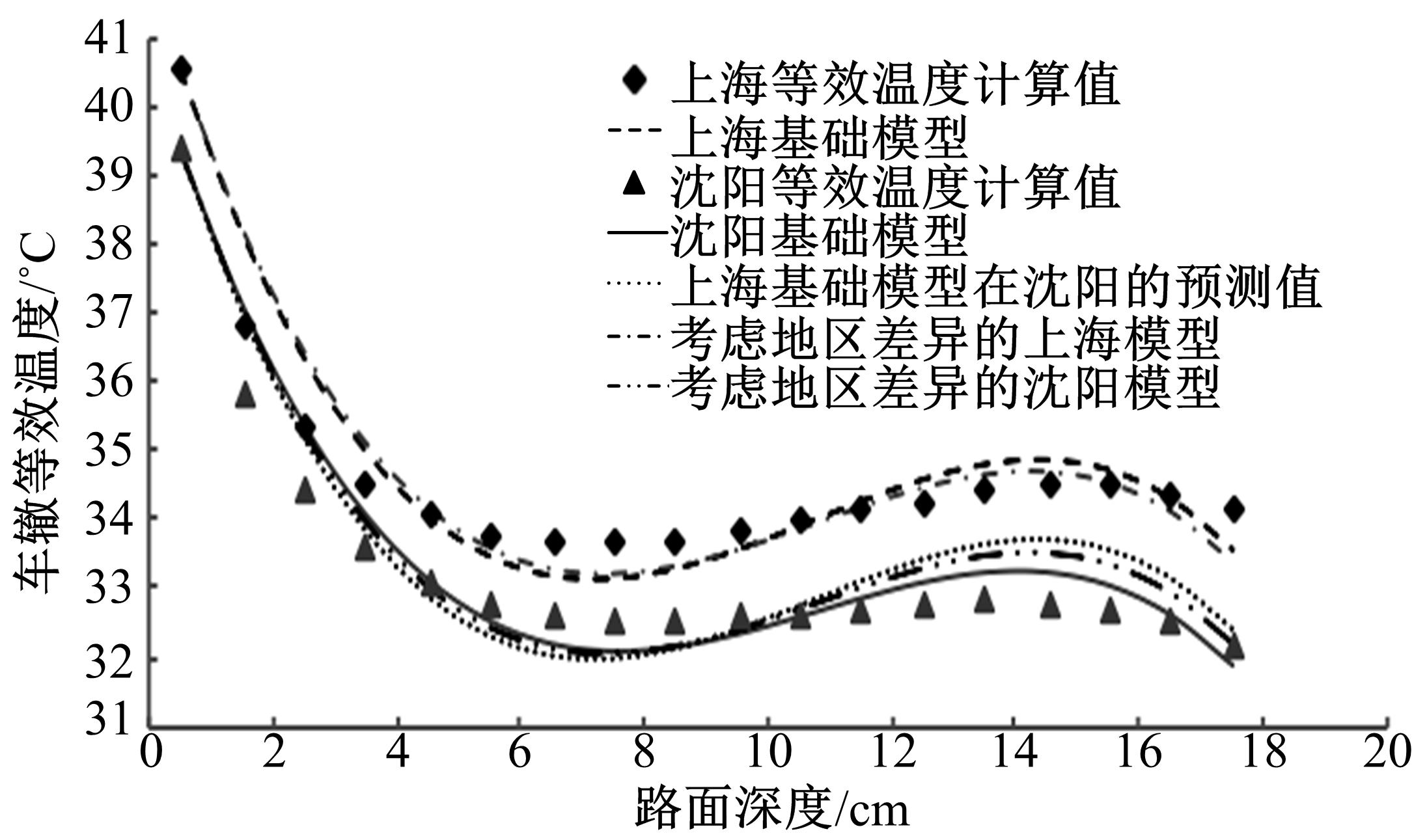
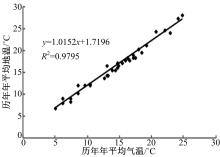
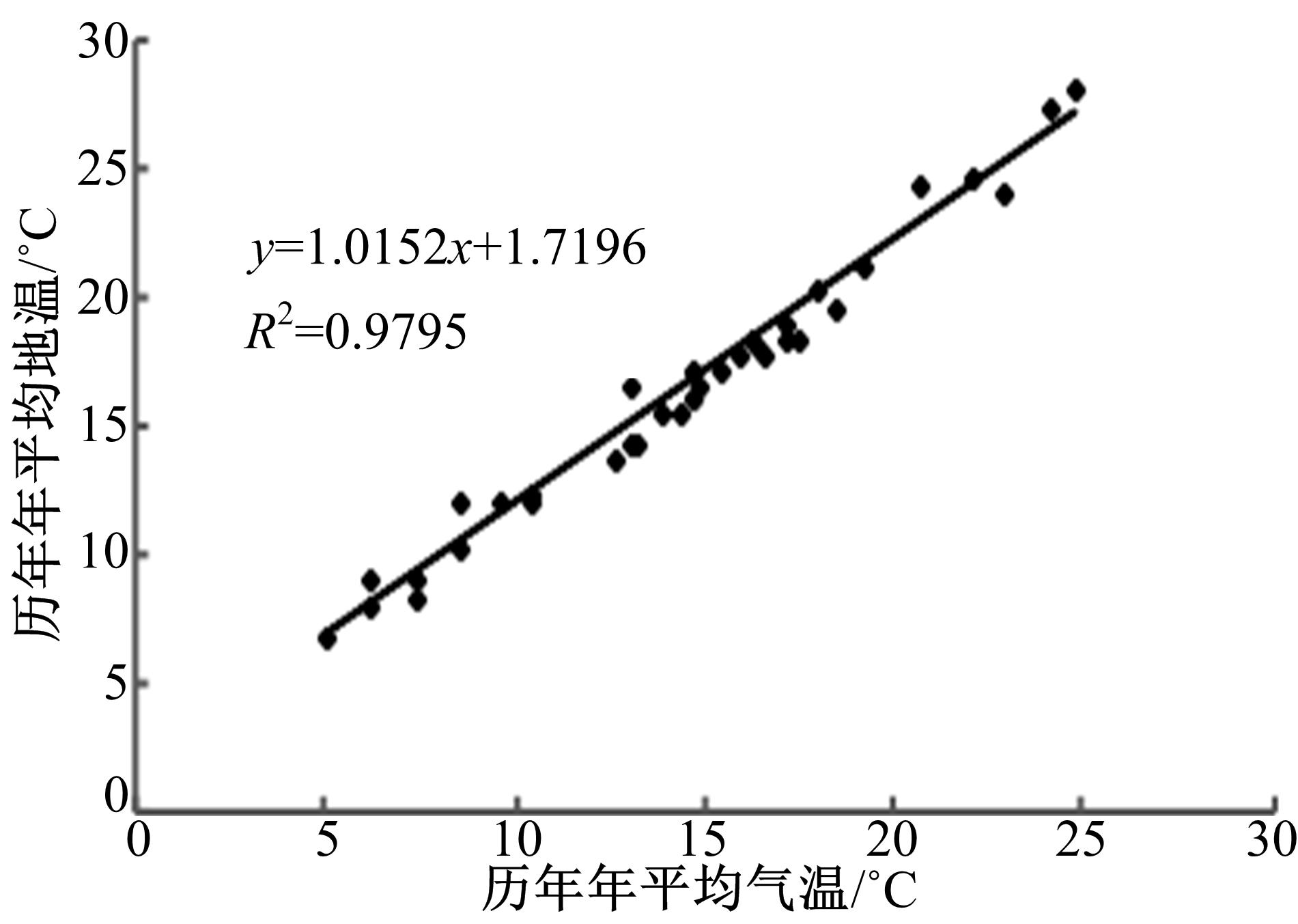
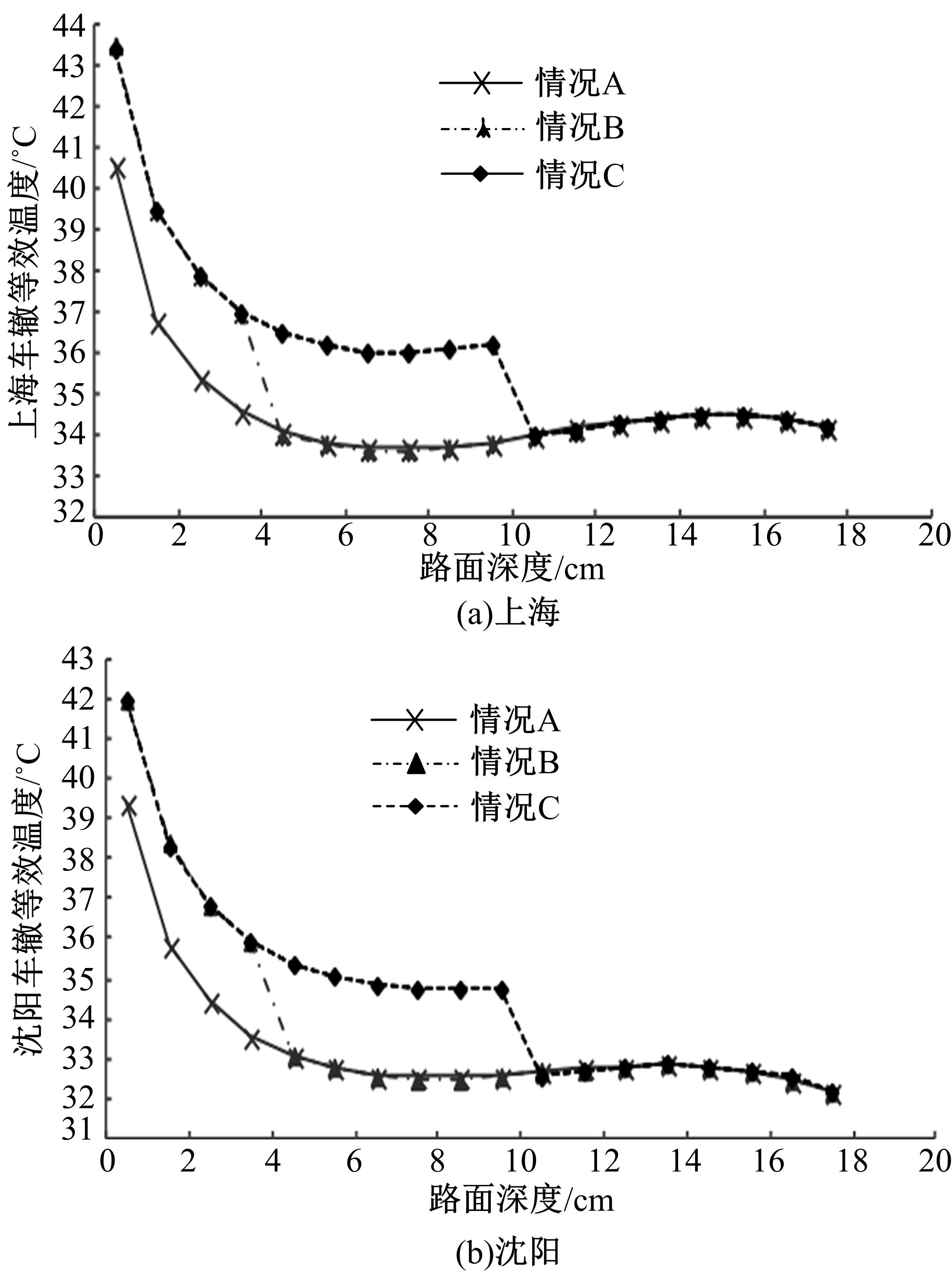
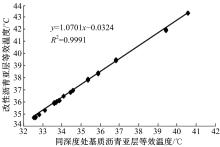
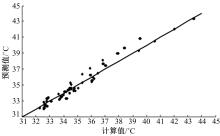
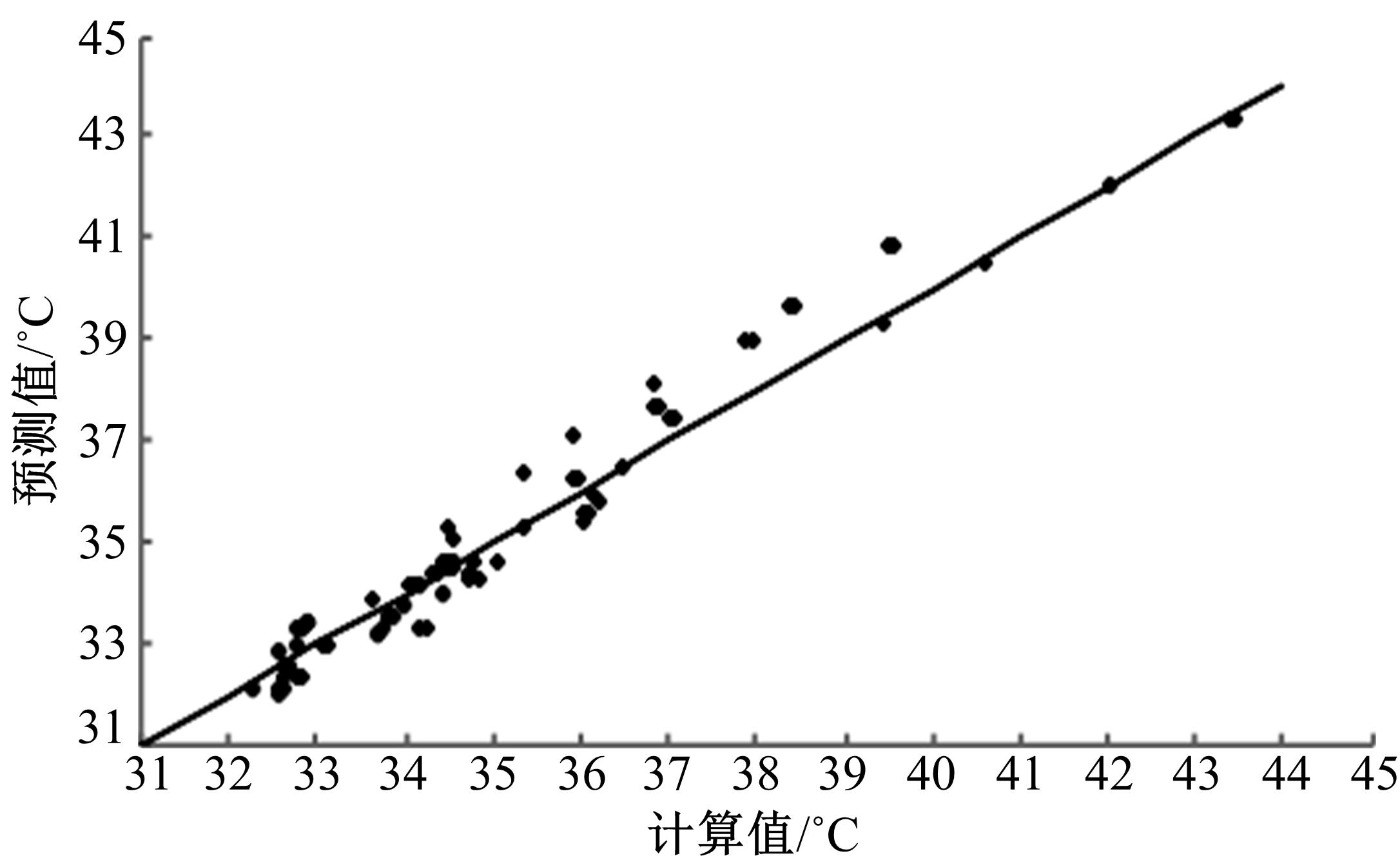
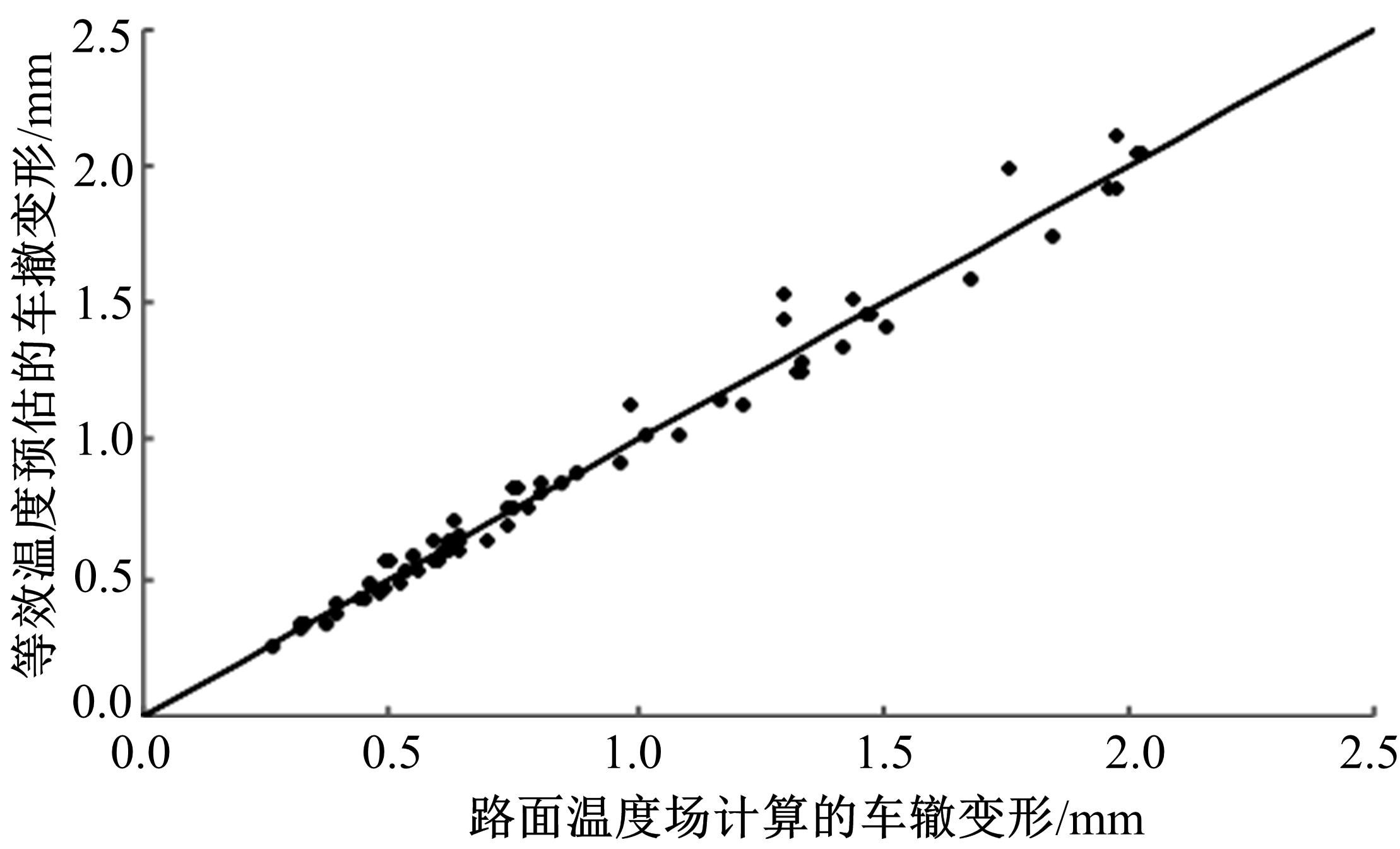
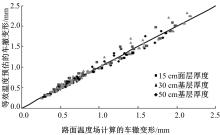
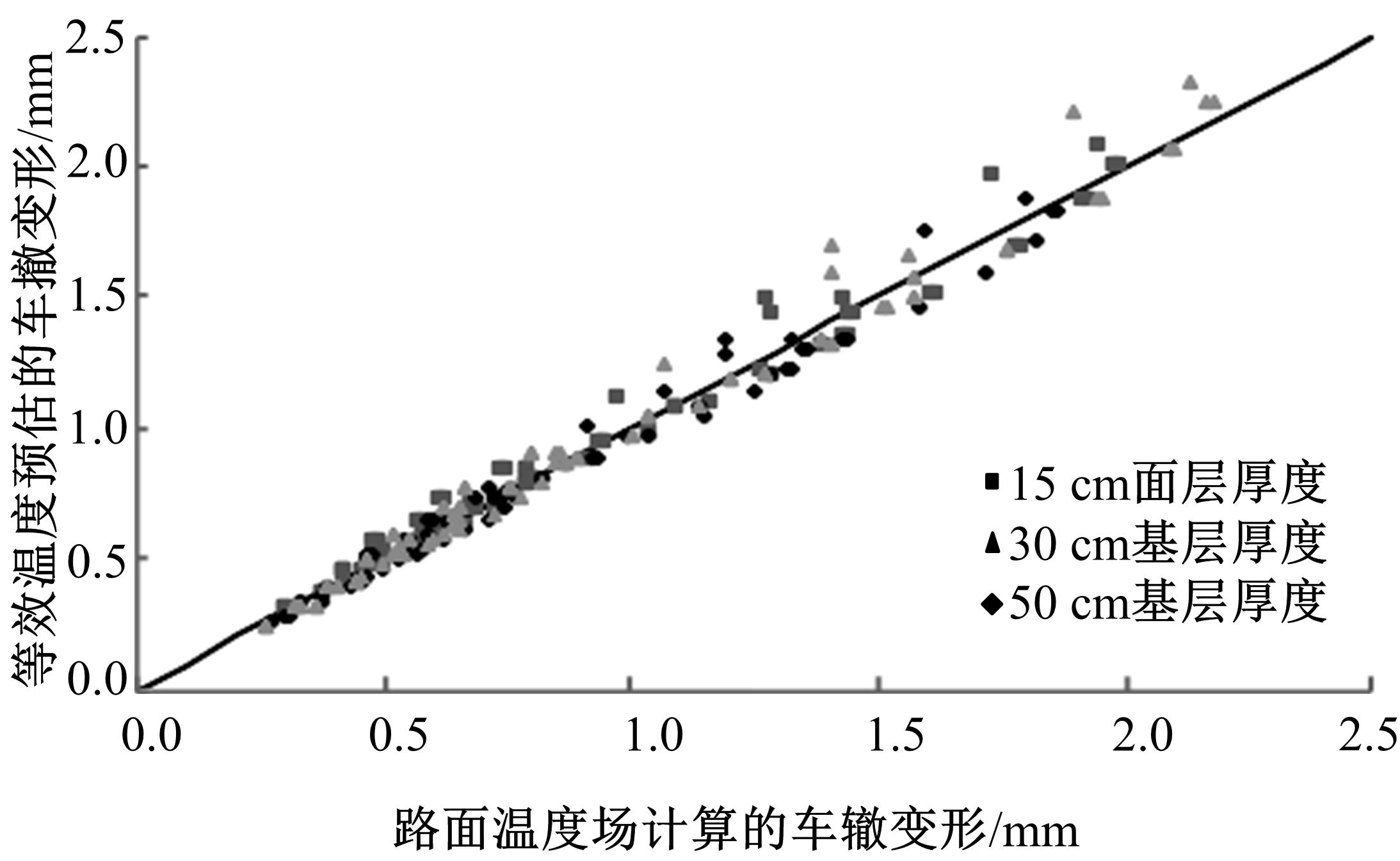
