吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1): 297-305.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180805
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
隐低秩结合低秩表示的多聚焦图像融合
- 1. 中国科学院 成都计算机应用研究所, 成都 610041
2. 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
Multi-focus image fusion based on latent low⁃rank representation combining low⁃rank representation
Man CHEN1,2( ),Yong ZHONG1,2,Zhen-dong LI1,2(
),Yong ZHONG1,2,Zhen-dong LI1,2( )
)
- 1. Chengdu Institute of Computer Applications, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610041, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
摘要:
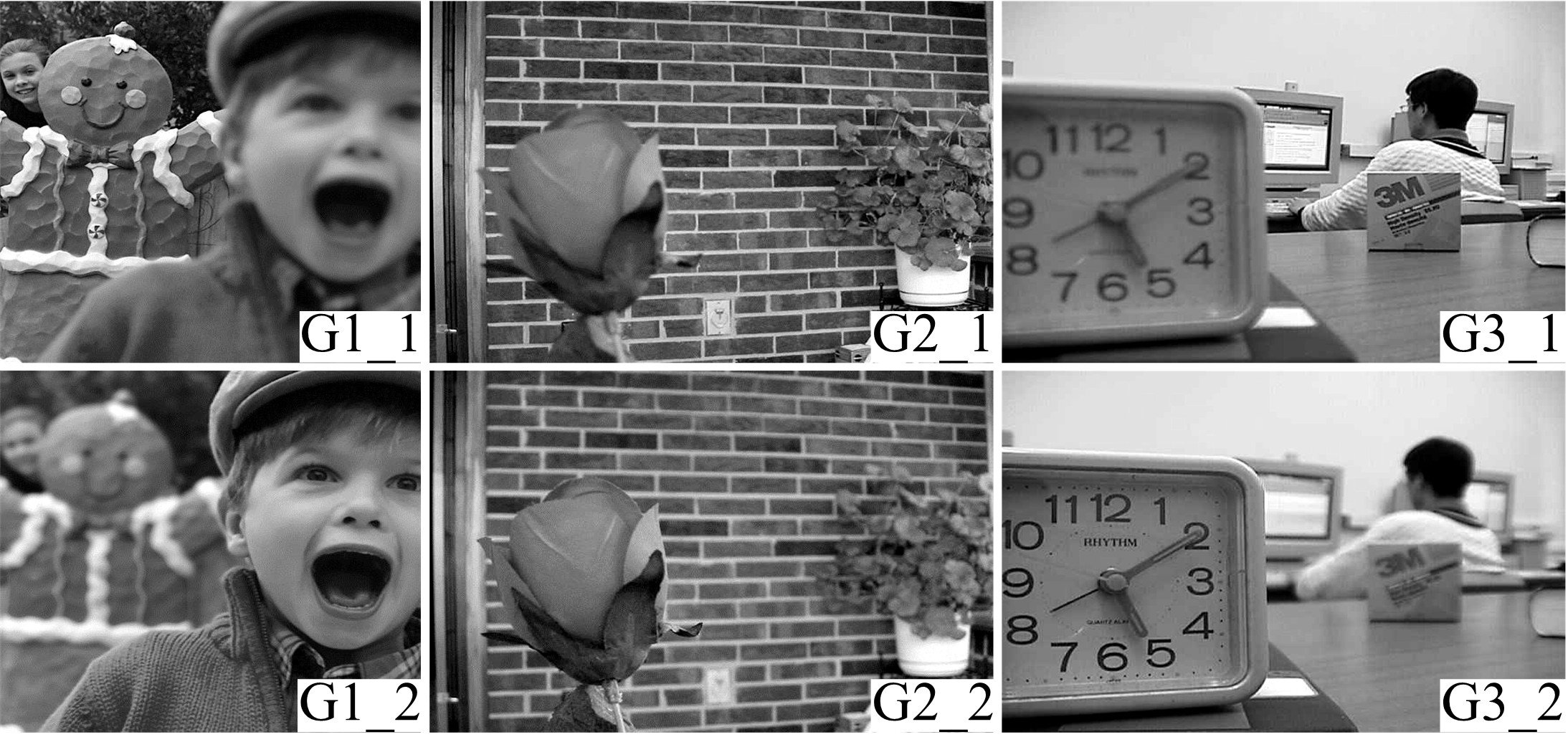
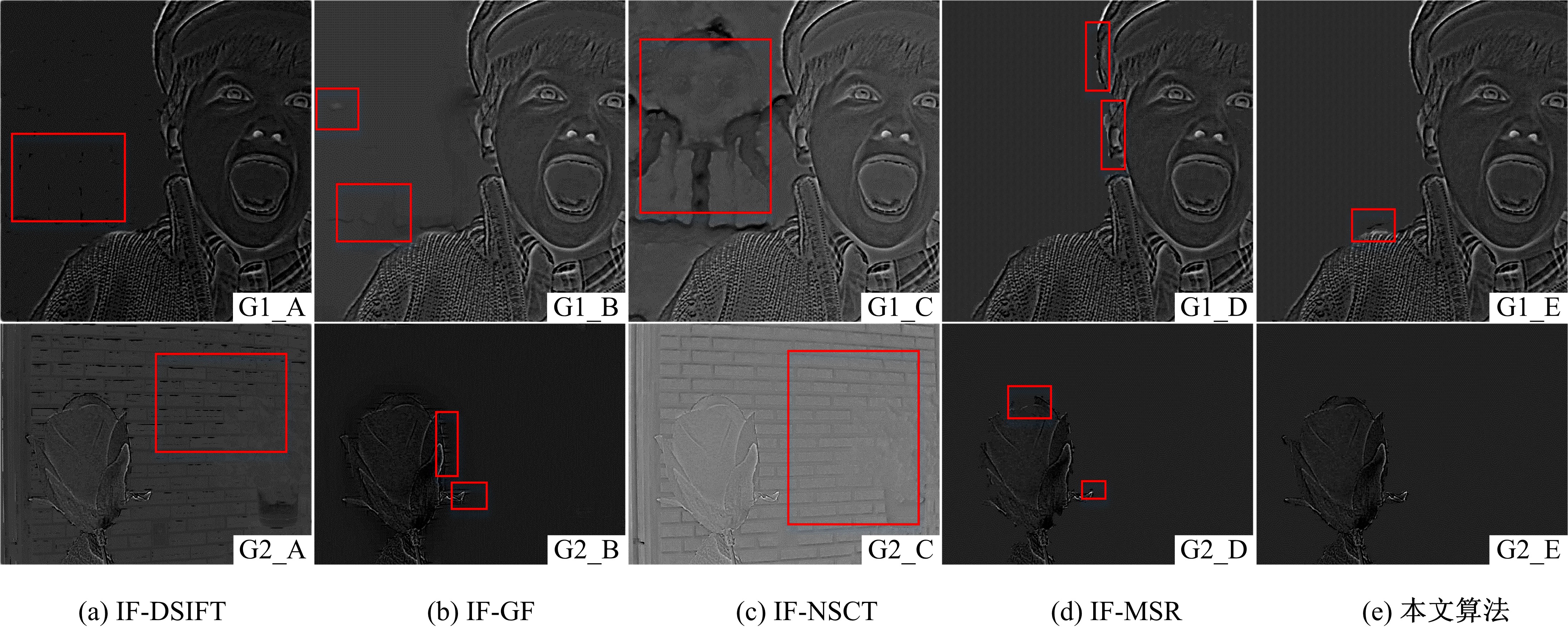
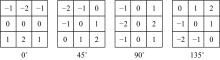
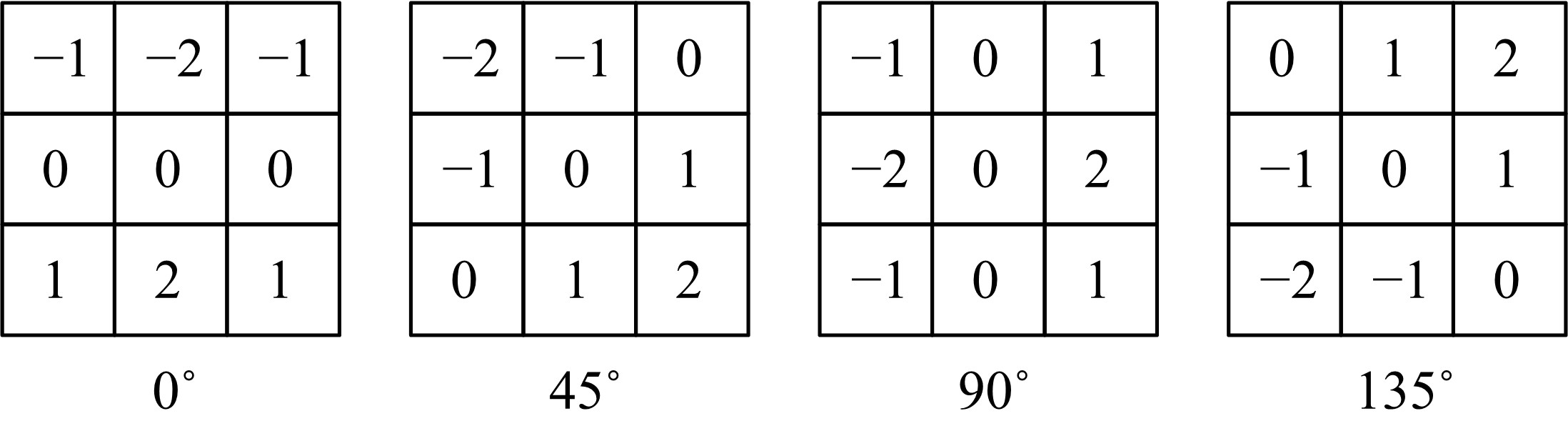
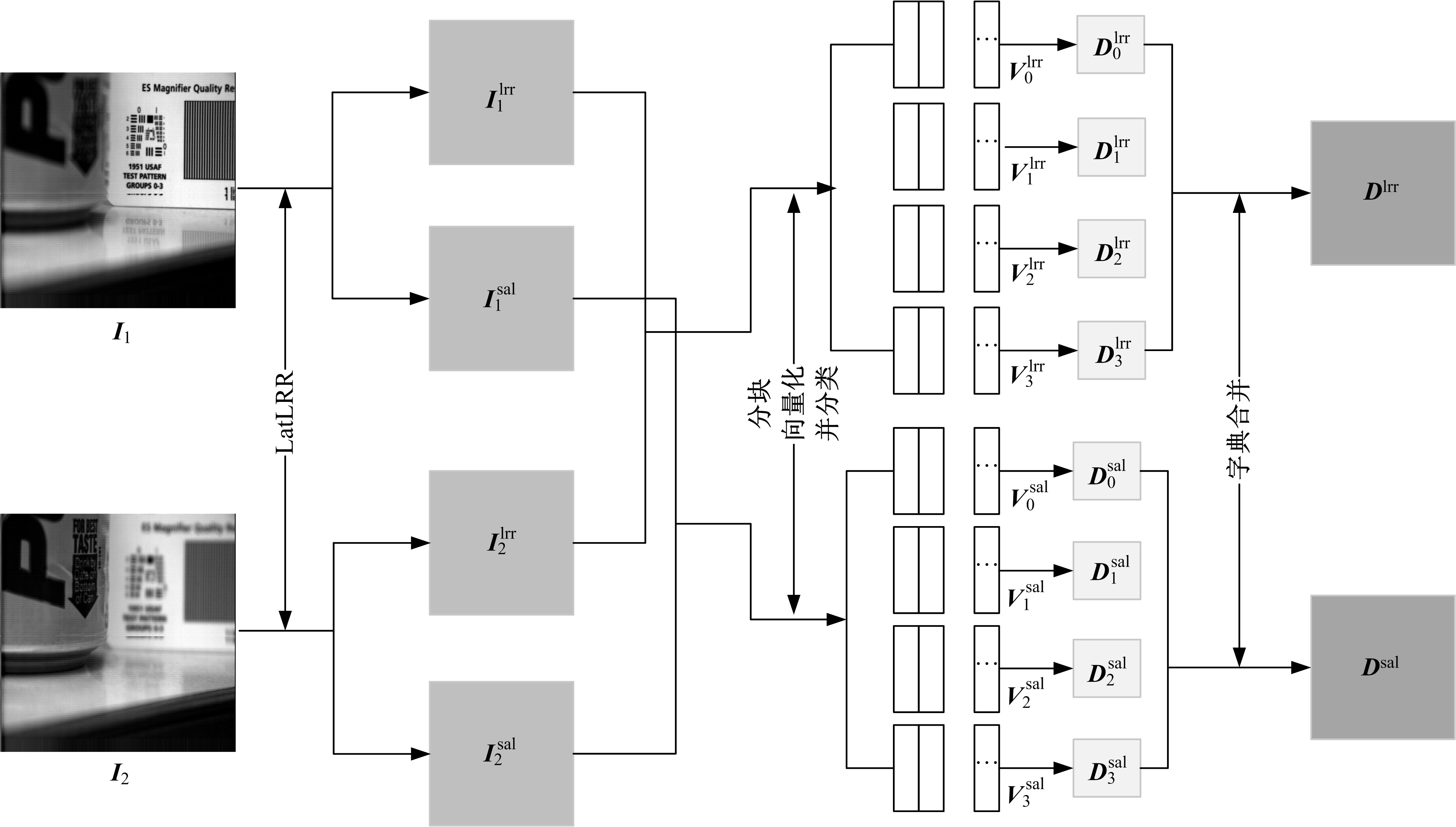
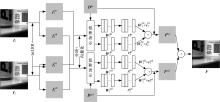
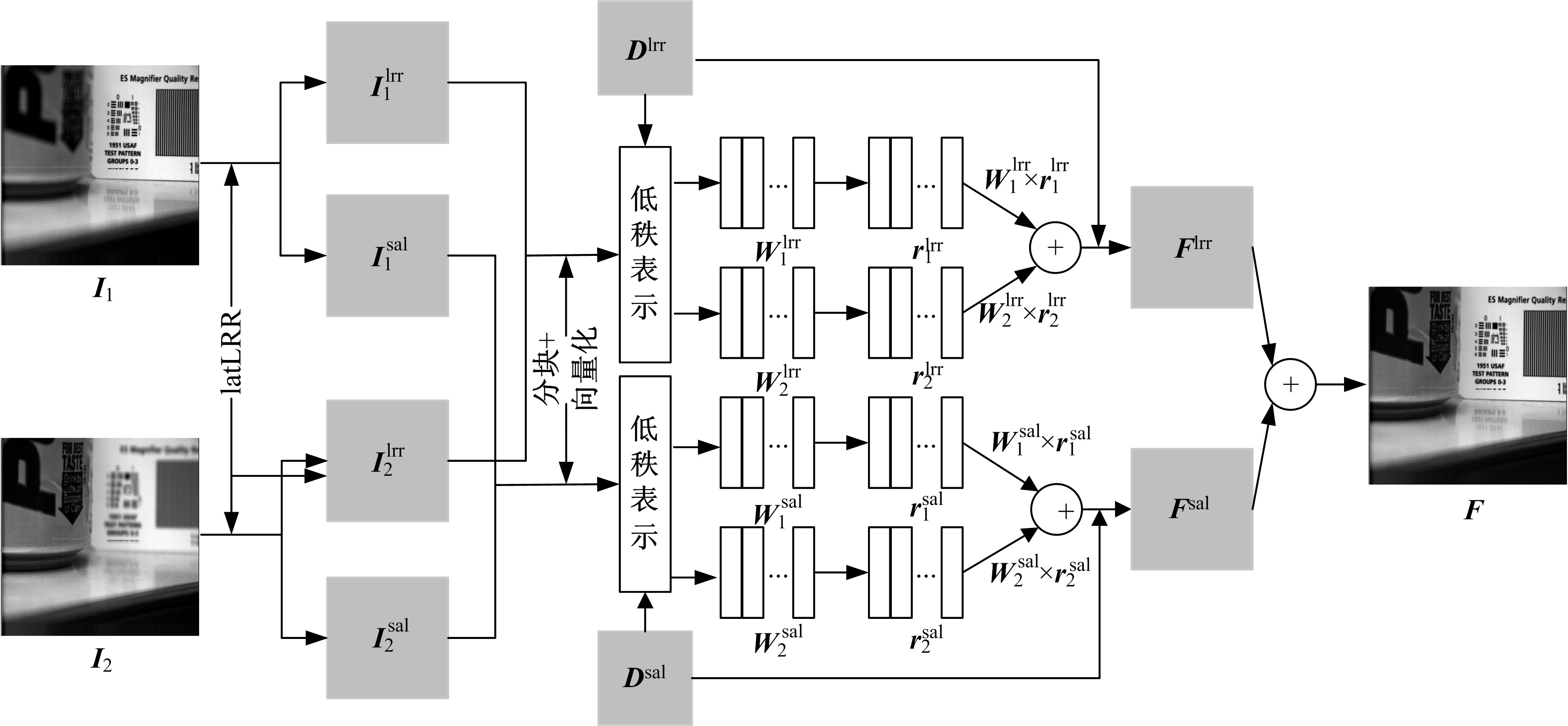
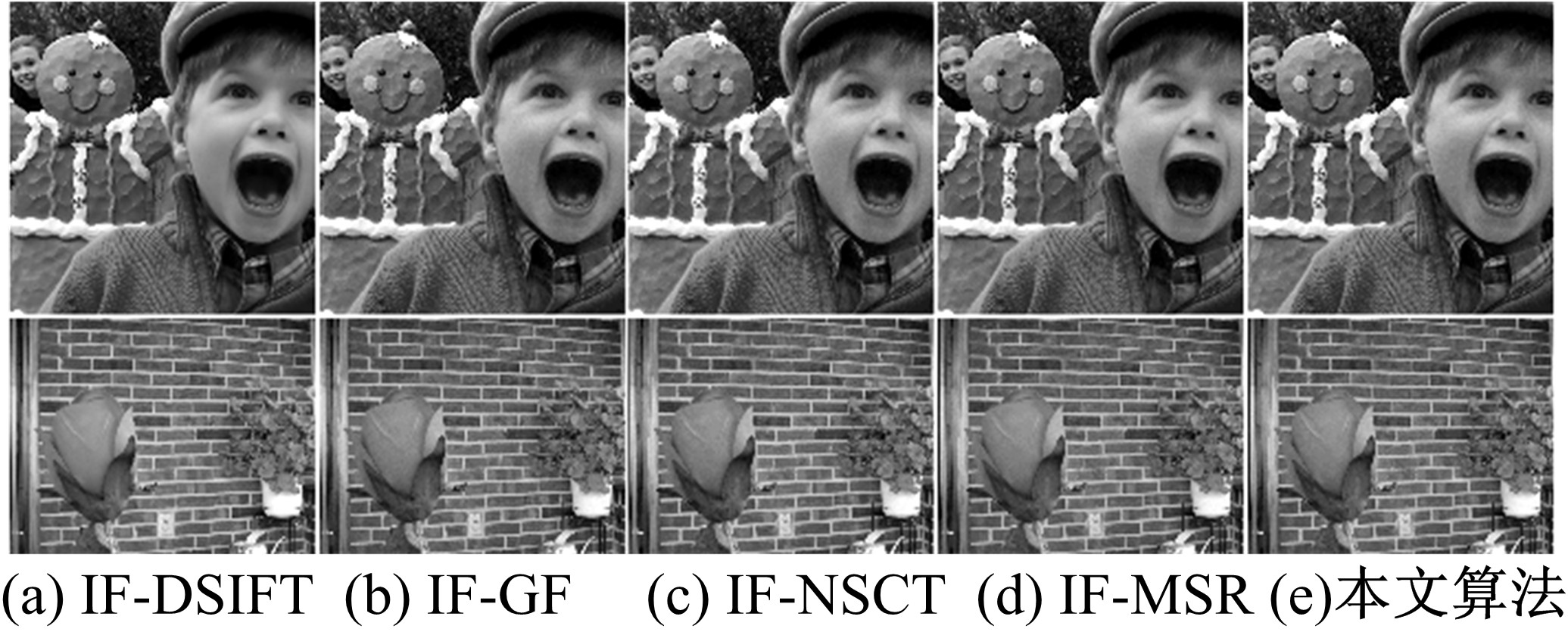
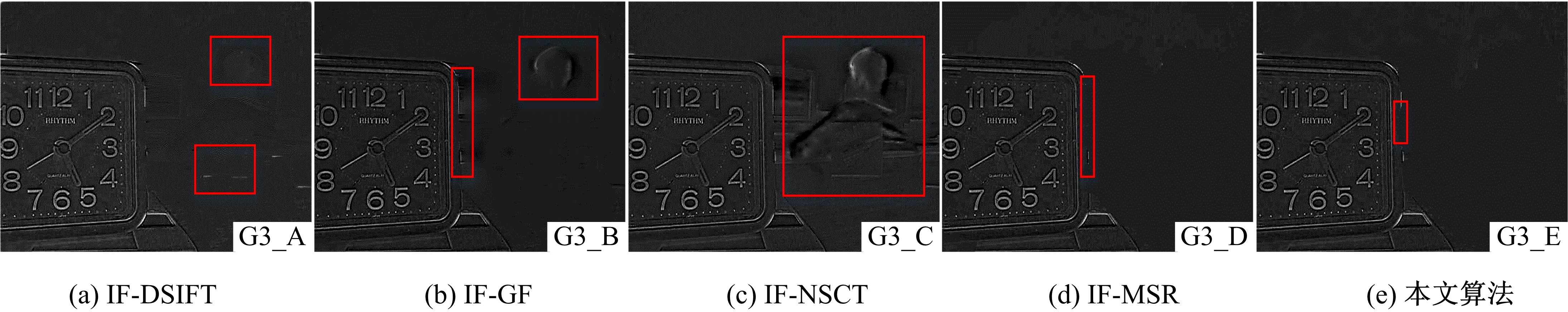