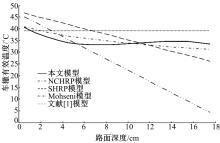
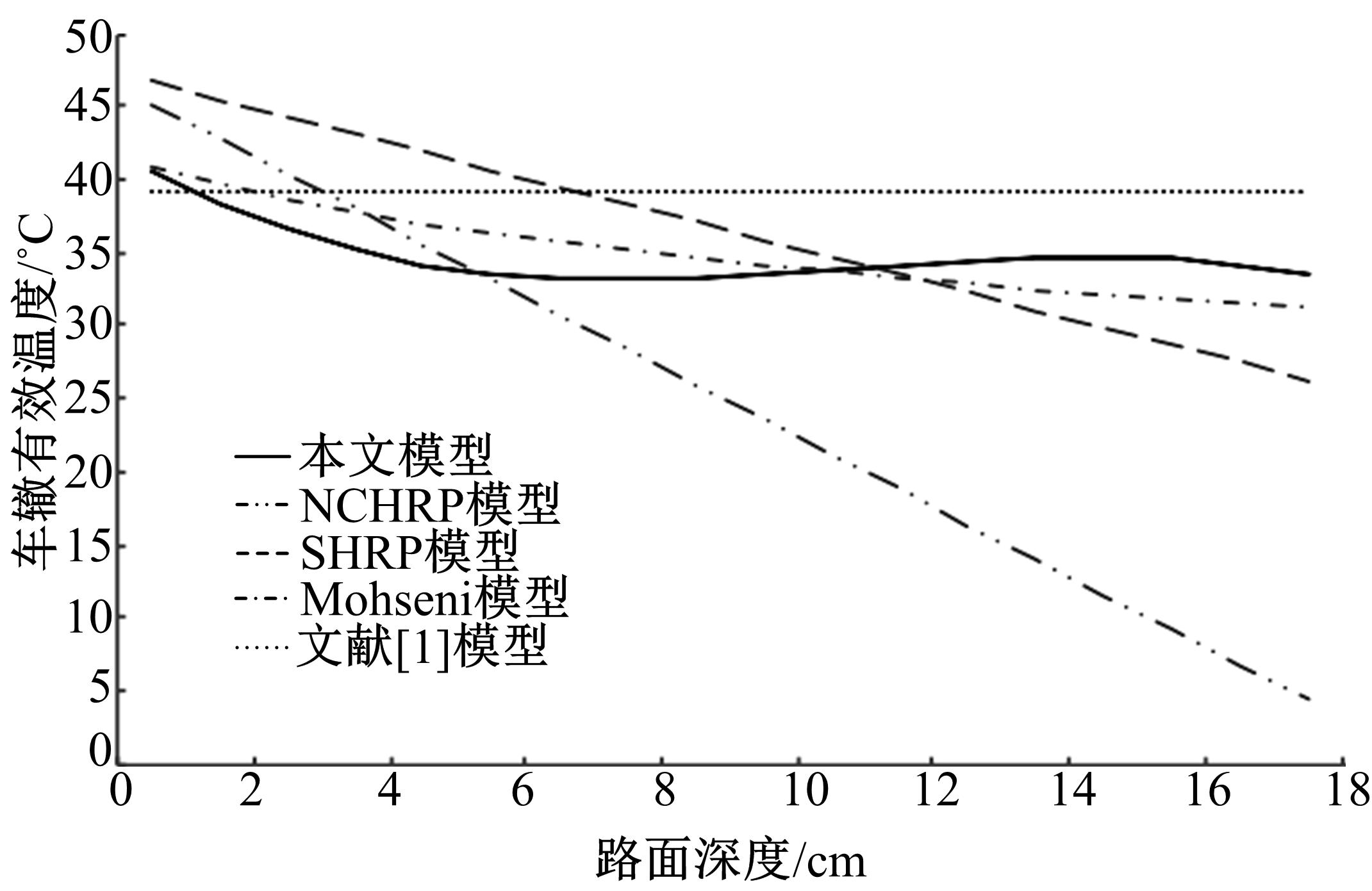
基于先期建立的沥青路面温度场预估模型和车辙预估模型,利用累积车辙等效原则,提出了路面不同深度车辙等效温度的计算方法,初步建立了考虑地区差异和沥青材料特性的等效温度预估模型,并进行了检验。与国内外已有车辙等效温度预估模型相比,该模型反映了不同面层深度、不同地区及不同沥青材料类型的差异性,具有更好的适用性。
中图分类号:
- U416
| [1] |
苏凯, 孙立军 . 车辙等效温度确定方法探讨[J]. 大连理工大学学报, 2006,46(增刊1):162-167.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8608.2006.z1.027 |
|