为使多聚焦图像的融合结果能保持全局性、保留局部的细节且对未配准源图像具有鲁棒性,提出了一种隐低秩表示结合低秩表示的多聚焦图像融合算法。该算法通过对源图像进行隐低秩表示,得到图像的低秩(全局)部分和显著(细节)部分,然后对低秩部分和显著部分分别使用滑动窗口技术分块,并将分块使用4个方向的Sobel算子进行分类学习子字典,将子字典合成完整字典后进行低秩表示,接着对低秩部分和显著部分的低秩系数分别进行融合,融合过程中引入导向滤波增强空间连续性,最后将融合的低秩系数分别乘以字典得到融合后的低秩部分和显著部分,两者相加则得到最终的融合图像。为验证算法的有效性,实验过程中选取3组数据,包括2组完全配准的多聚焦图像以及1组未完全配准的多聚焦图像,分析融合结果与源图像的残差,并使用4个融合质量评价指标进行量化分析。实验结果表明,该算法在主观视觉效果和客观质量评价分析方面都优于当前主流的多聚焦图像融合算法。
中图分类号:
- TP399
| 1 | James A P, Dasarathy B V. Medical image fusion: a survey of the state of the art[J]. Information Fusion, 2014, 19(1): 4-19. |
| 2 | Liu Y, Chen X, Wang X S, et al. Deep learning for pixel-level image fusion: recent advances and future prospects[J]. Information Fusion, 2018, 42(3): 158-173. |
| 3 | Jin X, Jiang Q, Yao S W, et al. A survey of infrared and visual image fusion methods[J]. Infrared Physics and Technology, 2017, 85: 478-501. |
| 4 | Ghassemian H. A review of remote sensing image fusion methods[J]. Information Fusion, 2016, 32: 75-89. |
| 5 | Wang W C, Chang F L. A multi-focus image fusion method based on Laplacian pyramid[J]. Journal of Computers, 2011, 6(12): 2559-2566. |