Su Kai, Sun Li-jun . Discussion of methods for determining effective temperature of rutting[J]. Journal of Dalian University of Technology, 2006,46(Sup.1):162-167.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8608.2006.z1.027 |
|
| [2] | 栗培龙, 张争奇, 王秉纲 . 考虑有效温度及荷载的沥青混凝土路面车辙等效温度研究[J]. 公路, 2011(2):6-11. |
| Li Pei-long, Zhang Zheng-qi, Wang Bing-gang . Research on rutting equivalent temperature of asphalt concrete pavement considering effective temperature and load[J]. Highway, 2011(2):6-11. | |
| [3] | 吁新华, 谈至明, 胡洪龙 , 等. 沥青面层的车辙等效温度[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2014,42(5):701-706,729. |
| Yu Xin-hua, Tan Zhi-ming, Hu Hong-long , et al. Rutting equivalent temperature for asphalt pavement[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science), 2014,42(5):701-706,729. | |
| [4] | 孙立军 . 沥青路面结构行为学[M]. 2版. 上海: 同济大学出版社, 2013. |
| [5] |
孙立军, 秦健 . 沥青路面温度场的预估模型[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2006,34(4):480-483.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2006.04.011 |
|
Sun Li-jun, Qin Jian . Prediction model on temperature field in asphalt pavement[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science), 2006,34(4):480-483.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2006.04.011 |
|
| [6] | Witczak M W . Effective temperature analysis for permanent deformation of asphaltic mixtures[R]. Washington DC: National Research Council, 1992. |
| [7] | Cominsky R J, Huber G A, Kennedy T W , et al. The Superpave mix design manual for new construction and overlays[R]. Washington DC: National Research Council, 1994. |
| [8] | Sotil A . Use of the dynamic modulus E * test as permanent deformation performance criteria for asphalt pavement systems [D]. Tempe: Arizona State University, 2005. |
| [9] | Monismith C L, Hicks R G, Finn F N , et al. Permanent deformation response of asphalt-aggregate mixes[R]. Washington DC:National Research Council, 1994. |
| [10] |
EI-Basyouny M, Jeong M G . Effective temperature for analysis of permanent deformation and fatigue distress on asphalt mixtures[J]. Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2009(2127):155-163.
doi: 10.3141/2127-18 |
| [11] | Moulthrop J, Witczak M W . A performance-related specification for hot-mix asphalt[R]. Washington DC: Transportation Research Board of the National Academies, 2011. |
| [12] | Mohseni A, Azari H. Effective temperature for permanent deformation testing of asphalt mixtures [C]//International Society of Asphalt Pavements, Raleigh, North Carolina, 2014: 1501-1511. |
| [13] | Witczak M W, Andrei D, Houston W N . Guide for mechanistic-empirical design of new and rehabilitated pavement structures[R]. Washington DC: Transportation Research Board of the National Academies, 2004. |
| [14] |
秦健, 孙立军 . 沥青路面温度场的分布规律[J]. 公路交通科技, 2006,23(8):18-21.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2006.08.005 |
|
Qin Jian, Sun Li-jun . Study on asphalt pavement temperature field distribution pattern[J]. Journal on Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2006,23(8):18-21.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2006.08.005 |
|
| [15] | Barber E S. Calculation of maximum pavement temperatures from weather reports [C]//Highway Research Board, Washington DC, 1957: 1-8. |
| [1] | 黄晓明,曹青青,刘修宇,陈嘉颖,周兴林. 基于路表分形摩擦理论的整车雨天制动性能模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 757-765. |
| [2] | 王静,吕翔,曲肖龙,钟春玲,张云龙. 路基土抗剪强度与化学及矿物成分的关系[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 766-772. |
| [3] | 臧国帅, 孙立军. 基于惰性弯沉点的刚性下卧层深度设置方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1037-1044. |
| [4] | 念腾飞, 李萍, 林梅. 冻融循环下沥青特征官能团含量与流变参数灰熵分析及微观形貌[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1045-1054. |
| [5] | 宫亚峰, 申杨凡, 谭国金, 韩春鹏, 何钰龙. 不同孔隙率下纤维土无侧限抗压强度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 712-719. |
| [6] | 程永春, 毕海鹏, 马桂荣, 宫亚峰, 田振宏, 吕泽华, 徐志枢. 纳米TiO2/CaCO3-玄武岩纤维复合改性沥青的路用性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 460-465. |
| [7] | 张仰鹏, 魏海斌, 贾江坤, 陈昭. 季冻区组合冷阻层应用表现的数值评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 121-126. |
| [8] | 季文玉, 李旺旺, 过民龙, 王珏. 预应力RPC-NC叠合梁挠度试验及计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 129-136. |
| [9] | 马晔, 尼颖升, 徐栋, 刁波. 基于空间网格模型分析的体外预应力加固[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 137-147. |
| [10] | 罗蓉, 曾哲, 张德润, 冯光乐, 董华均. 基于插板法膜压力模型的沥青混合料水稳定性评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1753-1759. |
| [11] | 尼颖升, 马晔, 徐栋, 李金凯. 波纹钢腹板斜拉桥剪力滞效应空间网格分析方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1453-1464. |
| [12] | 郑传峰, 马壮, 郭学东, 张婷, 吕丹, 秦泳. 矿粉宏细观特征耦合对沥青胶浆低温性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1465-1471. |
| [13] | 于天来, 郑彬双, 李海生, 唐泽睿, 赵云鹏. 钢塑复合筋带挡土墙病害及成因[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1082-1093. |
| [14] | 蔡氧, 付伟, 陶泽峰, 陈康为. 基于扩展有限元模型的土工布防荷载型反射裂缝影响分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 765-770. |
| [15] | 刘寒冰, 张互助, 王静. 失水干燥对路基压实黏质土抗剪强度特性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 446-451. |
|