| 6 | Yang Y. A novel DWT based multi-focus image fusion method[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2011, 24(1): 177-181. |
| 7 | Zhang Q, Guo B L. Multifocus image fusion using the nonsubsampled contourlet transform[J]. Signal Processing, 2009, 89(7):1334-1346. |
| 8 | Yang Wei, Chai Qi, Wang Li-ming. Multi-focus image fusion method based on dual-tree complex wavelet transform[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2007, 43(28): 12-14. |
| 9 | 杨扬, 戴明, 周箩鱼, 等. 基于非下采样Bandelet变换的多聚焦图像融合[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2014, 44(2): 525-530. |
| Yang Yang, Dai Ming, Zhou Luo-yu, et al. Multifocus image fusion based on nonsubsampled Bandelet transform[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2014, 44(2): 525-530. | |
| 10 | Li S T, Kang X D, Hu J W, et al. Image matting for fusion of multi-focus images in dynamic scenes[J]. Information Fusion, 2013, 14(2): 147-162. |
| 11 | Wang Z B, Ma Y D, Gu J. Multi-focus image fusion using PCNN[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2010, 43(6): 2003-2016. |
| 12 | Li S T, Kang X D, Hu J W. Image fusion with guided filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(7): 2864-2875. |
| 13 | Liu S P, Liu Y, Wang Z F. Multi-focus image fusion with dense SIFT[J]. Information Fusion, 2015, 23: 139-155. |
| 14 | Chen L, Li J B, Philip C C L. Regional multifocus image fusion using sparse representation[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(4): 5182-5197. |
| 15 | 尹明, 战荫伟, 裴海龙. 基于稀疏补算子学习的图像融合方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2016, 46(6): 2052-2058. |
| Yin Ming, Zhan Yin-wei, Pei Hai-long, Co-sparse analysis operator learning for image fusion[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016, 46(6): 2052-2058. | |
| 16 | Liu Y, Chen X, Ward R K, et al. Image fusion with convolutional sparse representation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(12): 1882-1886. |
| 17 | 首照宇, 胡蓉, 欧阳宁, 等. 基于多尺度稀疏表示的图像融合方法[J]. 计算机工程与设计, 2015, 36(1): 232-235. |
| Shou Zhao-yu, Hu Rong, Ouyang Ning, et al. Image fusion based on multi-scale sparse representation[J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2015, 36(1): 232-235. | |
| 18 | Li H, Wu X J. Multi-focus image fusion using dictionary learning and low-rank representation[J]. LNCS, 2017:675- 686. |
| 19 | Zhong J Y, Yang B, Li Y H, et al. Image fusion and super-resolution with convolutional neural network[C]∥ Chinese Conference on Pattern Recognition. Singapore: Springer, 2016, 663:78-88. |
| 20 | Liu Y, Chen X, Peng H, et al. Multi-focus image fusion with a deep convolutional neural network[J]. Information Fusion, 2017, 36: 191-207. |
| 21 | Du C B, Gao S S. Image segmentation-based multi-focus image fusion through multi-scale convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5(99):15750-15761. |
| 22 | Liu G, Yan S. Latent low-rank representation for subspace segmentation and feature extraction[C]∥International Conference on Computer Vision. Barcelona, Spain, 2011: 1615-1622. |
| 23 | Lin Z, Chen M, Ma Y. The augmented lagrange multiplier method for exact recovery of corrupted low-rank matrices[DB/OL]. [2010.9-29]. http:∥export.arxiv.org/abs/1009.5055. |
| 24 | Liu G C, Lin Z C, Yan S C, et al. Robust recovery of subspace structures by low-rank representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(1): 171-184. |
| 25 | He K M, Sun J, Tang X O. Guided image filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(6): 1397-1409. |
| 26 | Aharon M, Elad M, Bruckstein A. K-SVD: an algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(11): 4311-4322. |
| 27 | Liu Z, Blasch E, Xue Z, et al. Objective assessment of multiresolution image fusion algorithms for context enhancement in night vision: a comparative study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 34(1): 94-109. |
| [1] | 张笑东,夏筱筠,吕海峰,公绪超,廉梦佳. 大数据网络并行计算环境中生理数据流动态负载均衡[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 247-254. |
| [2] | 王晓辉,吴禄慎,陈华伟. 基于法向量距离分类的散乱点云数据去噪[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 278-288. |
| [3] | 邓钧忆,刘衍珩,冯时,赵荣村,王健. 基于GSPN的Ad⁃hoc网络性能和安全平衡[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 255-261. |
| [4] | 王铁君,王维兰. 基于本体的唐卡图像标注方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 289-296. |
| [5] | 李雄飞,王婧,张小利,范铁虎. 基于SVM和窗口梯度的多焦距图像融合方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 227-236. |
| [6] | 王洪雁,邱贺磊,郑佳,裴炳南. 光照变化下基于低秩稀疏表示的视觉跟踪方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 268-277. |
| [7] | 车翔玖,刘华罗,邵庆彬. 基于Fast RCNN改进的布匹瑕疵识别算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2038-2044. |
| [8] | 周炳海,吴琼. 考虑工具和空间约束的机器人装配线平衡优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2069-2075. |
| [9] | 赵宏伟,王鹏,范丽丽,胡黄水,刘萍萍. 相似性保持实例检索方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2045-2050. |
| [10] | 沈军,周晓,吉祖勤. 服务动态扩展网络及其结点系统模型的实现[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2058-2068. |
| [11] | 周柚,杨森,李大琳,吴春国,王岩,王康平. 基于现场可编程门电路的人脸检测识别加速平台[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2051-2057. |
| [12] | 李宾,周旭,梅芳,潘帅宁. 基于K-means和矩阵分解的位置推荐算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1653-1660. |
| [13] | 李雄飞,宋璐,张小利. 基于协同经验小波变换的遥感图像融合[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1307-1319. |
| [14] | 刘元宁,刘帅,朱晓冬,霍光,丁通,张阔,姜雪,郭书君,张齐贤. 基于决策粒子群优化与稳定纹理的虹膜二次识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1329-1338. |
| [15] | 李宾,申国君,孙庚,郑婷婷. 改进的鸡群优化算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1339-1344. |
|
||